VSI DECset for OpenVMS Code Management System Callable Routines Reference Manual
- Software Version:
- DECset Version 12.7 for OpenVMS
- Operating System and Version:
- VSI OpenVMS x86-64 Version 9.2-2 or higher
VSI OpenVMS IA-64 Version 8.4-1H1 or higher
VSI OpenVMS Alpha Version 8.4-2L1 or higher
Preface
This reference manual describes the set of callable routines for the Code Management System for OpenVMS (CMS). CMS is an online library system that helps track software development and maintenance. This manual provides reference information on how to use the CMS Callable Routines.
1. About VSI
VMS Software, Inc. (VSI) is an independent software company licensed by Hewlett Packard Enterprise to develop and support the OpenVMS operating system.
2. Intended Audience
This reference manual is intended for programmers who have a working knowledge of CMS, the OpenVMS operating system, and the languages used to call CMS.
3. Document Structure
Chapter 1, "Using CMS Callable Routines" provides an overview, general rules, and other information that you need to know to use the routines.
Chapter 2, "CMS Routine Descriptions" contains detailed descriptions of each routine. The routines are listed in alphabetical order with the routine name at the top of every page of each routine description.
Appendix A, "Summary of CMS Entry Points" lists each routine name and the arguments that you can pass to the routine.
Appendix B, "Examples of Calling CMS" provides examples of calling CMS from different languages.
4. Related Documents
The VSI DECset for OpenVMS Installation Guide contains instructions for installing CMS.
The Code Management System for OpenVMS Release Notes contain added information on the use and maintenance of CMS.
The VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System contains introductory and conceptual information about CMS.
The CMS Client User's Guide describes the installation and use of the CMS Client software in a Microsoft Windows environment.
The VSI DECset for OpenVMS Code Management System Reference Manual describes all the commands available for CMS.
The Using VSI DECset for OpenVMS Systems manual contains information on using the other components of DECset.
5. References to Other Products
Note
These references serve only to provide examples to those who continue to use these products with DECset.
Refer to the Software Product Description for a current list of the products that the DECset components are warranted to interact with and support.
6. OpenVMS Documentation
The full VSI OpenVMS documentation set can be found on the VMS Software Documentation webpage at https://docs.vmssoftware.com.
7. VSI Encourages Your Comments
You may send comments or suggestions regarding this manual or any VSI document by sending electronic mail to the following Internet address: <docinfo@vmssoftware.com>. Users who have VSI OpenVMS support contracts through VSI can contact <support@vmssoftware.com> for help with this product.
8. Typographical Conventions
|
Convention |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Ctrl/x |
A sequence such as Ctrl/x indicates that you must hold down the key labeled Ctrl while you press another key or a pointing device button. |
|
KPn |
A sequence such as KP1 indicates that you must press the key labeled with the number or character n on the numeric keypad. |
... |
A horizontal ellipsis in a figure or example indicates the
following possibilities:
|
. . . |
A vertical ellipsis indicates the omission of items from a code example or command format; the items are omitted because they are not important to the topic being described. |
| ( ) |
In command format descriptions, parentheses indicate that you must enclose multiple choices in parentheses. |
| [ ] |
In command format descriptions, brackets indicate optional choices. You can choose one or more items or no items. Do not type the brackets on the command line. However, you must include the brackets in the syntax for OpenVMS directory specifications and for a substring specification in an assignment statement. |
| { } |
In command format descriptions, braces indicate required choices; you must choose at least one of the items listed. Do not type the braces on the command line. |
|
bold type |
Bold type represents the introduction of a new term. It also represents the name of an argument,an attribute, or a reason. |
Example |
This typeface indicates code examples, command examples, and interactive screen displays. In text, this type also identifies URLs,UNIX commands and pathnames, PC-based commands and folders, and certain elements of the C programming language. |
|
italic type |
Italic type indicates important information, complete titles of manuals or variables. Variables include information that varies in system output (for example, Internal error number), in command lines (/PRODUCER=name), and in command parameters in text (where dd represents the predefined code for the device type). |
|
UPPERCASE TYPE |
Uppercase indicates the name of a command, routine, file, file protection code, or the abbreviation of a system privilege. |
- |
A hyphen at the end of a command format description,command line, or code line indicates that the command or statement continues on the following line. |
|
numbers |
All numbers in text are assumed to be decimal unless otherwise noted. Nondecimal radixes—binary, octal, or hexadecimal—are explicitly indicated. |
Chapter 1. Using CMS Callable Routines
The Code Management System for OpenVMS (CMS) provides a set of routines that you can use to access and manipulate CMS libraries from your programs. You should have an understanding of the basic CMS concepts and syntax before you use these routines.
Include in your program the appropriate declarations and calls to the routines.
Compile the program.
Link the compiled code with the CMS image.
Run the executable image.
As with the DCL-level interface, you can use files for input to and output from the CMS routines. You can also write routines that process input, output, and messages. The symbols for status condition codes are defined in the CMS image and are available for use in your program.
This chapter provides the basic information you need to know to call CMS routines. For descriptions of each routine, see Chapter 2. The examples in Chapters 1 and 2 of this manual are written in Fortran; Appendix B, "Examples of Calling CMS" shows examples of calling CMS from Fortran and other languages. For more detailed information about using CMS, see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System.
1.1. Generating Interface Descriptions Using SDL
To ease the writing of programs that use the CMS Callable Routines, an OpenVMS Structure Definition Language (SDL) description of the CMS Callable Routines is available. This programming language-independent description can be used to generate an interface description for supported programming languages. The description is contained in the file CMS$ROUTINES.SDL, located in the SYS$SYSROOT:[SYSHLP.EXAMPLES.CMS] directory.
- Ada
- Basic
- Bliss
- C
- Fortran
- Macro
- Pascal
- PL/I (Alpha and VAX only)
$ SDL/LANGUAGE=ADA SYS$SYSROOT:[SYSHLP.EXAMPLES.CMS]CMS$ROUTINES.SDL
This generates an Ada package specification, called CMS$ROUTINES, which includes definitions of the types, constants, and entry points of the CMS interface.
The SDL output generated from the SDL compiler varies in its comprehensiveness depending on the programming language being used. Therefore, it might be desirable to manually enhance the output before use. The examples of code throughout this manual do not assume the use of the SDL compiler; instead, they show how enhanced interface descriptions are used.
1.2. Calling CMS Routines
There is an entry point into CMS for each DCL-level command. In general, routines have the same names as the DCL-level commands. (An exception is the CMS RESERVE command, for which there is no corresponding CMS$RESERVE routine. To reserve an element in the CMS callable interface, you must specify the reserve argument in a call to the CMS$FETCH routine.)
When your program calls a CMS routine, it must pass arguments that provide CMS with information about elements, the library history, or whatever part of the CMS library you want to access. In addition to providing this information,your program must also allocate space for a library data block (LDB). An LDB is a user-allocated structure that CMS uses to maintain basic information about the library being accessed. For more information about the LDB, see Section 1.4.2, ''The Library Data Block''.
INTEGER*4 LDB(50) INTEGER*4 STATUS CHARACTER*14 DIRCHARACTER*13 ELEMENT INTEGER*4 CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY
INTEGER*4 CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT DIR = '[LENNON.SONGS]'
ELEMENT = 'LUCY.DIAMONDS' STATUS = CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY(LDB,DIR)
IF (.NOT. STATUS) GO TO 50 STATUS = CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT(LDB,ELEMENT)
. . . END $ CREATE/DIRECTORY [LENNON.SONGS] $ FORTRAN cmsprogram $ LINK cmsprogram
$ RUN cmsprogram
The LDB is declared as an integer array;the library directory and element name variables are declared as character strings. | |
The CMS routines are declared as routines returning integer values. | |
The directory and element names are assigned to the character string variables. | |
The call to the CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY routine includes arguments for the LDB and the empty directory to be used for the library. | |
The call to the CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT routine includes arguments for the LDB and the element name. Because the element is being created in the library referenced in the CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY call, it is not necessary to use CMS$SET_LIBRARY. | |
The execution sequence includes DCL commands that create the library directory and compile, link, and run the program. |
1.3. Rules for Writing Programs that Call CMS Routines
Most of the CMS routines are not AST-reentrant; therefore, you should not call a CMS routine (except CMS$ASYNCH_TERMINATE) from an AST routine that might currently be interrupting the execution of a CMS routine.
If your program uses event flags, you must use the OpenVMS Run-Time Library (RTL) routines provided for this purpose (LIB$RESERVE_EF, LIB$GET_EF, and LIB$FREE_EF). These routines coordinate the use of the event flags between your program and CMS.
Do not modify the contents of the LDB.
Except for the CMS$ASYNCH_TERMINATE, CMS$GET_STRING, and CMS$PUT_STRING routines, do not call CMS from within callback or message-handler routines. Doing so can result in a deadlock condition, where the latest call waits to lock the library that the earlier call is holding locked. See Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler'' for information about message routines and Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about callback routines.
1.4. Passing Arguments to CMS Routines
By reference
By descriptor
By immediate value
CMS accepts arguments that are passed by reference or by descriptor, as defined for each routine. CMS returns status codes by immediate value. For information about the arguments for each call, see the individual routine descriptions in Chapter 2, "CMS Routine Descriptions".
When you pass an argument by reference, you specify that the address of the argument's storage location is passed to the CMS routine. CMS expects objects such as the LDB, user-supplied routines, and flag values to be passed by reference.
When you pass an argument by descriptor, you specify that the address of a descriptor data structure is passed to the CMS routine. CMS expects character strings to be passed by descriptor.
If you are using callback routines (see Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'') you must use the CMS$GET_STRING and CMS$PUT_STRING routines to pass strings between the callback routine and CMS.
Each argument in a call to a CMS routine is evaluated according to the position that it occupies in the argument list. Therefore, you must be sure to specify null arguments correctly. If you omit an argument and do not include a placeholder in the call, CMS cannot correctly interpret the arguments that follow.
CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT(library_data_block,
element_name,
[remark],
[history],
[notes],
[position],
[keep],
[reserve],
[concurrent],
[reference_copy],
[input_file],
[input_routine],
[user_arg],
[msg_routine],
[review])CALL CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT(LDB,ELEMENT)CALL CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT(LDB,ELEMENT,,,,,,,,,,INPUT)This call creates an element with the name specified in the ELEMENT argument and uses data supplied by the INPUT routine. You must include the intervening commas as placeholders. For example, if you had used only one comma, CMS would interpret the input routine parameter as the remark argument.
CALL CMS$CREATE_CLASS(LDB,CLASS,,) CALL CMS$CREATE_CLASS(LDB,CLASS)
To omit arguments in a language that does not allow variable-length argument lists, you must pass the placeholder 0 by value, which CMS treats as a null argument.
1.4.1. Data Types
The routine descriptions in Chapter 2, "CMS Routine Descriptions" indicate the data type of each argument (or object) you pass to CMS (such as an LDB or element name). Table 1.1, ''Data Types of Objects Passed to CMS Routines'' describes the different data types for these objects.
|
Data Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
address |
Indicates a location in memory containing either data or code. String identifiers are addresses of string descriptors. CMS uses string identifiers to pass character strings to callback routines. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''. For information about callback routines, see Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines''. |
|
char_string |
Indicates a character-coded string. Character strings are passed by descriptor. |
|
cntrlblk |
Indicates a control block. A control block is a structure that is interpreted by CMS. The LDB and the FDB are control blocks. |
|
procedure |
Indicates a procedure (or routine) that you pass to a CMS routine. You pass callback routines and message routines to CMS by specifying the entry mask of the routine in the call. When you pass routines to CMS, the argument list must contain a pointer to the entry mask. (A compiler normally generates the entry mask as the first word of the routine.) Usually, you pass routines by reference; for examples of passing routine addresses to CMS, see Appendix B, "Examples of Calling CMS". For information about message routines, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''. For information about callback routines, see Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines''. |
|
longword_signed |
Indicates a 32-bit value. Flags (see Section 1.4.4, ''Specifying Flags as Arguments'') and signed integer counts are passed as signed longwords. |
|
mask_longword |
Indicates a longword mask. A mask is a group of flags or a bitmask to be interpreted by CMS. For example, you can use a mask to specify the IGNORE values for the CMS$DIFFERENCES routine. |
|
date_time |
Indicates a quadword system time value. This data type specifies a time value in the 64-bit system time format. Transaction times and file creation or revision times are expressed in the date_time data type. |
|
undefined |
Indicates an argument that CMS does not modify. These are intended for your use only; CMS passes these arguments to callback routines. For more information about user-defined arguments,see Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines''. |
|
vector_longword_unsigned |
Indicates a one-dimensional longword array. The signal and mechanism arrays that CMS passes to message routines are of type vector_longword_unsigned. For information about message routines, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''. |
1.4.2. The Library Data Block
The library data block (LDB) is a data structure that CMS uses to maintain information about the state of a particular CMS library. It is a required argument for most routine calls that access a library.
You must declare an integer array of 57 longwords to be used for an LDB. Then, use either the CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY or CMS$SET_LIBRARY routine to associate the LDB with one or more CMS libraries. When you specify the LDB in a call to a CMS routine, CMS accesses that corresponding library or list of libraries.
Caution
The LDB is designed to be filled by CMS. You should not modify the contents of the LDB (except for the fifth and sixth longword; see the following section). Using an LDB that you have modified might corrupt your library.
Figure 1.1, ''A CMS Library Data Block'' shows an LDB.
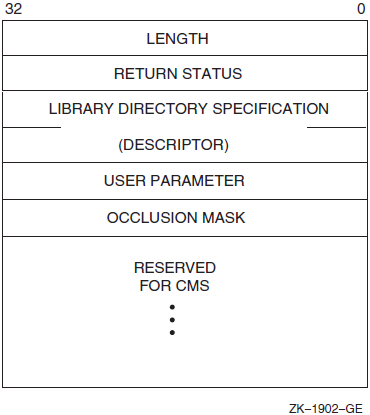
The first longword in the LDB contains a count of the total number of longwords used in the LDB. Although this count might be less than the total space allocated for the data block, you should not use any part of the LDB for your own purposes (except for the fifth and sixth longword). The second longword contains the return status for the call to CMS (the same value placed in R0). The third and fourth longwords contain a character string descriptor that points to the library directory specification for the entire search list of libraries. You can use the fifth longword to pass arguments to your callback routines. You should do this after entering CMS$SET_LIBRARY, which initializes the library.
|
Symbol |
Bit Position |
Mask Value |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$M_OCC_NOCLASS |
0 |
1 |
|
CMS$M_OCC_NOELEMENT |
1 |
2 |
|
CMS$M_OCC_NOGROUP |
2 |
4 |
|
CMS$M_OCC_NOOTHER |
3 |
8 |
See the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System for more information on occlusion.
1.4.3. The Fetch Data Block
The fetch data block (FDB) contains status information about the library. It is used as an argument only in calls to the CMS$FETCH_OPEN, CMS$FETCH_GET, and CMS$FETCH_CLOSE routines. You use these routines when you want to fetch an element from the library one line at a time. For the descriptions of these routines, see Chapter 2, "CMS Routine Descriptions".
Caution
The FDB is designed to be filled by CMS. You should not modify the contents of the FDB. Using an FDB that you have modified might corrupt your library.
1.4.4. Specifying Flags as Arguments
Some CMS routines recognize flags that specify certain actions. For example, to reserve an element, you specify a flag in a call to CMS$FETCH. A flag is a longword integer variable that is set to true (1) or false (0).You can set these flags to 1 or 0 as necessary, then pass the address of the flag as an argument to the CMS routine. CMS checks the low-order bit to determine the value of the flag.
INTEGER*4 LDB(50) CHARACTER*10 ELEMENT INTEGER*4 CONCURRENT. . . STATUS = CMS$SET_LIBRARY(LDB,DIRECTORY) . . . CONCURRENT = 0
STATUS = CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT(LDB,ELEMENT,,,,,,,CONCURRENT)
. . .
In Example 1.2, ''Passing a Concurrent Flag to CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT'', when the CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT routine is called,the position in the argument list corresponding to the concurrent flag contains an address of a location containing the value 0. CMS interprets the concurrent flag as follows: a value of 1 indicates concurrent access and a value of 0 indicates noconcurrent access. Thus, CMS creates an element that cannot be concurrently reserved.
You must pass flag values by reference for CMS to interpret them correctly. If you use the immediate value mechanism to pass the value 0 to a CMS routine, CMS interprets the argument list entry of 0 to mean an unspecified argument. An unspecified, or default, argument might have a different meaning than you intend; therefore, you must use the correct syntax for the calling language to ensure the correct representation on the argument stack.
|
Call Semantics |
Argument List |
Result |
|---|---|---|
|
Unspecified argument |
0 |
Concurrency allowed |
|
Passing 0 by value |
0 |
Concurrency allowed |
|
Passing 0 by reference |
Address pointing to location containing the value 0 |
Concurrency not allowed |
|
Passing 1 by value |
1 |
Probable access violation |
|
Passing 1 by reference |
Address pointing to location containing the value 1 |
Concurrency allowed |
1.4.5. Masks
Some routines (for example, CMS$ANNOTATE, CMS$DIFFERENCES, CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS, and CMS$DELETE_HISTORY) accept some of their arguments in the form of masks. A mask is a longword value that is interpreted as a bitmask. A bitmask is an integer value that is interpreted as a set of bits, some of them "on" and some "off." For each of the masks, CMS recognizes specific values that determine the action of the routine. Each of these values is defined as a universal symbol; thus,you have access to them when you link with the CMS image.
CHARACTER*16 LIBNAME CHARACTER*10 ELEMENT INTEGER*4 LDB(50) INTEGER*4 TRANSACTIONSEXTERNAL CMS$M_CMD_RESERVE
EXTERNAL CMS$M_CMD_REPLACE EXTERNAL OUTPUT_ROUTINE TRANSACTIONS = IOR(%LOC(CMS$M_CMD_RESERVE),%LOC(CMS$M_CMD_REPLACE))
LIBNAME = '[HARRISON.SONGS]' ELEMENT = 'BROWN.SHOE' CALL CMS$SET_LIBRARY(LDB,LIBNAME) CALL CMS$SHOW_HISTORY(LDB,OUTPUT_ROUTINE,,ELEMENT,,,,TRANSACTIONS)
. . .
TRANSACTIONS is declared as type (longword) INTEGER for the bitmask argument to be passed to CMS$SHOW_HISTORY. | |
External symbols for the bitmask (CMS$M_CMD_RESERVE and CMS$M_CMD_REPLACE) are declared. | |
The IOR intrinsic function sets the bits in the TRANSACTIONS mask. | |
CMS is called; CMS calls OUTPUT_ROUTINE once for each reservation and replacement of the specified element. |
1.4.6. Output Strings
STR$FREE1_DXNote that this applies only to the outputs from callable routines and not to the arguments passed to callback routines. The space used for arguments to callback routines is freed by the CMS implementation and need not be freed by the callback.
1.5. Condition Values Returned
The return value of a call to a CMS routine is a standard 32-bit OpenVMS condition code. CMS returns the value in register 0, and places it in the second longword of the LDB (see Section 1.4.2, ''The Library Data Block'').
The CMS condition codes are declared as universal symbols; therefore, you have access to these symbols when you link your program with the CMS image. The languages supported for accessing the defined symbols are: Ada, Basic, Bliss, C, COBOL, DIBOL, Fortran, Macro, Pascal, PL/I (Alpha and VAX only), and SCAN.
X: CONSTANT UNSIGNED_LONGWORD :=SYSTEM.IMPORT_VALUE(~EXTERNAL_SYMBOL~);
Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler'' describes how to write routines to handle messages generated by CMS. See the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System for a complete listing of CMS diagnostic messages.
1.5.1. CMS$_EOF Condition Value
When you provide a routine to handle input or output,the return value CMS$_EOF is used to indicate end-of-file. For information about writing routines for input and output, see Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines''.
1.5.2. CMS$_INUSE, CMS$_WAITING, and CMS$_PROCEEDING Messages
If another user is accessing a library when your program calls CMS to access the same library, CMS issues the CMS$_INUSE message and waits until the library is unlocked before executing your transaction. During this time, CMS periodically issues the CMS$_WAITING message. When the library is available, CMS issues the CMS$_PROCEEDING message and then executes your transaction.
If, instead of waiting, you prefer to abort the transaction from the message routine, you should have the message routine call CMS$ASYNCH_TERMINATE. This routine returns control to CMS, so it cleans up resources and exits properly.
1.6. Using Callback Routines
Typically, CMS uses files for input and output. For example, when you pass an element name to the CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT routine, CMS searches your default directory for a file that has the same name as the specified element. However, you can provide callback routines to handle input and output.
A callback routine is a routine that you specify in a call to CMS, and which in turn is invoked by CMS. You pass callback routines by specifying the entry mask of the routine in the call to the CMS routine. As a result, the argument list contains the address of the entry mask for the routine (CMS uses the CALLG and CALLS procedure call instructions to invoke callback routines). Usually, you pass routines by reference, but the method that you use to pass the routine address is dependent on the language that you are using. For examples of programs that pass routine addresses to CMS routines, see Appendix B, "Examples of Calling CMS".
CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT
CMS$DIFFERENCES
CMS$REPLACE
CMS$ANNOTATE
CMS$DELETE_HISTORY
CMS$DIFFERENCES
CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS
CMS$SHOW_keyword
The CMS$CMS routine allows you to specify input, output, confirm, and prompt routines. See the description of the CMS$CMS routine in Chapter 2, "CMS Routine Descriptions" for more information.
1.6.1. Rules for Writing Callback Routines
Every callback routine must return control to CMS. If your routine does not return control to CMS, CMS cannot finish the transaction and the library remains locked. (If your library becomes locked, you must use the VERIFY/RECOVER command to unlock it.) In addition, any resources used to process the command are not released.
Callback routines must return a defined condition value to CMS. You can use CMS$_NORMAL, CMS$_EXCLUDE, and CMS$_STOPPED to indicate successful completion of the callback routine, or you can return a condition code from an OpenVMS system service or other system software. CMS checks for the CMS$_EXCLUDE and CMS$_STOPPED values, and checks the low-order bit to determine if the status code indicates success. For information about callback return codes, see Section 1.6.4, ''Callback Return Codes''. If the callback routine returns a failure code, CMS exits with a primary status of CMS$_USERERR.
CMS$ASYNCH_TERMINATE, CMS$GET_STRING and CMS$PUT_STRING are the only CMS routines that you can use within a callback routine (see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines'').
When writing callback routines for CMS$DIFFERENCES and CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS, you cannot depend on the order in which CMS calls these callback routines. The calling sequence is not synchronous.
All routines that allow you to use callback input or output routines also provide an argument in the call syntax for your own use. CMS does not modify this value; it passes this value to the callback routine. This argument is labeled user_arg in the syntax of a call to CMS and user_param in the syntax of a call to a callback routine. (The term argument is used to identify an object that you pass to a CMS routine. The term parameter is used to identify an object that a CMS routine passes to a callback routine.)
When you do not specify user_arg in the call to CMS, the call frame entry for user_param points to a location containing the value 0. In this case, user_param is allocated as read-only storage. You receive an access violation error if you attempt to modify user_param under these circumstances. CMS allows you to pass arguments to callback routines by supplying a value in the fifth longword of the LDB. See Section 1.4.2, ''The Library Data Block'' for more information.
1.6.2. Callback Routines Used by CMS$CMS
The CMS$CMS routine provides a full command-line level interface into CMS; however, it performs no I/O to the terminal other than error messages. To perform confirmations, prompting, or display output, you must supply callback routines. The following sections describe these callback routines.
1.6.2.1. The Confirmation Routine
The CMS$CMS routine uses a caller-supplied callback routine for confirmation messages (for example, the results of a /CONFIRM qualifier, or when a module is being reserved or replaced with concurrent reservations in effect).
By specifying the confirm_routine argument to CMS$CMS, which affects the command being parsed and executed
By specifying the confirm_routine argument to CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY or CMS$SET_LIBRARY, which affects all operations performed using that LDB (until you reinitialize the LDB by performing another CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY or CMS$SET_LIBRARY operation)
If you do not specify a confirm callback, CMS does not request confirmation. It operates as if a callback had been specified and had returned the string "YES". CMS then proceeds with the operation.
For more information on confirmation routines, see the description of the CMS$CMS routine in Chapter 2, "CMS Routine Descriptions".
1.6.2.2. The Prompt Routine
The CMS$CMS routine uses a caller-supplied callback routine to prompt when CMS encounters an incomplete command line.
You set the address of the prompt routine by specifying the prompt_routine argument to CMS$CMS.
If you do not specify a prompt callback, CMS does not prompt you, but operates as if a callback had been specified and had returned the status RMS$_EOF (except in the case of prompting for a CMS remark, where the status is RMS$_NORMAL). The RMS$_EOF return status causes termination of command parsing (as if the user had pressed Ctrl/Z at the DCL prompt).
For more information on command-line prompting, see the description of the CMS$CMS routine in Chapter 2, "CMS Routine Descriptions".
1.6.2.3. The Output Routine
The CMS$CMS routine uses a caller-supplied callback routine for all terminal output (for example, the results of a SHOW or HELP command, or the listing of concurrent reservations for REPLACE and RESERVE).
By specifying the output_routine argument to CMS$CMS, which affects the command being parsed and executed
By specifying the output_routine argument to CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY or CMS$SET_LIBRARY, which affects all operations performed using that LDB (until you reinitialize the LDB by performing another CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY or CMS$SET_LIBRARY operation)
CMS directs output to SYS$OUTPUT if the message or output callback routines are not specified.
Note that if /OUTPUT is specified to redirect terminal output to a file, CMS opens, writes to, and closes the file normally and does not use the output callback routine.
For more information on output routines, see the description of the CMS$CMS routine in Chapter 2, "CMS Routine Descriptions".
1.6.3. Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines
CMS provides routines for passing strings between a callback routine and a CMS routine. CMS passes a string (such as an element name) to a callback routine using a string identifier. A string identifier is the address of a string descriptor. CMS passes string identifiers by reference. Figure 1.2, ''A String Identifier'' shows the relationship between the string identifier and the passed string.
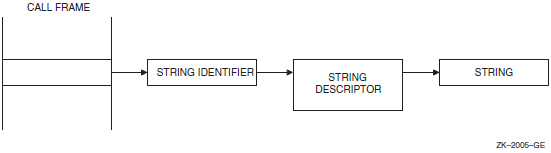
Within callback routines, you use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to process an output string from CMS, and the CMS$PUT_STRING routine to provide a string for input to CMS. You can manipulate the descriptors directly if the language allows it (as BLISS or C does, for example). See the descriptions of CMS$GET_STRING and CMS$PUT_STRING for more information.
1.6.3.1. Specifying End of Input
CMS passes an eof_status parameter to the input callback routines invoked by the CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT and CMS$REPLACE routines. Every time an input callback routine returns control to CMS,CMS checks the eof_status parameter for a value of true (1). When CMS encounters a true value in eof_status, the current input record (passed by CMS$PUT_STRING) is assumed to be insignificant. Thus, when you pass the last input record to CMS, you must wait until the next invocation of the callback routine to set eof_status to true.
It is important to specify a true status at the appropriate time during a wildcard or group CMS$REPLACE transaction. For more information about CMS$REPLACE, see Chapter 2, "CMS Routine Descriptions".
1.6.3.2. Determining End of Output
CMS sets the eof_status parameter to true after the last record has been passed to the callback routine. CMS does not set eof_status to true until the next invocation of the callback routine. Thus, when the callback routine encounters the end of output, the contents of output_record are undefined.
1.6.4. Callback Return Codes
Each time a callback routine returns control to CMS, CMS checks the low-order bit of the callback return code to determine success or failure. A success code directs CMS to continue processing; if there is more data for processing, CMS calls the callback routine again. Under certain circumstances, CMS also checks for CMS$_EXCLUDE and CMS$_STOPPED. CMS$_EXCLUDE directs CMS to continue processing, but it also indicates that the current record does not meet some requirement established by the callback routine. CMS$_STOPPED is used to halt a wildcard transaction.
For example, the CMS$DELETE_HISTORY routine calls the output callback routine once for each record to be deleted. The callback routine must return one of two values, CMS$_NORMAL to direct CMS to delete the record from the history file, or CMS$_EXCLUDE to prevent CMS from deleting the history record.
The CMS$SHOW_HISTORY routine provides another example of using CMS$_EXCLUDE. CMS passes a parameter to the callback routine that indicates whether the transaction is unusual. If the callback routine checks only for unusual transactions and there are none, it returns CMS$_EXCLUDE each time control is transferred to CMS. As a result, the CMS$SHOW_HISTORY routine returns CMS$_NOHIS (no history records found).
If the callback routine encounters an error during processing, it should abort the CMS call by returning an error status. This causes the CMS call to exit using CMS$_USERERR. To abort the transaction from the message routine without returning an error status, you should have the message routine call CMS$ASYNCH_TERMINATE to allow CMS to clean up resources.
For a list of the primary return codes, see the description of each routine in Chapter 2, "CMS Routine Descriptions".
1.7. Handling Error Conditions
If the condition is not fatal, CMS calls a message handler. You can provide a message routine to handle messages (see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''). If you do not provide a message routine, CMS calls its own message handler.
If the condition is fatal, CMS signals the error. Fatal conditions are those situations where execution cannot continue. CMS does not call the message routine (if supplied) under these circumstances.
If you have established a condition handler in the calling program and the condition handler encounters a fatal return value, do not return a value of SS$_CONTINUE from the condition handler or resignal SS$_CONTINUE, and do not issue additional calls to CMS until you have exited and reentered the image. The fatal error indicates that CMS cannot continue with the current invocation of the image.
If you supply a routine for input or output (see Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'') and you establish a condition handler within this routine, do not exit from the image (through either the condition handler or the routine itself). In addition, do not unwind the stack beyond the call to the user-supplied routine.
To exit the image, you should return an error (any status with the low bit clear) from your routine, causing CMS to terminate with CMS$_USERERR status. CMS$_USERERR status indicates that a callback routine returned an error.
1.8. Writing an Error-Message Handler
By default, CMS directs all diagnostic messages to SYS$OUTPUT and SYS$ERROR. However, you can write your own routine to handle messages. When you specify the msg_routine argument to any CMS routine, CMS passes control to your message handler instead of using the default handler. CMS does not call your message-handler routine if a fatal condition occurs, but instead notifies you by signaling the condition. If you receive a fatal error message, you should exit and reenter CMS—do not attempt to recall CMS within the same image invocation if CMS detected a fatal error.
You pass a message routine by specifying the entry mask of the routine in the call to the CMS routine. This places the address of the routine entry mask in the argument list (CMS uses the CALLG and CALLS procedure call instructions to invoke message routines). In general, you pass message routines by reference, but the method you use to pass the routine address depends on the language you are using. For examples of programs that pass routine addresses to CMS routines, see Appendix B, "Examples of Calling CMS".
- signal_array
- Type: vector_longword_unsigned
- Access: read
- Mechanism: by reference
- Specifies a standard OpenVMS signal array.
- mechanism_array
- Type: vector_longword_unsigned
- Access: read
- Mechanism: by reference
- Specifies a standard OpenVMS mechanism array.
- library_data_block
- Type: cntrlblk
- Access: modify
- Mechanism: by reference
- Specifies a valid LDB. Although the LDB can be modified, you should not change its contents. If you do so, you might corrupt your CMS library.
Do not invoke any CMS routines from a message routine (except CMS$ASYNCH_TERMINATE, CMS$GET_STRING, or CMS$PUT_STRING).
Do not unwind the stack, because it might corrupt your library.
Do not use the LIB$ESTABLISH Run-Time Library routine to enable the message routine as the exception handler for a CMS call. CMS uses its own exception handlers and calls the user-supplied message routine under the correct circumstances. (The message routine is only for handling messages,not for general exception handling during the execution of a CMS routine.)
10 INTEGER*4 LDB(50)
INTEGER*4 STATUS
CHARACTER*14 DIR
CHARACTER*8 CLASS,NEWNAME
C
INTEGER*4 CMS$MODIFY_CLASS
INTEGER*4 CMS$SET_LIBRARY
EXTERNAL MSG  C
100 DIR = '[LENNON.SONGS]'
CLASS = 'PRE_1968'
NEWNAME = 'PRE_1970'
C
STATUS = CMS$SET_LIBRARY(LDB,DIR)
IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$STOP(%VAL(STATUS))
STATUS = CMS$MODIFY_CLASS(LDB,CLASS,,NEWNAME,,,MSG)
C
100 DIR = '[LENNON.SONGS]'
CLASS = 'PRE_1968'
NEWNAME = 'PRE_1970'
C
STATUS = CMS$SET_LIBRARY(LDB,DIR)
IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$STOP(%VAL(STATUS))
STATUS = CMS$MODIFY_CLASS(LDB,CLASS,,NEWNAME,,,MSG)  IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$STOP(%VAL(STATUS))
C
END
C
INTEGER*4 FUNCTION MSG(SIGNAL,MECH,LIBDB)
INTEGER*4 SIGNAL(16),SIGNAL_COPY(16),MECH(5)
IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$STOP(%VAL(STATUS))
C
END
C
INTEGER*4 FUNCTION MSG(SIGNAL,MECH,LIBDB)
INTEGER*4 SIGNAL(16),SIGNAL_COPY(16),MECH(5)  INTEGER*4 LIBDB(50)
EXTERNAL CMS$_MODIFIED
EXTERNAL SYS$PUTMSG
IF (.NOT. SIGNAL(2)) THEN
DO I=1,16
SIGNAL_COPY(I) = SIGNAL(I)
END DO
SIGNAL_COPY(1) = SIGNAL_COPY(1) - 2
INTEGER*4 LIBDB(50)
EXTERNAL CMS$_MODIFIED
EXTERNAL SYS$PUTMSG
IF (.NOT. SIGNAL(2)) THEN
DO I=1,16
SIGNAL_COPY(I) = SIGNAL(I)
END DO
SIGNAL_COPY(1) = SIGNAL_COPY(1) - 2  CALL SYS$PUTMSG(SIGNAL_COPY)
ENDIF
MSG = 1
CALL SYS$PUTMSG(SIGNAL_COPY)
ENDIF
MSG = 1  RETURN
END
RETURN
ENDThe message routine is declared as an external routine. | |
The call to CMS$MODIFY_CLASS includes the address of the message routine. | |
The message routine is written as a function so it returns a value to CMS. In this case, 16 longwords are declared for the signal array; however, the size required is dependent on the number of messages that are generated. An additional array is declared to make a copy of the signal array. The mechanism array requires five longwords. | |
The message-handler routine checks the signal array for an error. If the test fails, the message routine returns control to CMS. If the test is successful, the signal array is copied and the longword count of the copied signal array is altered (in effect removing the PC and PSL at the end of the array). The array is then in a form that is compatible with the SYS$PUTMSG routine, which displays the message on the terminal. | |
The return value is set to true (1), and control is returned to CMS. |
1.9. Linking with the CMS Image
You do not have to specify the CMS shareable image in your LINK command because the installation procedure inserts CMSSHR.EXE into the default system shareable image library (SYS$LIBRARY:IMAGELIB.OLB), which is automatically searched by the linker.
LINK filename[,...]
$ LINK filename[,...],SYS$INPUT/OPTIONS Return CMSSHR/SHAREABLE Ctrl/Z
Chapter 2. CMS Routine Descriptions
This chapter describes the purpose of each CMS routine, the arguments and parameters used in routine calls, and the return status. For more information about diagnostic messages, see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Code Management System Reference Manual.
Read access–The routine can only read data.
Modify access–The routine can both read from and write to the address.
Write access–The routine writes into the address without reading the contents.
The passing mechanism indicates how the argument list is interpreted. The reference mechanism indicates that the argument list entry is the address of the object. The descriptor mechanism indicates that the argument list entry is an address that points to a descriptor containing the address of the object.
Each argument is evaluated according to the position it occupies in the argument list. Therefore, you must be sure you specify null arguments correctly. If you omit an argument and do not include a placeholder in the call, CMS cannot correctly interpret the arguments that follow. For more information about specifying null arguments, see Section 1.4, ''Passing Arguments to CMS Routines''.
Brackets ( [] ) surrounding arguments indicate that the enclosed item is optional.
CMS$ANNOTATE
CMS$ANNOTATE — Creates a line-by-line file listing the changes made in each specified element generation.
Format
CMS$ANNOTATE (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[generation_expression],
[merge_generation_expression],
[append],
[full],
[output_file],
[output_routine],
[user_arg],
[msg_routine],
[format])Arguments
library_data_block
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements, or groups of elements, to be annotated. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed. CMS creates one output file for each annotated element unless you also specify the append argument.
You must include a period (.) in the element expression to select one or more elements from the complete list of elements in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and selects elements based on the list of groups established in the library.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the generation to be annotated. If you do not provide a generation number or class name, CMS annotates the latest generation on the main line of descent.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the element generation to be merged into the annotated generation.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to append the output to a file. If you set the flag to 1, CMS appends the output to a file. If you set the flag to 0, CMS creates as many new output files as necessary. CMS ignores this argument if you provide an output routine.
When you set the append flag to 1, CMS appends the output to an existing file indicated by the output_file argument. If you do not specify an output file, CMS appends the output to a file with the same file name as the element file with the file type of .ANN. If no such file exists, CMS creates one.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to produce an annotated listing that indicates the file creation time, file revision time, and record format for the file used to create each generation, and shows the deletion history of the element. If you set the flag to 1, CMS produces a full listing. If you set the flag to 0, CMS produces a normal, annotated listing.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the name of the output file. By default, the file name is the element file name with the file type of .ANN. Use this argument if you want the output file to have a different name, or if you want CMS to put the file in a directory other than your current, default directory. Wildcards are allowed.
If you provide an output file specification and do not set the append flag to 1, CMS creates one output file for each element annotated. If more than one element is annotated and you do not include wildcards in the output file specification, CMS creates successive versions of the specified output file. (Note that if you provide a directory specification, but no file name or file type, CMS creates one output file for each element annotated and places each output file in the specified directory. In this case, each output file is named according to the default naming convention.) If you specify an output file, you cannot also specify an output routine.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine that processes data output by CMS$ANNOTATE. CMS calls the output routine once for each line of data. If you specify an output routine, you cannot also specify an output file. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the callback routine.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to the output_routine argument, using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | mask_longword |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the type of formatting to be performed on the data before it is placed in the output file. You must specify either the output_file or output_routine arguments with this argument. By default, the flag is set to 1, indicating ASCII output.
|
Data Format |
Bit Position |
Mask Value |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CMS$M_ASCII |
0 |
1 |
Specifies that data be presented as if each byte represents a value in the ASCII character set. This option is most useful when files contain text. If no data partition is specified, data is partitioned into records. This option is the default. |
|
CMS$M_DECIMAL |
1 |
2 |
Specifies that each value be displayed as a decimal numeral. If no data partition is specified, data is partitioned into longwords. You cannot specify both CMS$M_DECIMAL and CMS$M_RECORDS. |
|
CMS$M_HEXADECIMAL |
2 |
4 |
Specifies that each value be displayed as a hexadecimal numeral. If no data partition is specified, data is partitioned into longwords. You cannot specify both CMS$M_HEXADECIMAL and CMS$M_RECORDS. |
|
CMS$M_OCTAL |
3 |
8 |
Specifies that each value be displayed as an octal numeral. If no data partition is specified, data is partitioned into longwords. You cannot specify both CMS$M_OCTAL and CMS$M_RECORDS. |
|
Data Partition |
Bit Position |
Mask Value |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CMS$M_BYTE |
16 |
65,536 |
Specifies that the data displayed is to be partitioned into bytes. By default, records are not partitioned further unless the data format option indicates otherwise. |
|
CMS$M_LONGWORD |
17 |
131,072 |
Specifies that the data displayed is to be partitioned into longword values. This is the default partitioning for CMS$M_DECIMAL, CMS$M_HEXADECIMAL, and CMS$M_OCTAL. |
|
CMS$M_RECORDS |
18 |
262,144 |
Specifies that no further partitioning of data is to occur beyond the record partitioning already in the file. This partitioning is most useful when the files contain text. You can specify CMS$M_RECORDS only by itself or in conjunction with ASCII. It cannot be used with any other options. This qualifier is the default. |
|
CMS$M_WORD |
19 |
524,288 |
Specifies that the data displayed be partitioned into word values. By default, data records are not partitioned further unless the data format indicates otherwise. |
Callback Routine Parameters
first_call, library_data_block, user_param, element_id,
output_record_id, eof_statusThe callback routine must return a value to CMS. CMS checks the low-order bit of that value for success (1) or failure (0) status. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the current call to the output routine is the first call. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the current call is the first call. Otherwise, this flag is set to 0.
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$ANNOTATE. If you did not specify a user argument in the call syntax, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes the parameter user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$ANNOTATE.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the element name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the line of data produced by CMS$ANNOTATE. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the end-of-file status. CMS changes the value of eof_status from false (0) to true (1) after the last record has been passed to the output routine. When eof_status is true, the contents of output_record_id are undefined. See Section 1.6.3.2, ''Determining End of Output'' for more information on determining the end of output.
Description
A history
A source-file listing
The history includes the generation number, date, time, user, and remark of the transaction that created each generation of the element. In addition, if you specify the FULL argument, the history also includes information about file creation and revision times, and record format and attributes. Element generations are listed in reverse chronological order. The generation numbers of the specified generation and its ancestors are marked with an asterisk (*).
The source-file listing contains all the lines inserted or modified from generation 1 to the specified generation. The listing does not show lines deleted from the file. CMS inserts consecutive line numbers in the listing unless editor-assigned line numbers already exist. (The line numbers start with 1 for the first line and increase by 1 for each line.) The generation field starts at the first character position of each line. It contains the generation number of the most recent generation in which the line was inserted or modified. The generation field is blank if a line is unchanged since generation 1.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ANNOTATED |
CMS annotated the element. |
Success |
|
CMS$_ANNOTATIONS |
CMS annotated one or more elements. |
Success |
|
CMS$_ERRANNOTATIONS |
CMS annotated zero or more elements and encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOANNOTATE |
CMS did not annotate the specified element. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_USERERR |
User routine returned an error to CMS. |
Error |
CMS$ASYNCH_TERMINATE
CMS$ASYNCH_TERMINATE — Simulates a keyboard Ctrl/C (cancel). This routine enables calling programs to specify to the CMS function currently in progress that cancellation has been requested.
Format
CMS$ASYNCH_TERMINATEArguments
None.
Description
The CMS$ASYNCH_TERMINATE routine requests CMS to terminate processing at the next convenient point, just as if the user presses Ctrl/C during command execution. This termination might not occur immediately and in fact may not occur at all, depending on the operation.
You can call CMS$ASYNCH_TERMINATE from your own Ctrl/C handler, anywhere in your program, callback routines, and AST routines.
CMS$ASYNCH_TERMINATE sets a flag so CMS can recognize it at a convenient time. This flag is usable with both CMS$CMS and other lower-level callable CMS routines. CMS clears this flag on entry to a top-level callable routine.
CMS$CMS
CMS$CMS — Is a high-level entry point that enables calling programs to pass a DCL command line to CMS for processing. This function parses and executes the command line, then returns to the calling program.
Format
CMS$CMS ([command_line],
[msg_routine],
[prompt_routine],
[confirm_routine],
[output_routine],
[width])Arguments
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the address of a string descriptor that contains a command line. If you specify 0, CMS uses the prompt_routine argument to prompt you for a command line. If you do not specify this argument or a prompt routine, CMS returns the error RMS$_EOF (end-of-file detected).
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the address of a callback routine used instead of direct terminal input when a response is required from the user. This routine is used to handle missing command parameters and command continuation lines.
If this parameter is not specified, CMS does not prompt for missing command-line components—it returns RMS$_EOF. This return value causes the command line interpreter (CLI) to terminate command processing.
string_id—Specifies a string identifier passed by reference for the prompt string, which can then be displayed to the user. Use CMS$GET_STRING to retrieve the string value.
flag—Specifies a longword passed by reference, which designates the specific type of information being requested: 0 indicates a command line, 1 indicates a missing parameter, and 2 indicates are mark. The caller must determine what to do in each situation.
The prompt_routine argument must use CMS$PUT_STRING to return user input to CMS. Note that this convention is not compatible with direct use of LIB$GET_INPUT. However, it serves the same purpose as in other callable CMS routines in that it prevents difficulties due to the differing string descriptor support of various languages.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the address of a callback routine used instead of direct terminal input when either the /CONFIRM qualifier is specified, or a module is being reserved, unreserved, or replaced with concurrent reservations in effect.
This routine can work in either of two modes. It can return a string or the status of whatever operation it used to obtain the string (for example, LIB$GET_INPUT or $QIO status).
|
String |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
YES, 1, true |
Indicates positive confirmation |
|
ALL |
Indicates positive confirmation and that future actions of the current call to CMS should be carried out without confirmation |
|
NO, 0, false |
Indicates negative confirmation |
|
QUIT |
Indicates negative confirmation and that CMS performs no further actions |
|
Return Code |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
CMS$_CONFIRM |
Yes |
|
CMS$_NOCONFIRM |
No |
|
CMS$_ALL |
All |
|
CMS$_STOPPED |
Quit |
If the callback routine returns one of these codes, any string supplied through CMS$PUT_STRING is ignored.
For confirmations where ALL and QUIT are not meaningful (such as to confirm a concurrent reservation), ALL is equivalent to YES and QUIT is equivalent to NO.
If an invalid response is given, CMS prompts you again. Note that any response can be abbreviated to a single character. If a null string is returned, CMS defaults to NO. If a confirm routine is not specified, CMS does not prompt you; instead, it assumes positive confirmation (YES).
string_id—Specifies a string identifier passed by reference for the prompt string, which can then be displayed to the user. Use CMS$GET_STRING to retrieve the string value.
The confirm_routine argument should use CMS$PUT_STRING to return the user input string (if any) to CMS. Note that this convention is not compatible with direct use of LIB$GET_INPUT. However, it serves the same purpose as in other callable CMS routines in that it prevents difficulties due to the differing string descriptor support of various languages.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the address of a callback routine to handle output usually sent to SYS$OUTPUT. For example, all output from a SHOW command is directed to SYS$OUTPUT by default (in the absence of an overriding /OUTPUT qualifier). Reporting concurrent reservations or replacements (for FETCH, RESERVE, REPLACE, and UNRESERVE commands) is always to SYS$OUTPUT. This callback also receives the output for the commands FETCH/OUTPUT=SYS$OUTPUT:, DIFFERENCE/OUTPUT=SYS$OUTPUT:, and so forth.
If output_routine is not specified, CMS writes all output to SYS$OUTPUT.
string_id—Specifies a string identifier passed by reference for the output string, which can then be displayed to the user. Use CMS$GET_STRING to retrieve the string value.
flag—Specifies a longword passed by reference, which is set to –1 on the first invocation of the callback routine for a sequence of output. The flag is 0 for each following record of the sequence. After the final record of data in the output sequence, a final invocation of the callback sets the flag to 1, indicating that the output sequence is complete; in this case, the string_id argument is invalid because the final record has already been processed. The string_id parameter is valid when the flag is either –1 or 0.
For any call to a CMS entry point, it is possible to have more than one output sequence. For example, in a call to CMS$CMS with the command string FETCH/OUTPUT=TT: *.*, the text of each file is a separate output segment. In addition, the listing of concurrent reservations and replacements for each file is a separate output segment.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the maximum width of text that can be sent to the output callback routine. If this argument is not specified, the terminal width is used. If this is unavailable, the width defaults to the translation of CMS$WIDTH (if defined) or to 132 characters.
CMS$COPY_CLASS
CMS$COPY_CLASS — Copies an existing class to form a new class. The CMS$COPY_CLASS transaction preserves all class data and history.
Format
CMS$COPY_CLASS (library_data_block,
input_class_expression,
output_class_expression,
[remark],
[source_library_data_block],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB for the library in which the copy is to be placed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the class or classes to be copied. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
You must include a period (.) in the class expression to select one or more classes from the complete list of classes in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and makes selections based on the list of groups established in the library.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the name for the new class. The output_class_expression name cannot be the same as any existing class in the output library.
The output_class_expression value can be the same as the input_class_expression value only if you also specify a source library data block that points to a different library than the library data block.
You cannot use 00CMS as a class name component because it is reserved for CMS. If you used a comma list or wildcard in the input_class_expression, a wildcard must be used in the output_class_expression.
If you specify the source_library_data_block argument, the output_class_expression argument is optional.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB for the library from which the class is to be copied. When the copy is performed on different libraries and you specify the source_library_data_block argument, the output_class_expression argument is optional. By default, CMS searches the library associated with library_data_block.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$COPY_CLASS routine uses an existing library class to create a new class in the same library or in another library. The original class is left unchanged. The class history, file characteristics, and attributes are copied in full.
CMS must be able to create one new class for each old class. When you use wildcards in the input class specification, CMS builds a list of classes to be copied. CMS uses this list as the point of reference during the copy transactions. If the output class specification does not allow CMS to create a new class for each class in the input list, the results might not be what you intend.
If the existing class has the reference copy attribute enabled and the target library has a reference copy directory, CMS creates a reference copy for the new class and assigns the reference copy attribute to the new class. If there is no reference copy directory for the target library, the new class will not have the reference copy attribute, even if the existing class does.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_COPIED |
CMS copied the specified class. |
Success |
|
CMS$_COPIES |
CMS copied one or more classes. |
Success |
|
CMS$_ERRCOPIES |
CMS copied zero or more classes, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOCOPY |
CMS was unable to copy the specified class. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
Example
INTEGER*4 LDB(50)
CHARACTER*50 SOURCE_CLASS_NAME,DESTINATION_CLASS_NAMECALL
CMS$COPY_CLASS(LDB,SOURCE_CLASS_NAME, DESTINATION_CLASS_NAME)This call to CMS$COPY_CLASS copies a class between libraries. The newly created destination class is populated with the same element generations as those in the source class.
CMS$COPY_ELEMENT
CMS$COPY_ELEMENT — Copies an existing element to form a new element. The CMS$COPY_ELEMENT transaction preserves all element data and history.
Format
CMS$COPY_ELEMENT (library_data_block,
input_element_expression,
output_element,
[remark],
[source_library_data_block],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB for the library in which the copy is to be placed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the element or group of elements to be copied. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
You must include a period (.) in the element expression to select one or more elements from the complete list of elements in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and therefore selects elements based on the list of groups established in the library.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the element name for the new element. The output_element name cannot be the same as any existing element name in the output library.
The output_element name can be the same as input_element_expression only if you also specify a source library data block that points to a different library than the library data block.
You cannot use 00CMS as the file name component of an element name because it is reserved for CMS. If you used a comma list or wildcard in the input_element_expression, a wildcard must be used in the output_element.
If you specify the source_library_data_block argument, the output_element argument is optional.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB for the library from which the element is to be copied. When the copy is performed on different libraries and you specify the source_library_data_block argument, the output_element argument is optional. By default, CMS searches the library associated with library_data_block.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$COPY_ELEMENT routine uses an existing library element to create a new element in the same library or in another library. The original element is left unchanged. The generation history, file characteristics, and element attributes are copied in full.
CMS must be able to create one new element for each old element. When you use wildcards or a group name in the input element specification, CMS builds a list of elements to be copied. CMS uses this list as the point of reference during the copy transactions. If the output element specification does not allow CMS to create a new element for each element in the input list, the results might not be what you intend.
input element specification - *.FOR output element specification - NDATA.*
The first element that matches the input specification (*.FOR) produces one new element named NDATA.FOR. Each successive element that matches the input specification generates an error message because CMS can create only one unique element name from the given combination of wildcard expressions.
If the existing library element has the reference copy attribute enabled and the target library has a reference copy directory, CMS creates a reference copy for the new element and assigns the reference copy attribute to the new element. If there is no reference copy directory for the target library, the new element will not have the reference copy attribute, even if the existing element does.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_COPIED |
CMS copied the specified element. |
Success |
|
CMS$_COPIES |
CMS copied one or more elements. |
Success |
|
CMS$_ERRCOPIES |
CMS copied zero or more elements, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOCOPY |
CMS was unable to copy the specified element. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
Example
CHARACTER*10 DIR, SOURCE_DIRCHARACTER*10 ELEMENTCHARACTER*26 REMARK INTEGER*4 LDB(50)
INTEGER*4 SOURCE_LDB(50) INTEGER*4 STATUS INTEGER*4 CMS$SET_LIBRARY
INTEGER*4 CMS$COPY_ELEMENT DIR = '[COMP.LIB]' SOURCE_DIR = '[BASE.LIB]'
ELEMENT = 'TSTDAT.FOR' REMARK = 'Transfer from base library' STATUS = CMS$SET_LIBRARY(LDB,DIR)
IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$STOP(%VAL (STATUS)) STATUS = CMS$SET_LIBRARY(SOURCE_LDB,SOURCE_DIR) IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$STOP(%VAL (STATUS)) STATUS = CMS$COPY_ELEMENT(LDB,ELEMENT,,REMARK,SOURCE_LDB)
IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$STOP(%VAL (STATUS)) END
Character-string variables are declared for the directory specifications,element name, and remark. | |
The LDBs are declared as 50–word integer arrays. | |
The CMS routines are declared external to the program. | |
The character-string variables are assigned the appropriate values. | |
The CMS$SET_LIBRARY routine is called once for each library to be accessed. | |
The destination LDB, element name, remark, and source LDB are passed to the CMS$COPY_ELEMENT routine. Two commas are specified between the ELEMENT and the REMARK arguments; the second comma is required as a placeholder for the omitted argument (the output element name).In this case, it is not necessary to provide an output element name. Because the source and destination libraries are different, CMS creates a new element with the same name (as long as the destination library does not already contain an element with that name). |
CMS$COPY_GROUP
CMS$COPY_GROUP — Copies an existing group to form a new group. The CMS$COPY_GROUP transaction preserves all group data and history.
Format
CMS$COPY_GROUP (library_data_block,
input_group_expression,
output_group_expression,
[remark],
[source_library_data_block],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB for the library in which the copy is to be placed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the group or groups to be copied. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the name for the new group. The output_group_expression name cannot be the same as any existing group in the output library.
The output_group_expression value can be the same as the input_group_expression value only if you also specify a source library data block that points to a different library than the library data block.
You cannot use 00CMS as a group name component because it is reserved for CMS. If you used a comma list or wildcard in the input_group_expression, a wildcard must be used in the output_group_expression.
If you specify the source_library_data_block argument, the output_group_expression argument is optional.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB for the library from which the group is to be copied. When the copy is performed on different libraries and you specify the source_library_data_block argument, the output_group_expression argument is optional. By default, CMS searches the library associated with library_data_block.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$COPY_GROUP routine uses an existing library group to create a new group in the same library or in another library. The original group is left unchanged. The group history, file characteristics, and attributes are copied in full.
CMS must be able to create one new group for each old group. When you use wildcards in the input group specification, CMS builds a list of groups to be copied. CMS uses this list as the point of reference during the copy transactions. If the output group specification does not allow CMS to create a new group for each group in the input list, the results might not be what you intend.
If the existing group has the reference copy attribute enabled and the target library has a reference copy directory, CMS creates a reference copy for the new group and assigns the reference copy attribute to the new group. If there is no reference copy directory for the target library, the new group will not have the reference copy attribute, even if the existing group does.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_COPIED |
CMS copied the specified group. |
Success |
|
CMS$_COPIES |
CMS copied one or more groups. |
Success |
|
CMS$_ERRCOPIES |
CMS copied zero or more groups, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOCOPY |
CMS was unable to copy the specified group. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
Example
CHARACTER*8 SOURCE_GROUP_NAME CHARACTER*8 DESTINATION_GROUP_NAME EXTERNAL CMS$COPY_GROUP SOURCE_GROUP_NAME ='V1' DESTINATION_GROUP_NAME ='V2' CALL CMS$COPY_GROUP (LDB, SOURCE_GROUP_NAME, DESTINATION_GROUP_NAME)
This call to CMS$COPY_GROUP copies a group between libraries. The newly created destination group is populated with the same elements as those in the source group.
CMS$CREATE_CLASS
CMS$CREATE_CLASS — Creates an empty class in one or more CMS libraries.
Format
CMS$CREATE_CLASS (library_data_block,
class_name,
[remark],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the class to be created. Class and group names must be unique; CMS returns an error if you specify a name currently in use for an existing class or group. If a previously used class or group name has been removed with the CMS$DELETE_CLASS or CMS$DELETE_GROUP routine, you can use that name again with CMS$CREATE_CLASS. Wildcards are not allowed, but a comma list is allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file and associated with the class.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$CREATE_CLASS routine establishes a class. Once a class is established, you can place any set of element generations into that class by using the CMS$INSERT_GENERATION routine. The CMS$CREATE_CLASS routine does not place any generations in the created class.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_CREATED |
CMS created the class. |
Success |
|
CMS$_CREATES |
CMS created one or more classes. |
Success |
|
CMS$_ERRCREATES |
CMS created zero or more classes, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOCREATE |
CMS did not create the specified class. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT
CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT — Creates a new element in a CMS library or in the first library of a search list, if one was specified.
Format
CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT (library_data_block,
element_name,
[remark],
[history],
[notes],
[position],
[keep],
[reserve],
[concurrent],
[reference_copy],
[input_file],
[input_routine],
[user_arg],
[msg_routine],
[review])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the new element to be created. The element_name argument is required. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed; however, you cannot use wildcards if you specify input_routine.
If you do not specify the input_file argument,the element name must correspond to an existing file in your current, default directory. The name cannot be the same as any existing element name in the library. You cannot use the file name 00CMS because it is reserved for CMS.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the creation remark string to be logged in the history file and associated with the element and the first generation of the element.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the history string. If you include the historyargument in the call, CMS establishes or changes the history attribute for the element. If an element has a history attribute, its history is included in the file when it is retrieved by the CMS$FETCH routine. To disable the history attribute, specify a zero-length string. For a detailed explanation of the history element attribute, see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the notes string. If you include the notes argument in the call, CMS establishes or changes the notes attribute for the element. If an element has a notes attribute, notes are embedded in the lines of the file when it is retrieved by the CMS$FETCH routine. To disable the notes attribute, specify a zero-length string. Any element that has the notes attribute must have the position attribute. For a detailed explanation of the notes attribute, see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the position value to be used with the notes attribute. The position attribute determines the character position at which the note is to begin on the line. The position value must be an integer greater than zero. Any element that has the position attribute must have the notes attribute. For a detailed explanation of the position attribute, see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that prevents CMS from deleting copies of the input file after the element is created. By default, the flag is set to 0, indicating that CMS should delete the copies of the file in your default directory (or the area indicated by the input_file argument) after creating the new element. Set the flag to 1 to prevent CMS from deleting the copies of the input file. These settings can also be set library-wide, as well as by element.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to establish a reservation for the new element. By default, the flag is set to 0,and CMS does not mark the element as reserved. Set the reserve flag to 1 to reserve the element. In this case, CMS ignores the value of the keepflag and does not delete the file used to create the element.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating the access to the element. By default, the flag is set to 1, and CMS allows concurrent reservations of the element. Set the concurrent flag to 0 to prohibit concurrent reservations. These settings can also be set library-wide, as well as by element.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating whether CMS is to maintain a reference copy of the element when a new main-line generation is created.
If you do not specify this argument and a reference copy directory is already established, CMS enables the reference copy attribute for the element, and creates the reference copy.
If you specify a 0, or if you do not specify this argument and a reference copy directory is not established, CMS creates the element but does not enable the reference_copy attribute for the element, and does not create the reference copy.
If you specify a 1 for this argument and the reference copy directory is not established, you get an error.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the name of the file to be used to create the element. If you specify an input file, you cannot also specify an input routine. Wildcards are allowed, but must match the wildcards specified in element_name.
Use this argument if you want the element to be created from a file with a different name than that specified by the element_name argument. You can also use this argument to direct CMS to search a different location other than your current, default directory. When you specify an input file in an alternate directory, CMS deletes the file from the alternate directory (unless you specify the keep or reserve argument).
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine that provides data for the CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT transaction. CMS calls this routine once for each line of data until the callback routine indicates the end-of-file.
If you specify an input routine, you cannot also specify an input file, nor can you specify wildcards in the element_name argument. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the input routine.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to the input_routine argument, using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating whether CMS is to automatically mark new generations as pending review. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS marks new generations of the element as pending review only if the reserved generation was either rejected or has a review pending. Set the flag to 1 to indicate that new generations should be marked for review.
Callback Routine Parameters
first_call, library_data_block, user_param, element_id,
eof_status, sequence_flag, sequence_numberThe callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the current call to the input routine is the first call. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the current call is the first call. Otherwise, this is set to 0.
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the element name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the end-of-file status. The input routine must change the value of eof_status from false (0) to true (1) to indicate to CMS that input is terminated. When eof_status is true, CMS ignores the contents of the current input record (passed by CMS$PUT_STRING).
Therefore, you must set eof_status to true in the call following the last significant input record. See Section 1.6.3.1, ''Specifying End of Input'' for more information on specifying the end of input.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to create a sequenced element file. By default, the flag is set to 0, indicating that the input is not sequenced. Set the flag to 1 to direct CMS to create a sequenced element file.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a signed integer that indicates the sequence number of the input line. A value in the range of 1 to 65,536 characters indicates the sequence number.
When you use a callback routine to provide input for CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT, CMS uses the time of the CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT transaction as the file creation and revision times associated with generation 1 of the new element. CMS also uses the following record format and record attributes when you use a callback input routine. If you provide unsequenced input, generation 1 of the new element has variable-length records with the carriage return record attribute. If you provide sequenced input, the element generation has VFC 2-byte records with the carriage return record attribute.
Description
The CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT routine creates the first generation of a new element from a file in your current, default directory, or from the file specified by the input_file argument. After the element is created, CMS deletes the file used to create the new element (and any earlier versions of the file in the same directory, or the entire search list if the file is located in a search list). If you specify either the keep or reserve argument, CMS does not delete the file. When you create an element, you can also define the attributes (history, notes,position, concurrent access, reference copy, and review) for the element or establish a reservation.
CMS stores the creation date and time, format, revision date and time, file revision number, file characteristics, and any attributes of the file used to create the new element. When you fetch or reserve an element generation, CMS restores the times and file revision number associated with the file used to create the element generation. You can also obtain this information by using the CMS$SHOW_GENERATION routine.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_CREATED |
CMS created the specified new element. |
Success |
|
CMS$_CREATES |
CMS created one or more elements. |
Success |
|
CMS$_ERRCREATES |
CMS created zero or more elements, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOCREATE |
CMS did not create the specified element. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_USERERR |
User routine returned an error to CMS. |
Error |
CMS$CREATE_GROUP
CMS$CREATE_GROUP — Creates an empty group in one or more CMS libraries.
Format
CMS$CREATE_GROUP (library_data_block,
group_name,
[remark],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the group to be created. Group and class names must be unique; CMS returns an error if you specify a name currently in use for an existing group or class. However, if a previously used group or class name has been removed with the CMS$DELETE_GROUP or CMS$DELETE_CLASS routine, you can use that name again with CMS$CREATE_GROUP. Wildcards are not allowed, but a comma list is allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file and associated with the group.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$CREATE_GROUP routine establishes a group. (For more information about groups, see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System.) Once a group is established, you can place elements or groups into that group by using the CMS$INSERT_ELEMENT or CMS$INSERT_GROUP routine. The CMS$CREATE_GROUP routine does not place any elements or groups in the created group.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_CREATED |
CMS created the specified group. |
Success |
|
CMS$_CREATES |
CMS created one or more groups. |
Success |
|
CMS$_ERRCREATES |
CMS created zero or more groups, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOCREATE |
CMS did not create the group. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY
CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY — Creates a new CMS library in an existing empty directory, and adds that library to the passed library search list context.
Format
CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY (library_data_block,
directory,
[remark],
[reference_copy_dir],
[msg_routine],
[confirm_routine],
[output_routine],
[width],
[position],
[positional_dir_spec]
[revision_time],
[auto_create],
[concurrent],
[0],
[keep],
[extended_filenames],
[long_variant_names])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a valid LDB. The LDB might not be initialized, depending on whether you also specify the position and positional_dir_spec arguments.
If the position and positional_dir_spec arguments are specified, the library data block must have already been initialized by a previous call to CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY or CMS$SET_LIBRARY. If the position and positional_dir_spec arguments are not specified, the library data block is initialized by this call and points to the specified directory.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies an existing directory. The directory must not contain any files or subdirectories, or be an eighth-level directory. A directory to be used as a CMS library cannot be your current, default directory. Wildcards are not allowed, but a comma list is allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a valid OpenVMS directory to be used for reference copies of elements. The directory cannot be a CMS library. Wildcards are not allowed.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the address of the entry mask of a confirmation callback routine. For information about callback routines, see Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines''.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the address of the entry mask of a terminal output callback routine. For information about callback routines, see Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the maximum width of text that can be sent to the output callback routine. If this argument is not specified, the terminal width is used. If this is unavailable, the width defaults to the translation of CMS$WIDTH (if defined), or to 132 characters.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the position value to be used with the positional_dir_spec argument. The position value determines the position in the library search list at which the new library or libraries are to be inserted, or whether the new library or libraries are to supersede the existing library search list.
|
Value |
Result |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Indicates that a new library or libraries should supersede the existing library list. This is the default. |
|
1 |
Indicates that the new library or libraries should be inserted after an existing library in the library search list specified with the positional_dir_spec argument. |
|
2 |
Specifies that the new library or libraries should be inserted before an existing library in the library search list specified with the positional_dir_spec argument. |
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the name of a library in the current library search list before or after which the new library or libraries are to be inserted (depending on the value of the position argument).
If you omit the positional_dir_spec argument and specify a value of 1 for the position argument, new libraries are appended to the existing library search list. If you omit the positional_dir_spec argument and specify a value of 2 for the position argument, new libraries are inserted at the beginning of the existing library search list. If the position argument is specified as 0 or is omitted, the positional_dir_spec argument is ignored.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Controls whether CMS uses the original file revision time or the file storage time when a file is created in the CMS library. The default flag is set to 0, indicating the use of the original file revision time. Set the flag to 1 to use the file storage time.
| type: | longword_aligned |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to automatically create the library directory. A value of 1 tells CMS to automatically create the library directory. If the value of the flag is 0, CMS will not create the library directory. If the reference_copy_dir parameter has been set, the reference copy is also created automatically.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating access to the elements. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS allows concurrent reservations of the elements. Set this flag to 1 to prohibit concurrent reservations across the library, unless an individual element setting overrides it.
| type: | reserved for CMS |
| access: | reserved for CMS |
| mechanism: | by value |
Specifies a required argument reserved for use by CMS. You must either pass a value of 0 or include a placeholder for this argument in the call to the CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY routine, so the call frame entry for this argument contains a 0.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that prevents CMS from deleting copies of the input file after the element is created. By default, the flag is set to 0, indicating that CMS should delete all the copies of the file in your default directory (or the area indicated by the input_file argument) after creating the new element. Set the flag to 1 to prevent CMS from deleting input files across the library, unless an individual element setting overrides it.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Only valid on OpenVMS versions that support extended file specifications. The default 0 value does not allow extended file names. The value 1 allows extended file names.
| type: | mask_longword |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies whether variant names longer than a single character are allowed. The default value 0 does not allow long variant names. The value 1 allows variant names up to 255 alphabetic characters in length.
Description
The CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY routine builds CMS control files in a directory so it can be used as a CMS library. Once you have established a library with the CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY routine,you can call other CMS routines to manipulate the library using the same LDB now initialized and can be used by other routines. Your CMS library is set to the library directory specified in the directory argument.
The CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY routine establishes a CMS library search-list context with one or more CMS library directories. Once the search-list context has been established, you can use the resulting LDB in calls to other CMS routines.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_CREATED |
CMS created the library. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOCREATE |
CMS did not create the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOEXTENDED |
This version of CMS does not allow the use of extended filenames. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOEXTENDEDREF |
The reference copy directory is located on a disk that does not allow the use of extended filenames. |
Error |
CMS$DELETE_CLASS
CMS$DELETE_CLASS — Deletes one or more classes from a CMS library.
Format
CMS$DELETE_CLASS (library_data_block,
class_expression,
[remark],
[msg_routine],
[remove_contents])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more classes to be deleted. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Determines whether CMS removes the current contents of each class specified by class_expression prior to deletion. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS does not remove generations from each class. If you set the value to 1, CMS removes all element generations from each class prior to deleting the class itself.
Description
The CMS$DELETE_CLASS routine deletes one or more classes from a CMS library. If a class contains one or more element generations, set remove_contents to 1 to remove the content of the class prior to deletion. Otherwise, CMS issues an error message and does not delete the class. You cannot delete a class set to READ_ONLY. (See the CMS$REMOVE_GENERATION and CMS$MODIFY_CLASS routines for more information.)
Even though a class is deleted, records of transactions that created and used the class are retained in the project history. You can reuse the deleted class name to create a new class. However, there is no distinction between the two classes in the project history, except that their transactions are separated by entries for DELETE CLASS and CREATE CLASS commands.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_DELETED |
CMS deleted the class. |
Success |
|
CMS$_DELETIONS |
CMS deleted one or more classes. |
Success |
|
CMS$_ERRDELETIONS |
CMS deleted zero or more classes, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NODELETE |
CMS did not delete the class. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
CMS$DELETE_ELEMENT
CMS$DELETE_ELEMENT — Deletes one or more elements from a CMS library. The element cannot be in any groups, have current reservations or reviews pending, and there can be no generations of it in any classes.
Format
CMS$DELETE_ELEMENT (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[remark],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements to be deleted. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$DELETE_ELEMENT routine deletes one or more elements from a CMS library. If the element is set to /REFERENCE_COPY and there is a current reference copy directory for the CMS library, CMS deletes the corresponding file (if it exists) from the reference copy directory. There cannot be any existing reservations for the element, and the element cannot have any generations with reviews pending. The element cannot be a member of a group, nor can one of its generations belong to a class. If it is reserved, you must cancel the reservation (using the CMS$UNRESERVE routine) or replace the element in the library (using the CMS$REPLACE routine) before you can delete the element. If the element belongs to any groups or classes, use the CMS$REMOVE_ELEMENT or CMS$REMOVE_GENERATION routine to remove it. If the element has a review pending, use the CMS$REVIEW_GENERATION routine to resolve the review pending status.
Even though an element is deleted, records of transactions that created and used the element are retained in the project history. You can reuse the deleted element name to create a new element. However, there is no distinction between the two elements in the project history, except that their transactions are separated by entries for DELETE ELEMENT and CREATE ELEMENT commands.
You cannot restore a deleted element.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_DELETED |
CMS deleted the element. |
Success |
|
CMS$_DELETIONS |
CMS deleted one or more elements. |
Success |
|
CMS$_ERRDELETIONS |
CMS deleted zero or more elements, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NODELETE |
CMS did not delete the element. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
CMS$DELETE_GENERATION
CMS$DELETE_GENERATION — Deletes one or more generations of one or more elements.
Format
CMS$DELETE_GENERATION (library_data_block, element_expression, [remark], [generation_expression]?, [after_generation]?, [before_generation]?, [from_generation]?, [to_generation]?, [archive_file], [msg_routine])
Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements whose generations are to be deleted. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the particular generation to be deleted. If you do not specify this argument and do not specify either from_generation or to_generation, the most recent generation on the main line of descent (1+) is deleted. You cannot combine generation_expression with any of the following arguments: from_generation, to_generation, after_generation, and before_generation.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the start of a range of generations to be deleted, excluding the specified generation. You cannot combine both after_generation and from_generation, or both after_generation and generation_expression. You must specify the end of the range with either the before_generation or to_generation argument.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the end of a range of generations to be deleted, excluding the specified generation. You cannot combine both before_generation and to_generation, or both before_generation and generation_expression. You must specify the start of the range with either the after_generation or from_generation argument.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the start of a range of generations to be deleted, including the specified generation. You cannot combine both from_generation and after_generation, or both from_generation and generation_expression. You must specify the end of the range with either the before_generation or to_generation argument.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the end of a range of generations to be deleted, including the specified generation. You cannot combine both to_generation and before_generation, or both to_generation and generation_expression. You must specify the start of the range with either the after_generation or from_generation argument.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies that an archive file is to be created for every element specified in the element_expression argument. A new file is created for each element. By default, if you do not specify the element_expression argument or if you specify a wildcard, CMS creates an output file with the same name as the element and the file type .CMS_ARCHIVE, and places the file in your default directory.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$DELETE_GENERATION routine removes information about one or more generations of elements from the library. Once a generation is deleted, it cannot be restored to the CMS library. If the generation or range of generations to be deleted has a direct descendant generation (that is, a descendant generation on the same line of descent), the changes associated with those generations are combined, and those changes are combined with the changes in the descendant generation. If there is no descendant generation (that is, the generation or range of generations to be deleted is at the end of the line of descent), the changes associated with those generations are discarded.
You can specify a single generation with the generation_expression argument. You can also specify a range of generations with either the after_generation or from_generation arguments to delimit the beginning of a range, and either the before_generation or to_generation arguments to delimit the end of a range. These sets of arguments can be paired to specify ranges with inclusive or exclusive endpoints.
If you delete the latest generation on the main line of descent of an element that has the reference copy attribute, CMS deletes the generation's reference copy and creates a new reference copy that corresponds to the generation that is now the latest generation on the main line of descent.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_GENDELETED |
CMS deleted the generation. |
Success |
|
CMS$_GENDELETIONS |
CMS deleted one or more generations. |
Success |
|
CMS$_ERRGENDELETIONS |
CMS deleted zero or more generations, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOGENDELETED |
CMS did not delete the specified generation. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
CMS$DELETE_GROUP
CMS$DELETE_GROUP — Deletes one or more groups from a CMS library. The group cannot be a member of any other groups.
Format
CMS$DELETE_GROUP (library_data_block,
group_expression,
[remark],
[msg_routine],
[remove_contents])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more groups to be deleted. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Determines whether CMS removes the current contents of each group specified by group_expression prior to deletion. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS does not remove elements from each group. If you set the value to 1, CMS removes all elements from each group prior to deleting the group itself.
Description
The CMS$DELETE_GROUP routine deletes one or more groups from a CMS library. If a group contains one or more elements, set remove_contents to 1 to remove the content of the group prior to deletion. Otherwise, CMS issues an error message and does not deletethe group. You cannot delete a group set to READ_ONLY. For information on changing the READ_ONLY attribute, see the description of the CMS$MODIFY_GROUP routine. If the group is not empty, use the CMS$REMOVE_ELEMENT routine to remove any elements from the group, or use the CMS$REMOVE_GROUP routine to remove any other groups from the group. If the group belongs to any other groups, use the CMS$REMOVE_GROUP routine to remove it.
Even though a group is deleted, records of transactions that created and used the group are retained in the project history. You can reuse the deleted group name to create a new group. However, there is no distinction between the two groups in the project history, except that their transactions are separated by entries for DELETE GROUP and CREATE GROUP commands.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_DELETED |
CMS deleted the group. |
Success |
|
CMS$_DELETIONS |
CMS deleted one or more groups. |
Success |
|
CMS$_ERRDELETIONS |
CMS deleted zero or more groups, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NODELETE |
CMS did not delete the group. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
CMS$DELETE_HISTORY
CMS$DELETE_HISTORY — Deletes all or part of the library history.
Format
CMS$DELETE_HISTORY (library_data_block,
[remark],
before,
[transaction_mask],
[output_routine],
[user_arg],
[msg_routine],
[object],
[user])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a binary date and time value that CMS uses when deleting the library history. This argument is required.
| type: | mask_longword |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
|
Symbol |
Bit Position |
Mask Value |
Command |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CMS$M_CMD_COPY |
0 |
1 |
COPY CLASS |
|
COPY ELEMENT | |||
|
COPY GROUP | |||
|
CMS$M_CMD_CREATE |
1 |
2 |
CREATE CLASS |
|
CREATE ELEMENT | |||
|
CREATE GROUP | |||
|
CREATE LIBRARY | |||
|
CMS$M_CMD_DELETE |
2 |
4 |
DELETE CLASS |
|
DELETE ELEMENT | |||
|
DELETE GENERATION | |||
|
DELETE GROUP | |||
|
DELETE HISTORY | |||
|
CMS$M_CMD_FETCH |
3 |
8 |
FETCH |
|
CMS$M_CMD_INSERT |
4 |
16 |
INSERT ELEMENT |
|
INSERT GENERATION | |||
|
INSERT GROUP | |||
|
CMS$M_CMD_MODIFY |
5 |
32 |
MODIFY CLASS |
|
MODIFY ELEMENT | |||
|
MODIFY GENERATION | |||
|
MODIFY GROUP | |||
|
MODIFY LIBRARY | |||
|
MODIFY RESERVATION | |||
|
CMS$M_CMD_REMARK |
6 |
64 |
REMARK |
|
CMS$M_CMD_REMOVE |
7 |
128 |
REMOVE ELEMENT |
|
REMOVE GENERATION | |||
|
REMOVE GROUP | |||
|
CMS$M_CMD_REPLACE |
8 |
256 |
REPLACE |
|
CMS$M_CMD_RESERVE |
9 |
512 |
RESERVE |
|
CMS$M_CMD_UNRESERVE |
10 |
1024 |
UNRESERVE |
|
CMS$M_CMD_VERIFY |
11 |
2048 |
VERIFY |
|
CMS$M_CMD_SET |
14 |
16,384 |
SET ACL |
|
CMS$M_CMD_ACCEPT |
16 |
65,536 |
ACCEPT GENERATION |
|
CMS$M_CMD_CANCEL |
17 |
131,072 |
CANCEL REVIEW |
|
CMS$M_CMD_MARK |
18 |
262,144 |
MARK GENERATION |
|
CMS$M_CMD_REJECT |
19 |
524,288 |
REJECT GENERATION |
|
CMS$M_CMD_REVIEW |
20 |
1,048,576 |
REVIEW GENERATION |
The mask values are defined as universal symbols in the CMS image. You can use OR with these values to allow combinations of the values. This transaction mask is the same as the transaction mask used for the CMS$SHOW_HISTORY routine.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine that processes data output by CMS$DELETE_HISTORY. CMS calls the output routine once for each record to be deleted from the library history. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the callback routine.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to the output_routine argument, using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a string that contains the name of the object whose history is to be deleted.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a string that contains the name of the CMS user whose history is to be deleted.
Callback Routine Parameters
first_call, library_data_block, user_param, time, user_id,
command_id, object_id, remark_id, unusualThe callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the current call to the output routine is the first call. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the current call is the first call. Otherwise, this is set to 0.
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$DELETE_HISTORY. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$DELETE_HISTORY.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a quadword binary date and time value for the time of the transaction.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the user name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the command name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the element, group, or class involved in the transaction. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the remark. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the transaction is unusual. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the transaction is unusual. Otherwise, this is set to 0.
Description
The CMS$DELETE_HISTORY routine deletes all or part of the library history. Whenever you delete part of the library history, CMS records two transactions. As with other commands that modify the contents of the library, CMS records the DELETE HISTORY transaction. In addition, CMS logs a REMARK transaction at the point in the library that corresponds to the before value. The REMARK transaction record includes the remark text: "PREVIOUS HISTORYDELETED." Both the REMARK and the DELETE HISTORY transactions are unusual transactions. When you use the SHOW HISTORY command, CMS identifies unusual transactions by displaying an asterisk (*) in the first column of the transaction record.
You use a callback routine to control the action of the CMS$DELETE_HISTORY routine. To delete a history record, the callback routine must return a value of CMS$_NORMAL. To prevent CMS from deleting a history record, the callback routine must return a value of CMS$_EXCLUDE. In addition, you can use the transaction_mask argument that directs CMS to select for deletion only a specified set of transaction records.
Therefore, you can controlthe deletion transaction by filtering each history record, or by filtering a specified set of transaction records.
If you do not provide a callback routine, CMS deletes all history records prior to the specified before value.
To delete the history record, the callback routine must return a value of CMS$_NORMAL. To prevent CMS from deleting the history record, the callback routine must return a value of CMS$_EXCLUDE.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_HISTDEL |
CMS deleted the indicated number of records. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NODELETE |
CMS did not delete any history records. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_USERERR |
User routine returned an error to CMS. |
Error |
CMS$DIFFERENCES
CMS$DIFFERENCES — Compares two files, two generations of elements, or a file and a generation. If the files are different, CMS$DIFFERENCES creates a file containing the lines that differ between the two files. If the files are the same, it issues a message to that effect and does not create a differences file.
Format
CMS$DIFFERENCES (library_data_block?, [user_arg], [input_file1], [input_routine1], [generation_expression_1], [input_file2], [input_routine2], [generation_expression_2], [output_file], [output_routine], [append], [ignore_mask], [nooutput], [parallel], [full], [format], [width], [msg_routine], [page_break], [skip_lines], [begin_sentinel], [end_sentinel])
Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the library to be used in the differences transaction. You specify this argument only if you specify one or both of the generation_expression_1 or generation_expression_2 arguments.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to a callback routine (input_routine1, input_routine2, or output_routine) each time the routine is called by CMS.CMS passes the value to the routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the primary input file to be used in the CMS$DIFFERENCES transaction. You can specify both an input routine and input file (see Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines''). If you do not specify a primary input file, you must provide a primary input routine (using the input_routine1 argument)and either a secondary input file (input_file2) orroutine (input_routine2). You cannot specify wildcards or a comma list.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine that provides records for the CMS$DIFFERENCES transaction. You must provide the input_routine1 argument if you do not provide the input_file1 argument.See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the input routine.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies an element generation or a class name in the CMS library indicated by the library_data_block argument. If you specify this argument, CMS searches for an element with the name specified by input_file1.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a secondary input file for comparison against the contents of input_file1, or input provided by input_routine1. You cannot specify wildcards or a comma list.
If you do not specify either input_file2 or input_routine2, CMS uses the next lower version of the primary input file. If you do not specify input_file2 but you specify generation_expression1, CMS uses the latest version of input_file1 in your current default directory.
If you specify input_routine2 and you want CMS to use the next lower version of the primary input file, specify empty brackets ([]) as input_file2.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a secondary callback routine that provides records for comparison with the contents of input_file1, or input provided by input_routine1. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the input routine.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies an element generation or a class name in the CMS library indicated by the library_data_block parameter. If you specify this argument, CMS searches for an element with the name specified by input_file2.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the name of the output file. Use this argument if you want to specify a particular name for the output file, or if you want CMS to put the file in a directory other than your current default directory. If you do not specify output_file, nooutput, or output_routine, CMS creates a new file with the file name from input_file1 and the file type .DIF. Wildcards are not allowed.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine that processes the output of CMS$DIFFERENCES. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to append the output to a file. If you set the flag to 1, CMS appends the output to a file. If you set the flag to 0, CMS creates a new file (input_file1 .DIF). CMS ignores this argument if you provide an output routine.
When you set the append flag to 1, CMS appends theoutput to an existing file indicated by the output_fileargument. If you do not specify an output file, CMS appends the output tothe default file (input_file1.DIF). If no such file exists, CMS creates one.
| type: | mask_longword |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
|
Symbol |
Bit Position |
Mask Value |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CMS$M_IGNORE_FORM |
0 |
1 |
Ignore form-feed characters. |
|
CMS$M_IGNORE_LEAD |
1 |
2 |
Ignore blank or tab characters at the beginning of nonblank lines. |
|
CMS$M_IGNORE_TRAIL |
2 |
4 |
Ignore blank or tab characters at the end of nonblank lines. |
|
CMS$M_IGNORE_SPACE |
3 |
8 |
Compress all multiple spaces, tabs, or combinations of spaces or tabs to single spaces. |
|
CMS$M_IGNORE_CASE |
4 |
16 |
Ignore differences in case for characters A to Z. |
|
CMS$M_IGNORE_HISTORY |
5 |
32 |
Ignore history records found in the compared files. |
|
CMS$M_IGNORE_NOTES |
6 |
64 |
Ignore notes text found in the compared files. |
The mask values are defined as universal symbols in the CMS image. You can use OR with these values to allow combinations of the values. If you omit the ignore_mask argument, CMS does not ignore any fields during the differences transaction.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that prohibits CMS$DIFFERENCES output. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS produces output as designated by the other arguments. If you set the flag to 1, CMS executes a fast form of the comparison. In this case, CMS exits when it encounters the first difference and returns CMS$_DIFFERENT. If there are no differences, CMS returns CMS$_IDENTICAL.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating whether the output is in parallel format. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS does not display the output in parallel format. If you set the flag to 1, the differences from the first file (or input routine) are displayed on the left and differences from the second file (or input routine) are displayed on the right. This qualifier can only be used with record partitions.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to generate an extended listing that includes identical lines as well as lines that are different between the two input streams. If you set the flag to 1, CMS generates an extended listing. If you do not specify this argument or if you set the flag to 0, the output includes only the differences.
| type: | mask_longword |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the type of formatting to be performed on the data before it is placed into the output file. You must specify either the output_file or output_routine arguments with this argument. By default, the flag is set to 1, indicating formatted output. If you set the flag to 0, CMS produces unformatted output.
|
Data Format |
Bit Position |
Mask Value |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CMS$M_ASCII |
0 |
1 |
Specifies that data be presented as if each byte represents a value in the ASCII character set. This option is most useful when files contain text. If no data partition is specified, data is partitioned into records. This option is the default. |
|
CMS$M_DECIMAL |
1 |
2 |
Specifies that each value be displayed as a decimal numeral. If no data partition is specified, data is partitioned into longwords. You cannot specify both CMS$M_DECIMAL and CMS$M_RECORDS. |
|
CMS$M_HEXADECIMAL |
2 |
4 |
Specifies that each value be displayed as a hexadecimal numeral. If no data partition is specified, data is partitioned into longwords. You cannot specify both CMS$M_HEXADECIMAL and CMS$M_RECORDS. |
|
CMS$M_OCTAL |
3 |
8 |
Specifies that each value be displayed as an octal numeral. If no data partition is specified, data is partitioned into longwords. You cannot specify both CMS$M_OCTAL and CMS$M_RECORDS. |
|
Data Partition |
Bit Position |
Mask Value |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CMS$M_BYTE |
16 |
65,536 |
Specifies that the data displayed is to be partitioned into bytes. By default, records are not partitioned further unless the data format option indicates otherwise. |
|
CMS$M_LONGWORD |
17 |
131,072 |
Specifies that the data displayed is to be partitioned into longword values. This is the default partitioning for CMS$M_DECIMAL, CMS$M_HEXADECIMAL, and CMS$M_OCTAL. |
|
CMS$M_RECORDS |
18 |
262,144 |
Specifies that no further partitioning of data is to occur beyond the record partitioning already in the file. This partitioning is most useful when the files contain text. You can specify CMS$M_RECORDS by itself only, or in conjunction with ASCII. It cannot be used with any other options. This qualifier is the default for ASCII. |
|
CMS$M_WORD |
19 |
524,288 |
Specifies that the data displayed be partitioned into word values. By default, data records are not partitioned further unless the data format indicates otherwise. |
|
Generation Differences |
Bit Position |
Mask Value |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CMS$M_GENERATION_ |
23 |
8,388,608 |
Specifies that a list of generation differences is to be displayed. By default, generation differences are not displayed. |
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the page width value for CMS$DIFFERENCES output. The value can be from 48 to 500. By default, the default value is the same as the device page width for terminal devices and 132 otherwise.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating that page breaks are to be included in the output
file. By default, the flag is set to 0, indicating that page breaks are converted to
the string "
" in the output file. Set the flag to 1 to include
page breaks in the output file.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a positive integer value indicating the number of lines at the beginning of each file to be ignored during the comparison. By default, no lines are skipped.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a string used to delimit a section of text to be ignored during the comparison. The string must be shorter than 65,536 characters, must be contained within a single record, and cannot be the same string as end_sentinel. If this argument is specified, end_sentinel must also be specified.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a string used to delimit a section of text to be ignored during the comparison. The string must be shorter than 65,536 characters, must be contained within a single record, and cannot be the same string as begin_sentinel. If this argument is specified, begin_sentinel must also be specified.
Callback Routine Parameters
first_call, library_data_block, user_param, input_record_id,
eof_flag, file_name_id, generation_id, action,
sequence_flag, sequence_numberThe action parameter enables you to control the flow of data from the input file to CMS. The callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the current call to the input routine is the first call. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the current call is the first call. Otherwise, this is set to 0.
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library. This parameter does not contain any significant information if input is not being taken from a CMS library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$DIFFERENCES. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$DIFFERENCES.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the line of data being passed to CMS$DIFFERENCES. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates the end-of-file status. If there is no input file for this input stream, CMS sets eof_flag to false (0). The callback routine must set this flag to true (1) when input is finished.
If there is an input file for this input stream (for example, this input routine is being used as an input filter), CMS changes the value of eof_flag from false to true when it encounters the end of the input file. Optionally, the input (filter) routine can change the value to true before the end of the input file is reached to terminate input prematurely.
When eof_flag is set to true, CMS ignores the contents of the current input record (input_record_id or the string passed by CMS$PUT_STRING). Therefore, the input routine must set eof_flag to true in the call following the last significant input record.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the input file name. If you do not specify an input file for the data stream, file_name_id does not contain any meaningful data.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the generation number. The string identifier points to a descriptor for a null string if the input is not coming from a CMS library.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a value that controls the flow of data to CMS. It does not contain any meaningful information if the input routine is the only source of data for that input stream (that is, if no input file is specified).
|
Value |
Result |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Directs CMS to reject the current line of data. If you specify 0, you cannot modify input_record. |
|
1 |
Directs CMS to accept the current line of data. In this case, you can modify the input record by using CMS$PUT_STRING to pass a new string to CMS. |
|
2 |
Directs CMS to add data to the input stream before including the current line. You must use CMS$PUT_STRING to pass a new string descriptor to CMS in order to insert new data lines. (Note that you can call CMS$PUT_STRING only once during a single execution of the callback routine.) The current data line (input_record) is saved and passed again with the next call to the user routine. |
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to create a sequenced element file. By default, the flag is set to 0, indicating that input is not sequenced. Set the flag to 1 to direct CMS to create a sequenced element file. If there is no input file, the callback routine can set this flag. If there is no input file, the input is unsequenced.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a signed integer that indicates the sequence number of the input line. The sequence number is a value in the range of 1 to 65,536 characters.
Formatted Output Callback Routine Parameters
When you provide an output routine to process output text from CMS$DIFFERENCES, CMS passes different parameters depending on the value of the format argument. You must specify either the output_file or output_routine arguments with the format argument. By default, format is set to 1, indicating formatted output. If you set the flag to 0, CMS produces unformatted output.
first_call, library_data_block, user_param, output_record_id,
eof_flag, file_name_id, actionThe callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the current call to the output routine is the first call. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the current call is the first call. Otherwise, this is set to 0.
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library. This parameter does not contain any significant information if input is not being taken from a CMS library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$DIFFERENCES. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$DIFFERENCES.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the line of data being passed from CMS$DIFFERENCES. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the end-of-file status. CMS changes the value of eof_flag from false (0) to true (1) after the last record has been passed to the output routine. When eof_flag is true, the contents of output_record_id are undefined. See Section 1.6.3.2, ''Determining End of Output'' for more information on determining the end of output.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the output file name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a value that controls the flow of data from CMS. The value of this argument affects the status of the line of data referenced by output_record_id.
|
Value |
Result |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Directs CMS to reject the current line of data. If you specify 0, you cannot modify the output_record. |
|
1 |
Directs CMS to accept the current line of data. In this case, you can modify the output record by using CMS$PUT_STRING to pass a new string to CMS. |
|
2 |
Directs CMS to add data to the output stream before including the current line. You must use CMS$PUT_STRING to pass a new string to CMS in order to insert new data lines. (Note that you can call CMS$PUT_STRING only once during a single execution of the callback routine.) The current data line (output_record) is saved and passed again with the next call to the user routine. |
Unformatted Output Callback Routine Parameters
first_call, library_data_block, user_param, output_record_id,
eof_flag, line_number1, line_number2The callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the current call to the output routine is the first call. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the current call is the first call. Otherwise, this is set to 0.
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library. This parameter does not contain any significant information if input is not being taken from a CMS library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$DIFFERENCES. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$DIFFERENCES.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the line of data being passed from CMS$DIFFERENCES. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the end-of-file status. CMS changes the value of eof_flag from false (0) to true (1) after the last record has been passed to the output routine. When eof_flag is true, the contents of output_record_id are undefined. See Section 1.6.3.2, ''Determining End of Output'' for more information on determining the end of output.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the sequence number (if the input is sequenced), or the record number if the line originated from the first input stream (input_file1 or input_routine1.) This is –1 if the line did not originate in the first input stream.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the sequence number (if the input is sequenced) or the record number if the line originated from the second input stream (input_file2 or input_routine2.) This is –1 if the line did not originate in the second input stream.
Description
The CMS$DIFFERENCES routine compares the contents of two files. If CMS finds differences, it creates a file containing a listing of those differences. If the files are the same, it issues a message to that effect and does not create a differences file. By default, CMS compares two files not located in a CMS library. However, you can direct CMS to use element generations from a CMS library.
A line or lines in one file and not in the other.
N lines in one file that replace M lines in the other file. N and M might not be equal.
CMS outputs only the lines that differ, unless you set the fullargument to 1.
There is a heading at the beginning of the differences file that includes the name of the user that issued the command, the date and time the command was issued, and the file specifications of the two files being compared. If you direct CMS to use element generations and if you set the CMS$M_GENERATION_DIF flag bit in the format argument to 1, the differences listing contains a section labeled "Generation Differences" that contains the replacement history for the element. Each generation used in the comparison is identified by an asterisk (*) in the first column of the transaction record. The differences between the files are contained in a section labeled "Text Differences." By default, each difference is formatted with the line or lines from the first file followed by the differing line or lines from the second file. If a difference consists of a line or lines that exist in one file but not in the other, only the lines from the file containing the additional text are displayed.
You can use input files to provide data for one or both input streams.
You can use input routines to provide data for one or both input streams.
You can use input routines to filter one or both of the input streams coming from files. When you use an input routine to filter data from an input file, CMS provides a means of specifying the action to be taken for each line of input data.
Note
If you supply two input routines, CMS does not necessarily call them in a synchronous fashion. Therefore, you cannot rely on any established order for the calls to the input routines. In addition, if you supply an output routine, you cannot rely on a particular sequence of calls to the output routine relative to the calls to the input routines.
When using CMS$DIFFERENCES with a CMS library search list, if both input_file_1and input_file_2 are element generation specifications, both of the elements must reside in the same library of the library search list.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_BADFORMAT |
Invalid format specification. |
Error |
|
CMS$_DIFFERENT |
Input streams are different. |
Informational |
|
CMS$_IDENTICAL |
Input streams are identical. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOACCESS |
User does not have the required access to the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOFILE |
No input file found. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_OPENIN1 |
Error opening the first input file. |
Error |
|
CMS$_OPENIN2 |
Error opening the second input file. |
Error |
|
CMS$_OPENOUT |
Error opening the output file. |
Error |
|
CMS$_QUALCONFLICT |
Cannot specify both output file and no output. |
Error |
|
CMS$_READIN |
Error reading the input stream. |
Error |
|
CMS$_UNFOUT |
Cannot specify unformatted output. |
Error |
|
CMS$_UNSUPFRMT |
Error appending to file of this format. |
Error |
|
CMS$_USERERR |
User routine returned an error to CMS. |
Error |
Examples
CHARACTER*12 FILE1 EXTERNAL CMS$DIFFERENCES FILE1 = 'COMTRANS.COM' CALL CMS$DIFFERENCES(,,FILE1) END
This call to CMS$DIFFERENCES includes one file specification; CMS searches for the latest two versions of COMTRANS.COM in the current default directory. Note that the placeholders are required for the optional LDB and user-defined arguments.
CALL CMS$DIFFERENCES(LDB,,FILE1,,GEN1)This example shows a call to CMS$DIFFERENCES that uses a library element and the corresponding file in the current, default directory. Because a second file is not provided, CMS uses the latest version of the file specified by FILE1 in the default directory.
CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS
CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS — Compares the member generations in two classes. If the members differ between classes, CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS creates a file listing the differences. If the members in both classes are the same, CMS issues a message to that effect and does not create a differences file.
Format
CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS (library_data_block,
class_expression1,
class_expression2,
[append],
[format],
[full],
[ignore_mask],
[nooutput],
[parallel],
[show_mask],
[width],
[output_file],
[output_routine],
[user_arg],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the library to be used in the differences transaction.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the primary class name to be used in the CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS transaction. You cannot specify wildcards or a comma list.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a secondary class name to be used in the CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS transaction. You cannot specify wildcards or a comma list.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to append the output to a file. If you set the flag to 1, CMS appends the output to a file. If you set the flag to 0, CMS creates a new file (output_file1.DIF). CMS ignores this argument if you provide an output routine.
| type: | mask_longword |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the type of formatting to be performed on the data before it is placed into the output file. You must specify either the output_file or output_routine arguments with this argument. By default, the flag is set to 1, indicating formatted output. If you set the flag to 0, CMS produces unformatted output.
|
Data Format |
Bit Position |
Mask Value |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CMS$M_ASCII |
0 |
1 |
Specifies that data be presented as if each byte represents a value in the ASCII character set. This option is most useful when files contain text. If no data partition is specified, data is partitioned into records. This option is the default. |
|
CMS$M_DECIMAL |
1 |
2 |
Specifies that each value be displayed as a decimal numeral. If no data partition is specified, data is partitioned into longwords. You cannot specify both CMS$M_DECIMAL and CMS$M_RECORDS. |
|
CMS$M_HEXADECIMAL |
2 |
4 |
Specifies that each value be displayed as a hexadecimal numeral. If no data partition is specified, data is partitioned into longwords. You cannot specify both CMS$M_HEXADECIMAL and CMS$M_RECORDS. |
|
CMS$M_OCTAL |
3 |
8 |
Specifies that each value be displayed as an octal numeral. If no data partition is specified, data is partitioned into longwords. You cannot specify both CMS$M_OCTAL and CMS$M_RECORDS. |
|
Data Partition |
Bit Position |
Mask Value |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CMS$M_BYTE |
16 |
65,536 |
Specifies that the data displayed is to be partitioned into bytes. By default, records are not partitioned further unless the data format option indicates otherwise. |
|
CMS$M_LONGWORD |
17 |
131,072 |
Specifies that the data displayed is to be partitioned into longword values. This is the default partitioning for CMS$M_DECIMAL, CMS$M_HEXADECIMAL, and CMS$M_OCTAL. |
|
CMS$M_RECORDS |
18 |
262,144 |
Specifies that no further partitioning of data is to occur beyond the record partitioning already in the file. This partitioning is most useful when the files contain text. You can specify CMS$M_RECORDS by itself only, or in conjunction with ASCII. It cannot be used with any other options. This qualifier is the default for ASCII. |
|
CMS$M_WORD |
19 |
524,288 |
Specifies that the data displayed be partitioned into word values. By default, data records are not partitioned further unless the data format indicates otherwise. |
The format argument also contains a bit flag indicating that a list of generation differences is to be included in the output file. By default, the flag is set to 0, indicating that generation differences are not to be included. Set the flag to 1 to include generation differences in the output file.
|
Generation Differences |
Bit Position |
Mask Value |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CMS$M_GENERATION_ |
23 |
8,388,608 |
Specifies that a list of generation differences is to be displayed. By default, generation differences are not displayed. |
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to generate an extended listing that includes identical lines as well as lines that are different between the two input streams. If you set the flag to 1, CMS generates an extended listing. If you do not specify this argument or if you set the flag to 0, the output includes only the differences.
| type: | mask_longword |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies whether CMS ignores the first variant of a generation. The value CMS$M_IGNORE_FIRST_VARIANT directs CMS to ignore any differences where the generation in one class is the first variant of the generation in the second class. Specify the value 0 to have CMS treat the first variant as a difference. If you omit the ignore_mask argument, CMS does not ignore any fields during the differences transaction.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that prohibits CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS output. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS produces output as designated by the other arguments. If you set the flag to 1, CMS executes a fast form of the comparison. In this case, CMS exits when it encounters the first difference and returns CMS$_DIFFERENT. If there are no differences, CMS returns CMS$_IDENTICAL.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating whether the output is in parallel format. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS does not display the output in parallel format. If you set the flag to 1, the differences from the first file (or input routine) are displayed on the left and differences from the second file (or input routine) are displayed on the right. This qualifier can only be used with record partitions.
| type: | mask_longword |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
|
Symbol |
Bit Position |
Mask Value |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CMS$M_ELEMENT_DIF |
0 |
1 |
Include differences where an element is in one class but not the other. |
|
CMS$M_GENERATIONAL_DIF |
1 |
2 |
Include differences where one member generation differs from the other by more than just its variant. Directs CMS to show the difference if the generation in one class differs from the generation in the other class and the primary generation is not a variant of the other. |
|
CMS$M_VARIANT_DIF |
2 |
4 |
Include differences where one member generation differs from the other by its variant. Directs CMS to show the difference if the generation in one class differs from the generation in the other class and the primary generation is a variant of the other. |
The mask values are defined as universal symbols in the CMS image. You can use OR with these values to allow combinations of the values. A null parameter or a 0 value directs CMS to show all types of differences by default.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the page width value for CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS output. The value can be from 48 to 500. By default, the default value is the same as the device page width for terminal devices and 132 otherwise.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the name of the output file. Use this argument if you want to specify a particular name for the output file, or if you want CMS to put the file in a directory other than your current default directory. If you do not specify output_file, nooutput, or output_routine, CMS creates a new file with the file name output_file1 and the file type .DIF. Wildcards are not allowed.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine that processes the output of CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the callback routine.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to a callback routine (input_routine1, input_routine2, or output_routine) each time the routine is called by CMS.CMS passes the value to the routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Unformatted Output Callback Routine Parameters
first_call, library_data_block, user_param, eof_flag,
diff_flag, output_record_id1, output_record_id2,
entry_number1, entry_number2The callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the current call to the output routine is the first call. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the current call is the first call. Otherwise, this is set to 0.
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library. This parameter does not contain any significant information if input is not being taken from a CMS library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the end-of-file status. CMS changes the value of eof_flag from false (0) to true (1) after the last record has been passed to the output routine. When eof_flag is true, the contents of diff_flag, output_record_id1, output_record_id2, entry_number1, and entry_number2 are undefined.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies whether the two records are different. If diff_flag value is false (0), the two records are the same, even though they may differ textually. This can occur when a full listing is requested, there are generation members that differ between the two classes, but the members are not flagged as different due to the values of the show mask and ignore_mask arguments to CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS.
If diff_flag value is true (1), the output_record_id1, entry_number1, output_record_id2, and entry_number2 describe generation members for the same element whose generation number differs between the two classes. In addition, if the value of one of the entry numbers is –1, it means that this element exists in one class but not the other.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the generation member being passed from CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS() for class_expression1. This parameter is only valid if entry_number1 contains a value other than –1.
element-name(generation-name) "generation comment"
If both output_record_id1 and output_record_id2 are supplied on the same call, they identify different generations of the same element. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the generation member being passed from CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS() for class_expression2. This parameter is only valid if entry_number1 contains a value other than –1.
element-name(generation-name) "generation comment"
If both output_record_id1 and output_record_id2 are supplied on the same call, they identify different generations of the same element. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the position of the generation member in the list of members for
class_expression1. The generation members are
labeled from 1- n.
If a particular element is a member of one class but not the other, the element has a different entry number in each class. This parameter is –1 if an entry from class_expression1 is not being specified by this call. Meaning, the element is in class_expression2 but not class_expression1.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the position of the generation member in the list of members for
class_expression2. The generation members are
labeled from 1-n.
If a particular element is a member of one class but not the other, the element has a different entry number in each class. This parameter is –1 if an entry from class_expression2 is not being specified by this call. Meaning, the element is in class_expression1 but not class_expression2.
Description
The CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS routine compares the contents of two classes. If CMS finds differences between class membership, it creates a file containing a listing of those differences. If the classes are the same, it issues a message to that effect and does not create a differences file.
CMS outputs only the lines that differ, unless you set the fullargument to 1.
There is a heading at the beginning of the differences file that includes the name of the user that issued the command, the date and time the command was issued, and the specifications of the two classes being compared.
Each element generation used in the comparison is identified by an asterisk (*) in the first column of the transaction record. The differences between the classes are contained in a section labeled "Differences."
In addition, you can use an output routine to process the output of the differences transaction.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_BADFORMAT |
Invalid format specification. |
Error |
|
CMS$_DIFFCLASS |
Differences between the compared classes were detected. |
Informational |
|
CMS$_IDENTCLASS |
The classes being compared are identical. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOACCESS |
User does not have the required access to the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_OPENOUT |
Error opening the output file. |
Error |
|
CMS$_QUALCONFLICT |
Cannot specify both output file and no output. |
Error |
|
CMS$_UNFOUT |
Cannot specify unformatted output. |
Error |
|
CMS$_UNSUPFRMT |
Error appending to file of this format. |
Error |
|
CMS$_USERERR |
User routine returned an error to CMS. |
Error |
Examples
INTEGER*4 CMS$SET_LIBRARY, 1 CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS, 1 LDB(50)CHARACTER*9 DIR CHARACTER*5 F_CLASS CHARACTER*6 S_CLASS DIR = '[.CMSLIB]' F_CLASS = 'FIRST' S_CLASS = 'SECOND' STATUS = CMS$SET_LIBRARY (LDB, DIR) IF (STATUS) THEN MEMBER_FLAG = 1 STATUS = CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS (LDB,F_CLASS,S_CLASS) ENDIF
This call to CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS shows difference between the two classes (FIRST and SECOND) in a CMS library. It creates a differences file (FIRST.DIF) that contains the names of the generations that differ between the two classes.
If the elements each class are the same, CMS issues a message to that effect and does not create a differences file.
CALL CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS (LDB,F_CLASS,S_CLASS,,,,,,, CMS$M_ELEM)
This call to CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS shows differences where an element is in one class but not the other. It ignores the elements which are same in both classes but have different generations.
CMS$FETCH
CMS$FETCH — Retrieves a copy of an element from a CMS library. You can also specify the reserve argument to direct CMS to establish a reservation for a generation of the element.
Format
CMS$FETCH (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[remark],
[generation_expression],
[merge_generation_expression],
[reserve],
[nohistory],
[nonotes],
[concurrent],
[output_file],
[msg_routine],
[nooutput],
[history],
[notes],
[position])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements to be fetched (or reserved). Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
You must include a period (.) in the element expression to select one or more elements from the complete list of elements in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and selects elements based on the list of groups established in the library.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command. If you do not specify a remark and you do not establish a reservation, CMS does not record the transaction in the library history.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the generation to be retrieved. If you do not specify a generation number or class name, CMS fetches the latest generation on the main line of descent.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the element generation to be merged into the fetched generation. This argument can be a generation number or class name.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to establish a reservation for the fetched element. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS fetches the element without establishing a reservation. Set this flag to 1 to reserve the element.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to suppress the element history. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS provides the element history in the output file only if the history attribute is established for the element. If you set this flag to 1, CMS does not include the element history in the output file.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to suppress generation notes. By default, the flag is set to 0, and the file contains generation notes only if the notes attribute is established for the element. If you set this flag to 1, CMS does not include generation notes in the output file.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating the access to the element. By default, the flag is set to 1, and CMS allows concurrent reservations of the element. Set the concurrent flag to 0 to prohibit concurrent reservations.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the name of the output file. Use this argument if you want the output file to have a different name than the element, or if you want CMS to put the file in a directory other than your default directory. Wildcards are allowed. If you do not specify an output file name, CMS gives the file the same name as the element. This parameter is ignored if nooutput is specified as true.
Use caution when providing output file specifications. For example, if you fetch a group of elements and you provide an output file specification that does not allow CMS to assign a unique name to each fetched element file, CMS creates as many files with the same name as necessary.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates that CMS should execute the fetch or reserve operation without creating an output file. By default, the flag is set to 0 and CMS creates an output file. When you specify this argument, CMS does not perform file I/O; this causes CMS to operate faster than if you specify the null device (NLA0: or NL:) as the output file. This argument is useful for reserving an element that you will not use as the replacement file.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the history string. If you include this argument in the call, CMS includes the history in the retrieved file. If you specify history and reserve, CMS establishes the history string for the reservation. If you do not specify history, CMS uses the value of the element's current history attribute. This argument is useful to temporarily override an existing history format string. If an element has a history attribute, its history is included in the file when it is retrieved by CMS$FETCH. To disable the history attribute, specify a zero-length string. For a detailed explanation of the history attribute, see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the notes string. If you include this argument in the call, CMS includes the notes in the retrieved file. If you specify notes and reserve, CMS establishes the notes string for the reservation. If you do not specify notes, CMS uses the value of the element's current notes attribute. This argument is useful to temporarily override an existing notes format string. If an element has a notes attribute, notes are added to the ends of the lines of the file when it is retrieved by CMS$FETCH. To disable the notes attribute, specify a zero-length string. Any element that has the notes attribute must have the position attribute. For a detailed explanation of the notes attribute, see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the position value to be used with the notes attribute. The position attribute determines the character position at which the note is to begin on the line. The position value must be an integer greater than zero. If you specify notes and the element does not already have the position attribute established, you must also specify the position argument. For a detailed explanation of the position attribute, see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System.
Description
The CMS$FETCH routine delivers a copy of the specified element generation to your current, default directory or to the file specified in the output_file parameter. If you did not specify a value of 1 for the reserve argument, CMS does not allow you to replace a fetched element.
The presence or absence of a remark determines whether the CMS FETCH transaction is recorded in the library history. If you do not specify a remark and do not establish a reservation, CMS does not record the transaction.
When you retrieve an element from a CMS library, CMS restores the file creation and revision times. The file placed in your directory has the same creation and revision times as the file used to create the generation you are fetching. CMS does not restore the file expiration date or file backup date.
If you specify the reserve argument, each element indicated by the element_expression argument is marked reserved in the library database. Usually, after you have modified the element, you return a reserved element to the library with the CMS$REPLACE routine. Alternatively, you can cancel the reservation with the CMS$UNRESERVE routine.
CMS marks the reserved generation as a predecessor generation. This information is used to determine the generation number of the successor created by the REPLACE command. For more information on creating successive generations with the RESERVE and REPLACE commands, see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System.
If a version of the element file already exists in your default directory when you call CMS$FETCH, CMS creates a new version with the next higher version number.
If CMS encounters an element data file that has a bad checksum or was not closed by CMS, it retrieves the file but changes the success status to a warning status. If you want to know only if the file was retrieved, use the LIB$MATCH_COND routine to compare the returned status to the CMS return codes.
When fetching a concurrent reservation, you must specify the confirm_routineargument in the call to CMS$SET_LIBRARY or CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY (before calling CMS$FETCH), or you are not warned of any concurrent reservations, and the fetch transaction continues. To receive a confirmation prompt when there are existing concurrent reservations, you must specify the routine in the call to CMS$SET_LIBRARY or CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_FETCHED |
CMS fetched the element. |
Success |
|
CMS$_FETCHES |
CMS fetched one or more elements. |
Success |
|
CMS$_ERRFETCHES |
CMS fetched zero or more elements, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_ERRESERVATIONS |
CMS reserved zero or more elements, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOFETCH |
CMS did not fetch the element. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NORESERVATION |
CMS did not reserve the element. |
Error |
|
CMS$_RESERVATIONS |
CMS reserved one or more elements. |
Success |
|
CMS$_RESERVED |
CMS reserved the element. |
Success |
CMS$FETCH_CLOSE
CMS$FETCH_CLOSE — Terminates a fetch transaction initiated by CMS$FETCH_OPEN. Use the CMS$FETCH_CLOSE routine with the CMS$FETCH_GET and CMS$FETCH_OPEN routines.
Format
CMS$FETCH_CLOSE (fetch_data_block,
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an open FDB.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$FETCH_CLOSE routine terminates a line-by-line fetch transaction. You use this routine after a combination of CMS$FETCH_OPEN and CMS$FETCH_GET calls. If you do not end the fetch transaction with a call to CMS$FETCH_CLOSE, the library is left in a locked state.
For an example of a line-by-line fetch transaction, see the description of the CMS$FETCH_GET routine.
CMS$FETCH_GET
CMS$FETCH_GET — Retrieves one line of data from an element. Use this routine with the CMS$FETCH_OPEN and CMS$FETCH_CLOSE routines.
Format
CMS$FETCH_GET (fetch_data_block,
output_record,
[sequence_number],
[generation_number],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an open FDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a string descriptor that CMS fills in with the line of data retrieved from the library element. If the notes attribute is established for the element and you do not suppress notes in the call to CMS$FETCH_OPEN, the output record includes the notes string.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a location that CMS fills in with the sequence number of the data line, if any. CMS sets the value to –1 if there is no sequencing. If the value is in the range of 0 to 65,535, it is the sequence number of the data line. By default, CMS does not attempt to provide any sequence information.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a string descriptor to be filled in by CMS.CMS uses this argument to provide the generation number associated with the line of data. By default, CMS does not provide the generation information.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$FETCH_GET routine retrieves a single line of data from an element that you have opened with a call to CMS$FETCH_OPEN. After you have completed the series of CMS$FETCH_GET calls required to retrieve the entire element, you must end the fetch transaction with a call to CMS$FETCH_CLOSE.
CMS returns RMS$_EOF after the last record of the element has been fetched. When CMS$FETCH_GET returns RMS$_EOF, the contents of output_record are undetermined. You must invoke CMS$FETCH_GET as a function in order to determine end-of-file.
You should call CMS$FETCH_GET using the exact same FDB previously used by the last call to CMS$FETCH_GET.
When you execute a line-by-line transaction, you cannot reserve an element, and CMS does not enter the transaction in the library history.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_INVFETDB |
Invalid fetch data block |
Error |
|
RMS$_EOF |
End-of-file |
Warning |
Example
CHARACTER*11 LIBNAME
CHARACTER*9 ELE1,ELE2
CHARACTER*80 LINE
INTEGER STATUS,STATUS1,STATUS2
INTEGER*4 CMS$FETCH_GET
INTEGER*4 CMS$FETCH_OPEN
INTEGER*4 CMS$FETCH_CLOSE
EXTERNAL CMS$_EOF
DIMENSION FDB1(5),FDB2(5)
LIBNAME = '[DBASE.LIB]'
ELE1 = 'TEST1.TST'
ELE2 = 'TEST2.TST'
STATUS = CMS$FETCH_OPEN(FDB1,LIBNAME,ELE1)
IF (.NOT. STATUS) GOTO 60  STATUS = CMS$FETCH_OPEN(FDB2,LIBNAME,ELE2)
IF (.NOT. STATUS) GOTO 6030
STATUS1 = CMS$FETCH_GET(FDB1,LINE)
STATUS = CMS$FETCH_OPEN(FDB2,LIBNAME,ELE2)
IF (.NOT. STATUS) GOTO 6030
STATUS1 = CMS$FETCH_GET(FDB1,LINE)  IF (STATUS1) CALL PRINTLINE(LINE)40
STATUS2 = CMS$FETCH_GET(FDB2,LINE)
IF (STATUS1) CALL PRINTLINE(LINE)40
STATUS2 = CMS$FETCH_GET(FDB2,LINE)  IF (STATUS2) CALL PRINTLINE(LINE)
IF (STATUS1) GOTO 30
IF (STATUS2) CALL PRINTLINE(LINE)
IF (STATUS1) GOTO 30  IF (STATUS2) GOTO 40
STATUS = CMS$FETCH_CLOSE(FDB1)
IF (STATUS2) GOTO 40
STATUS = CMS$FETCH_CLOSE(FDB1)  STATUS = CMS$FETCH_CLOSE(FDB2)60
END
C routine to handle output string
INTEGER FUNCTION PRINTLINE(STRING)
CHARACTER*80 STRING
PRINT 90,STRING
RETURN90
FORMAT(' ',A)
END
STATUS = CMS$FETCH_CLOSE(FDB2)60
END
C routine to handle output string
INTEGER FUNCTION PRINTLINE(STRING)
CHARACTER*80 STRING
PRINT 90,STRING
RETURN90
FORMAT(' ',A)
ENDCMS$FETCH_OPEN is called once for each file to be fetched. Because the program uses two FDBs, it can fetch parallel lines from the elements without reinitializing the FDB each time the element is changed. | |
CMS$FETCH_GET is called for the first element. The fetched data line is displayed until CMS returns RMS$_EOF (severity level warning). | |
CMS$FETCH_GET is called for the second element, until end-of-file is encountered. | |
The tests for end-of-file transfer control. | |
Once end-of-file is encountered for both elements, CMS$FETCH_CLOSE is called for each element. |
CMS$FETCH_OPEN
CMS$FETCH_OPEN — Begins a line-by-line fetch transaction. Use the CMS$FETCH_OPEN routine with the CMS$FETCH_GET and CMS$FETCH_CLOSE routines.
Format
CMS$FETCH_OPEN (fetch_data_block,
directory,
element_name,
[generation_expression],
[nohistory],
[nonotes],
[actual_generation],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an FDB to be opened.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Note
Cannot contain wildcard characters
Cannot be a comma list of directory specifications
Cannot be a search list logical name
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the element to be fetched. Wildcards are not allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the generation of the element to be fetched. By default, CMS fetches the latest generation on the main line of descent.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to suppress the element history. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS provides the element history in the output file only if the history attribute is established for the element. If you set this flag to 1, CMS does not include the element history in the output file.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to suppress generation notes. By default, the flag is set to 0, and the file contains generation notes only if the notes attribute is established for the element. If you set this flag to 1, CMS does not include generation notes in the output file.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a string descriptor to be filled in by CMS.CMS uses this argument to provide the number of the generation accessed by calls to CMS$FETCH_GET. This is useful when you use a class name as the generation expression and want to know the generation number.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$FETCH_OPEN routine initiates a line-by-line fetch transaction. You use this routine with CMS$FETCH_CLOSE and CMS$FETCH_GET calls. You can execute concurrent fetch transactions by issuing multiple calls to CMS$FETCH_OPEN. You must define a unique FDB for each call to CMS$FETCH_OPEN. The FDB identifies the data stream to be processed by CMS$FETCH_GET.
When you execute a line-by-line fetch transaction, you cannot reserve an element or merge element generations. CMS does not enter the transaction in the library history.
Note
Do not use CMS$FETCH_OPEN with a library search list.
Cannot contain wildcard characters
Cannot be a comma list of directory specifications
Cannot be a search list logical name
For an example of a line-by-line fetch transaction, see the description of the CMS$FETCH_GET routine.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_INVFETDB |
Invalid fetch data block. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOFETCH |
CMS could not fetch the element. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_SEQUENCED |
The retrieved element is sequenced. |
Success |
CMS$GET_STRING
CMS$GET_STRING — Translates a string identifier.
Format
CMS$GET_STRING (string_id,
string)Arguments
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier. This is the address of the string descriptor containing the string that CMS passes to the callback routine.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a string descriptor that CMS fills in with the character string indicated by string_id. The method you use to provide this argument depends on the language from which you are calling CMS. For examples of calling CMS from different languages, see Appendix B, "Examples of Calling CMS".
Description
The CMS$GET_STRING routine translates a string_id that CMS passes to a callback routine. To use CMS$GET_STRING, you supply a character string variable, which is then filled by CMS. CMS$GET_STRING can return the same condition codes as the STR$COPY_DX function. For information about the STR$ condition codes, see the description of the STR$COPY_xx routines in the OpenVMS Run-Time Library (RTL) documentation. For examples of programs that contain calls to the CMS$GET_STRING routine, see Appendix B, "Examples of Calling CMS".
CMS$INSERT_ELEMENT
CMS$INSERT_ELEMENT — Places one or more elements in the specified group or groups.
Format
CMS$INSERT_ELEMENT (library_data_block,
element_expression,
group_expression,
[remark],
[if_absent],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the name of the element or group of elements to be inserted into group_name. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
You must include a period (.) in the element expression to select one or more elements from the complete list of elements in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and selects elements based on the list of groups established in the library.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more groups into which the elements, indicated by element_expression, are being inserted. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to insert the element only if that element does not already belong to the group. If you do not specify this argument and the group already contains the element, CMS returns an error. Set the flag to 1 to direct CMS to insert the element only if it is absent. If the element is already in the group, CMS takes no action and returns CMS$_NORMAL.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$INSERT_ELEMENT routine places one or more elements into one or more existing groups (see the description of the CMS$CREATE_GROUP routine). If you use the CMS$INSERT_ELEMENT routine to insert group A into group B, group B contains all the elements that belong to group A when the insertion transaction completes. If the contents of group A change at a later time, the contents of group B are not affected.
You cannot insert any elements into a group that has the READ_ONLY attribute. For information on the READ_ONLY and NOREAD_ONLY attributes, see the description of the CMS$MODIFY_GROUP routine.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRINSERTIONS |
CMS inserted zero or more elements, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_INSERTED |
CMS inserted the element. |
Success |
|
CMS$_INSERTIONS |
CMS inserted one or more elements. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOINSERT |
CMS did not insert the element. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
CMS$INSERT_GENERATION
CMS$INSERT_GENERATION — Places one or more element generations in the specified class or classes.
Format
CMS$INSERT_GENERATION (library_data_block,
element_expression,
class_expression,
[remark],
[generation_expression],
[always],
[supersede],
[if_absent],
[msg_routine],
[before])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements whose generations are to be inserted into the class or classes. Only one generation of a given element can belong to a specific class. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
You must include a period (.) in the element expression to select one or more elements from the complete list of elements in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and selects elements based on the list of groups established in the library.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more classes into which the element generation is to be inserted. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the generation expression indicating which generation of the element is to be inserted into the class or classes. By default, CMS inserts the latest generation on the main line of descent.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to insert the element generation into the class, regardless of whether it already belongs to the class. To always insert the element generation, set this flag to 1. By default (and if you do not specify other arguments that affect the insertion transaction), CMS inserts the element generation only if the class does not already contain a generation from that element.
When you specify always and the class already contains a generation of the given element, the existing element generation is removed from the class and the new generation takes its place.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating whether CMS inserts the element generation if the class already contains another generation of that element. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS does not supersede any existing class association for the element. If you set the flag to 1, CMS supersedes the previous class association for that element. When you set this flag, and the class does not contain a generation from the specified element, CMS returns an error.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to insert the generation only if a generation of the element does not already belong to the class. If you do not specify this argument and the class already contains a generation from that element, CMS returns an error. Set the flag to 1 to direct CMS to insert the generation only if it is absent. If the generation is already in the class, CMS takes no action and returns an error.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a binary date and time value that CMS uses to select the generation to insert into the class.
Description
The CMS$INSERT_GENERATION routine places one or more specified element generations into one or more classes. The class or classes must already exist. (See the description of the CMS$CREATE_CLASS routine.) A class can contain only one generation of an element. You cannot insert any generations into a class that has the READ_ONLY attribute. For information on the READ_ONLY and NOREAD_ONLY attributes, see the description of the CMS$MODIFY_CLASS routine.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRINSERTIONS |
CMS inserted zero or more generations,but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_GENINSERTED |
CMS inserted the generation. |
Success |
|
CMS$_GENNOINSERT |
CMS did not insert the generation. |
Error |
|
CMS$_INSERTIONS |
CMS inserted one or more generations. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
CMS$INSERT_GROUP
CMS$INSERT_GROUP — Places one or more groups into the specified group or groups.
Format
CMS$INSERT_GROUP (library_data_block,
sub_group_expression,
group_expression,
[remark],
[if_absent],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more groups to be inserted into group_expression. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more groups into which sub_group_expression is to be inserted. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to insert the group only if that group does not already belong to the group. If you do not specify this argument and the group already contains the group, CMS returns an error. Set the flag to 1 to direct CMS to insert the group only if it is absent. If the group is already in the group, CMS takes no action and returns an error.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$INSERT_GROUP routine inserts one or more existing groups into one or more other existing groups. (See the description of the CMS$CREATE_GROUP routine.) When you use the CMS$INSERT_GROUP routine to insert group A into group B,the elements that can be accessed through group B change as the contents of group A change. CMS does not allow you to define recursive groups. For example, you cannot insert group A into group B if group A already contains group B.
You cannot insert any groups into a group that has the READ_ONLY attribute. For information on the READ_ONLY and NOREAD_ONLY attributes, see the description of the CMS$MODIFY_GROUP routine.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRINSERTIONS |
CMS inserted zero or more groups, but encountered one or more errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_INSERTED |
CMS inserted the groups. |
Success |
|
CMS$_INSERTIONS |
CMS inserted one or more groups. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOINSERT |
CMS did not insert the group. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
CMS$MODIFY_CLASS
CMS$MODIFY_CLASS — Changes the characteristics of the specified class or classes.
Format
CMS$MODIFY_CLASS (library_data_block, class_expression, [remark], [new_name]?, [new_remark]?, [read_only]?, [msg_routine])
Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more classes to be modified. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed, unless you specify new_name.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the new class name. Class names and group names must be unique; CMS returns an error if you specify a name already used for an existing class or group. If a previously used class or group name has been removed by a DELETE CLASS or DELETE GROUP transaction, you can use that name again. You cannot specify wildcards or a comma list. In addition, if you specify the new_name argument,you cannot specify wildcards or a comma list in the class_expression argument.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a new remark to be substituted for the existing creation remark for the class.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that changes the access to the class. If you set the flag to 1, CMS sets the class to READ_ONLY. If you set the flag to 0, CMS sets the class to NOREAD_ONLY. By default, the existing access is not changed.
If you want to change the attributes of a READ_ONLY class,you can set the read_only flag to 0 in the same call that you use to change other attributes. In addition,you can change the attributes of a NOREAD_ONLY class and set the class to READ_ONLY in the same call.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The name of the class.
The remark associated with the CMS CREATE CLASS command for the specified class.
The access to the class (READ_ONLY or NOREAD_ONLY). You cannot change the contents or the name of a class that has been set to READ_ONLY.
You must specify one or more of the new_name, new_remark, or read_only arguments in the call to CMS$MODIFY_CLASS. If a class is set to READ_ONLY, you must change it to NOREAD_ONLY to change any other characteristics.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRMODIFIES |
CMS modified zero or more classes, but encountered one or more errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_MODIFICATIONS |
CMS modified one or more classes. |
Success |
|
CMS$_MODIFIED |
CMS modified the class. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOMODIFY |
CMS did not modify the class. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
Example
CHARACTER*14 DIR CHARACTER*8 CLASSCHARACTER*8 NEWNAME INTEGER*4 READONLY
INTEGER*4 LDB(50)
INTEGER*4 CMS$SET_LIBRARY
INTEGER*4 CMS$MODIFY_CLASS DIR = '[LENNON.SONGS]' CLASS = 'PRE_1968'
NEWNAME = 'PRE_1970' READONLY = 1 STATUS = CMS$SET_LIBRARY(LDB,DIR)
IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$STOP(%VAL(STATUS)) STATUS = CMS$MODIFY_CLASS(LDB,CLASS,,NEWNAME,,READONLY)
IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$STOP(%VAL(STATUS)) END
Character string variables are declared for the directory specification,existing class name, and new class name. | |
A longword integer variable is declared for the read_only flag. | |
The LDB is declared as a 50–word integer array. | |
The CMS routines are declared external to the program. | |
The character string variables are assigned values and the read_only flag is set to change the access to the class. | |
CMS$SET_LIBRARY is called to initialize the LDB. | |
CMS$MODIFY_CLASS is called with the library_data_block, class_expression, new_name, and read_only arguments. Extra commas are used as placeholders for the omitted arguments. Note that you can change the access to the class in the same call that you use to change the characteristics (in this case, the class name). |
CMS$MODIFY_ELEMENT
CMS$MODIFY_ELEMENT — Changes the characteristics of each specified element.
Format
CMS$MODIFY_ELEMENT (library_data_block, element_expression, [remark], [new_name]?, [new_remark]?, [history]?, [notes]?, [position]?, [concurrent]?, [reference_copy]?, [msg_routine], [review]?)
Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements to be modified. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed, unless you specify new_name.
You must include a period (.) in the element expression to select one or more elements from the complete list of elements in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and selects elements based on the list of groups established in the library.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the new element name. You cannot use 00CMS as the file name component of an element name because it is reserved for CMS. If you specify this argument, you cannot specify wildcards or a comma list in the element_expression argument.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a new remark to be substituted for the existing creation remark for the element. If you change this remark, the remark associated with generation 1 of the element is not altered. To change the remark associated with generation 1 of the element, use CMS$MODIFY_GENERATION.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the history string. If you include the historyargument in the call, CMS establishes or changes the history attribute for the element. By default, CMS does not alter the existing history attribute (if any). If an element has a history attribute, its history is included in the file when it is retrieved by the CMS$FETCH routine. To disable the history attribute, specify a zero-length string. For a detailed explanation of the history attribute, see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the notes string. If you include the notes argument in the call, CMS establishes or changes the notes attribute for the element. By default, CMS does not alter the existing notes attribute (if any). If an element has a notes attribute, notes are added to the ends of the lines of the file when it is retrieved by the CMS$FETCH routine. To disable the notes attribute, specify a zero-length string. Any element that has the notes attribute must have the position attribute. For a detailed explanation of the notes attribute, see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the position value to be used with the notes attribute. The position attribute determines the character position at which the note is to begin on the line. The position value must be an integer greater than zero. Any element that has the position attribute must have the notes attribute. For a detailed explanation of the position attribute, see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating the access to the element. Set the flag to 1 to allow concurrent reservations of the element. Set the concurrent flag to 0 to prohibit concurrent reservations. By default, the existing concurrency characteristic is not changed.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating whether CMS is to maintain a reference copy of the element when a new main line generation is created. If you set the flag to 1, CMS creates a reference copy for the element and enables the reference_copy attribute for the element. If you set the flag to 0, CMS deletes the reference copy and disables the reference copy attribute from the element.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating whether CMS is to automatically mark new generations as pending review. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS marks new generations of the element as pending review only if the reviewed generation was either rejected or has a review pending. Set the flag to 1 to indicate that new generations should be marked for review.
Description
Concurrent access to the element
The history string inserted in the element historywhen the element is reserved or fetched
The notes string and related position attribute
The element name
The creation remark stored in the library history
The reference copy attribute of the element
The review attribute of the element
You must specify one or more of the new_name, new_remark, concurrent, history, notes, position, reference_copy, or review arguments in the call to CMS$MODIFY_ELEMENT. If a generation of the element is currently reserved, you can change only the remark, reference copy, and review attributes of the element.
If you specify the new_name, notes and position, or history arguments, the reference copy directory is updated (provided the reference copy attribute is set).
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRMODIFIES |
CMS modified zero or more elements, but encountered one or more errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_MODIFICATIONS |
CMS modified one or more elements. |
Success |
|
CMS$_MODIFIED |
CMS modified the element. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOMODIFY |
CMS did not modify the element. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
CMS$MODIFY_GENERATION
CMS$MODIFY_GENERATION — Alters information associated with one or more generations of an element.
Format
CMS$MODIFY_GENERATION (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[remark],
[generation_expression],
new_remark,
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements whose generations are to be modified. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the particular generation to be modified. By default, the most recent generation on the main line of descent is modified.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a new remark to be stored with the generation being modified. You must specify this argument. The remark associated with the element is not altered, even if you modify the remark for generation 1. To change the remark associated with the element, use the CMS$MODIFY_ELEMENT routine. If you change this remark, the remark associated with the element is not altered. To change the remark associated with the element, use the routine CMS$MODIFY_ELEMENT.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$MODIFY_GENERATION routine enables you to change the remark associated with each generation of an element in the library.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRMODIFIES |
CMS modified zero or more generations, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_MODIFICATIONS |
CMS modified one or more generations. |
Success |
|
CMS$_MODIFIED |
CMS modified the generation. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOMODIFY |
CMS did not modify the specified generation. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
CMS$MODIFY_GROUP
CMS$MODIFY_GROUP — Alters the information associated with one or more groups.
Format
CMS$MODIFY_GROUP (library_data_block, group_expression, [remark], [new_name]?, [new_remark]?, [read_only]?, [msg_routine])
Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more groups to be modified. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed, unless you specify new_name.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the new name of the group. You cannot specify wildcards or a comma list. If you specify this argument, you cannot specify wildcards or a comma list in the group_name argument.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a new remark to be substituted for the existing creation remark for the group.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that changes the access to the group. If you set the flag to 1, CMS sets the group to READ_ONLY. If you set the flag to 0, CMS sets the group to NOREAD_ONLY. By default, the existing access is not changed.
If you want to change the attributes of a READ_ONLY group,you can set the read_only flag to 0 in the same call that you use to change other attributes. In addition,you can change the attributes of a NOREAD_ONLY group and set the group to READ_ONLY in the same call.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The name of the group.
The remark associated with the CREATE GROUP command for the specified group.
The access to the group (READ_ONLY or NOREAD_ONLY). You cannot change the contents of a group set to READ_ONLY access.
You must specify one or more of the new_name, new_remark, or read_only arguments in the call to CMS$MODIFY_GROUP. If a group is set to NOREAD_ONLY, you must change it to READ_ONLY to change any other characteristics.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRMODIFIES |
CMS modified zero or more groups, but encounteredone or more errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_MODIFICATIONS |
CMS modified one or more groups. |
Success |
|
CMS$_MODIFIED |
CMS modified the group. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOMODIFY |
CMS did not modify the group. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
CMS$MODIFY_LIBRARY
CMS$MODIFY_LIBRARY — Changes the characteristics of a CMS library.
Format
CMS$MODIFY_LIBRARY (library_data_block,
[remark],
reference_copy_dir,
[msg_routine],
[revision_time],
[concurrent],
[0],
[keep],
[extended_filenames],
[long_variant_names])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a valid OpenVMS directory to be used for reference copies of elements, or a zero-length string to disable the reference copy directory. The directory cannot be a CMS library. Wildcards are not allowed. This argument is required.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Controls whether CMS uses the original file revision time or the file storage time when a file is created in the CMS library. The default flag is set to 0, indicating the use of the original file revision time. Set the flag to 1 to use the file storage time.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating access to the elements. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS allows concurrent reservations of the elements. Set the concurrent flag to 1 to prohibit concurrent reservations across the library, unless an individual element setting overrides it.
| type: | reserved for CMS |
| access: | reserved for CMS |
| mechanism: | by value |
Specifies a required argument reserved for use by CMS. You must either pass a value of 0, or include a placeholder for this argument in the call to the CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY routine, so that the call frame entry for this argument contains a 0.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that prevents CMS from deleting copies of the input file after the element is created. By default, the flag is set to 0,indicating that CMS should delete all the copies of the file in your default directory (or the area indicated by the input_file argument) after creating the new element. Set the flag to 1 to prevent CMS from deleting input files across the library, unless an individual element setting overrides it.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Only valid on OpenVMS versions that support extended file specifications. The default 0 value does not allow extended file names. The value 1 allows extended file names.
| type: | mask_longword |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies whether variant names longer than a single character are allowed. The default value 0 does not allow long variant names. The value 1 allows variant names up to 255 alphabetic characters in length.
Description
The CMS$MODIFY_LIBRARY routine alters the connection between the reference copy directory and the CMS library.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_MODIFIED |
CMS modified the library. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOMODIFY |
CMS did not modify the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the specified library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOEXTENDED |
This version of CMS does not allow the use of extended file names. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOEXTENDEDREF |
The reference copy directory is located on a disk that does not allow the use of extended file names. |
Error |
|
CMS$_EXTFOUND |
The library contains extended file names and cannot be set to no extended file names. |
Error |
CMS$MODIFY_RESERVATION
CMS$MODIFY_RESERVATION — Alters the remark information associated with one or more reservations.
Format
CMS$MODIFY_RESERVATION (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[generation_expression],
[identification_number],
[modify_command_remark],
new_remark_for_reservation,
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements whose reservation remarks are to be changed. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
You must include a period (.) in the element expression to select one or more elements from the complete list of elements in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and selects elements based on the list of groups established in the library.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the generation of an element reservation that is to be changed.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the reserved generation of the element whose remark is to be changed. CMS assigns a unique reservation identification number to each element when it is reserved. If an element generation has only one reservation, you can replace that reservation by specifying the generation expression. However, if multiple reservations exist for the element generation, you must specify the identification number of the exact reservation to be replaced. Use the CMS$SHOW_RESERVATIONS routine to determine the reservation number of a generation.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the new remark string to be logged in the history file along with the command.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the new remark string to replace the remark string currently associated with the reservation.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$MODIFY_RESERVATION routine alters the remark string currently associated with one or more reservations. new_remark_for_reservation contains a string that is used to replace the remark currently associated with the reservation identified by element_expression, generation_expression, and identification_number.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRMODIFIES |
CMS modified zero or more element reservations but encountered one or more errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_MODIFICATIONS |
CMS modified one or more element reservations. |
Success |
|
CMS$_MODIFIED |
CMS modified the specified element reservation. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOMODIFY |
CMS did not modify the element reservation. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
Example
INTEGER*4 LDB(50)
CHARACTER*50 ELEMENTNAME
NEWREMARKELEMENTNAME='SAMPLE.C'
NEWREMARK='FIXING PROBLEM REPORT 154'
CALL CMS$MODIFY_RESERVATION(LDB, ELEMENTNAME,,,, NEWREMARK,)This call to CMS$MODIFY_RESERVATION finds the latest generation of the element sample.c in the library specified by CMS$LIB. It then checks the reservation for the current user and replaces the original reservation remark with the new remark value, as declared by NEWREMARK.
CMS$PUT_STRING
CMS$PUT_STRING — Passes a string from a callback routine to CMS.
Format
CMS$PUT_STRING (string)Arguments
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a string to be passed to CMS.
Description
The CMS$PUT_STRING routine provides the method of passing strings to CMS from within a callback routine. You must use this routine within the callback routines that provide input for the CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT, CMS$DIFFERENCES, and CMS$REPLACE routines.
CMS accepts only one input string during a single execution of an input callback routine. Thus, you should call CMS$PUT_STRING only once during a single execution of a callback routine. CMS returns CMS$_NORMAL after the first call to CMS$PUT_STRING. If you call CMS$PUT_STRING again before the callback routine returns control to CMS, the string buffer is overwritten with the new string. In this case, CMS returns CMS$_MULTCALL with a warning severity level.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_MULTCALL |
You have called CMS$PUT_STRING more than once during a single invocation of an input callback routine. |
Warning |
Example
INTEGER*4 FUNCTION INPUT_ROUTINE (FIRST_CALL,LIBDB,USER_PARAM,
1 ELEMENT_ID,EOF_STATUS,SEQUENCE_FLAG,SEQUENCE_NUM)
IMPLICIT INTEGER*4 (A-Z)
EXTERNAL CMS$PUT_STRING
INTEGER*4 LIBDB(50)
CHARACTER*80 DATA_LINE
LOGICAL FIRST_CALL
IF (FIRST_CALL) CALL OPEN_FILE  READ (1,END=100) DATA_LINE
CALL CMS$PUT_STRING(DATA_LINE)
READ (1,END=100) DATA_LINE
CALL CMS$PUT_STRING(DATA_LINE)  INPUT_ROUTINE = 1
GO TO 200
100 EOF_STATUS = %LOC(CMS$_EOF)
INPUT_ROUTINE = 1
GO TO 200
100 EOF_STATUS = %LOC(CMS$_EOF)  CALL CLOSE_FILE
INPUT_ROUTINE = 1
RETURN
200
END
CALL CLOSE_FILE
INPUT_ROUTINE = 1
RETURN
200
ENDDuring the first invocation of the input routine, a routine is called to open the input file. | |
The string supplied by the READ statement is passed to CMS with the CMS$PUT_STRING routine. | |
When end-of-file is encountered by the READ statement, eof_status is set, the input file is closed, and control is transferred back to CMS. |
For additional examples of programs that contain calls to the CMS$PUT_STRING routine, see Appendix B, "Examples of Calling CMS".
CMS$REMARK
CMS$REMARK — Places a remark in the library history.
Format
CMS$REMARK (library_data_block,
remark,
[msg_routine],
[unusual])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command. This argument is required.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the transaction is unusual, and marks it as an unusual occurrence in the history file with the command. Set the flag to 1 if the transaction is unusual. Otherwise, set it to 0. By default, the remark is not an unusual occurrence.
Description
date time username REMARK "remark"
CMS$REMOVE_ELEMENT
CMS$REMOVE_ELEMENT — Removes one or more elements from each specified group.
Format
CMS$REMOVE_ELEMENT (library_data_block,
element_expression,
group_expression,
[remark],
[if_present],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements to be removed. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
You must include a period (.) in the element expression to select one or more elements from the complete list of elements in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and selects elements based on the list of groups established in the library.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more groups from which the elements (indicated by element_expression) are to be removed. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to remove the element from the group only if it already belongs to the group. If you set the flag to 1 and the element does not belong to the group, CMS returns CMS$_NORMAL. If you use wildcards in the element_expression argument, CMS ignores the value of the if_present flag and assumes the value to be 1. If you specify a single element, do not specify if_present (or if you set the flag to 0), and the element does not belong to the group, CMS returns an error.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$REMOVE_ELEMENT routine removes one or more elements from each specified group. The routine does not delete the elements from the library, but there is no longer any association between the elements and the groups. You cannot remove any elements from agroup that has the READ_ONLY attribute. For information on the READ_ONLY and NOREAD_ONLY attributes, see the description of the CMS$MODIFY_GROUP routine.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERREMOVALS |
CMS removed zero or more elements, but encountered one or more errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREMOVAL |
CMS did not remove the element. |
Error |
|
CMS$_REMOVALS |
CMS removed one or more elements. |
Success |
|
CMS$_REMOVED |
CMS removed the element. |
Success |
CMS$REMOVE_GENERATION
CMS$REMOVE_GENERATION — Removes one or more element generations from each specified class.
Format
CMS$REMOVE_GENERATION (library_data_block,
element_expression,
class_expression,
[remark],
[if_present],
[msg_routine],
[generation])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements whose generations are to be removed. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
You must include a period (.) in the element expression to select one or more elements from the complete list of elements in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and selects elements based on the list of groups established in the library.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more classes from which the element generation is to be removed. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to remove the element generation from the class only if it already belongs to the class. If you set the flag to 1 and the class does not contain a generation from the element, CMS returns CMS$_NORMAL. If you use wildcards in the element_expression argument, CMS ignores the value of the if_present flag and assumes the value to be 1. If you specify a single element, do not specify if_present (or if you set the flag to 0), and the element does not belong to the class, CMS returns an error.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a string descriptor containing the generation to be removed. CMS returns an error if the generation is not located in the class, and if the element_expression argument does not contain a wildcard or a group.
Description
The CMS$REMOVE_GENERATION routine removes one or more element generations from each specified class. The routine does not delete the element or the generation from the library, but the generation is no longer associated with the class. You cannot remove any generations from a class that has the READ_ONLY attribute.
For information on the READ_ONLY and NOREAD_ONLY attributes, see the description of the CMS$MODIFY_CLASS routine.
To remove one element generation from a class and replace it with another generation of the same element, specify the supersede argument to the CMS$INSERT_GENERATION routine.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERREMOVALS |
CMS removed zero or more generations, but encountered one or more errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_GENNOREMOVE |
CMS did not remove the generation. |
Error |
|
CMS$_GENREMOVED |
CMS removed the generation. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_REMOVALS |
CMS removed one or more generations. |
Success |
CMS$REMOVE_GROUP
CMS$REMOVE_GROUP — Removes one or more groups from another group or groups.
Format
CMS$REMOVE_GROUP (library_data_block,
sub_group_expression,
group_expression,
[remark],
[if_present],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more groups to be removed from group_expression. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more groups from which sub_group_expressionis to be removed. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to remove sub_group_expression from group_expression only if it belongs to the group. If you set the flag to 1 and group_expression does not contain sub_group_expression, CMS returns CMS$_NORMAL. When either group name contains wildcards, CMS ignores the value of the if_present flag and assumes the value to be 1. If you specify a single group, do not specify if_present (or if you set the if_present flagto 0), and sub_group_expression does not belong to group_expression, CMS returns an error.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$REMOVE_GROUP routine removes one or more groups from another group or groups. The routine does not delete the group from the library, but there is no longer any association between the respective groups. You cannot remove any groups from a group that has the READ_ONLY attribute. For information on the READ_ONLY and NOREAD_ONLY attributes, see the description of the CMS$MODIFY_GROUP routine.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERREMOVALS |
CMS removed zero or more groups, but encountered one or more errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREMOVAL |
CMS did not remove the group. |
Error |
|
CMS$_REMOVALS |
CMS removed one or more groups. |
Success |
|
CMS$_REMOVED |
CMS removed the group. |
Success |
CMS$REPLACE
CMS$REPLACE — Returns one or more reserved generations to the library and creates a new generation of one or more elements to identify the changes.
Format
CMS$REPLACE (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[remark],
[variant],
[reserve],
[keep],
[input_file],
[input_routine],
[user_arg],
[msg_routine],
[if_changed],
[generation_expression],
[identification_number],
[insert_into_class])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more reserved elements or groups of elements to be replaced. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
You must include a period (.) in the element expression to select one or more elements from the complete list of elements in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and selects elements based on the list of groups established in the library.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies an alphabetic character used to label the variant line of descent. If you specify this argument, CMS starts a variant line of descent. The number of the new generation is the predecessor's number, followed by the variant letter, followed by the numeral 1.
If an element generation is reserved more than once, the replaced generations cannot be on the same line of descent. Thus, one can be replaced as a direct descendant of the reserved generation and the rest must be replaced as variants.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to extend the reservation established for the generation. By default, the flag is set to 0,and CMS does not reserve the new generation. Set the reserve flag to 1 to extend the reservation. In this case, CMS ignores the value of the keep flag and does not delete the file used to create the new generation.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that prevents CMS from deleting the input files. If you set the value of the flag to 1, CMS does not delete the files. By default, the flag is set to 0 and CMS deletes the files across the library, unless an individual element setting overrides it.
Note that if you set the reserve flag to 1, CMS does not delete the file, regardless of the value of the keep flag.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the location of the file whose contents are used to create anew generation of the element whose reservation is being replaced. If you specify an input file, you cannot also specify an input routine. Wildcards are allowed.
Use this argument if the input file name is different from the name of the reserved generation's element, or if the file is in some directory other than your current, default directory. If you provide a directory specification, but no file name or file type, CMS searches the specified directory for a file with the same name as the element whose generation is being replaced. When you specify an input file in an alternate directory, CMS deletes the file from the alternate location (unless you specify the keep or reserve argument).
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine that provides data for the CMS$REPLACE transaction. CMS calls this routine once for each line of data until the callback routine indicates the end of the file. If you specify an input routine, you cannot also specify an input file. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the input routine.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to the input_routine argument, using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies that a new generation is to be created only if the input file is different from the generation that was reserved. If there are no changes, the reservation is canceled (the generation is unreserved) and the input file is not deleted. By default, a new generation is created, regardless of the existence of any differences.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the reserved generation of the element to be replaced into the library. This argument can be used when you have multiple reservations on the same element, but not on the same generation of the same element. If multiple reservations exist for the element generation, you must specify the identification number of the exact reservation to be unreserved (canceled).
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the reserved generation of the element to be replaced into the library. CMS assigns a unique reservation identification number to each element when it is reserved. If an element generation has only one reservation, you can replace that reservation by specifying the generation expression. However, if multiple reservations exist for the element generation, you must specify the identification number of the exact reservation to be replaced. Use the CMS$SHOW_RESERVATIONS routine to determine the reservation number of a generation.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more classes into which newly created generations are to be inserted. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
Callback Routine Parameters
first_call, library_data_block, user_param, element_id,
eof_status, sequence_flag, sequence_numberThe callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the current call to the input routine is the first call. CMS sets the flag to 1 if it is the first call. Otherwise, it is set to 0.
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$REPLACE. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$REPLACE.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the element name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
When you use a callback routine to replace an element, CMS passes the name of the element in this parameter. If you are replacing more than one element (by specifying a group name, wildcards, or a comma list in the element_expression argument in the call to CMS$REPLACE), CMS advances to the next reservation each time you set the eof_status parameter to true (1).
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the end-of-file status. The input routine must change the value of eof_status from false (0) to true (1) to indicate to CMS that input is terminated. When eof_status is true, CMS ignores the contents of the current input record (passed by CMS$PUT_STRING). Therefore, you must set eof_status to true in the call following the last significant input record. See Section 1.6.3.1, ''Specifying End of Input'' for more information on specifying the end of input.
When you indicate that you are replacing more than one element (by using a group name or wildcard expression), CMS builds the list of elements to be replaced by comparing the element expression with the list of elements that you have reserved. As the transaction progresses, you must set eof_statusat the appropriate time to direct CMS to finish the current element replacement and continue to the next element on the list.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to create a sequenced element generation. By default, the flag is set to 0, indicating that input is not sequenced. Set the flag to 1 to direct CMS to create a sequenced element generation.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a location that you fill in with a signed integer that indicates the sequence number of the line being replaced. This is a value in the range 1 to 65,536.
Description
The CMS$REPLACE routine transfers the latest version of a file corresponding to a reserved element generation from your current, default directory to your CMS library, thus creating a new generation. You can direct CMS to use a file in a different location by specifying the input_file argument. After the reservation is replaced, CMS deletes the file used to create the new generation (and any earlier versions of the file in the same directory). If you specify either the keep or the reserve argument, CMS does not delete the file. The element must have been reserved by the user who is replacing it, unless you have BYPASS access to the element (see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System). After the replace transaction is completed, the reservation is ended. CMS stores the creation date and time, revision date and time, and file revision number of the file used to create the new generation. When you fetch or reserve an element generation, CMS restores the times and file revision number associated with the file used to create the element generation. You can also obtain this information by using the CMS$SHOW_GENERATION routine.
By default, the number of the new generation is the number of its predecessor with the rightmost level number increased by 1.
When making a concurrent replacement, you must specify the confirm_routine argument in the call to CMS$SET_LIBRARY or CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY (before calling CMS$REPLACE), or you are not warned of any concurrent reservations, and the replace transaction continues. To receive a confirmation prompt when there are existing concurrent reservations, you must specify the routine in the call to CMS$SET_LIBRARY or CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY.
When you use a callback routine to provide input for CMS$REPLACE, CMS uses the time of the replacement transaction as the file creation and revision times associated with the new generation of the element. CMS also uses the following record format and record attributes when you use a callback input routine. If you provide unsequenced input, the new generation of the element has variable-length records with the carriage return record attribute. If you provide sequenced input, the element generation has VFC 2-byte records with the carriage return record attribute (contains variable-length records–first two bytes are the length of the record).
If the element you are replacing has the reference copy attribute enabled, CMS updates the reference copy for the element in the reference copy directory.
Replacing an Element Generation with the History or Notes Attribute
If you reserve a generation of an element with the history attribute and then replace it, the REPLACE command strips the history records from the input file before creating the new generation. That is, it does not copy the history into your CMS library. If you add text to the file in or above the history (relative to #B), or in or below the history (relative to #H), the REPLACE command issues an error message and the command is not executed.
If you reserve a file with embedded notes and then replace it, the REPLACE command does not copy the notes to the CMS library. If, while editing the file,you insert text that looks like an embedded note, it is deleted when the file is replaced.
For more information about concurrent reservations and replacements, and for information on embedded histories and notes, see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERREPLACEMENTS |
CMS replaced zero or more elements, but encountered one or more errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_GENCREATED |
CMS replaced the element. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOCHANGE |
CMS did not change the element, but did reserve it. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREPLACE |
CMS did not replace the element. |
Error |
|
CMS$_REPLACEMENTS |
CMS replaced one or more elements. |
Success |
|
CMS$_USERERR |
User routine returned an error to CMS. |
Error |
CMS$RETRIEVE_ARCHIVE
CMS$RETRIEVE_ARCHIVE — Retrieves one or more generations from one or more archive files.
Format
CMS$RETRIEVE_ARCHIVE ([library_data_block],
archive_file_spec,
[generation_spec],
[output_file_spec],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library. This argument is optional.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the address of a string descriptor containing the name of the archive file. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the address of a string descriptor containing the number of the generation to be retrieved from the archive file. Wildcards are allowed. By default, if you do not specify a generation number on this argument, CMS retrieves the latest generation of the archived element.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the address of a string descriptor containing the file specification of an output file into which CMS retrieves the archived generations. Wildcards are allowed. One version of the output file specification is created for each generation retrieved.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$RETRIEVE_ARCHIVE routine retrieves one or more generations of an element from one or more archive files. By default, CMS restores the latest generation of an existing element that has been archived. CMS puts the generation into a file in your default directory and gives it the same name as the element from which it was archived. You can override this default behavior by using the output_file_spec argument.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRETRIEVALS |
CMS retrieved zero or more generations, but one or more errors occurred. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NORETRIEVE |
Error retrieving generation. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOTFOUND |
CMS could not find the specified object. |
Error |
|
CMS$_RETRIEVALS |
CMS retrieved one or more generations. |
Success |
|
CMS$_RETRIEVED |
Generation retrieved from archive file. |
Success |
CMS$REVIEW_GENERATION
CMS$REVIEW_GENERATION — Associates a review comment with each specified element generation currently under review, and enables you to change the review status of each specified generation.
Format
CMS$REVIEW_GENERATION (library_data_block,
element_expression,
action,
[remark],
[generation_expression],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements whose generations are to be reviewed. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
|
Action |
Description |
|---|---|
|
CMS$K_ACCEPT = 0 |
Specifies that the generation, which must currently have a review pending,is to be accepted and removed from the pending review list. |
|
CMS$K_CANCEL = 1 |
Specifies that the pending review for this generation is to be canceled. |
|
CMS$K_MARK = 2 |
Specifies that this generation is to be marked as pending review, and placed on the review pending list. |
|
CMS$K_REJECT = 3 |
Specifies that the generation, which must currently have a review pending,is to be rejected and removed from the review pending list. |
|
CMS$K_REVIEW = 4 |
Specifies that the remark be associated as a review remark with the specified generation, which must currently have a review pending. |
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file, and,if you specified CMS$K_REVIEW as the action argument, the remark string is associated with the generation.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies which generation is to be reviewed. If you do not specify this argument, the element's most recently created generation that has a review pending will be reviewed, unless the action was CMS$K_MARK, in which case the most recent generation on the main line of descent (1+) is marked.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$REVIEW_GENERATION routine causes a generation of an element to undergo review, be placed on the library's review pending list, or be removed from the list and marked as accepted or rejected.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ACCEPTANCES |
CMS accepted one or more generations. |
Success |
|
CMS$_ACCEPTED |
CMS accepted the generation. |
Success |
|
CMS$_CANCELATIONS |
CMS canceled one or more reviews. |
Success |
|
CMS$_CANCELED |
CMS canceled the review. |
Success |
|
CMS$_ERRACCEPTANCES |
CMS accepted zero or more generations, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_ERRCANCELATIONS |
CMS canceled zero or more reviews, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_ERRMARKS |
CMS marked zero or more generations, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_ERRREJECTIONS |
CMS rejected zero or more generations, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_ERRREVIEWS |
CMS associated the review remark with zero or more generations, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_ILLACT |
Illegal review action specified. |
Error |
|
CMS$_MARKED |
CMS marked the generation for review. |
Success |
|
CMS$_MARKS |
CMS marked one or more generations for review. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOACCEPT |
CMS did not accept the specified generation. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOCANCEL |
CMS did not cancel the specified review. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOMARK |
CMS did not mark the specified generation. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREJECT |
CMS did not reject the specified generation. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREVIEW |
CMS did not associate the review remark with the generation. |
Error |
|
CMS$_REJECTED |
CMS rejected the generation. |
Success |
|
CMS$_REJECTIONS |
CMS rejected one or more generations. |
Success |
|
CMS$_REVIEWED |
CMS associated the review remark with the generation. |
Success |
|
CMS$_REVIEWS |
CMS associated the review remark with one or more generations. |
Success |
CMS$SET_ACL
CMS$SET_ACL — Manipulates the access control list (ACL) on various objects in the CMS library.
Format
CMS$SET_ACL (library_data_block,
object_type,
object_expression,
[remark],
[acl],
[after],
[default],
[delete],
[like],
[new],
[replace],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | byreference |
CMS$K_ACL_ELEMENT = 1
CMS$K_ACL_CLASS = 2
CMS$K_ACL_GROUP = 3
CMS$K_ACL_LIBRARY = 4
CMS$K_ACL_COMMAND = 5
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more objects whose ACLs are to be modified. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies an ACL to be associated with the object.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
A string specifying the ACL in the existing ACL after which this new list (specified by the acl argument) is to be added.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates that the ACL to be placed on the object is the default for objects of that type. By default, the flag is set to 0. You must set the flag to 1 to place the default ACL on the objects.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates that the ACL entry or entries (specified by the acl argument) are to be removed from the object. If the acl argument is not specified and delete is set to 1, the entire ACL is deleted. By default, the flag is set to 0, indicating that the ACL entry remains on the object. You must set the flag to 1 to remove the ACL from the object.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
A string specifying the object whose ACL is to be copied tothis object. You do not need to pass the acl argument if a value for like is passed. The object specified by the like argument must be the same type as the object being modified.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates that the ACL (specified by the acl argument) is to supersede any existing ACL on the object.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
A string specifying the ACL entry or entries that should replace the access control entries (ACEs) specified on the acl argument. Any ACEs specified on the acl argument must be listed in the order in which they appear in the ACL.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$SET_ACL routine manipulates the ACL associated with the specified object. The action taken on the ACL depends on the parameters specified. The after, default, delete, like, new, and replace arguments cannot be specified in the same call.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRMODACLS |
CMS modified zero or more ACLs, but encountered errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_MODACL |
CMS modified the ACL. |
Success |
|
CMS$_MODACLS |
CMS modified one or more ACLs. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOMODACL |
CMS did not modify the specified ACL. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
CMS$SET_LIBRARY
CMS$SET_LIBRARY — Enables access to an existing CMS library. This routine initializes a library data block for use with other CMS callable routines.
Format
CMS$SET_LIBRARY (library_data_block,
directory,
[msg_routine],
[verify],
[confirm_routine],
[output_routine],
[width],
[position],
[positional_dir_spec])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a valid LDB. The LDB might not be initialized, depending on whether you also specify the position and positional_dir_spec arguments.
If the position and positional_dir_spec arguments are specified, the LDB must have already been initialized by a previous call to CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY or CMS$SET_LIBRARY. If the position and positional_dir_spec arguments are not specified, the LDB is initialized by this call and points to the specified directory.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a single directory, or a list of directories separated by commas. Each must contain a valid CMS library. If the directory argument specifies a logical name, it must translate into one or more library directory specifications. Wildcards are not allowed.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that causes CMS to perform validity checking on the CMS library. If you do not specify this argument, the flag is set to 1, and CMS performs validity checking. If you set the flag to 0, CMS suppresses validity checking. Validity checking improves performance and avoids the possibility of waiting for a locked library.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the address of the entry mask of a confirmation callback routine. Specify this argument to confirm an action such as a delete or replace transaction.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the address of the entry mask of a terminal output callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the maximum width of text that can be sent to the output callback routine. If this argument is not specified, the terminal width is used. If this is unavailable, the width defaults to the translation of CMS$WIDTH (if defined), or to 132 characters.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the position value to be used with the positional_dir_spec argument. The position value determines the position in the library search list at which the new library or libraries are to be inserted, or whether the new library or libraries are to supersede the existing library search list.
|
Value |
Result |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Indicates that a new library or libraries should supersede the existing library list. This is the default. |
|
1 |
Indicates that the new library or libraries should be inserted after an existing library in the library search list specified with the positional_dir_spec argument. |
|
2 |
Specifies that the new library or libraries should be inserted before an existing library in the library search list specified with the positional_dir_spec argument. |
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the name of a library in the current library search list before or after which the new library or libraries are to be inserted (depending on the value of the position argument).
If you omit the positional_dir_spec argument and specify a value of 1 for the position argument, new libraries are appended to the existing library search list. If you omit the positional_dir_spec argument and specify a value of 2 for the position argument, new libraries are inserted at the beginning of the existing library search list. If the position argument is omitted or has the value 0, the positional_dir_spec argument is ignored.
Description
The CMS$SET_LIBRARY routine establishes a CMS library search list context with one or more CMS library directories. You should call CMS$SET_LIBRARY before you make calls to any other routines. Once the search list context has been established, you can use the resulting LDB in calls to other CMS routines. The specified directories must contain valid CMS libraries that were created with the CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY routine.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_CONTROLC |
Ctrl/C interrupt has been handled. |
Warning |
|
CMS$_LIBSET |
Successful completion. (This message is not passed to the message handler.) |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
CMS$SET_NOLIBRARY
CMS$SET_NOLIBRARY — Removes one or more libraries from the current library search list.
Format
CMS$SET_NOLIBRARY (library_data_block,
[directory])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a single directory, or a list of directories separated by commas. Each must contain a valid CMS library. If this argument specifies a logical name, it must translate into one or more library directory specifications. Wildcards are not allowed.
Description
The CMS$SET_NOLIBRARY routine removes one or more libraries from the current library search list (see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System for more information on library search lists). This routine should be called after all other calls to CMS routines have been made to deallocate the virtual memory used to store the CMS library search list context.
If you do not specify a directory, all the libraries in the library search list are removed from the search list and the LDB becomes invalid. In this case, you must reinitialize the LDB with a CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY or CMS$SET_LIBRARY command before reusing it in subsequent calls to other CMS routines.
CMS$SHOW_ACL
CMS$SHOW_ACL — Displays the ACL associated with one or more specified objects.
Format
CMS$SHOW_ACL (library_data_block,
output_routine,
object_type,
[user_arg],
[object_expression],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine to process the output of CMS$SHOW_ACL. You must specify this routine. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the output routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
CMS$K_ACL_ELEMENT = 1
CMS$K_ACL_CLASS = 2
CMS$K_ACL_GROUP = 3
CMS$K_ACL_LIBRARY = 4
CMS$K_ACL_COMMAND = 5
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to the output_routine argument, using the same mechanism you used to pass it to CMS.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more objects whose ACLs are to be displayed. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Callback Routine Parameters
first_call, library_data_block, user_param, object_id, ace_id
The callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_unsigned |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
|
Value |
Result |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Indicates that the call contains the first ACE of a new ACL (after the first call). |
|
1 |
Indicates the first call to the output routine. The ace_id argument contains the first ACE of the first ACL. |
|
2 |
Indicates that the call contains the next ACE in the current ACL. |
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$SHOW_ACL. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$SHOW_ACL.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the object name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the object's ACL entry. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier.
Description
The CMS$SHOW_ACL routine retrieves and passes the ACL for the specified object to the output routine one ACE at a time.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRPAREXP |
Error parsing element expression. |
Error |
|
CMS$_ILLOBJTYP |
Illegal object type. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOCLS |
No classes found. |
Warning |
|
CMS$_NOCMD |
No commands found. |
Warning |
|
CMS$_NOELE |
No elements found. |
Warning |
|
CMS$_NOGRP |
No groups found. |
Warning |
|
CMS$_NOOBJ |
No objects found. |
Warning |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NORMAL |
Normal successful completion. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOTFOUND |
CMS could not find the specified object. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOWLDCARD |
Wildcards are not allowed in generation expressions. |
Error |
CMS$SHOW_ARCHIVE
CMS$SHOW_ARCHIVE — Displays information about the contents of one or more archive files.
Format
CMS$SHOW_ARCHIVE (archive_file_spec,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the address of a string descriptor containing the name of one or more archive files. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine to process the output of CMS$SHOW_ARCHIVE.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to the output_routine argument, using the same mechanism you used to pass it to CMS.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Callback Routine Parameters
new_file, user_param, archive_history_id, generation_id,
user_name_id, trans_time, creation_time, revision_time,
remark_id, format, attributes, revision_number,
record_size, review_statusThe callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
|
Value |
Result |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Indicates that the call contains generation information about a new archive file (after the first call). |
|
1 |
Indicates the first call to the output routine. |
|
2 |
Indicates that the call contains information about the same file as the previous call. |
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$SHOW_ARCHIVE. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes this argument to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$SHOW_ARCHIVE.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the archive history line, which contains the element and date the archive file was created. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the generation number. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the name of the user who created the element generation. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a quadword containing the date and time of the transaction that created the generation.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a quadword containing the creation date and time of the file used to create the generation.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a quadword containing the date and time the file used to create the generation was revised.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the remark. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the record format of the file used to create the element generation. The value of the longword corresponds to the record format field (FAB$B_RFM) in the file access block. The value is contained in the low-order byte of the passed longword. For more information about the RFM field, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the record attributes of the file used to create the element generation. The value of the longword corresponds to the record attributes field (FAB$B_RAT) in the file access block. The value is contained in the low-order byte. For more information about the RAT field, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the revision number of the file used to create the element generation.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the record size for files with fixed-length records. The low-order two bytes of this parameter contain the maximum record size for the generation(regardless of record format). This value corresponds to the FAB$W_MRS field in the file access block. A record size of zero indicates that no maximum record size was stored when this generation was created.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
|
Value |
Result |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Indicates that the generation has been accepted |
|
1 |
Indicates that the generation does not have a review pending |
|
2 |
Indicates that the generation does have a review pending |
|
3 |
Indicates that the generation was rejected |
Description
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_NORMAL |
Normal successful completion. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOTFOUND |
CMS could not find the specified object. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NULLSTR |
Null string is not allowed. |
Error |
|
CMS$_OPENARC |
Error opening archive file. |
Error |
|
CMS$_READERR |
Error reading archive file. |
Error |
|
CMS$_USERERR |
User routine returned an error to CMS. |
Error |
CMS$SHOW_CLASS
CMS$SHOW_CLASS — Provides information about one or more classes in a CMS library.
Format
CMS$SHOW_CLASS (library_data_block,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[class_expression],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine to process the output of CMS$SHOW_CLASS.CMS calls this routine once for each class that matches the class argument. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the output routine.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to the output_routine argument, using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more classes to be displayed. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed. By default, CMS produces a list of all classes in the library.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Callback Routine Parameters
first_call, library_data_block, user_param, class_id, remark_id,
read_onlyThe callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the current callt o the output routine is the first call. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the current call is the first call. Otherwise, this is set to 0.
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$SHOW_CLASS. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$SHOW_CLASS.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the class name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about interpreting strings passed to callback routines, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the remark. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating whether the contents of the class list can be modified. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the class list is set to READ_ONLY access. If the flag is set to 0, the class list can be modified.
Description
The CMS$SHOW_CLASS routine provides information about one or more established classes. If you specify more than one class, CMS processes the class list in alphabetical order. CMS calls the output routine once for each class that you specify.
Class name
Creation remark
Read-only status
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRPAREXP |
Error parsing class. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOCLS |
No classes found. |
Warning |
|
CMS$_NORMAL |
Normal successful completion. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOTFOUND |
CMS could not find the specified class. |
Error |
|
CMS$_USERERR |
User routine returned an error to CMS. |
Error |
CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT
CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT — Provides information about one or more elements in a CMS library.
Format
CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT (library_data_block,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[element_expression],
[member_list],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine that processes the output of CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT.CMS calls this routine once for each element described by the element_expression argument. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the output routine.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to the output_routine argument, using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed. If you do not explicitly specify one or more elements, CMS produces a list of all elements in the library.
You must include a period (. ) in the element expression to select one or more elements from the complete list of elements in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and therefore selects elements based on the list of groups established in the library.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to produce a list of the groups to which the element belongs (see the description of the group_list_id callback parameter). If you set the flag to 0, CMS does not generate a group list. Set the flag to 1 to direct CMS to generate the list.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Callback Routine Parameters
first_call, library_data_block, user_param, element_id,
remark_id, history_string_id, notes_string_id, position,
concurrent, reference_copy, group_list_id, reviewThe callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the current call to the output routine is the first call. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the current call is the first call. Otherwise, this is set to 0.
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the element name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the remark. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the history string. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the notes string. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the position value for the generation notes.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates the concurrent access to the element. CMS sets the flag to 1 if concurrent reservations of the element are allowed. Otherwise, this is set to 0.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates the reference copy attribute. CMS sets the flag to 1 if a reference copy is being maintained inthe current reference copy directory (if any). Otherwise, this is set to 0.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the list of groups to which the element belongs. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
This parameter is significant only if you specify the member_list argument in the call to CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT. If you do not specify the member_list argument,the group list is a null string.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating whether CMS is to automatically mark new generations as pending review. CMS sets the flag to 1 if newly created generations are automatically marked for review. Otherwise, this is set to 0.
Description
Element name
Creation remark
Member list
History
Notes
Position
Concurrent attribute
Reference copy attribute
Review attribute
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRPAREXP |
Error parsing element expression. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOELE |
No elements found. |
Warning |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NORMAL |
Normal successful completion. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOTFOUND |
CMS could not find the specified element. |
Error |
|
CMS$_USERERR |
User routine returned an error to CMS. |
Error |
CMS$SHOW_GENERATION
CMS$SHOW_GENERATION — Displays information about one or more element generations in a CMS library.
Format
CMS$SHOW_GENERATION (library_data_block,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[element_expression],
[generation_expression],
[from_generation_expression],
[ancestors],
[descendants],
[member_list],
[msg_routine],
[before],
[since])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine that processes the output of CMS$SHOW_GENERATION. CMS calls this routine once for each generation indicated in the call to this function. When you specify ancestors or descendants, CMS calls the output routine once for each generation included in the specified range of ancestors or descendants for the particular element. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the output routine.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to the output_routine argument, using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed. If you do not explicitly specify one or more elements, CMS produces generation information about all elements in the library.
You must include a period (.) in the element expression to select one or more elements from the complete list of elements in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and selects elements based on the list of groups established in the library.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the particular generation of the element to be displayed. By default, CMS displays information about the latest generation (1+) on the main line of descent.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the generation that begins the list of ancestors. If you specify this argument in a call to CMS$SHOW_GENERATION, you must also specify the ancestors argument in the same call.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to output information about the ancestors of the specified generation. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS outputs information only about the specified generation. If you set the flag to 1, CMS outputs information about the ancestors of the specified generation in addition to the specified generation. You cannot specify both ancestors and descendants in the same call.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to output information about the descendants of the specified generation. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS outputs information about only the specified generations. If you set the flag to 1, CMS outputs information about both the generation and the descendants of the specified generation. In this case, the default for generation_expression is generation 1. You cannot specify both descendants and ancestors in the same call.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to produce a list of the classes to which the element generation belongs. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS does not generate the list. If you set the flag to 1, CMS generates the list (see Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the class_list_id parameter).
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the quadword date and time value that CMS uses to select generation information for output. CMS outputs information about element generations that occurred before the specified date and time. This value must be specified in the absolute time value format. If a date and time value of 0 is specified, CMS outputs a list of element generations up to the present date and time.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the quadword date and time value that CMS uses to select generation information for output. CMS outputs information about element generations that occurred after the specified date and time. This value must be specified in the absolute time value format. If a date and time value of 0 is specified, CMS outputs a list of element generations for the present date, up to the current time.
Callback Routine Parameters
new_element, library_data_block, user_param, element_id,
generation_id, user_name_id, trans_time, creation_time,
revision_time, remark_id, class_list_id, format,
attributes, revision_number, reservations, record_size,
review_statusThe callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
|
Value |
Result |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Indicates that the call contains generation information about a new element (after the first call) |
|
1 |
Indicates the first call to the output routine |
|
2 |
Indicates that the call contains information about the same element as the previous call |
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$SHOW_GENERATION. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$SHOW_GENERATION.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the element name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the generation number. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the name of the user who created the element generation. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a quadword containing the date and time of the transaction that created the element generation.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a quadword containing the creation date and time of the file used to create the element generation.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a quadword containing the revision date and time of the file used to create the element generation.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the remark. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the list of classes to which the generation belongs. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
This parameter is significant only if you specify the member_list argument in the call to CMS$SHOW_GENERATION. If you do not specify member_list, the class_list_id parameter is a null string.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the record format of the file used to create the element generation. The value of the longword corresponds to the record format field (FAB$B_RFM) in the file access block. The value is contained in the low-order byte of the passed longword. For more information about the RFM field, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the record attributes of the file used to create the element generation. The value of the longword corresponds to the record attributes field (FAB$B_RAT) in the file access block. The value is contained in the low-order byte. For more information about the RAT field, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the revision number of the file used to create the element generation.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether any current reservations are established for the element generation. If the flag is set to 1, the element generation is reserved.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the record size for files with fixed-length records. The low-order two bytes of this parameter contain the maximum record size for the generation (regardless of record format). This value corresponds to the FAB$W_MRS field in the file access block. A record size of zero indicates that no maximum record size was stored when this generation was created.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
|
Value |
Result |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Indicates that the generation has been accepted |
|
1 |
Indicates that the generation does not have a review pending |
|
2 |
Indicates that the generation has a review pending |
|
3 |
Indicates that the generation has been rejected |
Description
Element name
Generation number
User name
Transaction date and time (quadword)
Creation date and time of the file used in the replace transaction(quadword)
Revision date and time of the file used in the replace transaction(quadword)
Creation remark
Class list
Reservation status
File characteristics
Review status
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_GENNOTFOUND |
Specified generation not found. |
Error |
|
CMS$_ERRPAREXP |
Error parsing element expression. |
Error |
|
CMS$_ILLCHAR |
Illegal character in generation expression. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOELE |
No elements found. |
Warning |
|
CMS$_NOGEN |
No generation match. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NORMAL |
Normal successful completion. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOTFOUND |
CMS could not find the specified element. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOWLDCARD |
Wildcards are not allowed in generation expressions. |
Error |
|
CMS$_USERERR |
User routine returned an error to CMS. |
Error |
CMS$SHOW_GROUP
CMS$SHOW_GROUP — Provides information about one or more groups in a CMS library.
Format
CMS$SHOW_GROUP (library_data_block,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[group_expression],
[msg_routine],
[contents])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine that processes the output of CMS$SHOW_GENERATION.CMS calls this routine once for each group indicated in the call to CMS$SHOW_GROUP. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the output routine.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to the output_routine argument, using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more groups. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed. If you do not explicitly specify one or more groups, CMS produces a list of all groups in the library.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
nohead
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to produce a list of the elements and groups contained in this group. You can specify an integer value (n) that directs CMS to display nested groups down to and including the level indicated by n. For example, a value of 1 displays one nested level of contents; a value of 2 displays two nested levels of contents. You can also specify a value of –1 to display all levels of contained groups or elements.
Callback Routine Parameters
first_call, library_data_block, user_param, group_id,
remark_id, read_only, level, contents_idThe callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the current call to the output routine is the first call. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the current call is the first call. Otherwise, this is set to 0.
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$SHOW_GROUP. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$SHOW_GROUP.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the group name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the remark. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating whether the contents of the group list can be modified. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the group list is set to READ_ONLY access. If the flag is set to 0, the group list can be modified.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a value indicating the current level of contents information passed through the contents_id parameter. The level argument is significant only if you also specified the contents argument in the call to CMS$SHOW_GROUP.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the list of elements or groups of elements contained in this group. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''. This parameter is significant only if you specified the contents argument in the call to CMS$SHOW_GROUP. Otherwise, this parameter points to a null descriptor.
Description
Group name
Creation remark
Read-only status
Contents
Member list
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRPAREXP |
Error parsing group. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOGRP |
No groups found. |
Warning |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NORMAL |
Normal successful completion. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOTFOUND |
CMS could not find the specified class. |
Error |
|
CMS$_USERERR |
User routine returned an error to CMS. |
Error |
CMS$SHOW_HISTORY
CMS$SHOW_HISTORY — Provides (in chronological order) records of transactions performed on aCMS library.
Format
CMS$SHOW_HISTORY (library_data_block,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[object_name],
[user],
[before],
[since],
[transaction_mask],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine that processes the output of CMS$SHOW_HISTORY. CMS calls this routine once for each history record that meets the criteria imposed by the arguments passed to this function. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the output routine.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to the output_routine argument, using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the name of the element, group, or class. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
If you include a period (.) in the object_name string, CMS selects history records based on the element or class names that match the string. If you do not include a period, CMS selects history records based on group or class names that match the object_name string.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the name of the user about whom CMS is to output information. By default, CMS outputs information about all library users.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the quadword binary date and time value that CMS uses to select transactions for output. CMS outputs information about transactions that occurred before the specified date and time. You must specify this argument in the absolute time value format. If you specify a date and time value of 0, CMS outputs a list of transactions up to the present day and time.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the quadword binary date and time value that CMS uses to select transactions for output. CMS outputs information about transactions that occurred after the specified date and time. You must specify this argument in the absolute time value format. If you specify a date and time value of 0, CMS outputs a list of transactions up to the present day and time.
| type: | mask_longword |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
|
Symbol |
Bit Position |
Mask Value |
Command |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CMS$M_CMD_COPY |
0 |
1 |
COPY CLASS |
|
COPY ELEMENT | |||
|
COPY GROUP | |||
|
CMS$M_CMD_CREATE |
1 |
2 |
CREATE CLASS |
|
CREATE ELEMENT | |||
|
CREATE GROUP | |||
|
CREATE LIBRARY | |||
|
CMS$M_CMD_DELETE |
2 |
4 |
DELETE CLASS |
|
DELETE ELEMENT | |||
|
DELETE GROUP | |||
|
DELETE HISTORY | |||
|
CMS$M_CMD_FETCH |
3 |
8 |
FETCH |
|
CMS$M_CMD_INSERT |
4 |
16 |
INSERT ELEMENT |
|
INSERT GENERATION | |||
|
INSERT GROUP | |||
|
CMS$M_CMD_MODIFY |
5 |
32 |
MODIFY CLASS |
|
MODIFY ELEMENT | |||
|
MODIFY GROUP | |||
|
MODIFY LIBRARY | |||
|
MODIFY RESERVATION | |||
|
CMS$M_CMD_REMARK |
6 |
64 |
REMARK |
|
CMS$M_CMD_REMOVE |
7 |
128 |
REMOVE ELEMENT |
|
REMOVE GENERATION | |||
|
REMOVE GROUP | |||
|
CMS$M_CMD_REPLACE |
8 |
256 |
REPLACE |
|
CMS$M_CMD_RESERVE |
9 |
512 |
RESERVE |
|
CMS$M_CMD_UNRESERVE |
10 |
1024 |
UNRESERVE |
|
CMS$M_CMD_VERIFY |
11 |
2048 |
VERIFY |
|
CMS$M_CMD_SET |
14 |
16,384 |
SET ACL |
|
CMS$M_CMD_ACCEPT |
16 |
65,536 |
ACCEPT GENERATION |
|
CMS$M_CMD_CANCEL |
17 |
131,072 |
CANCEL REVIEW |
|
CMS$M_CMD_MARK |
18 |
262,144 |
MARK GENERATION |
|
CMS$M_CMD_REJECT |
19 |
524,288 |
REJECT GENERATION |
|
CMS$M_CMD_REVIEW |
20 |
1,048,576 |
REVIEW GENERATION |
The mask values are defined as universal symbols in the CMS image. You can use OR with these values to enable combinations of the values. This transaction mask is the same as the transaction mask used by the CMS$DELETE_HISTORY routine.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Callback Routine Parameters
first_call, library_data_block, user_param, time, user_id,
command_id, object_id, remark_id, unusualThe callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the current call to the output routine is the first call. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the current call is the first call. Otherwise, this is set to 0.
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$SHOW_HISTORY. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$SHOW_HISTORY.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a quadword binary date and time value for the time of the transaction.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the user name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the command name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the element, group, or class involved in the transaction. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the remark. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the transaction is unusual. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the transaction is unusual. Otherwise, this is set to 0.
Description
Transaction time
User name associated with the transaction
Command as entered (command name, subcommand name, option, qualifiers,and parameters)
Remark entered with the command
Unusual status
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ABSTIM |
Absolute date-time value required. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOHIS |
No history records found. |
Warning |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NORMAL |
Normal successful completion. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOSINCE |
Error executing a since operation. |
Error |
|
CMS$_TIMEORDER |
BEFORE and since time values cannot be resolved. |
Error |
|
CMS$_USERERR |
User routine returned an error to CMS. |
Error |
Example
IMPLICIT INTEGER*4 (A-Z)
INTEGER*4 LDB(50)
CHARACTER*14 DIR
EXTERNAL CMS$_NOHIS
INTEGER*4 CMS$SET_LIBRARY
INTEGER*4 CMS$SHOW_HISTORY
INTEGER*4 OUTPUT_ROUTINE
DIR = '[LENNON.SONGS]'
STATUS = CMS$SET_LIBRARY(LDB,DIR)
IF (.NOT. STATUS) GO TO 1000
STATUS = CMS$SHOW_HISTORY(LDB,OUTPUT_ROUTINE)
IF (STATUS .EQ. %LOC(CMS$_NOHIS)) GO TO 1000
.
.
.
1000 END
C
INTEGER*4 FUNCTION OUTPUT_ROUTINE
(FIRST_CALL,LIBDB,USER_PARAM,1
TIME,USER_ID,COMMAND_ID,2
OBJECT_ID,REMARK_ID,UNUSUAL)
INTEGER*4 UNUSUAL
EXTERNAL CMS$_NORMAL
EXTERNAL CMS$_EXCLUDE
OUTPUT_ROUTINE = %LOC(CMS$_NORMAL)
IF (.NOT. UNUSUAL) THEN
OUTPUT_ROUTINE = %LOC(CMS$_EXCLUDE)
ENDIF
RETURN
ENDThis example checks only for unusual transactions; if there are no unusual transactions, the callback routine returns CMS$_EXCLUDE each time control is transferred to CMS. As a result, the CMS$SHOW_HISTORY routine returns CMS$_NOHIS (no history records found) and the routine transfers control elsewhere.
CMS$SHOW_LIBRARY
CMS$SHOW_LIBRARY — Provides information about the current library.
Format
CMS$SHOW_LIBRARY (library_data_block,
[reference_copy_dir],
[statistics],
[msg_routine],
[verify],
[output_routine],
[user_arg])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a descriptor that CMS fills in with the specification for the reference copy directory (if any).
| type: | vector_longword_unsigned |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an array of 10 longwords that CMS fills in with information about the library. Figure 2.1, ''Statistics Array'' shows the content of the statistics array. Each entry in the array is an integer count of the number of indicated objects (elements, groups, classes, and so on).
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that causes CMS to lock the library as part of the CMS$SHOW_LIBRARY routine. By default, the flag is set to 1, indicating that locking is performed. The library must be locked for CMS to fill in the reference_copy_dir and statistics parameters. If verify is specified as 0, CMS returns zeros in these parameters. Library locking is also necessary for CMS to determine basic library integrity. If recovery is necessary, it is not detected until another operation is performed.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine that processes output of CMS$SHOW_LIBRARY. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the output routine.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to the output_routine argument, using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS.
Callback Routine Parameters
verify, first_call, user_param, library_spec_id,
reference_copy_id, statistics_block, revision_time,
concurrent, 0, keep, extended_filenamesThe callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the value passed to the CMS$SHOW_LIBRARY routine. This value is passed to the output routine to determine if the reference_copy_id and statistics_block contents are valid.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that indicates whether the current call to the output routine is the first call. CMS sets the flag to 1 if the current call is the first call. Otherwise, this is set to 0.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$SHOW_RESERVATIONS. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$SHOW_RESERVATIONS.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for a library directory specification. If the current library search list consists of more than one library, successive calls to output_routine return all individual library directory specifications, one at a time. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the reference copy directory specification. If there is no reference copy directory, the length of the string is 0.
| type: | vector_longword_unsigned |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an array of 10 longwords that CMS fills with information about the library. See Figure 2.1, ''Statistics Array'' for information about the content of the statistics array. Each entry in the array is an integer count of the number of indicated objects (elements, groups, classes, and so on).
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Indicates whether CMS used the file revision time, or the original file storage time, when the element was created or modified. The value 1 indicates the file revision time, whereas the value 0 indicates the original file storage time.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Contains a value indicating the access to the object. The value 1 indicates no concurrent reservations are allowed, whereas the value 0 indicates concurrent reservations are allowed.
| type: | reserved for CMS |
| access: | reserved for CMS |
| mechanism: | by value |
Specifies a required parameter reserved for use by CMS. You must either pass a value of 0 or include a placeholder for this argument in the call to the CMS$SHOW_LIBRARY routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Contains the value of the KEEP attribute, which prevents CMS from deleting copies of the input file. The value 0 indicates that CMS should delete all the copies of the file, whereas the value 1 indicates that CMS should keep all the input files.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Only valid on OpenVMS versions supporting extended file specifications. The default 0 value does not allow extended file names. The value 1 allows extended file names.
Description
The CMS$SHOW_LIBRARY routine identifies the reference copy directory (if any) for the current library. This routine also provides information about the number of elements, current reservations, concurrent replacements, reviews pending, and classes and groups in the library.
CMS$SHOW_RESERVATIONS
CMS$SHOW_RESERVATIONS — Provides information about all current reservations and concurrent replacements in effect at the time the routine is called.
Format
CMS$SHOW_RESERVATIONS (library_data_block,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[element_expression],
[generation_expression],
[user],
[msg_routine],
[identification_number])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine that processes CMS$SHOW_RESERVATIONS output. CMS calls this routine once for each reservation or concurrent replacement in effect for each element generation indicated in the call to CMS$SHOW_RESERVATIONS. This argument is required. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the output routine.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to the output_routine argument, using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the output routine.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed. By default, CMS outputs information about any existing reservations for generations of all elements in the library.
You must include a period (.) in the element expression to select one or more elements from the complete list of elements in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and selects elements based on the list of groups established in the library.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the particular generation of the element to be displayed. By default, CMS displays information about any existing reservations for all generations of the elements indicated by element_expression.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the user name that CMS uses to select reservation information for output. By default, CMS outputs information about any existing reservations for all library users.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the reserved generation of the element to be displayed. CMS assigns a unique reservation identification number to each element when it is reserved.
Callback Routine Parameters
new_element, library_data_block, user_param, element_id,
generation_id, time, user_id, remark_id, concurrent,
merge_generation_id, nonotes, nohistory, access,
reservation_idThe callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Indicates whether the current call to the output routine contains information about a generation of a new element. If there are any concurrent reservations or concurrent replacements for a given element, CMS calls the output routine once for each concurrent reservation and replacement. The value of this parameter also indicates whether it is the first call to the output routine.
|
Value |
Result |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Indicates that the call contains reservation information about the next element in the list of elements specified by the element_expression argument (after the first call) |
|
1 |
Indicates the first call to the output routine |
|
2 |
Indicates that the call contains information about the same element as the previous call |
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$SHOW_RESERVATIONS. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$SHOW_RESERVATIONS.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the element name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the generation number. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a quadword binary date and time value for the time of the transaction.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the user name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the remark. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
|
Value |
Result |
|---|---|
|
–1 |
Concurrent replacement |
|
0 |
Current reservation |
|
1 |
Concurrent reservation |
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the merge generation. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. If there is no merge generation, the length of the string is 0. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating whether CMS suppressed notes in the reservation transaction. If the flag is set to 1, notes were suppressed; if the flag is set to 0, notes were not suppressed.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag indicating whether CMS suppressed the element history in the reservation transaction. If the flag is set to 1, the history was not included in the output file; if the flag is set to 0, the element history was included.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
|
Value |
Result |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Concurrent reservations are allowed. |
|
1 |
Concurrent reservations are not allowed. |
|
3 |
The existing reservation does not allow other reservations. |
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Returns the identification number of the reservation.
Description
The CMS$SHOW_RESERVATIONS routine provides information about the reservations and concurrent replacements in effect for one or more elements in a library. If you specify more than one element, CMS processes the element list in alphabetical order. CMS calls the output routine once for each reservation.
Element name
Generation number
Time of reservation or replacement
User name
Remark
Concurrent status
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRPAREXP |
Error parsing element expression. |
Error |
|
CMS$_ILLCHAR |
Illegal character in generation expression. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NORES |
No reservations found. |
Warning |
|
CMS$_NORMAL |
Normal successful completion. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOTFOUND |
CMS could not find the specified element. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOWLDCARD |
Wildcards are not allowed in generation expression. |
Error |
|
CMS$_USERERR |
User routine returned an error to CMS. |
Error |
CMS$SHOW_REVIEWS_PENDING
CMS$SHOW_REVIEWS_PENDING — Displays a list of element generations that currently have review pending status. This routine also displays any review remarks that have been associated with the generation currently under review.
Format
CMS$SHOW_REVIEWS_PENDING (library_data_block,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[element_expression],
[generation_expression],
[user],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a callback routine to process the output of CMS$SHOW_REVIEWS_PENDING. This argument is required. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the output routine.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies a value that you supply and that CMS passes to the output_routine argument, using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS. See Section 1.6, ''Using Callback Routines'' for information about the parameters that CMS passes to the output routine.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements whose generations with reviews pending are to be displayed. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed. If you do not specify this argument, all element generations pending review in the library are displayed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the particular generation of the element to be displayed. By default, reviews pending for all of the element's generations are displayed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the name of the user whose generations with pending reviews are to be displayed. By default, pending reviews for generations created by all users are displayed.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Callback Routine Parameters
new_element, library_data_block, user_param, element_id,
generation_id, generation_time, generation_user_id,
generation_remark_id, review_time, review_user_id,
review_remark_idThe callback routine must return a defined condition code to CMS. The following parameter descriptions define the access to the object from the perspective of the callback routine.
| type: | longword_unsigned |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
|
Value |
Result |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Indicates that the call contains information about a different element than the previous call |
|
1 |
Indicates the first call to the output routine |
|
2 |
Indicates that the call contains information about a different generation of the same element as the previous call |
|
3 |
Indicates that the call contains information about the same generation of the same element as the previous call |
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the LDB for the current library.
| type: | undefined |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | undefined |
Specifies the user argument as it was passed to CMS$SHOW_REVIEWS_PENDING. If you did not specify a user argument, this parameter points to a read-only storage location containing the value 0. CMS passes user_param to your routine using the same mechanism that you used to pass it to CMS$SHOW_REVIEWS_PENDING.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the element name. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the generation number. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a binary quadword date-time value representing the time the generation was created.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the name of the user who created the generation.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the remark entered when the generation was replaced. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | date_time |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a binary quadword date-time value representing the time the generation was placed under review, or the date and time the review remark was entered.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the name of the user who marked the generation for review or the user who entered the review remark. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
| type: | address |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a string identifier for the remark entered when the generation or the review of the generation was marked. Use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to translate the string identifier. For information about string identifiers, see Section 1.6.3, ''Passing Strings Between CMS and Callback Routines''.
Description
The CMS$SHOW_REVIEWS_PENDING routine retrieves information about generations with reviews pending and passes that information to the output routine. If this routine is called multiple times with information about the same generation of the same element, these calls contain review remark information.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRPAREXP |
Error parsing element expression. |
Error |
|
CMS$_ILLCHAR |
Illegal character in generation expression. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREV |
No pending reviews were found for the generations. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NORMAL |
Normal successful completion. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOTFOUND |
CMS could not find the specified element. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOWLDCARD |
Wildcards are not allowed in generation expression. |
Error |
|
CMS$_USERERR |
User routine returned an error to CMS. |
Error |
CMS$SHOW_VERSION
CMS$SHOW_VERSION — Provides version identification of the CMS system currently in use.
Arguments
| type: | char_string |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a descriptor to be filled in by CMS. The full form of the version identification includes the product identification string and the version number.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies a descriptor to be filled in by CMS. The brief form of version identification includes only the version number.
| type: | longword_unsigned |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by reference |
|
Literal Version Number |
Absolute Version Number |
|---|---|
|
3.7 |
100177 |
|
3.8 |
100184 |
|
3.9 |
100189 |
|
4.0 |
100191 |
|
4.1 |
100194 |
|
4.2 |
100205 |
|
4.3 |
100209 |
Description
The CMS$SHOW_VERSION routine identifies the version of CMS currently in use.
CMS$UNRESERVE
CMS$UNRESERVE — Cancels a reservation for one or more generations.
Format
CMS$UNRESERVE (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[remark],
0,
[delete_file],
[msg_routine],
[generation_expression],
[identification_number],
[delete_file_spec])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements with a reservation to be canceled.
You must include a period (. ) in the element expression to select one or more elements from the complete list of elements in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and selects elements based on the list of groups established in the library. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | reserved for CMS |
| access: | reserved for CMS |
| mechanism: | by value |
Specifies a required argument reserved for use by CMS. You must either pass 0 by value, or include a placeholder for this argument in the call to the CMS$UNRESERVE routine, so the call frame entry for this argument contains a 0.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to delete the files with the same file name and file type in your default directory (unless you specify another location by also specifying the delete_file_spec argument). By default, the flag is set to 0,and CMS does not delete any files. If you set the flag to 1, CMS deletes the corresponding files from your default directory.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the reserved generation of the element to be unreserved. This argument can be used when you have multiple reservations on the same element, but not on the same generation of the same element. If multiple reservations exist for the element generation, you must specify the identification number of the exact reservation to be unreserved (canceled).
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies the reserved generation of the element to be unreserved. CMS assigns a unique reservation identification number to each element when it is reserved. If an element generation has only one reservation, you can unreserve (cancel) that reservation by specifying the generation expression. However, if multiple reservations exist for the element generation, you must specify the identification number of the exact reservation to be unreserved (canceled). Use the CMS$SHOW_RESERVATIONS routine to determine the reservation number of a generation.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the files to be deleted and their location. All the versions of the specified file are deleted. Any valid OpenVMS file specification can be used; however, it cannot contain a node name or file version number. By default, CMS uses the current default device and directory. If the delete_file_spec argument is omitted or contains a zero, CMS uses the delete_file argument (if specified) to determine what files should be deleted. If the delete_file_spec argument contains a file specification, the delete_file argument is ignored. If none of these arguments is specified, no files are deleted.
Description
The CMS$UNRESERVE routine cancels an existing reservation.
Each reservation of an element is assigned a unique reservation identification number. If an element generation has only one reservation, you can unreserve (cancel) that reservation by specifying the generation expression. If multiple reservations exist for the element generation, you must specify the identification number of the reservation to be unreserved (canceled).
When canceling a concurrent reservation, you must specify the confirm_routine argument in the call to CMS$SET_LIBRARY or CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY (before calling CMS$UNRESERVE), or you are not warned of any concurrent reservations, and the unreserve transaction continues. To receive a confirmation prompt when there are existing concurrent reservations, you must specify the routine in the call to CMS$SET_LIBRARY or CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_ERRUNRESERVES |
CMS canceled zero or more reservations and encountered one or more errors during the transaction. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NORMAL |
Normal successful completion. |
Success |
|
CMS$_NOUNRESERVE |
CMS did not cancel the reservation. |
Error |
|
CMS$_UNRESERVED |
CMS canceled the reservation. |
Success |
|
CMS$_UNRESERVES |
CMS canceled one or more reservations. |
Success |
CMS$VERIFY
CMS$VERIFY — Performs a series of checks on your CMS library to confirm that the library structure and library files are in a valid form.
Format
CMS$VERIFY (library_data_block,
[element_expression],
[remark],
[recover],
[repair],
[msg_routine])Arguments
| type: | cntrlblk |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies an initialized LDB.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies one or more elements or groups of elements to be verified.
You must include a period (.) in the element expression to select one or more elements from the complete list of elements in the library. If you do not include a period, CMS interprets the parameter as a group name and selects elements based on the list of groups established in the library. Wildcards and a comma list are allowed.
| type: | char_string |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Specifies the remark string to be logged in the history file with the command.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to execute a recovery transaction. By default, the flag is set to 0, and CMS does not execute the recovery procedure. Set the flag to 1 to recover the library. You cannot use both the recover and the repair arguments in the same call to CMS$VERIFY.
| type: | longword_signed |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a flag that directs CMS to execute a repair transaction. By default, the flag is set to 0,and CMS does not execute the repair procedure. Set the flag to 1 to repair the library or the elements indicated by the element_expression argument. You cannot use both the recover and the repair arguments in the same call to CMS$VERIFY.
| type: | procedure |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Specifies a message-handler routine. For information about writing a message-handler routine, see Section 1.8, ''Writing an Error-Message Handler''.
Description
The CMS$VERIFY routine performs a series of consistency checks on your library. If you call CMS$VERIFY under normal conditions,the routine executes successfully, indicating that the information in your library is correct. However, if the data in the library is invalid, the routine returns an error message saying that there is an error in the verification of the library. In this case, you must recover or repair the library as indicated by the error message. You cannot use both the recover and the repair arguments in the same call to CMS$VERIFY.
Recovery and repair transactions are marked as unusual occurrences in the library history. For more information about the verify transaction, see the VSI DECset for OpenVMS Guide to the Code Management System.
|
Return Code |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
|
CMS$_NORECOVER |
CMS did not recover the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREF |
Error accessing the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOREPAIR |
CMS did not repair the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_NOVERIFY |
CMS did not verify the library. |
Error |
|
CMS$_RECOVERED |
CMS recovered the library. |
Success |
|
CMS$_REPAIRED |
CMS repaired the library. |
Success |
|
CMS$_VERIFY |
CMS verified the library. |
Success |
Appendix A. Summary of CMS Entry Points
CMS$ANNOTATE (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[generation_expression],
[merge_generation_expression],
[append],
[full],
[output_file],
[output_routine],
[user_arg],
[msg_routine],
[format])CMS$ASYNCH_TERMINATEThis
routine has no arguments.CMS$CMS ([command_line],
[msg_routine],
[prompt_routine],
[confirm_routine],
[output_routine],
[width])CMS$COPY_CLASS (library_data_block,
input_class_expression,
output_class_expression,
[remark],
[source_library_data_block],
[msg_routine])CMS$COPY_ELEMENT (library_data_block,
input_element_expression,
output_element,
[remark],
[source_library_data_block],
[msg_routine])CMS$COPY_GROUP (library_data_block,
input_group_expression,
output_group_expression,
[remark],
[source_library_data_block],
[msg_routine])CMS$CREATE_CLASS (library_data_block,
class_name,
[remark],
[msg_routine])CMS$CREATE_ELEMENT (library_data_block,
element_name,
[remark],
[history],
[notes],
[position],
[keep],
[reserve],
[concurrent],
[reference_copy],
[input_file],
[input_routine],
[user_arg],
[msg_routine],
[review])CMS$CREATE_GROUP (library_data_block,
group_name,
[remark],
[msg_routine])CMS$CREATE_LIBRARY (library_data_block,
directory,
[remark],
[reference_copy_dir],
[msg_routine],
[confirm_routine],
[output_routine],
[width],
[position],
[positional_dir_spec]
[revision_time],
[auto_create],
[concurrent],
[0],
[keep],
[extended_filenames],
[long_variant_names])CMS$DELETE_CLASS (library_data_block,
class_expression,
[remark],
[msg_routine],
[remove_contents])CMS$DELETE_ELEMENT (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[remark],
[msg_routine])CMS$DELETE_GENERATION (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[remark],
[generation_expression],
[after_generation],
[before_generation],
[from_generation],
[to_generation],
[archive_file],
[msg_routine])A
generation or range of generations must be specified with a combination of one or more of the
after_generation, before_generation, from_generation, or to_generation arguments.CMS$DELETE_GROUP (library_data_block,
group_expression,
[remark],
[msg_routine],
[remove_contents])CMS$DELETE_HISTORY (library_data_block,
[remark],
before,
[transaction_mask],
[output_routine],
[user_arg],
[msg_routine],
[object],
[user])CMS$DIFFERENCES (library_data_block,
[user_arg],
[input_file1],
[input_routine1],
[generation_expression_1],
[input_file2],
[input_routine2],
[generation_expression_2],
[output_file],
[output_routine],
[append],
[ignore_mask],
[nooutput],
[parallel],
[full],
[format],
[width],
[msg_routine],
[page_break],
[skip_lines],
[begin_sentinel],
[end_sentinel])The
library_data_block argument is a required parameter only if
you also specify a generation_expression parameter.CMS$DIFFERENCES_CLASS (library_data_block,
class_expression1,
class_expression2,
[append],
[format],
[full],
[ignore_mask],
[nooutput],
[parallel],
[show_mask],
[width],
[output_file],
[output_routine],
[user_arg],
[msg_routine])CMS$FETCH (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[remark],
[generation_expression],
[merge_generation_expression],
[reserve],
[nohistory],
[nonotes],
[concurrent],
[output_file],
[msg_routine],
[nooutput],
[history],
[notes],
[position])CMS$FETCH_CLOSE (fetch_data_block,
[msg_routine])CMS$FETCH_GET (fetch_data_block,
output_record,
[sequence_number],
[generation_number],
[msg_routine])CMS$FETCH_OPEN (fetch_data_block,
directory,
element_name,
[generation_expression],
[nohistory],
[nonotes],
[actual_generation],
[msg_routine])CMS$GET_STRING (string_id,
string)CMS$INSERT_ELEMENT (library_data_block,
element_expression,
group_expression,
[remark],
[if_absent],
[msg_routine])CMS$INSERT_GENERATION (library_data_block,
element_expression,
class_expression,
[remark],
[generation_expression],
[always],
[supersede],
[if_absent],
[msg_routine],
[before])CMS$INSERT_GROUP (library_data_block,
sub_group_expression,
group_expression,
[remark],
[if_absent],
[msg_routine])CMS$MODIFY_CLASS (library_data_block,
class_expression,
[remark],
[new_name],
[new_remark],
[read_only],
[msg_routine])At
least one of the new_name, new_remark, or read_only arguments is
required.CMS$MODIFY_ELEMENT (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[remark],
[new_name],
[new_remark],
[history],
[notes],
[position],
[concurrent],
[reference_copy],
[msg_routine],
[review])At
least one of the new_name, new_remark, history, notes, position, concurrent, reference_copy, or review arguments is required.CMS$MODIFY_GENERATION (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[remark],
[generation_expression],
new_remark,
[msg_routine])CMS$MODIFY_GROUP (library_data_block,
group_expression,
[remark],
[new_name],
[new_remark],
[read_only],
[msg_routine])At
least one of the new_name, new_remark, or read_only arguments is
required.CMS$MODIFY_LIBRARY (library_data_block,
[remark],
reference_copy_dir,
[msg_routine],
[revision_time],
[concurrent],
[0],
[keep],
[extended_filenames],
[long_variant_names])CMS$MODIFY_RESERVATION (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[generation_expression],
[identification_number],
[modify_command_remark],
new_remark_for_reservation,
[msg_routine])CMS$PUT_STRING (string)CMS$REMARK (library_data_block,
remark,
[msg_routine],
[unusual])CMS$REMOVE_ELEMENT (library_data_block,
element_expression,
group_expression,
[remark],
[if_present],
[msg_routine])CMS$REMOVE_GENERATION (library_data_block,
element_expression,
class_expression,
[remark],
[if_present],
[msg_routine],
[generation])CMS$REMOVE_GROUP (library_data_block,
sub_group_expression,
group_expression,
[remark],
[if_present],
[msg_routine])CMS$REPLACE (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[remark],
[variant],
[reserve],
[keep],
[input_file],
[input_routine],
[user_arg],
[msg_routine],
[if_changed],
[generation_expression],
[identification_number],
[insert_into_class])CMS$RETRIEVE_ARCHIVE ([library_data_block],
archive_file_spec,
[generation_spec],
[output_file_spec],
[msg_routine])CMS$REVIEW_GENERATION (library_data_block,
element_expression,
action,
[remark],
[generation_expression],
[msg_routine])CMS$SET_ACL (library_data_block,
object_type,
object_expression,
[remark],
[acl],
[after],
[default],
[delete],
[like],
[new],
[replace],
[msg_routine])CMS$SET_LIBRARY (library_data_block,
directory,
[msg_routine],
[verify],
[confirm_routine],
[output_routine],
[width],
[position],
[positional_dir_spec])CMS$SET_NOLIBRARY (library_data_block,
[directory])CMS$SHOW_ACL (library_data_block,
output_routine,
object_type,
[user_arg],
[object_expression],
[msg_routine])CMS$SHOW_ARCHIVE (archive_file_spec,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[msg_routine])CMS$SHOW_CLASS (library_data_block,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[class_expression],
[msg_routine])CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT (library_data_block,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[element_expression],
[member_list],
[msg_routine])CMS$SHOW_GENERATION (library_data_block,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[element_expression],
[generation_expression],
[from_generation_expression],
[ancestors],
[descendants],
[member_list],
[msg_routine],
[before],
[since])CMS$SHOW_GROUP (library_data_block,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[group_expression],
[msg_routine],
[contents])CMS$SHOW_HISTORY (library_data_block,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[object_name],
[user],
[before],
[since],
[transaction_mask],
[msg_routine])CMS$SHOW_LIBRARY (library_data_block,
[reference_copy_dir],
[statistics],
[msg_routine],
[verify],
[output_routine],
[user_arg])CMS$SHOW_RESERVATIONS (library_data_block,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[element_expression],
[generation_expression],
[user],
[msg_routine],
[identification_number])CMS$SHOW_REVIEWS_PENDING (library_data_block,
output_routine,
[user_arg],
[element_expression],
[generation_expression],
[user],
[msg_routine])CMS$SHOW_VERSION ([full],
[brief],
[absolute])At
least one of these arguments is required.CMS$UNRESERVE (library_data_block,
element_expression,
[remark],
0,
[delete_file],
[msg_routine],
[generation_expression],
[identification_number],
[delete_file_spec])
CMS$VERIFY (library_data_block,
[element_expression],
[remark],
[recover],
[repair],
[msg_routine])
Appendix B. Examples of Calling CMS
This appendix shows examples of calling the CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT routine from the Ada, Basic, BLISS, C, COBOL, Fortran, Pascal, PL/I, and SCAN languages. Each program uses an output routine to display a list of the library elements and the groups to which each element belongs.
B.1. Calling CMS from Ada
with SYSTEM; use SYSTEM;package CONDITION_HANDLING_UTILITIES is type COUNT is new INTEGER; type STATUS_TYPE is record SEVERITY : COUNT range 0..2**3-1; CODE : COUNT range 0..2**12-1; FAC_SP : BOOLEAN; FAC_NO : COUNT range 0..2**12-1; INHIB_MSG : BOOLEAN; FILLER_1 : COUNT range 0..2**3-1; end record; function SS_NORMAL return STATUS_TYPE; pragma INLINE(SS_NORMAL); type SIGARG_TYPE(ARGS : NATURAL) is record NAME : STATUS_TYPE; ARGn : UNSIGNED_LONGWORD_ARRAY(2..ARGS); end record; package MCHARG_PKG is type COUNT is new INTEGER; subtype COUNT_NATURAL is COUNT range 0..COUNT'last; subtype COUNT_POSITIVE is COUNT range 1..COUNT'last; FRAME : constant COUNT := COUNT_NATURAL'first; DEPTH : constant COUNT := FRAME + 1; SAVR0 : constant COUNT := DEPTH + 1; SAVR1 : constant COUNT := SAVR0 + 1; type MCHARG_COMPONENT_ARRAY is array(COUNT_POSITIVE range <>) of SYSTEM.UNSIGNED_LONGWORD; type MCHARG_TYPE(ARGS : COUNT_NATURAL) is record ARGn : MCHARG_COMPONENT_ARRAY(1..ARGS); end record; private for MCHARG_TYPE use record ARGS at 0 range 0..31; -- ARGn at 4 range 0...; end record; end; subtype MCHARG_TYPE is MCHARG_PKG.MCHARG_TYPE; procedure PUTMSG ( MSGVEC : in SIGARG_TYPE; ACTRTN : in SYSTEM.ADDRESS := ADDRESS_ZERO; FACNAM : in STRING := STRING'NULL_PARAMETER; ACTPRM : in SYSTEM.UNSIGNED_LONGWORD := 0); private for STATUS_TYPE use record SEVERITY at 0 range 0..2; CODE at 0 range 3..14; FAC_SP at 0 range 15..15; FAC_NO at 0 range 16..27; INHIB_MSG at 0 range 28..28; FILLER_1 at 0 range 29..31; end record; for SIGARG_TYPE use record ARGS at 0 range 0..31; NAME at 4 range 0..31; -- ARGn at 8 range 0...; end record; pragma INTERFACE(SYS, PUTMSG); pragma IMPORT_PROCEDURE(PUTMSG, external => "SYS$PUTMSG", mechanism => (REFERENCE, VALUE, DESCRIPTOR(S), VALUE)); end; package body CONDITION_HANDLING_UTILITIES is function SS_NORMAL return STATUS_TYPE is begin return STATUS_TYPE'(SEVERITY => 1, CODE => 0, FAC_SP => FALSE, FAC_NO => 0, INHIB_MSG => FALSE, FILLER_1 => 0); end; end; with CONDITION_HANDLING_UTILITIES, SYSTEM; use CONDITION_HANDLING_UTILITIES, SYSTEM; package CMS is type LDB_TYPE is
limited private; type FDB_TYPE is limited private; type FLAG_TYPE is new BOOLEAN; procedure GET_STRING( STATUS : out STATUS_TYPE; STRING_ID : in ADDRESS; STRING : out STANDARD.STRING); procedure SET_LIBRARY( STATUS : out STATUS_TYPE; LIBRARY_DATA_BLOCK : in out LDB_TYPE; DIRECTORY : in STRING; MSG_ROUTINE : in ADDRESS := ADDRESS_ZERO); procedure SHOW_ELEMENT( STATUS : out STATUS_TYPE; LIBRARY_DATA_BLOCK : in out LDB_TYPE; OUTPUT_ROUTINE : in ADDRESS; USER_ARG : in UNSIGNED_LONGWORD := 0; ELEMENT_EXPRESSION : in STRING := "*.*"; MEMBER_FLAG : in FLAG_TYPE := FALSE; MSG_ROUTINE : in ADDRESS := ADDRESS_ZERO); -- Examples of OUTPUT_ROUTINE and MESSAGE_ROUTINE declarations -- -- procedure OUTPUT_ROUTINE( -- STATUS : out STATUS_TYPE; -- FIRST_CALL : in FLAG_TYPE; -- LDB : in out LDB_TYPE; -- USER_PARAM : in UNSIGNED_LONGWORD; -- ELEMENT_ID : in ADDRESS; -- REMARK_ID : in ADDRESS; -- HISTORY_STRING_ID : in ADDRESS; -- NOTES_STRING_ID : in ADDRESS; -- POSITION : in INTEGER; -- CONCURRENT : in FLAG_TYPE; -- REFERENCE_COPY : in FLAG_TYPE; -- GROUP_LIST_ID : in ADDRESS -- REVIEW : in FLAG_TYPE); -- pragma EXPORT_VALUED_PROCEDURE(OUTPUT_ROUTINE, -- external => "<some unique symbol>"); -- -- procedure MSG_ROUTINE( -- STATUS : out STATUS_TYPE; -- SIGNAL_ARRAY : in SIGARG_TYPE; -- MECHANISM_ARRAY : in MCHARG_TYPE; -- LIB_DB : in out LDB_TYPE); -- pragma EXPORT_VALUED_PROCEDURE(MSG_ROUTINE, -- external => "<some unique symbol>"); private -- Library Data Block -- type LDB_TYPE is record LENGTH : INTEGER; RETURN_STATUS : STATUS_TYPE; LIB_DIR_LEN : NATURAL range 0..65_535; LIB_DIR_DTYPE : UNSIGNED_BYTE; LIB_DIR_CLASS : UNSIGNED_BYTE; LIB_DIR_ADDRESS : ADDRESS; PRIVATE_PART : UNSIGNED_LONGWORD_ARRAY(1..46); end record; for LDB_TYPE use record LENGTH at 0 range 0..31; RETURN_STATUS at 4 range 0..31; LIB_DIR_LEN at 8 range 0..15; LIB_DIR_DTYPE at 10 range 0..7; LIB_DIR_CLASS at 11 range 0..7; LIB_DIR_ADDRESS at 12 range 0..31; PRIVATE_PART at 16 range 0..46*32-1; end record; for LDB_TYPE'size use 32*50; -- Fetch Data Block -- type FDB_TYPE is new SYSTEM.UNSIGNED_LONGWORD_ARRAY(1..5); for FDB_TYPE'size use 32*5; -- The FLAG_TYPE must occupy a whole longword -- for FLAG_TYPE'size use 32; -- Routines -- pragma INTERFACE(CMS, GET_STRING); pragma IMPORT_VALUED_PROCEDURE(GET_STRING, external => "CMS$GET_STRING", mechanism => (VALUE, REFERENCE, DESCRIPTOR(S))); pragma INTERFACE(CMS, SET_LIBRARY); pragma IMPORT_VALUED_PROCEDURE(SET_LIBRARY, external => "CMS$SET_LIBRARY", mechanism => (VALUE, REFERENCE, DESCRIPTOR(S), VALUE)); pragma INTERFACE(CMS, SHOW_ELEMENT); pragma IMPORT_VALUED_PROCEDURE(SHOW_ELEMENT, external => "CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT", mechanism => (VALUE, REFERENCE, VALUE, REFERENCE, DESCRIPTOR(S), REFERENCE, VALUE)); end; function LAST_NON_BLANK(STRING : STANDARD.STRING) return NATURAL is L : NATURAL := STRING'last; begin loop exit when L < STRING'first or else STRING(L) /= ' '; L := L - 1; end loop; return L; end; with LAST_NON_BLANK; function TRIM(STRING : STANDARD.STRING) return STANDARD.STRING is
begin return STRING(STRING'first..LAST_NON_BLANK(STRING)); end; with CMS, CONDITION_HANDLING_UTILITIES, SYSTEM, TEXT_IO, TRIM; use CMS, CONDITION_HANDLING_UTILITIES, SYSTEM, TEXT_IO;
procedure OUTPUT_ROUTINE( STATUS : out STATUS_TYPE; FIRST_CALL : in FLAG_TYPE; LDB : in out LDB_TYPE; USER_PARAM : in UNSIGNED_LONGWORD; ELEMENT_ID : in ADDRESS; REMARK_ID : in ADDRESS; HISTORY_STRING_ID : in ADDRESS; NOTES_STRING_ID : in ADDRESS; POSITION : in INTEGER; CONCURRENT : in FLAG_TYPE; REFERENCE_COPY : in FLAG_TYPE; GROUP_LIST_ID : in ADDRESS; REVIEW : in FLAG_TYPE) is GET_STATUS : STATUS_TYPE; STRING : STANDARD.STRING(1..65_535); begin GET_STRING(GET_STATUS, ELEMENT_ID, STRING); PUT_LINE(TRIM(STRING)); GET_STRING(GET_STATUS, GROUP_LIST_ID, STRING); PUT_LINE(TRIM(STRING)); STATUS := SS_NORMAL; end; pragma EXPORT_VALUED_PROCEDURE(OUTPUT_ROUTINE, external=>"OUTPUT_ROUTINE"); with CMS, CONDITION_HANDLING_UTILITIES, STARLET, SYSTEM; use CMS, CONDITION_HANDLING_UTILITIES, STARLET, SYSTEM; procedure MSG_ROUTINE(
STATUS : out STATUS_TYPE; SIGNAL_ARRAY : in SIGARG_TYPE; MECHANISM_ARRAY : in MCHARG_TYPE; LIB_DB : in out LDB_TYPE) is begin case SIGNAL_ARRAY.NAME.SEVERITY is when STS_K_WARNING | STS_K_ERROR | STS_K_SEVERE => declare COPY : SIGARG_TYPE(SIGNAL_ARRAY.ARGS) := SIGNAL_ARRAY; begin COPY.NAME.SEVERITY := STS_K_INFO; PUTMSG(COPY); end; when others => null; end case; STATUS := CONDITION_HANDLING_UTILITIES.SS_NORMAL; end; pragma EXPORT_VALUED_PROCEDURE(MSG_ROUTINE, external=>"MSG_ROUTINE"); with CMS, CONDITION_HANDLING_UTILITIES, MSG_ROUTINE, OUTPUT_ROUTINE, TRIM; use CMS, CONDITION_HANDLING_UTILITIES; procedure SHOW_ELEMENT_EXAMPLE is LDB : LDB_TYPE; STATUS : STATUS_TYPE; begin SET_LIBRARY(STATUS, LDB, "CMS$LIB", MSG_ROUTINE => MSG_ROUTINE'address); SHOW_ELEMENT(STATUS, LDB, OUTPUT_ROUTINE'address, MEMBER_FLAG => TRUE, MSG_ROUTINE => MSG_ROUTINE'address); end;
This section sets up and establishes the message-handling package. | |
This section sets up and establishes the CMS interface package. | |
The TRIM routine is created, which trims blank spaces off the ends of strings. | |
The callback output routine (which will get passed to CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT) is declared. | |
The callback message routine is declared. |
B.2. Calling CMS from Basic
DIM LONG LIB_DB(50) ! Declaration for the library data block ! EXTERNAL declarations for CMS routines and the output routine ! EXTERNAL LONG FUNCTION CMS$SET_LIBRARY (LONG, STRING) EXTERNAL LONG FUNCTION CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT (LONG, LONG, STRING, STRING, LONG, LONG) EXTERNAL LONG OUTPUT_ROUTINE ! Declare OUTPUT_ROUTINE as an external ! long integer, so the starting address ! of the routine can be passed as a ! parameter. DECLARE LONG RETURN_STATUS, MEMBER_FLAG RETURN_STATUS = CMS$SET_LIBRARY (LIB_DB(0), "CMS$LIB") MEMBER_FLAG = 1 RETURN_STATUS = CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT (LIB_DB(0), OUTPUT_ROUTINE, , , MEMBER_FLAG,) END ! The output routine ! SUB OUTPUT_ROUTINE (LONG F_FIRST, & RFA LDB, USR_PARAM, & LONG ELEMENT_ID, REMARK_ID, HISTORY_ID, & NOTES_ID, POSITION, CONCURRENT, & REF_COPY, GROUP_LIST_ID, REVIEW) DECLARE STRING ELEMENT_NAME, GROUP_LIST_NAMES, LONG RETURN_STATUS ! EXTERNAL declaration for CMS$GET_STRING (used to translate string ! identifiers into a form that Basic can understand) ! EXTERNAL LONG FUNCTION CMS$GET_STRING (LONG, STRING) ! Display the results ! RETURN_STATUS = CMS$GET_STRING (ELEMENT_ID, ELEMENT_NAME) RETURN_STATUS = CMS$GET_STRING (GROUP_LIST_ID, GROUP_LIST_NAMES) PRINT ,ELEMENT_NAME PRINT ,GROUP_LIST_NAMES END SUB
B.3. Calling CMS from BLISS
MODULE SHOWELE (MAIN = MAIN, ADDRESSING_MODE (EXTERNAL = GENERAL) ) =
BEGIN
FORWARD ROUTINE
MAIN,
OUTPUT_ROUTINE;
EXTERNAL ROUTINE
CMS$SET_LIBRARY, ! EXTERNAL declarations for CMS routines
CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT, ! and LIB$ routine for output
LIB$PUT_OUTPUT;
GLOBAL ROUTINE MAIN =
BEGIN
LOCAL LDB : VECTOR[50], ! Declaration for library data block and
STATUS; ! a variable for return value from calls
STATUS = CMS$SET_LIBRARY (LDB, %ASCID 'CMS$LIB');
IF NOT .STATUS
THEN ! Exit with error code if
RETURN .STATUS; ! unable to set library
STATUS = CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT (LDB, OUTPUT_ROUTINE, 0, 0, %REF(1));  IF NOT .STATUS
THEN ! Exit with error code if call
RETURN .STATUS; ! to CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT fails
RETURN 1; ! Exit with success value
END;
ROUTINE OUTPUT_ROUTINE (FIRST_CALL, LIBDB, USER_PARAM, ELEMENT_ID,
REMARK_ID, HISTORY_ID, NOTES_ID, POSITION,
ACCESS, REF_COPY, GROUP_LIST_ID, REVIEW) =
BEGIN
BIND
ELEMENT_NAME = ..ELEMENT_ID, ! BIND declaration for
GROUP_LIST_NAME = ..GROUP_LIST_ID; ! string identifiers
LIB$PUT_OUTPUT (ELEMENT_NAME);
IF NOT .STATUS
THEN ! Exit with error code if call
RETURN .STATUS; ! to CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT fails
RETURN 1; ! Exit with success value
END;
ROUTINE OUTPUT_ROUTINE (FIRST_CALL, LIBDB, USER_PARAM, ELEMENT_ID,
REMARK_ID, HISTORY_ID, NOTES_ID, POSITION,
ACCESS, REF_COPY, GROUP_LIST_ID, REVIEW) =
BEGIN
BIND
ELEMENT_NAME = ..ELEMENT_ID, ! BIND declaration for
GROUP_LIST_NAME = ..GROUP_LIST_ID; ! string identifiers
LIB$PUT_OUTPUT (ELEMENT_NAME);  LIB$PUT_OUTPUT (GROUP_LIST_NAME);
RETURN 1;
END;
ENDELUDOM
LIB$PUT_OUTPUT (GROUP_LIST_NAME);
RETURN 1;
END;
ENDELUDOMThe member list flag is set to true (1) in the call to CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT. By using the %REF function, the call frame contains the address of a temporary data segment containing the value 1. | |
Within the callback routine it is not necessary to use the CMS$GET_STRING routine to manipulate string identifiers. BLISS allows you to use the dot operator to specify the address path. The BIND declaration is used as a more concise method of handling the string identifiers that CMS passes to the output routine. |
B.4. Calling CMS from C
#include stdio #include descrip /* OPENVMS DESCRIPTOR DEFINITIONS */ /* DESCRIPTOR MACROS */ #define builddesc(name) \ struct dsc$descriptor name = {0, DSC$K_DTYPE_T, DSC$K_CLASS_D, 0} #define filldesc(name, str) \ name.dsc$w_length = strlen(str); \ name.dsc$a_pointer = str main() { int lib_db[50]; int output_routine (); int f_member_list = 1; char *lib_name = "CMS$LIB"; builddesc (d_lib); /* BUILD A DESCRIPTOR FOR THE LIBRARY NAME */ filldesc (d_lib, lib_name); /* FILL IN THE DESCRIPTOR */ /* PASS THE LIBRARY DATA BLOCK AND THE LIBRARY NAME DESCR. BY REFERENCE */ cms$set_library (&lib_db, &d_lib); /* PASS THE LDB, entry point, AND FLAG FOR THE MEMBER LIST BY REFERENCE */ cms$show_element (&lib_db, output_routine, 0, 0, &f_member_list, 0); } /* THE OUTPUT ROUTINE */ output_routine (a_f_first_call, a_lib_db, a_user_param, element_id, remark_id, history_string_id, notes_string_id, position, concurrent, ref_copy, group_list_id, review) int *a_f_first_call, *a_lib_db, *a_user_param, **remark_id, **history_string_id, **notes_string_id, *position, *concurrent, *ref_copy, *review; struct dsc$descriptor **element_id, **group_list_id;{ char *string_from_cms; /* TO HOLD STRING EXTRACTED FROM DESCRIPTOR */ struct dsc$descriptor_s *descriptor; /* VARIABLE TO HANDLE STRING IDs */ char *calloc(); descriptor = *element_id;
string_from_cms = calloc (1, descriptor -> dsc$w_length + 1); strncpy (string_from_cms, descriptor -> dsc$a_pointer,
descriptor -> dsc$w_length); printf ("%s\n", string_from_cms); descriptor = *group_list_id; string_from_cms = calloc (1, descriptor -> dsc$w_length + 1); strncpy (string_from_cms, descriptor -> dsc$a_pointer,
descriptor -> dsc$w_length); printf ("%s\n", string_from_cms); return (1); }
Because C enables you to manipulate addresses directly,it is not necessary to use the CMS$GET_STRING routine when you are calling CMS from the C language. This example illustrates one way to handle the string identifiers.
The strings containing the element name and the group list are passed by string identifier. To handle the extra level of indirection, the element_id and group_list_id parameters are declared with two asterisk operators. | |
The address of the element name descriptor is put in the contents of descriptor. | |
Descriptor is then used as an argument to the calloc and strncpy functions to provide the string for output. | |
The same steps are used to handle the group list string. |
B.5. Calling CMS from COBOL
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION. PROGRAM-ID. SHOELE. * * SHOW ELEMENT * ENVIRONMENT DIVISION. DATA DIVISION. WORKING-STORAGE SECTION. 01 LIB_DB PIC X(200). 01 LIBRARY PIC X(21) VALUE "CMS$LIB". * The flag signaling /MEMBER * 01 MEM PIC S9 VALUE 1. * The user-supplied output routine. * 01 OUT_ROUT PIC S9(9) COMP VALUE EXTERNAL OUTP. / PROCEDURE DIVISION. 0. CALL "CMS$SET_LIBRARY" USING BY REFERENCE LIB_DB BY DESCRIPTOR LIBRARY. CALL "CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT" USING BY REFERENCE LIB_DB BY VALUE OUT_ROUT BY VALUE 0 BY VALUE 0 BY REFERENCE MEM. EXIT PROGRAM.
The program SHOELE contains a declaration for the callback routine(named OUTP) that handles output from CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT. The following example shows this subroutine. You must compile OUTP separately to pass the address of the routine to CMS.
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. OUTP.
*
* Output subroutine for SHOW ELEMENT
*
ENVIRONMENT DIVISION.
DATA DIVISION.
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
* Strings to hold the data extracted from the descriptors;
* status to be returned to CMS.
*
01 ELEMENT_NAME PIC X(15).
01 GROUP_LIST_NAMES PIC X(100).
01 CALL_STATUS_VAL COMP PIC 9(9).
01 RET_STATUS_VAL COMP PIC 9(9).
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 F_FIRST_CALL PIC 99.
01 LIB_DATA_BLOCK PIC X(200).
01 USER_PARAM PIC 99.
01 ELEMENT_ID PIC 9(9).
01 REMARK_ID PIC 9(9).
01 HISTORY_ID PIC 9(9).
01 NOTES_ID PIC 9(9).
01 POSITION_VAL PIC 9(9).
01 CONCURRENT_FLAG PIC 9(9).
01 REF_COPY PIC 9(9).
01 GROUP_LIST_ID PIC 9(9).
01 REVIEW PIC 9(9).
/
PROCEDURE DIVISION USING F_FIRST_CALL
LIB_DATA_BLOCK
USER_PARAM
ELEMENT_ID
REMARK_ID
HISTORY_ID
NOTES_ID
POSITION_VAL
CONCURRENT_FLAG
REF_COPY
GROUP_LIST_ID
REVIEW
GIVING RET_STATUS_VAL.
0.
* Extract the string data from the descriptors.
*
MOVE 1 to CALL_STATUS_VAL.
CALL "CMS$GET_STRING" USING ELEMENT_ID
BY DESCRIPTOR ELEMENT_NAME
GIVING CALL_STATUS_VAL.
IF (CALL_STATUS_VAL = 1)
DISPLAY ELEMENT_NAME
CALL "CMS$GET_STRING" USING GROUP_LIST_ID
BY DESCRIPTOR GROUP_LIST_NAMES
GIVING CALL_STATUS_VAL
IF (CALL_STATUS_VAL = 1)
DISPLAY GROUP_LIST_NAMES
END-IF
END-IF
* Return the call status to CMS.
*
MOVE CALL_STATUS_VAL TO RET_STATUS_VAL.
EXIT PROGRAM.B.6. Calling CMS from Fortran
IMPLICIT INTEGER*4 (A-Z)
INTEGER*4 CMS$SET_LIBRARY,  1 CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT,
1 LDB(50),
1 MEMBER_FLAG
EXTERNAL OUTPUT_ROUTINE
1 CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT,
1 LDB(50),
1 MEMBER_FLAG
EXTERNAL OUTPUT_ROUTINE  STATUS = CMS$SET_LIBRARY (LDB, 'CMS$LIB')
IF (STATUS) THEN
MEMBER_FLAG = 1
STATUS = CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT (LDB, OUTPUT_ROUTINE, , ,
MEMBER_FLAG)
END IF
END
INTEGER*4 FUNCTION OUTPUT_ROUTINE (FIRST_CALL, LIBDB,
STATUS = CMS$SET_LIBRARY (LDB, 'CMS$LIB')
IF (STATUS) THEN
MEMBER_FLAG = 1
STATUS = CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT (LDB, OUTPUT_ROUTINE, , ,
MEMBER_FLAG)
END IF
END
INTEGER*4 FUNCTION OUTPUT_ROUTINE (FIRST_CALL, LIBDB,  USER_PARAM,
1 ELEMENT_ID, REMARK_ID, HISTORY_ID,
1 NOTES_ID, POSITION, ACCESS,
1 REF_COPY, GROUP_LIST_ID, REVIEW)
IMPLICIT INTEGER*4 (A-Z)
INTEGER*4 LIBDB(50)
CHARACTER ELEMENT_NAME*80,
1 GROUP_LIST_NAMES*80
EXTERNAL CMS$GET_STRING
CALL CMS$GET_STRING (ELEMENT_ID, ELEMENT_NAME)
USER_PARAM,
1 ELEMENT_ID, REMARK_ID, HISTORY_ID,
1 NOTES_ID, POSITION, ACCESS,
1 REF_COPY, GROUP_LIST_ID, REVIEW)
IMPLICIT INTEGER*4 (A-Z)
INTEGER*4 LIBDB(50)
CHARACTER ELEMENT_NAME*80,
1 GROUP_LIST_NAMES*80
EXTERNAL CMS$GET_STRING
CALL CMS$GET_STRING (ELEMENT_ID, ELEMENT_NAME)  CALL CMS$GET_STRING (GROUP_LIST_ID, GROUP_LIST_NAMES)
PRINT *, ELEMENT_NAME
PRINT *, GROUP_LIST_NAMES
OUTPUT_ROUTINE = 1
RETURN
END
CALL CMS$GET_STRING (GROUP_LIST_ID, GROUP_LIST_NAMES)
PRINT *, ELEMENT_NAME
PRINT *, GROUP_LIST_NAMES
OUTPUT_ROUTINE = 1
RETURN
ENDThe CMS routines are declared as INTEGER*4 so the return status is available for error checking. | |
The output routine is declared EXTERNAL to pass the address of the routine to CMS. | |
The output routine is written as a function because it must return a value to CMS. | |
CMS$GET_STRING is used to translate the string identifier and provide access to the element name and group list strings. |
B.7. Calling CMS from Pascal
PROGRAM SHOELE (INPUT, OUTPUT); (* SHOW ELEMENT *)
TYPE
LDB = ARRAY [1..50] OF INTEGER;
STRING = VARYING [256] OF CHAR;
VAR
LIB_DB : LDB;
LIBNAM : STRING;
MEMBER_FLAG : INTEGER;
(* External CMS routines *)
PROCEDURE CMS$SET_LIBRARY
(%REF LIB_DB : LDB;
%DESCR LIBDIR : STRING);
EXTERNAL;
PROCEDURE CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT
(%REF LIB_DB : LDB;
FUNCTION OUTPUT_ROUTINE
(VAR FIRST : INTEGER;
VAR LIB : LDB;
VAR PARAM : INTEGER;
VAR ELEMENT : INTEGER;
VAR REMARK : INTEGER;
VAR HISTORY : INTEGER;
VAR NOTES : INTEGER;
VAR POSITION : INTEGER;
VAR CONCURRENT : INTEGER;
VAR REF_COPY : INTEGER;
VAR GROUP_LIST : INTEGER;
VAR REVIEW : INTEGER) : INTEGER;
%IMMED USER_PARAM : INTEGER := 0;
%IMMED ELEMENT_EXP : INTEGER := 0;
%REF MEMBER_FLAG : INTEGER;
%IMMED MSG_ROUTINE : INTEGER := 0);
EXTERNAL;
PROCEDURE CMS$GET_STRING
(%REF DATA : INTEGER;
%DESCR DEST : STRING);
EXTERNAL;
(* The output routine *)
FUNCTION OUTPUT_ROUTINE
(VAR FIRST : INTEGER;
VAR LIB : LDB;
VAR PARAM_ID : INTEGER;
VAR ELEMENT_ID : INTEGER;
VAR REMARK_ID : INTEGER;
VAR HISTORY_ID : INTEGER;
VAR NOTES_ID : INTEGER;
VAR POSITION : INTEGER;
VAR CONCURRENT : INTEGER;
VAR REF_COPY : INTEGER;
VAR GROUP_LIST_ID : INTEGER;
VAR REVIEW : INTEGER) : INTEGER;
VAR
ELEMENT_NAME : STRING;
GROUP_LIST_NAMES : STRING;
BEGIN
(* NOTE: this routine must return a value equivalent to
true, or CMS will assume the user is returning an error. *)
(* write out the actual data *)
CMS$GET_STRING (ELEMENT_ID, ELEMENT_NAME);
WRITELN (ELEMENT_NAME);
CMS$GET_STRING (GROUP_LIST_ID, GROUP_LIST_NAMES);
WRITELN (GROUP_LIST_NAMES);
OUTPUT_ROUTINE := 1;
END; (* end of output routine *)
(* Main program body - Set the CMS library, set the member flag to true,
and call CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT *)
BEGIN
LIBNAM := 'CMS$LIB';
CMS$SET_LIBRARY (LIB_DB, LIBNAM);
MEMBER_FLAG := 1;
CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT (LIB_DB, %IMMED OUTPUT_ROUTINE, , , MEMBER_FLAG);
END.Key to Example B.7, ''Calling CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT from Pascal'':
The formal parameter list for the CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT routine includes declarations for all of the actual parameters that you can pass to the routine. The list includes several %IMMED declarations that assign a value of zero to the parameter. Because the actual parameter list does not override these declarations, the call frame contains a zero in the position allocated for each of these unused parameters. The zero serves as a placeholder;thus, the member flag argument is interpreted as being in the correct position.
Note that the actual parameter list in the call to CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT specifies the %IMMED passing mechanism for the callback routine argument. This is necessary to generate the address of the entry point in the call frame.
B.8. Calling CMS from PL/I (Alpha and VAX)
SHOELMEM: PROCEDURE OPTIONS (MAIN); /* SHOW ELEMENT/MEMBER */ DECLARE MEMBER_FLAG FIXED BINARY (31); DECLARE LIB_DB(50) FIXED BINARY (31); DECLARE LIBDIR CHARACTER(50) VARYING; DECLARE CMS$SET_LIBRARY ENTRY ((50) FIXED BINARY (31), CHARACTER(*) VARYING); DECLARE CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT ENTRY ((50) FIXED BINARY (31), /* ldb */ ENTRY VALUE,/* routine */ FIXED BINARY (31), /* user param */ CHARACTER (*), /* elem-expr */ FIXED BINARY (31), /* group-list flag */ ENTRY VALUE) /* msg routine*/ OPTIONS (VARIABLE);
DECLARE CMS$GET_STRING ENTRY (FIXED BINARY(31), CHARACTER(*) VARYING); LIBDIR = 'CMS$LIB'; MEMBER_FLAG = 1; CALL CMS$SET_LIBRARY (LIB_DB, LIBDIR); CALL CMS$SHOW_ELEMENT (LIB_DB, OUTPUT_ROUTINE, , , MEMBER_FLAG);
/* the output routine */ OUTPUT_ROUTINE : PROCEDURE (FIRST, LDB, PARAM, ELEMENT, COMM, HIST, NOTES, POS, CONC, REFCOP, GROUP_LIST, REVIEW) RETURNS (FIXED BINARY(31) VALUE); DECLARE FIRST FIXED BINARY(1), LDB (50) FIXED BINARY(31), (PARAM, ELEMENT, COMM, HIST, NOTES, POS, CONC, REFCOP, GROUP_LIST, REVIEW) FIXED BINARY(31); DECLARE ELEMENT_NAME CHARACTER(79) VARYING; DECLARE GROUP_LIST_NAMES CHARACTER(120) VARYING; /* write the lines of data */ CALL CMS$GET_STRING (ELEMENT, ELEMENT_NAME); PUT SKIP LIST (ELEMENT_NAME); CALL CMS$GET_STRING (GROUP_LIST, GROUP_LIST_NAMES); PUT SKIP LIST (GROUP_LIST_NAMES); RETURN (1); END OUTPUT_ROUTINE; END;
The output routine must be passed by value to place the address of the entry point in the call frame. | |
If you specify the OPTIONS (VARIABLE) attribute in the routine declaration,you can omit unnecessary arguments from the call to the CMS routine. | |
Although the OPTIONS(VARIABLE) attribute is used,you must use commas as placeholders for intermediate arguments. You do not need to include placeholders for trailing default arguments. |
B.9. Calling CMS from SCAN
MODULE cms_example;
!+
! This example program accesses the CMS library pointed to by the
CMS$LIB
! logical name. It prompts for an element name, and then displays
its
! contents.
!-
!+
! Declarations.
!-
TYPE cms_fdb : FILL (20);  CONSTANT cms$_normal EXTERNAL INTEGER;
CONSTANT rms$_eof EXTERNAL INTEGER;
CONSTANT scn$_endinpstm EXTERNAL INTEGER;
CONSTANT ss$_normal EXTERNAL INTEGER;
EXTERNAL PROCEDURE cms$fetch_open
( REFERENCE cms_fdb,
DESCRIPTOR DYNAMIC STRING,
DESCRIPTOR DYNAMIC STRING,
DESCRIPTOR DYNAMIC STRING,
REFERENCE BOOLEAN,
REFERENCE BOOLEAN,
DESCRIPTOR DYNAMIC STRING,
REFERENCE INTEGER ) OF INTEGER;
EXTERNAL PROCEDURE cms$fetch_get
( REFERENCE cms_fdb,
DESCRIPTOR DYNAMIC STRING,
REFERENCE INTEGER,
DESCRIPTOR DYNAMIC STRING,
REFERENCE INTEGER ) OF INTEGER;
EXTERNAL PROCEDURE cms$fetch_close
( REFERENCE cms_fdb,
REFERENCE INTEGER ) OF INTEGER;
!+
! Global values shared between the procedures.
!-
DECLARE fdb : cms_fdb;
DECLARE status : INTEGER;
DECLARE buffer : DYNAMIC STRING;
!+
! Simple token and macro to compress a sequence of blanks and tabs
! to a single blank.
!-
TOKEN space { { ' ' | s'ht' }... };
MACRO compress TRIGGER { space };
CONSTANT cms$_normal EXTERNAL INTEGER;
CONSTANT rms$_eof EXTERNAL INTEGER;
CONSTANT scn$_endinpstm EXTERNAL INTEGER;
CONSTANT ss$_normal EXTERNAL INTEGER;
EXTERNAL PROCEDURE cms$fetch_open
( REFERENCE cms_fdb,
DESCRIPTOR DYNAMIC STRING,
DESCRIPTOR DYNAMIC STRING,
DESCRIPTOR DYNAMIC STRING,
REFERENCE BOOLEAN,
REFERENCE BOOLEAN,
DESCRIPTOR DYNAMIC STRING,
REFERENCE INTEGER ) OF INTEGER;
EXTERNAL PROCEDURE cms$fetch_get
( REFERENCE cms_fdb,
DESCRIPTOR DYNAMIC STRING,
REFERENCE INTEGER,
DESCRIPTOR DYNAMIC STRING,
REFERENCE INTEGER ) OF INTEGER;
EXTERNAL PROCEDURE cms$fetch_close
( REFERENCE cms_fdb,
REFERENCE INTEGER ) OF INTEGER;
!+
! Global values shared between the procedures.
!-
DECLARE fdb : cms_fdb;
DECLARE status : INTEGER;
DECLARE buffer : DYNAMIC STRING;
!+
! Simple token and macro to compress a sequence of blanks and tabs
! to a single blank.
!-
TOKEN space { { ' ' | s'ht' }... };
MACRO compress TRIGGER { space };  ANSWER ' ';
END MACRO /* compress */;
!+
! Input procedure to read the lines of the CMS element.
!-
PROCEDURE read_line
( buffer_length : INTEGER,
ANSWER ' ';
END MACRO /* compress */;
!+
! Input procedure to read the lines of the CMS element.
!-
PROCEDURE read_line
( buffer_length : INTEGER,  buffer_ptr : POINTER TO FIXED STRING (132) ) OF INTEGER;
status = cms$fetch_get( fdb, buffer, *, *, * );
IF status = rms$_eof
buffer_ptr : POINTER TO FIXED STRING (132) ) OF INTEGER;
status = cms$fetch_get( fdb, buffer, *, *, * );
IF status = rms$_eof  THEN
RETURN scn$_endinpstm;
ELSE
buffer_length = LENGTH( buffer );
buffer_ptr -> = buffer;
RETURN ss$_normal;
END IF;
END PROCEDURE /* read_line */;
!+
! Main procedure that "opens" the cms element, scans the input
! stream, and "closes" the cms element.
!-
PROCEDURE main MAIN;
DECLARE element_name : DYNAMIC STRING;
READ PROMPT ( 'element name: ' ) element_name;
THEN
RETURN scn$_endinpstm;
ELSE
buffer_length = LENGTH( buffer );
buffer_ptr -> = buffer;
RETURN ss$_normal;
END IF;
END PROCEDURE /* read_line */;
!+
! Main procedure that "opens" the cms element, scans the input
! stream, and "closes" the cms element.
!-
PROCEDURE main MAIN;
DECLARE element_name : DYNAMIC STRING;
READ PROMPT ( 'element name: ' ) element_name;  status = cms$fetch_open ( fdb, 'CMS$LIB', element_name,
*, TRUE, TRUE, *, * );
status = cms$fetch_open ( fdb, 'CMS$LIB', element_name,
*, TRUE, TRUE, *, * );  START SCAN
INPUT PROCEDURE read_line
OUTPUT FILE 'sys$output';
status = cms$fetch_close( fdb, * );
END PROCEDURE /* main */;
END MODULE /* cms_example */;
START SCAN
INPUT PROCEDURE read_line
OUTPUT FILE 'sys$output';
status = cms$fetch_close( fdb, * );
END PROCEDURE /* main */;
END MODULE /* cms_example */;A fetch data block of 20 bytes (five longwords) is declared. | |
The compress macro performs the space compression. | |
Procedure read_line calls CMS$FETCH_GET to read the lines. | |
At the end of the input, the program returns SCN$_ENDINPSTM to indicate that there is no more data. | |
This line prompts the user to provide an element name. | |
Asterisks mean that these parameters are being omitted. |
A generation or range of generations must be specified with a combination of one or more of these arguments.
This is a required parameter only if you also specify a generation_expression parameter.
At least one of these arguments is required.
At least one of these arguments is required.
At least one of these arguments is required.
At least one of these arguments is required.