System Services Reference Manual: GETUTC–Z
- Operating System and Version:
- VSI OpenVMS IA-64 Version 8.4-1H1 or higher
VSI OpenVMS Alpha Version 8.4-2L1 or higher
VSI OpenVMS x86-64 Version 9.2-1 or higher
Preface
1. About VSI
VMS Software, Inc. (VSI) is an independent software company licensed by Hewlett Packard Enterprise to develop and support the OpenVMS operating system.
2. Intended Audience
This manual is intended for system and application programmers who want to call system services.
3. System Services Support for OpenVMS Alpha 64-bit Addressing
As of Version 7.0, the OpenVMS Alpha operating system provides support for 64-bit virtual memory addresses. This support makes the 64-bit virtual address space defined by the Alpha architecture available to the OpenVMS Alpha operating system and to application programs. In the 64-bit virtual address space, both process-private and system virtual address space extend beyond 2 GB. By using 64-bit address features, programmers can create images that map and access data beyond the previous limits of 32-bit virtual addresses.
New OpenVMS system services are available, and many existing services have been enhanced to manage 64-bit address space. The system services descriptions in this manual indicate the services that accept 64-bit addresses. A list of the OpenVMS system services that accept 64-bit addresses is available in the VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
The following section briefly describes how 64-bit addressing support affects OpenVMS system services. For complete information about OpenVMS Alpha 64-bit addressing features, refer to the VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
3.1. 64-Bit System Services Terminology
- 32-Bit System Service
A 32-bit system service only supports 32-bit addresses on any of its arguments that specify addresses. If passed by value on OpenVMS Alpha, a 32-bit virtual address is actually a 64-bit address that is sign-extended from 32 bits.
- 64-Bit Friendly Interface
A 64-bit friendly interface can be called with all 64-bit addresses. A 32-bit system service interface is 64-bit friendly if, without a change in the interface, it needs no modification to handle 64-bit addresses. The internal code that implements the system service might need modification, but the system service interface will not.
- 64-Bit System Service
A 64-bit system service is defined to accept all address arguments as 64-bit addresses (not necessarily 32-bit sign-extended values). A 64-bit system service also uses the entire 64 bits of all virtual addresses passed to it.
Use of the _64 Suffix
The 64-bit system services include the _64 suffix for services that accept 64-bit addresses by reference. For promoted services, this suffix distinguishes the 64-bit capable version from its 32-bit counterpart. For new services, it is a visible reminder that a 64-bit-wide address cell will be read/written.
3.2. Sign-Extension Checking
The OpenVMS system services that do not support 64-bit addresses and all user-written system services that are not explicitly enhanced to accept 64-bit addresses receive sign-extension checking. Any argument passed to these services that is not properly sign-extended causes the error status SS$_ARG_GTR_32_BITS to be returned.
4. Related Documents
The VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual contains useful information for anyone who wants to call system services.
High-level language programmers can find additional information about calling system services in the language reference manual and language user's guide provided with the OpenVMS language.
Application developers using XA-compliant or other resource managers should refer to the VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual
VSI OpenVMS Guide to OpenVMS File Applications
VSI OpenVMS Guide to System Security
DECnet-Plus for OpenVMS Introduction and User's Guide
VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual
VSI OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual
VSI OpenVMS Alpha Guide to Upgrading Privileged-Code Applications
5. VSI Encourages Your Comments
You may send comments or suggestions regarding this manual or any VSI document by sending electronic mail to the following Internet address: <docinfo@vmssoftware.com>. Users who have VSI OpenVMS support contracts through VSI can contact <support@vmssoftware.com> for help with this product.
6. OpenVMS Documentation
The full VSI OpenVMS documentation set can be found on the VMS Software Documentation webpage at https://docs.vmssoftware.com.
7. Typographical Conventions
| Convention | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Ctrl/x | A sequence such as Ctrl/x indicates that you must hold down the key labeled Ctrl while you press another key or a pointing device button. |
| PF1 x | A sequence such as PF1 x indicates that you must first press and release the key labeled PF1 and then press and release another key (x) or a pointing device button. |
... |
A horizontal ellipsis in examples indicates one of the
following possibilities:
|
. . . | A vertical ellipsis indicates the omission of items from a code example or command format; the items are omitted because they are not important to the topic being discussed. |
| ( ) | In command format descriptions, parentheses indicate that you must enclose choices in parentheses if you specify more than one. |
| [ ] | In the VSI OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual, brackets generally indicate default arguments. If an argument is optional, it is specified as such in the argument text. |
| | | In command format descriptions, vertical bars separate choices within brackets or braces. Within brackets, the choices are optional; within braces, at least one choice is required. Do not type the vertical bars on the command line. |
| { } | In command format descriptions, braces indicate required choices; you must choose at least one of the items listed. Do not type the braces on the command line. |
| bold type | Bold type represents the name of an argument, an attribute, or a reason. Bold type also represents the introduction of a new term. |
| italic type | Italic type indicates important information, complete titles of manuals, or variables. Variables include information that varies in system output (Internal error number), in command lines (/PRODUCER=name), and in command parameters in text (where dd represents the predefined code for the device type). |
| UPPERCASE TYPE | Uppercase type indicates a command, the name of a routine, the name of a file, or the abbreviation for a system privilege. |
Example |
This typeface indicates code examples, command examples, and interactive screen displays. In text, this type also identifies URLs, UNIX commands and pathnames, PC-based commands and folders, and certain elements of the C programming language. |
| – | A hyphen at the end of a command format description, command line, or code line indicates that the command or statement continues on the following line. |
| numbers | All numbers in text are assumed to be decimal unless otherwise noted. Nondecimal radixes—binary, octal, or hexadecimal—are explicitly indicated. |
System Service Descriptions
System services provide basic operating system functions, interprocess communication, and various control resources.
Condition values returned by system services indicate not only whether the service completed successfully, but can also provide other information. While the usual condition value indicating success is SS$_NORMAL, other values are also defined. For example, the condition value SS$_BUFFEROVERF, which is returned when a character string returned by a service is longer than the buffer provided to receive it, is a success code, but it also provides additional information.
Warning returns and some error returns indicate that the service might have performed some, but not all, of the requested function.
The particular condition values that each service can return are described in the Condition Values Returned section of each individual service description.
Returns
| OpenVMS usage: | cond_value |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Longword condition value. All system services (except $EXIT) return by immediate value a condition value in R0.
$GETUTC
Get UTC Time — Returns the current time in 128-bit UTC format. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$GETUTC utcadrC Prototype
int sys$getutc (unsigned int *utcadr [4]);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | coordinated universal time |
| type: | utc_date_time |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and I64) |
The 128-bit time value to be returned.
Description
The Get UTC Time service returns the current system time in 128-bit UTC format. System time is updated every 10 milliseconds.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, the frequency at which system time is updated varies, depending on the clock frequency of the Alpha or Integrity servers processor.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ASCUTC, $BINUTC, $NUMUTC, $TIMCON
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The argument was not accessible for write in the mode of the caller.
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Get Alignment Fault Data — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, obtains data from the user image alignment fault buffer if buffered user alignment fault data reporting has been enabled. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA buffer ,buffer_size ,return_sizeC Prototype
int sys$get_align_fault_data
(void *buffer, int buffer_size, int *return_size);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read/write |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The user buffer in which the alignment fault data is to be stored. The
buffer is the 32- or 64-bit address of this user
buffer.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | longword (signed) |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by value |
The size, in bytes, of the buffer specified by the buffer
argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_signed |
| type: | longword (signed) |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The amount of data, in bytes, stored in the buffer. The return_size
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a naturally aligned longword into which the
service returns the size of the buffer. The return_size
is set to 0 if there is no data in the buffer.
Description
The Get Alignment Fault Data service obtains data from the user image alignment fault buffer if buffered user alignment fault data reporting has been enabled.
When buffered user alignment fault data reporting is enabled, the operating system writes each alignment fault into a user-defined buffer. The user must poll this buffer periodically to read the data.
The user must call the $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service to enable buffered user alignment fault data reporting.
For more information about buffered user alignment fault data reporting, see the $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT system service.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT, $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The buffer named in the
bufferargument is not accessible.- SS$_AFR_NOT_ENABLED
Alignment fault reporting has not been enabled.
- SS$_BADPARAM
The buffer size is smaller than the minimum defined by the AFR$K_USER_LENGTH symbol.
$GET_ARITH_EXCEPTION (Alpha Only)
Get Arithmetic Exception Information — On Alpha systems, returns information about the exception context for a given arithmetic exception. There are two forms the signal argument vectors: one for use with 32-bit addresses and one for use with 64-bit addresses. For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS Calling Standard.
Format
SYS$GET_ARITH_EXCEPTION sigarg ,mcharg ,bufferC Prototype
int sys$get_arith_exception
(void *sigarg, void *mcharg, void *buffer);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | signal array |
| type: | vector_longword_signed |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of the signal array for the given arithmetic exception.
| OpenVMS usage: | mech array |
| type: | vector_quadword_unsigned |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of the mechanism array for the given arithmetic exception.
| OpenVMS usage: | vector_quadword |
| type: | vector_quadword_unsigned |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Four-quadword buffer to receive additional exception context. The
buffer argument is the address of a descriptor that points to
this buffer.
Description
buffer argument, the following information for a given
arithmetic exception in an array of quadwords:First quadword, the PC of the triggering instruction in the trap shadow
Second quadword, a copy of the triggering instruction
Third quadword, the exception summary
Fourth quadword, the register write mask
Required Access or Privilege
None
Required Quota
None
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The specified buffer cannot be written.
- SS$_BADBUFLEN
The specified buffer length is invalid or out of range.
$GET_DEFAULT_TRANS
Get Default Transaction — Returns the default transaction of the calling process.
Format
SYS$GET_DEFAULT_TRANS tidC Prototype
int sys$get_default_trans (unsigned int tid [4]);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | trans_id |
| type: | octaword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of an octaword in which the identifier (TID) of the default transaction of the calling process is returned.
Description
A precondition for the successful completion of $GET_DEFAULT_TRANS is that the calling process must have a default transaction.
$GET_DEFAULT_TRANS may fail for various reasons, including:
The precondition was not met.
The default transaction was being changed at the time of the call.
| Postcondition | Meaning |
|---|---|
| The identifier of the default transaction of the calling process is returned. | The identifier (TID) of the default transaction of the calling process
is returned in the tid argument. |
Required Privileges
None
Required Quotas
None
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW, $CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW, $END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW, $JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW, $START_TRANS, $START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The request was successful.
- SS$_INSFARGS
A required argument was missing.
- SS$_INSFMEM
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
- SS$_NOCURTID
The calling process did not have a default transaction.
- SS$_WRONGSTATE
The default transaction was being changed at the time of the call.
$GET_GALAXY_LOCK_INFO (Alpha Only)
Get OpenVMS Galaxy Lock Information — Returns "interesting" fields from the specified lock. Note that this system service is supported only in an OpenVMS Alpha Galaxy environment. For more information about programming with OpenVMS Galaxy system services, refer to the VSI OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
Format
SYS$GET_GALAXY_LOCK_INFO
handle ,name ,timeout ,size ,ipl ,rank ,flags [,name_length]C Prototype
int sys$get_galaxy_lock_info
(unsigned __int64 lock_handle, char *name, unsigned int *timeout,
unsigned int *size, unsigned int *ipl, unsigned int *rank,
unsigned short int *flags unsigned short int *name_length);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | handle for the galaxy lock |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | input by value |
The 64-bit lock handle that identifies the lock on which to return information. This value is returned by SYS$CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | zero-terminated string |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | output by reference |
Pointer to a buffer. This buffer must be large enough to receive the name of the lock. Locks names are zero-terminated strings with a maximum size of 16 bytes.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | output by reference |
Pointer to a longword. The value returned is the timeout value of the lock.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | output by reference |
Pointer to a longword. The value returned is the size of the lock in bytes.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | output by reference |
Pointer to a longword. The value returned is the IPL of the lock.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | output by reference |
Pointer to a longword. The value returned is the rank of the lock.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | output by reference |
Pointer to a word. The value returned is the word mask of lock flags.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | output by reference |
Length of the string returned in the name argument.
Description
This service returns all "interesting" fields from the specified lock. See the $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK service for detailed information regarding these values.
Required Access or Privileges
Read access to lock.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ACQUIRE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE, $DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK, $DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE, $GET_GALAXY_LOCK_SIZE, $RELEASE_GALAXY_LOCK
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Normal completion.
- SS$_IVLOCKID
Invalid lock id.
- SS$_IVLOCKTBL
Invalid lock table.
$GET_GALAXY_LOCK_SIZE (Alpha Only)
Get OpenVMS Galaxy Lock Size — Returns the minimum and maximum size of an OpenVMS Galaxy lock. Note that this system service is supported only in an OpenVMS Alpha Galaxy environment. For more information about programming with OpenVMS Galaxy system services, refer to the VSI OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
Format
SYS$GET_GALAXY_LOCK_SIZE min_size ,max_sizeC Prototype
int sys$get_galaxy_lock_size
(unsigned int *min_size, unsigned int *max_size);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | output by reference |
Pointer to a longword. The value returned is minimum legal size of a galaxy lock structure.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | output by reference |
Pointer to a longword. The value returned is maximum legal size of a galaxy lock structure.
Description
This service returns the minimum and maximum size of an OpenVMS Galaxy lock. If a lock is created with the maximum size, the locking services will record acquire and release information in the lock.
The lock sizes can be used to determine the value of the
section_size parameter to the $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE
service.
Required Access or Privileges
Read access to lock.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ACQUIRE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE, $DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK, $DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE, $GET_GALAXY_LOCK_INFO, $RELEASE_GALAXY_LOCK
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Normal completion.
$GET_REGION_INFO (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Get Information About a Specified Virtual Region — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, gets information about a specified virtual region. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$GET_REGION_INFO
function_code ,region_id_64 ,start_va_64 ,nullarg ,buffer_length
,buffer_address_64 ,return_length_64C Prototype
int sys$get_region_info
(unsigned int function_code, struct _generic_64 *region_id_64,
void *start_va_64, void *reserved, unsigned int buffer_length,
void *buffer_address_64, unsigned int *return_length_64);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | function code |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Function code specifying how the information you are requesting should be looked up. All
function codes return region summary information in the return buffer in the format of the Region
Summary Buffer. The Region Summary Buffer format is shown in Table 2 in the
buffer_address_64 argument.
If less buffer space is specified than the length of the Region Summary Buffer, only the amount of information requested is returned. If more buffer space is specified than the length of the Region Summary Buffer, the service will fill in the buffer. The return length will reflect the amount of useful information written to the buffer, the size of the Region Summary Buffer.
|
Symbolic Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
VA$_REGSUM_BY_ID |
Return the region summary information for the region whose ID is specified in the
|
|
VA$_REGSUM_BY_VA |
Return the region summary information for the region that contains the virtual address
specified in the |
|
VA$_NEXT_REGSUM_BY_VA |
Return the region summary information for the region containing the starting address. If the starting address is not in a region, return the region summary information for the next region with a starting address higher than the specified address. Note: For the VA$_NEXT_REGSUM_BY_VA function, OpenVMS
checks for a This function code can be used for wildcard operations. See the description of the
|
| OpenVMS usage: | region identifier |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region about which information is requested. This argument is read only if the function code VA$_REGSUM_BY_ID is specified.
|
Symbol |
Region |
|---|---|
|
VA$C_P0 |
Program region |
|
VA$C_P1 |
Control region |
|
VA$C_P2 |
64-bit program region |
Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can be specified.
| OpenVMS usage: | input address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Virtual address associated with region about which information is requested. This argument is
read only if the function_code argument is VA$_REGSUM_BY_VA or
VA$_NEXT_REGSUM_BY_VA.
If the function_code argument is VA$_REGSUM_BY_VA, this argument is a
virtual address within the region about which you are requesting information.
start_va_64 argument specified as -1. For
subsequent calls, specify start_va_64 as the sum of the previous region's
start address and length. Call the $GET_REGION_INFO service in a loop until the condition
SS$_NOMOREREG is returned.Note
Before performing the lookup function, OpenVMS sign-extends the 64-bit starting address so that it represents a properly formed virtual address for the CPU.
| OpenVMS usage: | null_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to OpenVMS.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Length of the buffer into which information is returned.
| OpenVMS usage: | varying_arg |
| type: | unspecified |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a quadword-aligned buffer into which to return
information if the buffer_length argument is non-zero.
buffer_length argument is zero.|
Field name |
Meaning |
Field Size (Bytes) |
Field Offset (Decimal) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
VA$L_FLAGS |
Flags used when region was created |
4 |
8 |
|
VA$L_REGION_PROTECT |
Create and owner mode of region |
4 |
12 |
|
VA$Q_REGION_ID |
Region identifier |
8 |
0 |
|
VA$PQ_START_VA |
Starting (lowest) virtual address of region |
8 |
16 |
|
VA$Q_REGION_SIZE |
Total length of region |
8 |
24 |
|
VA$PQ_FIRST_FREE_VA |
First free virtual address in region |
8 |
32 |
|
VA$C_REGSUM_LENGTH |
Length of Region Summary Buffer |
constant |
40 |
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned longword into which the service returns the length of the information in bytes.
Description
The Get Information About a Specified Virtual Region service is a kernel mode service
that can be called from any mode. This service gets the requested information about the specified
region or the next region in a wildcard search. If the returned value of this service is not a
successful condition value, a value cannot be returned in the memory
locations pointed to by the buffer_address_64 or
return_length_64 arguments.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CREATE_REGION_64, $DELETE_REGION_64
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
buffer_address_64argument or thereturn_length_64argument cannot be written by the caller.- SS$_BADPARAM
Unrecognized function code.
- SS$_IVREGID
Invalid region ID specified in conjunction with the VA$_REGSUM_BY_ID function code.
- SS$_NOMOREREG
No region at a higher address than specified in the
start_va_64argument, which was specified in conjunction with the wildcard function code VA$_NEXT_REGSUM_BY_VA.- SS$_PAGNOTINREG
The value specified in the
start_va_64argument is not within a region and was specified in conjunction with the function code VA$_REGSUM_BY_VA.
$GET_SECURITY
Get Security Characteristics — Retrieves the security characteristics of an object.
Format
SYS$GET_SECURITY
[clsnam] ,[objnam] ,[objhan] ,[flags] ,[itmlst] ,[contxt] ,[acmode]C Prototype
int sys$get_security
(void *clsnam, void *objnam, unsigned int *objhan, unsigned int flags,
void *itmlst, unsigned int *contxt, unsigned int *acmode);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
clsnam argument is the address of a
descriptor pointing to a string containing the name of the object class. The following
is a list of protected object class names:- CAPABILITY
- COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER
- DEVICE
- FILE
- GLXSYS_GLOBAL_SECTION
- GLXGRP_GLOBAL_SECTION
- GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION
- ICC_ASSOCIATION
- LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE
- QUEUE
- RESOURCE_DOMAIN
- SECURITY_CLASS
- SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION
- VOLUME
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Name of the protected object whose associated security profile is going to be retrieved. The
objnam argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a
string containing the name of the protected object.
|
Object Class |
Object Name Format |
|---|---|
|
CAPABILITY |
A character string. Currently, the only capability object is VECTOR. |
|
COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER |
Name of the event flag cluster, as defined in the Associate Common Event Flag Cluster ($ASCEFC) system service. |
|
DEVICE |
Standard device specification, described in the VSI OpenVMS User's Manual. |
|
FILE |
Standard file specification, described in the VSI OpenVMS User's Manual. |
|
GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION |
Section name, as defined in the Create and Map Section ($CRMPSC) system service. |
| ICC_ASSOCIATION |
ICC security object name node::association_name. The special node name, ICC$::, refers to entries in the clusterwide registry. For registry entries, the Access Access Type does not apply. |
|
LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE |
Table name, as defined in the Create Logical Name Table ($CRELNT) system service. |
|
QUEUE |
Standard queue name, as described in the Send to Job Controller ($SNDJBC) system service. |
|
RESOURCE_DOMAIN |
An identifier or octal string enclosed in brackets. |
|
SECURITY_CLASS |
Any class name shown in column 1, or a class name followed by a period (.) and the template name. Use the DCL command SHOW SECURITY to display possible template names. |
|
SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION |
Section name, as defined in the Create and Map Section ($CRMPSC) system service. |
|
VOLUME |
Volume name or name of the device on which the volume is mounted. |
| OpenVMS usage: | object_handle |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
objhan argument is an address of a
longword containing the object handle. You can use the objhan
argument as an alternative to the objnam argument; for example,
channel number clearly specifies the file open on the channel and can serve as an object
handle. The following table shows the format of the object classes.|
Object Class |
Object Handle Format |
|---|---|
|
COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER |
Event flag number |
|
DEVICE |
Channel number |
|
FILE |
Channel number |
|
RESOURCE_DOMAIN |
Resource domain identifier |
|
VOLUME |
Channel number |
| OpenVMS usage: | flags |
| type: | mask_longword |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
flags argument is a longword
bit vector wherein a bit, when set, specifies the processing option. The
flags argument requires the contxt
argument. The following table describes each flag.|
Symbolic Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
OSS$M_RELCTX |
Release the context structure at the completion of this request. |
|
OSS$M_WLOCK |
Maintain a write lock on the security profile at the completion of this request. $GET_SECURITY ignores the flag if the context has already been established. |
These symbolic names are defined in the $OSSDEF macro. You construct the
flags argument by specifying the symbolic names of each
flag.
| OpenVMS usage: | item_list_3 |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Item list specifying which information about the process or processes is to be returned. The
itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors,
each of which describes an item of information. The list of item descriptors is
terminated by a longword of 0.
With the item list, the user retrieves the protected object's characteristics. The user
defines which security characteristics to retrieve. If this argument is not present,
only the flags argument is processed. Without the
itmlst argument, you can only manipulate
the security profile lock or release contxt resources.
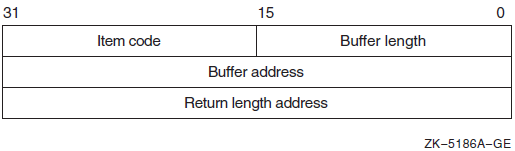
|
Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Buffer length |
A word containing an integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer in which $GET_SECURITY is to write the information. The length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too small, $GET_SECURITY truncates the data. |
|
Item code |
A word containing a symbolic code specifying the item of information that $GET_SECURITY is to return. The $OSSDEF macro defines these codes. A description of each item code is given in the Item Codes section. |
|
Buffer address |
A longword containing the address of the buffer in which $GET_SECURITY is to write the information. |
|
Return length address |
A longword containing the address of a word in which $GET_SECURITY writes the length (in bytes) of the information it actually returns. |
| OpenVMS usage: | context |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Value used to maintain the processing context when dealing with a single protected object across multiple $GET_SECURITY/$SET_SECURITY calls. Whenever the context value is nonzero, the class name, object name, or object handle arguments are disregarded. An input value of 0 indicates that a new context should be established.
Because an active context block consumes process memory, be sure to release the context block by setting the RELCTX flag when the profile processing is complete. $GET_SECURITY sets the context argument to 0 once the context is released.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Access mode to be used in the object protection check. The acmode
argument is the address of a longword containing the access mode. The
acmode argument defaults to kernel mode; however, the system
compares acmode with the caller's access mode and uses the least
privileged mode. The access modes are defined in the system macro $PSLDEF library. VSI
recommends that this argument be omitted (passed as zero).
Item Codes
The following table provides a summary of item codes that are valid in an item
descriptor in the itmlst argument. Complete descriptions of each
item code are provided after the table.
|
Item Identifier |
Description |
|---|---|
|
OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES |
Returns access bitname translation table for the class. |
|
OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES_LENGTH |
Returns the size (in bytes) of the access bitname translation table. |
|
OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY |
Locates an access control entry (ACE). |
|
OSS$_ACL_FIND_NEXT |
Positions to the next ACE. |
|
OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE |
Locates an ACE of specified type. |
|
OSS$_ACL_GRANT_ACE |
Locates an ACE that either grants or denies access. |
|
OSS$_ACL_LENGTH |
Returns the length of the access control list (ACL). |
|
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_BOTTOM |
Sets a marker that points to the end of the ACL. |
|
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_TOP |
Sets a marker that points to the beginning of the ACL. |
|
OSS$_ACL_READ |
Reads the entire ACL. |
|
OSS$_ACL_READ_ENTRY |
Reads an ACE. |
|
OSS$_CLASS_NAME |
Returns the full object class name. |
|
OSS$_FIRST_TEMPLATE |
Returns the name of the first template profile of a Security_Class object. |
|
OSS$_NEXT_OBJECT |
Returns the name of the next Security_Class object. |
|
OSS$_NEXT_TEMPLATE |
Returns the name of the next template profile of a Security_Class object. |
|
OSS$_OBJECT_NAME |
Returns the name of the object. The FILE class does not return an object name. |
|
OSS$_OWNER |
Returns the UIC or general identifier of the object's owner. |
|
OSS$_PROTECTION |
Returns the protection code of the object. |
OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES
When you specify OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES, $GET_SECURITY returns the access name translation table in the buffer pointed to by the buffer address field of the item descriptor.
The access name translation table is a 32-quadword vector followed by a variable section containing the access names. Each bit in the vector represents a single access type. The contents of the quadword is a string descriptor that corresponds to the ASCII bitname string. Undefined access types have zero-length names. The return length, if present, returns the length of the table.
OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES_LENGTH
When you specify OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES_LENGTH, $GET_SECURITY returns the length of the access name translation table.
OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY
When you specify OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY, $GET_SECURITY locates an ACE pointed to by the buffer address. OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY sets the position within the ACL for succeeding ACL operations; for example, for a deletion or modification of the ACE. If the buffer address is 0, it returns SS$_ACCVIO.
OSS$_ACL_FIND_NEXT
When you specify OSS$_ACL_FIND_NEXT, $GET_SECURITY advances the current position to the next ACE in the ACL.
OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE
When you specify OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE, $GET_SECURITY returns an ACE of a particular type if there is one in the buffer pointed to by the buffer address. OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE sets the position within the ACL for succeeding ACL operations. If the buffer address is 0, it returns SS$_ACCVIO.
OSS$_ACL_GRANT_ACE
When you specify OSS$_ACL_GRANT_ACE, $GET_SECURITY returns the ACE in the object's ACL that grants or denies the user access to that object. OSS$_ACL_GRANT_ACE returns the ACE found in the buffer pointed to by the buffer address.
OSS$_ACL_LENGTH
When you specify OSS$_ACL_LENGTH, $GET_SECURITY returns the size (in bytes) of the object's ACL. The buffer address field points to a longword that receives the size.
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_BOTTOM
When you specify OSS$_ACL_POSITION_BOTTOM, $GET_SECURITY sets the ACL position to point to the bottom of the ACL.
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_TOP
When you specify OSS$_ACL_POSITION_TOP, $GET_SECURITY sets the ACL position to point to the top of the ACL.
OSS$_ACL_READ
When you specify OSS$_ACL_READ, $GET_SECURITY returns the portion of the object's ACL to the buffer pointed to by the buffer address.
OSS$_ACL_READ_ENTRY
When you specify OSS$_ACL_READ_ENTRY, $GET_SECURITY reads the ACE pointed to by the buffer address.
OSS$_CLASS_NAME
When you specify OSS$_CLASS_NAME, $GET_SECURITY returns the full object class name.
OSS$_FIRST_TEMPLATE
When you specify OSS$_FIRST_TEMPLATE, $GET_SECURITY returns the name of the first
template profile for the object named in the objnam argument.
This item code is valid only for security class objects. If the
clsnam is not Security_Class, SS$_INVCLSITM is returned.
OSS$_NEXT_OBJECT
When you specify OSS$_NEXT_OBJECT, $GET_SECURITY returns the name of the next
object. A return length of 0 indicates the end of the list. This item code is valid
only for security class objects. If the clsnam is not
Security_Class, SS$_INVCLSITM is returned.
OSS$_NEXT_TEMPLATE
When you specify OSS$_NEXT_TEMPLATE, $GET_SECURITY returns the name of the next
template. This item code allows you to step through a list of an object's templates.
A return length of 0 indicates the end of the list. This item code is valid only for
security class objects. If the clsnam is not Security_Class,
SS$_INVCLSITM is returned.
OSS_OBJECT_NAME
When you specify OSS$_OBJECT_NAME, $GET_SECURITY returns the name of the object.
OSS$_OWNER
When you specify OSS$_OWNER, $GET_SECURITY returns the owner of the object.
OSS$_PROTECTION
When you specify OSS$_PROTECTION, $GET_SECURITY returns the protection code of the object.
Description
The Get Security service returns information about security characteristics of a selected object. Security characteristics include such information as the protection code, the owner, and the access control list (ACL). The security management services, $GET_SECURITY and $SET_SECURITY, maintain a single master copy of a profile for every security object in an OpenVMS Cluster environment. They also ensure that only one process at a time can modify an object's security profile.
Whenever the
contxtargument has a nonzero value, $GET_SECURITY uses the context to select the object and ignores the class name, object name, and object handle.With some types of objects, such as a file or a device, it is possible to select an object on the basis of its
objhanandclsnamvalues.If neither a nonzero
contxtargument nor anobjhanargument is provided, $GET_SECURITY uses an object's class name (clsnam) and object name (objnam) to select the object.
When you call $GET_SECURITY, the service selects the specified protected object and fetches a local copy of the object's security profile.
The context for a security management operation can be established through either $GET_SECURITY or $SET_SECURITY. Whenever the context is set by one service, the other service can use it, provided the necessary locks are being held. If you intend to modify the profile, you must set the write lock flag (OSS$M_WLOCK) when you establish the context.
There are many situations in which the contxt argument is essential. By
establishing a context for an ACL operation, for example, a caller can retain an ACL
position across calls to $GET_SECURITY so that a set of ACEs can be read and modified
sequentially. A security context is released by a call to $SET_SECURITY or $GET_SECURITY
that sets the OSS$M_RELCTX flag. Once the context is released, the user-supplied context
longword is set to 0.
Required Access or Privileges
Read or control access to the object is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The parameter cannot be read and the buffer cannot be written.
- SS$_BADPARAM
You specified an invalid object, attribute code, or item size.
- SS$_INSFARG
The
clsnamandobjnamarguments are not specified, theclsnamandobjhanarguments are not specified, or thecontxtargument is not specified.- SS$_INVCLSITM
The item code that you specified is not supported for the class.
- SS$_NOCLASS
The named security class does not exist.
- SS$_OBJLOCKED
The selected object is currently write locked.
$GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Get System Alignment Fault Data — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, obtains data from the system alignment fault buffer if buffered system alignment fault data reporting has been enabled. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA buffer ,buffer_size ,return_sizeC Prototype
int sys$get_sys_align_fault_data
(void *buffer, int buffer_size, int *return_size);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read/write |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The user buffer in which the alignment fault data is to be stored. The
buffer argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of this
buffer.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | longword (signed) |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by value |
The size, in bytes, of the buffer specified by the buffer
argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_signed |
| type: | longword (signed) |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The amount of data, in bytes, stored in the buffer. The return_size
argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned longword into which
the service returns the amount of data, in bytes, stored in the buffer. The
return_size argument is set to 0 if there is no data in the
buffer.
Description
The Get System Alignment Fault Data service obtains data from the system alignment fault buffer if buffered system alignment fault data reporting has been enabled.
When buffered system alignment fault data reporting is enabled, the operating system writes each alignment fault into a system-allocated buffer. The user must poll this buffer periodically to read the data.
The user must call the $INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service to enable buffered system alignment fault data reporting. For more information, see the $INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service.
Required Access or Privileges
CMKRNL privilege is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT, $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The buffer named in the
bufferargument is not accessible.- SS$_AFR_NOT_ENABLED
Alignment fault reporting has not been enabled.
- SS$_BADPARAM
The buffer size is smaller than the minimum defined by the AFR$K_VMS_LENGTH or the AFR$K_EXTENDED_LENGTH symbol.
$GET_UNWIND_ENTRY_INFO (Integrity servers Only)
Get Unwind Entry Info Routine — Gets fixed-up unwind entry information.
Format
SYS$GET_UNWIND_ENTRY_INFO pc, get_ue_block, nameC Prototype
int SYS$GET_UNWIND_ENTRY_INFO
(unsigned __int64 pc, void *get_ue_block, void *name);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | PC value |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Input quadword, target PC (that is, the PC for a code region the user wants unwind information for).
| OpenVMS usage: | unwind_entry_data_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a 4-quadword block to be filled in. That is, input the address of a 4 quadword block and, on successful returned status, that block will be updated with the following information:
code_start_va - Output quadword, the process virtual starting c unwind region containing the input IP.
code_end_va - Output quadword, the process virtual ending code address of the unwind region containing the input IP.
uib_start_va - Output quadword, the process virtual address of the UIB for the unwind region containing the input IP.
gp_value - Output quadword, the GP value for this code region.
| OpenVMS usage: | pseudo-image-name |
| type: | character-code-text-string |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by descriptor-fixed-length string descriptor |
Optional, that is, may be zero. If the name parameter is specified and if a name was registered for the unwind region, then the descriptor pointer and length are updated to point to that stored name. Note that if the name parameter is specified but no name exists in the unwind tables, then the name descriptor is updated to zero length.
Description
Get fixed up unwind entry information relevant to the input instruction pointer (IP).
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
SYS$SET_UNWIND_TABLE, SYS$CLEAR_UNWIND_TABLE. Also see LIB$GET_UIB_INFO in VSI OpenVMS Calling Standard.
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Routine completed successfully.
- SS$_IVADDR
Invalid PC.
- SS$_NODATA
No unwind information found.
$GET_USER_CAPABILITY (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Reserve a User Capability — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, reserves a user capability, indicating to other processes that the resource is in use. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$GET_USER_CAPABILITY
cap_num [,select_num] [,select_mask] [,prev_mask] [,flags]C Prototype
int sys$get_user_capability
(*cap_num, int *select_num, struct _generic_64 *select_mask,
struct _generic_64 *prev_mask, struct _generic_64 *flags);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Capability number to be reserved by the calling kernel thread. This number can range
from 1 to 16 for an explicit request, or the symbolic constant CAP$K_GET_FREE_CAP can be
specified to get the next available user capability. The cap_num
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of the longword containing the user capability
number or symbolic constant.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The number of the user capability selected by the service call. The
select_num argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a longword
into which the system writes the user capability number. For an explicit numeric
request, the value returned in this longword will match that specified in
cap_num; otherwise, this cell contains the next available user
capability.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_quadword |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
A quadword bit mask with a single bit position set, reflecting the user capability
selected by the service. The select_mask argument is the 32- or
64-bit address of a quadword into which the system writes the selected user capability
bit mask. This bit mask is the most efficient method for indicating the reserved user
capability with the $CPU_CAPABILITIES and $PROCESS_CAPABILITIES services.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_quadword |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The previous user capability reservation mask before execution of this service call.
The prev_mask argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword
into which the service writes a quadword bit mask specifying the previously reserved
user capabilities taken from the global cell SCH$GQ_RESERVED_USER_CAPS.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_quadword |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Options selected for the user capability reservation. The
flags argument is a quadword bit vector wherein a bit
corresponds to an option.
Each option (bit) has a symbolic name, which the $CAPDEF macro defines. The
flags argument is constructed by performing a logical OR
operation using the symbolic names of each desired option.
At this time, all bits are reserved to OpenVMS and must be 0.
Description
The Reserve a User Capability service provides a way for discrete processes to communicate and synchronize their use of a user capability in the system. This service uses the global cell SCH$GQ_RESERVED_USER_CAPS to indicate that a particular user capability has been reserved. $GET_USER_CAPABILITY can also return the current reservation state of all user capabilities in the system.
Reservation of a user capability can be made for an explicit number or for the next
available number. The selected user capability is returned to the caller through a numeric
value in select_num or by a quadword bit mask in
select_mask.
This service does not directly enforce unique use of the individual user capabilities; it simply provides a common informational and control resource for processes using the other capability scheduling services. Code threads that do not use this service to verify whether a user capability is available are still at risk if differing usages conflict.
Required Privileges
The caller must have both ALTPRI and WORLD privileges to call $GET_USER_CAPABILITY to reserve a user capability. No privileges are required if $GET_USER_CAPABILITY is called only to retrieve the current user capability reservation mask.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$FREE_USER_CAPABILITY, $CPU_CAPABILITIES, $PROCESS_CAPABILITIES
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more arguments.
- SS$_INSFARG
Fewer than the required number of arguments were specified, or no operation was specified.
- SS$_NOPRIV
Insufficient privilege for the attempted operation.
- SS$_NOSUCH_OBJECT
No more user capabilities are available.
- SS$_OBJECT_EXISTS
A specifically requested user capability has already been reserved.
- SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
Too many arguments were presented to the system service.
$GOTO_UNWIND (Alpha Only)
Unwind Call Stack — On Alpha systems, unwinds the call stack. On Integrity server systems, do not use this service; use $GOTO_UNWIND_64 instead.
Format
SYS$GOTO_UNWIND target_invo ,target_pc ,[new_r0] ,[new_r1]C Prototype
int sys$goto_unwind
(void *target_invo, void *(*(target_pc)), unsigned __int64 *new_r0,
unsigned __int64 *new_r1);
Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | invo_handle |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The address of a location that contains a handle for the target invocation.
If you do not specify the target_invo argument, or if the handle value
is 0, an exit unwind is initiated.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The address of a location that contains the address at which execution should continue in the target invocation.
If the target_pc argument is omitted or the value is 0, a
system-defined target PC is assumed and execution resumes at the location specified at
the return address for the call frame of the target procedure invocation.
| OpenVMS usage: | quadword_unsigned |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The address of a location that contains the value to place in the saved R0 location of the mechanism argument vector. The contents of this location are then loaded into the processor R0 register at the time that execution continues in the target invocation.
If the new_r0 argument is omitted, the contents of the processor R0
register at the time of the call to $GOTO_UNWIND are used.
| OpenVMS usage: | quadword_unsigned |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a location that contains the value to place in the saved R1 location of the mechanism argument vector. The contents of the location are then loaded into the processor R1 register at the time that execution continues in the target invocation.
If the new_r1 argument is omitted, the contents of the processor R1
register at the time of the call to $GOTO_UNWIND are used.
Description
The Unwind Call Stack service provides the function for a procedure to unwind the call stack.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$UNWIND
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The specified
target_invo,target_pc,new_r0, ornew_r1argument is not accessible.
$GOTO_UNWIND_64 (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Unwind Call Stack — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, unwinds the call stack.
Format
SYS$GOTO_UNWIND target_invo ,target_pc ,[NewRetVal] , [NewRetVal2]C Prototype
int sys$goto_unwind_64
(void *target_invo_64, void *(*(target_pc_64)),
unsigned_int64 *new_retval, unsigned_int64 *newretval2);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | invo_handle |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The address of a location that contains a handle for the target invocation.
If you do not specify the target_invo argument, or if the
handle value is 0, the effect of the call is undefined.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The address of a location that contains the address at which execution should continue in the target invocation.
If the target_pc argument is omitted or the value is 0,
execution resumes at the location specified at the return address for the call frame of
the target procedure invocation.
If the target_invo argument is omitted or the value is 0, the
target_pc argument is ignored. In this case, a system-defined
target PC is assumed.
| OpenVMS usage: | quadword_unsigned |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The address of a location that contains the value to place in the saved RetVal location of the mechanism argument vector. The contents of this location are then loaded into RetVal at the time that execution continues in the target invocation.
If the NewRetVal argument is omitted, the contents of RetVal
at the time of the call to $GOTO_UNWIND_64 are used.
This argument is called New_R0 in SYS$GOTO_UNWIND for
compatibility with Alpha.
| OpenVMS usage: | quadword_unsigned |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The address of a location that contains the value to place in the saved RetVal2 location of the mechanism argument vector. The contents of the location are then loaded into RetVal2 at the time that execution continues in the target invocation.
If the NewRet2 argument is omitted, the contents of RetVal2 at
the time of the call to $GOTO_UNWIND_64 are used.
This argument is called New_R1 in SYS$GOTO_UNWIND for
compatibility with Alpha.
Description
The Unwind Call Stack service provides the function for a procedure to unwind the call stack.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$UNWIND
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_ACCVIO
An invalid address was given.
$GRANTID
Grant Identifier to Process — Adds the specified identifier record to the rights list of the process or the system.
Format
SYS$GRANTID [pidadr] ,[prcnam] ,[id] ,[name] ,[prvatr]C Prototype
int sys$grantid
(unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, struct _generic_64 *id, void *name,
unsigned int *prvatr, unsigned int segment);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Process identification (PID) number of the process affected when $GRANTID completes execution.
The pidadr argument is the address of a longword containing the
PID of the process to be affected. You use –1 to indicate the system rights list.
When pidadr is passed, it is also returned; therefore, you must
pass it as a variable rather than a constant. If you specify neither
pidadr nor prcnam, your own process is
used.
| OpenVMS usage: | process_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Process name on which $GRANTID operates. The prcnam argument is the
address of a character string descriptor containing the process name. The maximum length
of the name is 15 characters. Because the UIC group number is interpreted as part of the
process name, you must use pidadr to specify the rights list of a
process in a different group. If you specify neither pidadr nor
prcnam, your own process is used.
| OpenVMS usage: | rights_holder |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Identifier and attributes to be granted when $GRANTID completes execution. The
id argument is the address of a quadword containing the
binary identifier code to be granted in the first longword and the attributes in the
second longword.
Use the
id argument to modify the attributes of the identifier.
|
Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC |
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the process rights database using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST. |
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS |
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem attribute. |
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE |
Allows holders of an identifier to charge disk space to the identifier. It is used only for file objects. |
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM |
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in the subsystem. |
You must specify either id or name. Because the
id argument is returned as well as passed if you specify
name, you must pass it as a variable rather than a constant
in this case.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the identifier granted when $GRANTID completes execution. The
name argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to the name of the identifier. The identifier is granted as it is created. You must specify either
id or
name.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Previous attributes of the identifier. The prvatr argument is the
address of a longword used to store the attributes of the identifier if it was
previously present in the rights list. If you added rather than modified the identifier,
prvatr is ignored.
Description
The Grant Identifier to Process service adds the specified identifier to the rights list of the process or the system. If the identifier is already in the rights list, its attributes are modified to those specified. This service is meant to be used by a privileged subsystem to alter the access rights profile of a user, based on installation policy. It is not meant to be used by the general system user.
pidadr or the prcnam
argument, or both, to SYS$GRANTID is summarized in the following table. |
prcnam |
pidadr |
Result |
|---|---|---|
|
Omitted |
Omitted |
Current process ID is used; process ID is not returned. |
|
Omitted |
0 |
Current process ID is used; process ID is returned. |
|
Omitted |
Specified |
Specified process ID is used. |
|
Specified |
Omitted |
Specified process name is used; process ID is not returned. |
|
Specified |
0 |
Specified process name is used; process ID is returned. |
|
Specified |
Specified |
Specified process ID is used and process name is ignored. |
name or the id
argument, or both, to SYS$GRANTID is summarized in the following table.|
name |
id |
Result |
|---|---|---|
|
Omitted |
Omitted |
Illegal. The INSFARG condition value is returned. |
|
Omitted |
Specified |
Specified identifier value is used. |
|
Specified |
Omitted |
Specified identifier name is used; identifier value is not returned. |
|
Specified |
0 |
Specified identifier name is used; identifier value is returned. |
|
Specified |
Specified |
Specified identifier value is used and identifier name is ignored. |
Note that a value of 0 in either of the preceding tables indicates that the contents of the address specified by the argument is the value 0. The word omitted indicates that the argument was not supplied.
Required Access or Privileges
You need CMKRNL privilege to invoke this service. In addition, you need GROUP privilege to modify the rights list of a process in the same group as the calling process (unless the process has the same UIC as the calling process). You need WORLD privilege to modify the rights list of a process outside the caller's group. You need SYSNAM privilege to modify the system rights list.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CHECK_ACCESS, $CHKPRO, $CREATE_RDB, $ERAPAT, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $FORMAT_ACL, $FORMAT_AUDIT, $GET_SECURITY, $HASH_PASSWORD, $IDTOASC, $MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT, $MTACCESS, $PARSE_ACL, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID, $SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully; the rights list did not contain the specified identifier.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully; the rights list already held the specified identifier.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
pidadrargument cannot be read or written;prcnamcannot be read;idcannot be read or written; thenamecannot be read; orprvatrcannot be written.- SS$_INSFARG
You did not specify either the
idor thenameargument.- SS$_INSFMEM
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights database.
- SS$_IVIDENT
The specified identifier name is invalid; the identifier name is longer than 31 characters, contains an illegal character, or does not contain at least one nonnumeric character.
- SS$_IVLOGNAM
You specified an invalid process name.
- SS$_NONEXPR
You specified a nonexistent process.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The caller does not have CMKRNL privilege or is not running in executive or kernel mode, or the caller lacks GROUP, WORLD, or SYSNAM privilege as required.
- SS$_NOSUCHID
The specified identifier name does not exist in the rights database. Note that the binary identifier, if given, is not validated against the rights database.
- SS$_NOSYSNAM
The operation requires SYSNAM privilege.
- SS$_RIGHTSFULL
The rights list of the process or system is full.
- RMS$_PRV
The user does not have read access to the rights database.
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes, refer to the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$HASH_PASSWORD
Hash Password — Applies the hash algorithm you select to an ASCII password string and returns a quadword hash value that represents the encrypted password.
Format
SYS$HASH_PASSWORD pwd ,alg ,[salt] ,usrnam ,hashC Prototype
int sys$hash_password
(void *pwd, unsigned char alg, unsigned short int salt, void *usrnam,
struct _generic_64 *hash);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor – fixed-length string descriptor |
ASCII password string to be encrypted. The pwd argument is the
address of a character string descriptor pointing to the ASCII password. The password
string can contain between 1 and 32 characters and use the uppercase characters A
through Z, the numbers 0 through 9, the dollar sign ($), and the underscore
(_).
The caller must validate the password string before calling $HASH_PASSWORD to ensure that only permitted characters are included.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte_unsigned |
| type: | byte (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Algorithm used to hash the ASCII password string. The alg
argument is an unsigned byte specifying the hash algorithm.
|
Symbolic Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
UAI$K_AD_II |
Uses a CRC algorithm and returns a longword hash value. This algorithm was used in releases prior to VAX/VMS Version 2.0. |
|
UAI$C_PURDY |
Uses a Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a blank-padded user name and returns a quadword hash value. This algorithm was used during VAX/VMS Version 2.0 field test. |
|
UAI$C_PURDY_V |
Uses the Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a variable-length user name and returns a quadword hash value. This algorithm was used in releases prior to VMS Version 5.4. |
|
UAI$K_PURDY_S |
Uses the Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a variable-length user name and returns a quadword hash value. This algorithm is used to hash all new passwords in VMS Version 5.4 and later. |
|
UAI$C_PREFERED_ALGORITHM? |
Represents the latest encryption algorithm that the operating system uses to encrypt new passwords. Currently, it equates to UAI$C_PURDY_S. VSI recommends that you use this symbol in source modules because it always equates with the most recent algorithm. |
Values ranging from 128 to 255 are reserved for customer use; the constant UAI$K_CUST_ALGORITHM defines the start of this range.
You can use the UAI$_ENCRYPT and UAI$_ENCRYPT2 item codes with the $GETUAI system service to retrieve the primary and secondary password hash algorithms for a user.
| OpenVMS usage: | word_unsigned |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Value used to increase the effectiveness of the hash. The salt
argument is an unsigned word containing 16 bits of data that is used by the hash
algorithms when encrypting a password for the associated user name. The $GETUAI item
code UAI$_SALT is used to retrieve the SALT value for a given user. If you do not
specify a SALT value, $HASH_PASSWORD uses the value of 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor – fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the user associated with the password. The usrnam
argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a character text string containing
the user name. The current password encryption algorithm (UAI$C_PURDY_S) folds the user
name into the ASCII password string to ensure that different users with the same
password produce different hash values. This argument must be supplied for all calls to
$HASH_PASSWORD but is ignored when using the CRC algorithm (UAI$C_AD_II).
| OpenVMS usage: | quadword_unsigned |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Output hash value representing the encrypted password. The hash
argument is the address of an unsigned quadword to which $HASH_PASSWORD writes the
output of the hash. If you use the UAI$C_AD_II algorithm, the second longword of the
hash is always set to 0.
Description
The Hash Password service applies the hash algorithm you select to an ASCII password string and returns a quadword hash value that represents the encrypted password.
Other OpenVMS password services allow spaces, tabs, and other blank characters from the user, but they remove those spaces before passing the string to $HASH_PASSWORD. Before calling $HASH_PASSWORD, all white space must be removed from the password string to ensure proper comparison with passwords created by other services.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GETUAI, $SETUAI.
Use $GETUAI to get the values for the salt and
alg arguments. Use $SETUAI to store the resulting hash using
the item codes UAI$_PWD and UAI$_PWD2.
For more information, see the appendix on implementing site-specific security policies in the VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The input or output buffer descriptors cannot be read or written to by the caller.
- SS$_BADPARAM
The specified hash algorithm is unknown or invalid.
$HIBER
Hibernate — Allows a process to make itself inactive but to remain known to the system so that it can be interrupted; for example, to receive ASTs.
Format
SYS$HIBERC Prototype
int sys$hiber (void);Arguments
None.
Description
The Hibernate service allows a process to make itself inactive but to remain known to the system so that it can be interrupted; for example, to receive ASTs. A hibernate request is a wait-for-wake-event request. When you call the Wake Process from Hibernation ($WAKE) service or when the time specified with the Schedule Wakeup ($SCHDWK) service occurs, the process continues execution at the instruction following the Hibernate call.
In VAX MACRO, you can call the Hibernate service only by using the $name_S macro.
A hibernating process can be swapped out of the balance set if it is not locked into the balance set.
An AST can interrupt the wait state caused by $HIBER if the access mode at which the AST is to execute is equal to or more privileged than the access mode from which the hibernate request was issued and the process is enabled for ASTs at that access mode.
When the AST service routine completes execution, the system reexecutes the $HIBER service on behalf of the process. If a wakeup request has been issued for the process during the execution of the AST service routine (either by itself or another process), the process resumes execution. If a wakeup request has not been issued, it continues to hibernate.
If one or more wakeup requests are issued for the process while it is not hibernating, the next hibernate call returns immediately; that is, the process does not hibernate. No count of outstanding wakeup requests is maintained.
ISTAT=SYS$HIBER()Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND, $WAKE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
$ICC_ACCEPT
Accept for Intra-Cluster Communications (ICC) — Responds to an incoming connection request. This call is used to complete an ICC connection from the server side. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_ACCEPT
conn_handle ,[accept_buf] ,[accept_len] ,[user_context] ,[flags]C Prototype
int sys$icc_accept
(unsigned int conn_handle, char * accept_buf, unsigned int accept_len,
unsigned int user_context, unsigned int flags);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | connection_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The handle of the requested connection.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte_stream |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
A buffer of up to 1000 bytes of accept data that is sent to the source of the connection at the completion of the connection process.
| OpenVMS usage: | buffer_length |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The actual number of bytes in accept_buf to be sent.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | quadword (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
A user-specified value that is subsequently returned on any disconnect or data events on this connection.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
ICC$M_SYNCH_MODE can be specified to indicate that the data transmission and reception routines $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_RECEIVE, and $ICC_REPLY are allowed to return the status SS$_SYNCH in the case of synchronous completion, and that the AST will not be called.
Description
This service is used by a server to respond to an incoming connection request. The $ICC_ACCEPT service may only be called after receiving a connection request AST.
At the completion of the service, the connection is open and data can be exchanged. Once opened, there is no logical distinction between a connection opened by a client with the Connect service or a server with the Accept service.
A server can reject a Connection request by calling the $ICC_REJECT service.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
$ICC_ACCEPT changes the process BYTLM quota for the length of the
accept_buf parameter, as well as a fixed value for each potential
Receive buffer on the connection. The number of potential Receive buffers is specified by
the MAXFLOWBUFCNT parameter in the $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC service.
Related Services
$ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW, $ICC_DISCONNECT, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW, $ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE, $ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Normal completion.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Access violation on parameter.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Bad parameter value specified.
- SS$_CLEARED
Remote association closed the link before it was accepted.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
Exceeded BYTCNT/BYTLM.
- SS$_INSFARG
Too few arguments supplied.
- SS$_INSFMEM
Not enough system resources or process virtual memory available.
- SS$_IVMODE
Attempted to accept a connection from a more privileged access mode than the requested association.
- SS$_IVCHAN
Connection not found or Invalid connection handle.
- SS$_LINKDISCON
The connection is valid, but the physical link has started to disconnect.
- SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
Too many arguments specified.
- SS$_WRONGSTATE
Connection is in the wrong state for the request.
$ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC
Close Association for Intra-Cluster Communications (ICC) — Closes the application's association with ICC.
Format
SYS$ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC assoc_handleC Prototype
int sys$icc_close_assoc (unsigned int assoc_handle);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | association_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The handle of the association to be closed.
Description
This service closes the application's association with ICC. If multiple associations are open, only the specified association is closed. When an association is closed, any active connections on that association are disconnected. If not explicitly closed by the application, associations opened in user mode will be closed at image exit; associations opened in inner modes will be closed at process termination.
All operations on an association must occur in the access mode at which the association was opened.
When an association is closed, the entry (if any) in the simple clusterwide association registry is removed.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW, $ICC_DISCONNECT, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW, $ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE, $ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Normal completion.
- SS$_INSFARG
The
assoc_handlewas not supplied.- SS$_IVCHAN
Invalid association handle.
- SS$_IVMODE
Attempted to close an association from a more privileged access mode than the requested association.
- SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
Too many arguments specified.
$ICC_CONNECT
Connect for Intra-Cluster Communications (ICC) — Establishes a connection to a remote application over an open association. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_CONNECT
ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,assoc_handle ,conn_handle ,remote_assoc
,[remote_node] ,[user_context] ,[conn_buf] ,[conn_buf_len] ,[return_buf]
,[return_buf_len] ,[retlen_addr] ,[flags]C Prototype
int sys$icc_connect
(struct _ios_icc *ios_icc, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params),
__int64 astprm, unsigned int assoc_handle, unsigned int *conn_handle,
void *remote_assoc, void *remote_node, unsigned int user_context,
char *conn_buf, unsigned int conn_buf_len, char *return_buf,
unsigned int return_buf_len, unsigned int *retlen_addr,
unsigned int flags);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |

Completion status values:
SS$_NORMAL, SS$_BUFFEROVF, SS$_EXQUOTA, SS$_INSFMEM, SS$_IVBUFLEN, SS$_LINKABORT, SS$_LINKDISCON, SS$_NOLOGNAM, SS$_NOSUCHOBJ, SS$_NOSUCHNODE, SS$_PATHLOST, SS$_REJECT, SS$_SSFAIL, SS$_UNREACHABLE, SS$_WRONGSTATE
The second longword is undefined unless the completion code is SS$_REJECT. In this case, the application-defined rejection reason code is supplied by the server when $ICC_REJECT is called.
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure_entry_mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The AST routine to be executed when the operation completes.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 64-bit value (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
| OpenVMS usage: | association_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The handle of the association on which the connection is to be opened. The constant ICC$C_DFLT_ASSOC_HANDLE, if used, indicates that the default association is to be used (and opened if necessary).
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of a longword into which $ICC_CONNECT writes the connection handle of the created connection on a successful call.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
An ASCII character string (31 characters maximum) specifying the name of the target application to connect to. Association names are case sensitive.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The name of the node where the target association resides. A null or blank string can be used to indicate the local node. If omitted (by passing zero by value), the simple clusterwide association registry is to be used. Each node name is a one-to-six character SCS node name. A comma-delimited list of nodes may be specified, indicating that one is to be chosen at random.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | quadword (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
A user-specified value to be subsequently returned on any disconnect or data events on this connection.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte_stream |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
A buffer of up to 1000 bytes of connection data to be sent to the target of the connection during the connection process.
| OpenVMS usage: | buffer_length |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The number of bytes in conn_buf to be sent.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte_stream |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
A buffer of up to 1000 bytes in length to receive any incoming connection accept or reject data returned.
| OpenVMS usage: | buffer_length |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The length of the supplied return_buf.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of a longword
into which $ICC_CONNECT writes the actual length (in bytes) of any user accept or reject
data returned in the buffer return_buf.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
ICC$M_SYNCH_MODE can be specified to indicate that the data transmission and reception routines $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_RECEIVE, and $ICC_REPLY are allowed to return the status SS$_SYNCH in the case of synchronous completion, indicating that the AST will not be called.
Description
This service establishes a connection to a remote application over an open association. Connections must be opened in the same mode as their association. If the user provides the default association constant ICC$C_DFLT_ASSOC_HANDLE as its association handle, the default association will be used; it will be opened if it is not already open. Multiple connections are possible over a single association. When completion is signaled by the AST routine, the application must check the completion status field of the IOS_ICC to determine if the server has accepted or rejected the connection request. The number of connections is subject to process BYTLM quota.
At image exit, as a result of closing any open user mode associations, all user mode connections are disconnected. Inner mode connections are the responsibility of the inner mode code, but are disconnected at process termination when inner mode associations are closed. Connections are only visible to the mode in which they were opened.
A client opens connections with the $ICC_CONNECT service; a server opens connections with the $ICC_ACCEPT service.
Required Access or Privileges
SYSNAM, or access via ICC Security Object. For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
Required Quota
$ICC_CONNECT changes the process BYTLM quota for the length of the
conn_buf parameter, as well as a fixed value for each potential
Receive buffer on the connection. The number of potential Receive buffers is specified by
the MAXFLOWBUFCNT parameter in the $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC service.
If $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC is not called before $ICC_CONNECT, the default value of MAXFLOWBUFCNT is used (currently 5).
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECTW, $ICC_DISCONNECT, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW, $ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE, $ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Normal completion.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Access violation on parameter.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Bad parameter value specified.
- SS$_BUFFEROVF
Overflow on inbound accept or reject data.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
Not enough AST quota (asynchronous request) or insufficient BYTLM/BYTCNT.
- SS$_INSFARG
Too few arguments were supplied, or required arguments not supplied.
- SS$_INSFMEM
Not enough system resources or process virtual memory available.
- SS$_INSFP1POOL
Not enough process P1 space available.
- SS$_IVBUFLEN
The length of the context data or the accept or reject data buffer is more than 1000 bytes.
- SS$_IVCHAN
Invalid association handle.
- SS$_IVMODE
Attempted to open a connection from a more privileged access mode than the requested association.
- SS$_LINKABORT
The communications link to the target node was lost.
- SS$_LINKDISCON
The communications link to the target node was lost.
- SS$_NOLINKS
Too many connections open.
- SS$_NOLOGNAM
The underlying layers failed to start properly during system initialization.
- SS$_NOPRIV
No privilege to connect to the specified association. Connection access is granted either through an ICC security object or through the SYSNAM privilege. If no security object exists and the caller lacks the SYSNAM privilege, SS$_NOPRIV is returned rather than SS$_NOSUCHOBJ.
- SS$_NOSUCHOBJ
The remote association name and/or node was not found.
- SS$_NOSUCHNODE
The target node is not known.
- SS$_PATHLOST
The communications link to the target node was lost.
- SS$_REMRSRC
Insufficient resources at remote node.
- SS$_REJECT
The remote association or node rejected the connection request.
- SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
Too many arguments specified.
- SS$_UNREACHABLE
Target node currently unreachable.
- SS$_WRONGSTATE
Connection is in the wrong state for the request.
$ICC_CONNECTW
Connect for Intra-Cluster Communications and Wait — Establishes a link between two ICC associations. The $ICC_CONNECTW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller after the server has either accepted or rejected the connection request. For asynchronous completion, use the $ICC_CONNECT service; $ICC_CONNECT returns to the caller as soon as the connection request has been sent to the server, without waiting for a response from the server. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_CONNECTW
ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,assoc_handle ,conn_handle ,remote_assoc
,[remote_node] ,[user_context] ,[conn_buf] ,[conn_buf_len] ,[return_buf]
,[return_buf_len] ,[retlen_addr] ,[flags]C Prototype
int sys$icc_connectw
(struct _ios_icc *ios_icc, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params),
__int64 astprm, unsigned int assoc_handle, unsigned int *conn_handle,
void *remote_assoc, void *remote_node, unsigned int user_context,
char *conn_buf, unsigned int conn_buf_len, char *return_buf,
unsigned int return_buf_len, unsigned int *retlen_addr,
unsigned int flags);$ICC_DISCONNECT
Disconnect for Intra-Cluster Communications (ICC) — Terminates the specified connection. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_DISCONNECT
conn_handle ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[disc_buf] ,[disc_buf_len]C Prototype
int sys$icc_disconnect
(unsigned int conn_handle, struct _iosb, *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char * disc_buf,
unsigned int disc_buf_len);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | connection_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The ID of the connection to be disconnected.
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Completion status values:
SS$_NORMAL, SS$_EXQUOTA, SS$_LINKDISCON, $ICC_REJECT
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure_entry_mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The AST routine to be executed when the operation completes.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 64-bit value (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte_stream |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
A buffer of up to 1000 bytes of disconnect data to be sent to the partner in the connection when notifying it that disconnection is being initiated. Delivery of this data is not guaranteed.
| OpenVMS usage: | buffer_length |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The number of bytes in disc_buf to be sent.
Description
This service must be called in the mode in which the association was opened.
This service terminates the specified connection. After this service is called, no further communication is possible over this connection. All outstanding data transmission and reception functions are terminated with an error before completion is signaled by calling the AST (if supplied).
A connection may be disconnected by either party. Proper programming procedure for network communications strongly recommends that the party that last received a message initiate the disconnection. If the party that last sent a message initiates the disconnection, there is no guarantee that the message was delivered.
Similarly, although this interface provides the ability to send disconnect data, only noncritical information should be transmitted with the disconnect data mechanism, because there is no guarantee that the data will have been received or acted upon by the other party to the connection.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
BYTLM (disc_buf)
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW, $ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE, $ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Normal completion.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Access violation on parameter.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Bad parameter value specified.
- SS$_INSFMEM
Not enough nonpaged pool.
- SS$_IVBUFLEN
The length of the disconnect data buffer is more than 1000 bytes.
- SS$_IVCHAN
Unknown connection specified or invalid connection handle.
- SS$_IVMODE
Attempted to disconnect a connection from a more privileged access mode than the requested connection.
- SS$_LINKDISCON
The remote association closed the connection before it was accepted or rejected.
- SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
Too many arguments specified.
$ICC_DISCONNECTW
Disconnect and Wait for Intra-Cluster Communications (ICC) — Terminates a link between two ICC associations. The $ICC_DISCONNECTW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller after the connection has completely finished the disconnection request. For asynchronous completion, use the $ICC_DISCONNECT service; $ICC_DISCONNECT returns to the caller as soon as the disconnection request has been sent to the transport layer, without waiting for notification that the disconnection has completed. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_DISCONNECTW
conn_handle ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[disc_buf] ,[disc_buf_len]C Prototype
int sys$icc_disconnectw
(unsigned int conn_handle, struct _iosb, *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char * disc_buf,
unsigned int disc_buf_len);$ICC_OPEN_ASSOC
Open Association for Intra-Cluster Communications (ICC) — Declares an application association with ICC. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_OPEN_ASSOC
assoc_handle ,[assoc_name] ,[logical_name] ,[logical_table]
,[conn_event_rtn] ,[disc_event_rtn] ,[recv_rtn] ,[maxflowbufcnt]
,[prot]C Prototype
int sys$icc_open_assoc
(unsigned int *assoc_handle, void *assoc_name, void *logical_name,
void *logical_table, void (*conn_event_rtn)(__unknown_params),
void (*disc_event_rtn)(__unknown_params),
void (*recv_rtn)(__unknown_params), unsigned int maxflowbufcnt,
unsigned int prot);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | association_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) into which $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC writes the handle assigned to the opened association.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
An ASCII character string of up to 31 characters in length specifying the name of the application opening the association. Null (0 length), and empty or blank association names are not allowed. If this argument is omitted (that is, a zero is passed in by value), it signifies that the user wants to open the default association. This argument is case sensitive.
| OpenVMS usage: | logical name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
A logical name in a clusterwide logical name table used to maintain the simple association registry. The logical name represents the name of the service provided by the application. Logical names are case sensitive.
| OpenVMS usage: | logical name table |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The table containing the logical name logical_name. Logical name
tables are converted to uppercase. Unless your application requires an application-specific
logical name table, this argument should be either the default ICC Registry search list
(ICC$REGISTRY), or the default registry table (ICC$REGISTRY_TABLE).
| OpenVMS usage: | user_routine |
| type: | procedure_entry_mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The address of the AST routine to be called for incoming connect events. This routine will be called in the mode of the caller. (No mechanism is provided for the routine to be called at a different mode).
You must have a conn_event_rtn to operate as a server.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_routine |
| type: | procedure_entry_mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The address of the AST routine to be called for incoming disconnect events. This routine
will be called in the mode of the caller. (No mechanism is provided for the routine to be
called at a different mode). The arguments, conn_event_rtn, and
disc_event_rtn, may reference the same routine.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_routine |
| type: | procedure_entry_mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The address of the AST routine to be called for incoming new data events.
If the user provides this routine, it indicates that the user will supply a buffer of
the size required (specified in an argument to the recv_rtn at each
call) each time one is requested. If the user supplies this routine, receive calls should
only be issued after receive events arrive and sufficient buffer space has been allocated
to handle the incoming data.
This routine will be called in the mode of the caller. (No mechanism is provided for the routine to be called at a different mode).
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The maximum number of pending inbound messages (per connection) that ICC will allow the user before initiating flow control. A message is pending if it is being held within ICC but no receive call(s) are outstanding from the user.
Default = 5 (Pass 0 to get the default)
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
This argument is ignored for non-server applications.
The default protection scheme for this association is as follows:
0 - access for everyone (default)
1 - stops WORLD access
2 - stops both WORLD and GROUP access
Advanced access control is provided by ICC Security objects. For information about ICC system management and security, see the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
Description
This service declares an application association with ICC. Servers must make this call to declare or register their name and to indicate their readiness to receive incoming connections. Although a client is permitted to call this routine, it is unnecessary for simple applications. A client application that wishes to be notified of disconnection events or Receive Data events must call the $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC service.
A client can open a connection without specifying an open association; this automatically creates a default association name of ICC$PID_nnnnnnnn (where nnnnnnnn is a character representation of the Process ID).
NETMBX privilege is required to open any association.
The association name space is a controlled resource. For information about managing this resource, see the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
An attempt to open an association with a name not authorized as described in the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual will fail with the error SS$_NOPRIV returned to the caller. In addition to making entries in the system's local association name space, a call to $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC may also make an entry in a simple clusterwide registry of active associations.
An association may only be accessed from the mode in which it was opened. Inner modes are prevented from using the default association.
An application can open any number of associations subject to available process BYTLM quota. Currently, there is a systemwide limit of 512 open associations. There is no limit imposed clusterwide.
Description of User-Supplied Routines (ASTs)
When opening an association, the user may optionally supply a connect/disconnect AST and/or a Data Event AST. These routines will be used for all connections established over the specified association. In addition, for any of the asynchronous services (those provided with both an immediate return and a "W" form), a completion AST may be supplied by the user. This section describes these ASTs.
1. Connect and Disconnect AST
The user chooses the name of this routine and supplies the procedure name as an argument to the Open Association service. Seven arguments will be passed to the user.
The first argument notifies the user whether this is an incoming new connection or a disconnection of an existing connection. The second identifies the connection. The third and fourth provide access to incoming connect or disconnect data (if any) sent by the cooperating application. The fifth argument provides the number of bytes available for any optional Accept or Reject data (in the case of a connect request) or the disconnect reason supplied by the cooperating application (if any).
For connect events, the sixth and seventh arguments are the EPID and user name of the process requesting the connect, respectively.
The user has the choice of using and declaring a common routine or separate routines as specified when calling $OPEN_ASSOCIATION.
Format
ConnDiscRtn event_type ,conn_handle ,data_len ,data_bfr ,P5 ,P6 ,P7
C Prototype
void ConDiscRtn
(unsigned int event_type, unsigned int conn_handle,
unsigned int data_len, char *data_bfr,
unsigned int P5, unsigned int P6, char *P7);Arguments
event_type
Type: longword (unsigned)
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
This field will contain a code describing the type of event. The possible event codes are defined in ICCDEF:
ICC$C_EV_CONNECT - Connection event ICC$C_EV_DISCONNECT - Disconnection event
conn_handle
Type: longword (unsigned)
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
The handle of the connection associated with the event.
data_len
Type: longword (unsigned)
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
The length (in bytes) of the incoming data. This value specifies the length of the
buffer data_bfr, and will be between 0 and 1000, with zero
indicating no data.
data_bfr
Type: character-coded text string
Access: read only
Mechanism: by 32-bit or 64-bit value (Alpha and Integrity servers)
The 32-bit address of the P1-space buffer containing the data, or zero if no data is
available. The length of this buffer is specified by the argument
data_len.
Upon return from the AST, the address of the data is no longer valid. An application wishing to reference the Connection or Disconnection data after Return must copy the data from the supplied buffer to storage owned by the application.
P5
Type: longword (unsigned)
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
The usage of this argument is dependent on the specified event type code
(event_type).
For connect events (event_type=ICC$C_EV_CONNECT), this
argument contains the length (in bytes) of the buffer available for a reply.
For disconnect events (event_type=ICC$C_EV_DISCONNECT), this
argument contains the user-defined disconnect reason/status from the remote
partner.
P6
Type: quadword (Alpha and Integrity servers
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
The usage of this argument is dependent on the specified event type code
(event_type).
For connect events (event_type=ICC$C_EV_CONNECT), this
argument contains the EPID of the process requesting the connection, passed by
value.
For disconnect events (event_type=ICC$C_EV_DISCONNECT), this
argument contains the user-defined user_context supplied when the
connection was opened. For a client, the user_context is that
supplied to the $ICC_CONNECT call. For a server, it is the value supplied to
$ICC_ACCEPT.
P7
Type: character-coded text string
Access: read only
Mechanism: by reference
For connect events: Username, passed by reference (to P1 space buffer) as a 12-character, space-filled string.
The application must copy this information to local storage before exiting from the connect routine.
For disconnect events, this argument is zero (0).
2. Data Event Routine
This routine, if supplied by the user when opening the association, allows the user to be notified of any pending data events over any connections subsequently opened over that association.
If the user has supplied this routine, the Receive service must only be called in response to incoming data events signaled by this routine, and must be called with a buffer large enough to handle the message size specified.
Use of this routine obligates the user to allocate buffers up to the size requested by the cooperating application. The only recovery provided at this time if a sufficiently large buffer cannot be allocated is to disconnect the connection. Failure to issue a receive call or disconnect may stall all further communication on this connection.
Format
DataEventRtn message_size ,conn_handle ,user_context
C Prototype
void DataEventRtn
(unsigned int message_size, unsigned int conn_handle,
unsigned int user_context);Arguments
message_size
Type: longword (unsigned)
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
This field will contain the number of bytes in the pending data event.
conn_handle
Type: longword (unsigned)
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
The handle of the connection associated with the event. This value should be used as
the conn_handle argument to $ICC_RECEIVE.
user_context
Type: quadword (Alpha and Integrity servers
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
The user-defined user_context supplied when the connection was
opened. For a client, the user context is that supplied to the $ICC_CONNECT call. For a
server, it is the value supplied to $ICC_ACCEPT.
3. Completion ASTs
Completion ASTs may be supplied to the $ICC_CONNECT[W], $ICC_DISCONNECT[W], $ICC_TRANSMIT[W], $ICC_RECEIVE[W], $ICC_TRANSCEIVE[W], and $ICC_REPLY[W] services. In all cases, they are called at the completion of the requested operation, with the single argument, the AST parameter supplied when the original service was called, passed by value.
Completion ASTs are not called if the service returns an error prior to initiating the operation. $ICC_CONNECT and $ICC_ACCEPT accept the flag ICC$V_SYNCH_MODE which indicates that the routines $ICC_TRANSMIT[W], $ICC_RECEIVE[W], and $ICC_REPLY[W] are permitted to return the status SS$_SYNCH, which will indicate that completion has already occurred and the AST will not be called.
Required Access or Privileges
For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
Required Quota
BYTCNT, BYTLM
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW, $ICC_DISCONNECT, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW, $ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE, $ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Normal completion.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Access violation on parameter.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Bad parameter value specified.
- SS$_DUPLNAM
Specified association name is already registered (already exists), or default association is already open.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
One or more process quotas has been exceeded (probably BYTCNT/BYTLM).
- SS$_INSFARG
Too few arguments supplied.
- SS$_INSFMEM
Not enough system resources or process virtual memory available.
- SS$_IVMODE
Attempt to open default association from other than user mode.
- SS$_NOLINKS
Too many associations open for this process.
- SS$_NONETMBX
Request requires NETMBX privilege.
- SS$_NOPRIV
No privilege for association name access or logical name table access if using the Registry.
- SS$_SSFAIL
Transport association name table is full, systemwide.
- SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
Too many arguments were specified. Any failures from the system services: $ENQ, $DEQ, $CRELNM, $TRNLNM.
$ICC_RECEIVE
Receive for Intra-Cluster Communications (ICC) — Receives a single message over a connection. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_RECEIVE
conn_handle ,ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,recv_buf ,recv_buf_lenC Prototype
sys$icc_receive
(unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc *ios_icc,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm,
char *recv_buf, unsigned int recv_buf_len);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | connection_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The handle of the fully established connection.
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | four longwords (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Completion codes:
SS$_NORMAL, SS$_EXQUOTA, SS$_INSFMEM, SS$_LINKDISCON, SS$_BUFOVL, SS$_ACCVIO
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure_entry_mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The AST routine to be executed when the operation completes.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 64-bit value (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte_stream |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of the buffer to
receive the incoming data. The length of this buffer is specified by the argument
recv_buf_len.
| OpenVMS usage: | buffer_length |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The length (in bytes) of the buffer available to hold the incoming data. This value
specifies the length of the buffer recv_buf.
IOS_ICC Arguments:
| OpenVMS usage: | longword unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by value |
This parameter is returned in the ios_icc.
$ICC_RECEIVE writes the actual length of the incoming data
message received from the target application (in bytes) into offset
ios_icc$l_rcv_len of the ios_icc.
| OpenVMS usage: | request_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by value |
This parameter is returned in the ios_icc.
$ICC_RECEIVE writes the Request/Response handle into offset
ios_icc$l_req_handle of the ios_icc. The
request_handle argument is nonzero if the application is expected
to reply to this message.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by value |
This parameter is returned in the ios_icc. The
$ICC_RECEIVE service writes the maximum length (in bytes) of
the expected Reply message into offset ios_icc$l_reply_len of the
ios_icc, if request_handle is
nonzero.
Description
This service receives a single message over a connection. If a Request ID is returned at completion, the partner has used a Transceive system service and requires data to be returned with a Reply service.
For efficiency reasons, the number of parameters on this routine has been limited to six
parameters. Three additional values are returned by the ios_icc data
structure.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW, $ICC_DISCONNECT, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVEW, $ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE, $ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Normal completion.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Access violation on parameter.
- SS$_EXBYTLM
Insufficient byte count quota.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
One or more process quotas has been exceeded.
- SS$_INSFARG
Too few arguments supplied.
- SS$_IVCHAN
Unknown connection specified or invalid connection handle.
- SS$_IVMODE
Attempted to use a connection from a more privileged access mode than the mode in which it was opened.
- SS$_LINKDISCON
The connection has been disconnected.
- SS$_SYNCH
If synchronous mode was requested at connection time, this return value indicates that completion has already occurred and the AST routine, if specified, will not be called.
- SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
Too many arguments specified.
- SS$_WRONGSTATE
Connection is in the wrong state for the request.
$ICC_RECEIVEW
Receive and Wait for Intra-Cluster Communications (ICC) — The Intra-Cluster Communications Receive and Wait service queues a receive request to the specified connection. The $ICC_RECEIVEW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller with data. For asynchronous completion, use the $ICC_RECEIVE service; $ICC_RECEIVE returns to the caller as soon as the receive request is queued, without waiting for data on the connection. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_RECEIVEW
conn_handle ,ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,recv_buf ,recv_buf_lenC Prototype
sys$icc_receivew
(unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc *ios_icc,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm,
char *recv_buf, unsigned int recv_buf_len);$ICC_REJECT
Reject for Intra-Cluster Communications (ICC) — Refuses a connection request. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_REJECT
conn_handle, [reject_buf], [reject_buf_len], [reason]C Prototype
int sys$icc_reject
(unsigned int conn_handle, char * reject_buf,
unsigned int reject_buf_len, unsigned int reason);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | connection_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The handle of the requested connection.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte_stream |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
A buffer of up to 1000 bytes of reject data to be sent to the source of the connection at the completion of the rejection process.
| OpenVMS usage: | buffer_length |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The number of bytes in reject_buf to be sent.
| OpenVMS usage: | cond_code |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
User-specified reject reason code to be supplied to the remote application.
Default = SS$_REJECT
Description
This service is used by a server to refuse an incoming connection request. The $ICC_REJECT service may only be called after receiving a connection request AST. After the completion of the service, the client is notified that the connection was not opened.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW, $ICC_DISCONNECT, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE, $ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Normal completion.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Access violation on parameter.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Bad parameter value specified.
- SS$_CLEARED
Remote association closed the link before it was rejected.
- SS$_INSFARG
Too few arguments supplied.
- SS$_IVCHAN
Connection not found or Invalid connection handle.
- SS$_LINKDISCON
The transport layer has initiated disconnect before the Reject could be sent to the requester.
- SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
Too many arguments specified.
- SS$_WRONGSTATE
Connection is already open and cannot be rejected. To close the connection, call $ICC_DISCONNECT.
$ICC_REPLY
Reply for Intra-Cluster Communications (ICC) — Sends a single message over a connection. This service is used in response to the reception of a Request Handle in a previous $ICC_RECEIVE system service. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_REPLY
conn_handle ,ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,reply_buf ,reply_lenC Prototype
sys$icc_reply
(unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc *ios_icc,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char *reply_buf,
unsigned int reply_len);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | connection_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The handle of the fully established connection.
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |

Completion status values:
SS$_NORMAL, SS$_EXQUOTA, SS$_INSFMEM, SS$_LINKABORT, SS$_LINKDISCON
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure_entry_mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The AST routine to be executed when the operation completes.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 64-bit value (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte_stream |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of the buffer
containing the reply data to be sent. The length of this buffer is specified by the
argument reply_len.
| OpenVMS usage: | buffer_length |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The length (in bytes) of the reply data to be sent over the connection. This value
specifies the length of the buffer reply_buf. ICC segments larger
buffers internally.
The maximum Reply length is the smaller of the Reply buffer size supplied in the $ICC_RECEIVE call, or 1MB.
IOS_ICC Argument:
| OpenVMS usage: | request_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
This parameter is passed through the ios_icc. The
Request/Response handle from the received Transceive request is placed at offset
ios_icc$l_replyto_handle of the
ios_icc.
Description
This service is almost identical to the $ICC_TRANSMIT system service in that it sends a single message over a connection. The only difference is that it is used in response to the reception of a Request Handle in a previous Receive Data system service.
When completion is signaled by calling the AST (if supplied), the data has been delivered to the communications system, but not necessarily to the application at the other end of the connection. The user can reuse the buffer after completion has been signaled.
Alternatively, if the synchronous completion option was requested at connection time, the service may return the optional success status, SS$_SYNCH. When SS$_SYNCH is returned, completion has occurred, and no AST will be delivered.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
BYTLM (for Reply buffer)
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW, $ICC_DISCONNECT, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW, $ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE, $ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Normal completion.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Access violation on parameter.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Bad parameter value specified.
- SS$_EXBYTLM
Insufficient byte count quota.
- SS$_INSFARG
Too few arguments supplied.
- SS$_IVCHAN
Unknown connection specified or invalid connection handle.
- SS$_IVMODE
Attempted to use a connection from a more privileged access mode than the mode in which it was opened.
- SS$_LINKDISCON
An Incoming disconnect event is already in progress.
- SS$_NOSUCHID
The
request_handleis invalid.- SS$_SYNCH
If synchronous mode was requested at connection time, this return value indicates that completion has already occurred and the AST routine, if specified, will not be called.
- SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
Too many arguments specified.
- SS$_WRONGSTATE
Connection is in the wrong state for the request.
$ICC_REPLYW
Reply and Wait for Intra-Cluster Communications (ICC) — The Intra-Cluster Communications Reply and Wait service transmits a single message over a connection in response to a $ICC_TRANSCEIVE[W] request. The $ICC_REPLYW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller when the underlying transport layer has released use of the reply buffer. For asynchronous completion, use the $ICC_REPLY service; $ICC_REPLY returns to the caller as soon as the transmission request has been queued to the transport layer, without waiting for notification that the transport layer has released control of the data buffer. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_REPLYW
conn_handle, ios_icc, [astadr], [astprm], reply_buf, reply_lenC Prototype
sys$icc_replyw
(unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc *ios_icc,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm,
char *reply_buf, unsigned int reply_len);$ICC_TRANSCEIVE
Transceive for Intra-Cluster Communications (ICC) — Sends a single message over a connection and then waits for a reply. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_TRANSCEIVE
conn_handle ,ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,send_buf ,send_lenC Prototype
sys$icc_transceive
(unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc *ios_icc,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char *send_buf,
unsigned int send_len);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | connection_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The handle of the fully established (open) connection.
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | five longwords (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Completion status values:
SS$_NORMAL, SS$_EXQUOTA, SS$_INSFMEM, SS$_BUFOVFL, SS$_LINKABORT, SS$_LINKDISCON
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure_entry_mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The AST routine to be executed when the operation completes.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 64-bit value (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte_stream |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of the buffer
containing the data to be sent. The length of this buffer is specified by the argument
send_len.
| OpenVMS usage: | buffer size |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The length (in bytes) of the data to be sent over the connection. This value
specifies the length of the buffer send_buf.
IOS_ICC Arguments:
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by value |
This parameter is passed through the ios_icc. The
$ICC_TRANSCEIVE service writes the actual length (in bytes) of
the reply data received into offset ios_icc$l_txrcv_len of the
ios_icc. This value represents how much data in
reply_buf was returned by the target application.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte_stream |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
This parameter is passed through the ios_icc. The 32-bit or
64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of the buffer available to receive
the incoming reply message is placed in offset
ios_icc$a_reply_buffer of the
ios_icc.
| OpenVMS usage: | buffer_size |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
This parameter is passed through the ios_icc. The length (in
bytes) of the buffer to receive the reply message. This value specifies the length of the
buffer reply_buf. This value is placed in offset
ios_icc$l_txreply_len of the
ios_icc.
Description
This service sends a single message over a connection and then waits for a reply. When completion is signaled by calling the AST (if supplied), the data has been delivered to the application at the other end of the connection and that application has delivered a reply, now present in the reply buffer. The user can reuse the send and reply buffers after completion.
For efficiency reasons, the number of parameters on this routine has been limited to six
parameters. Three additional parameters are passed by the ios_icc
data structure.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
BYTLM (Send and Reply buffers)
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW, $ICC_DISCONNECT, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW, $ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Normal completion.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Access violation on parameter.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Bad parameter value specified.
- SS$_EXBYTLM
Insufficient byte count quota.
- SS$_INSFARG
Too few arguments were supplied.
- SS$_INSFMEM
Insufficient process or system memory to complete the request.
- SS$_IVCHAN
Unknown connection specified or invalid connection handle.
- SS$_IVMODE
Attempted to use a connection from a more privileged access mode than the mode in which it was opened.
- SS$_LINKDISCON
An Incoming disconnect event is in progress.
- SS$_SYNCH
If synchronous mode was requested at connection time, this return value indicates that completion has already occurred and the AST routine, if specified, will not be called.
- SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
Too many arguments were specified.
- SS$_WRONGSTATE
Connection is in wrong state for request.
$ICC_TRANSCEIVEW
Transceive and Wait for Intra-Cluster Communications (ICC) — Sends a single message over a connection and waits for a reply. The $ICC_TRANSCEIVEW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller when the data from the reply is available. For asynchronous completion, use the $ICC_TRANSCEIVE service; $ICC_TRANSCEIVE returns to the caller when the transmit portion of the transceive request has been queued to the transport layer, but without waiting for notification that the transport layer has released control of the data buffer or for the reply data from the receiving end of the connection. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_TRANSCEIVEW
conn_handle ,ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,send_buf ,send_lenC Prototype
sys$icc_transceivew
(unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc *ios_icc,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char *send_buf,
unsigned int send_len);$ICC_TRANSMIT
Transmit for Intra-Cluster Communications (ICC) — Sends a single message over a connection. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_TRANSMIT
conn_handle ,ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,send_buf ,send_lenC Prototype
sys$icc_transmit
(unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc *ios_icc,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm,
char *send_buf, unsigned int send_len);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | connection_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The handle of the fully established (open) connection to send the data over.
| OpenVMS usage: | ios_status_block |
| type: | structure IOS_ICC |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
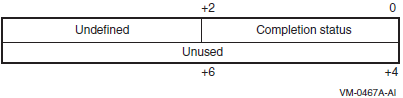
Completion status values:
SS$_NORMAL, SS$_EXQUOTA, SS$_INSFMEM, SS$_LINKABORT, SS$_LINKDISCON
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure_entry_mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The AST routine to be executed when the operation completes.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 64-bit value (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte_stream |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of the buffer
containing the data to be sent. The length of this buffer is specified by the argument
send_len.
| OpenVMS usage: | buffer_length |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The length (in bytes) of the data to be sent over the connection. This value
specifies the length of the buffer send_buf. The maximum
transmission size is 1MB.
Description
This service sends a single message over a connection. When completion is signalled by calling the AST (if supplied), the data has been delivered to the communications system, but not necessarily to the system or application at the other end of the connection. After completion, the user can reuse the buffer.
Alternatively, if the synchronous completion option was requested at connection time, the service may return the optional success status, SS$_SYNCH. When SS$_SYNCH is returned, completion has occurred, and no AST will be delivered.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
BYTLM (send_buf)
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW, $ICC_DISCONNECT, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW, $ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE, $ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Normal completion.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Access violation on parameter.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Bad parameter value specified.
- SS$_EXBYTLM
Insufficient byte count quota.
- SS$_INSFARG
Too few arguments were supplied.
- SS$_INSFMEM
Insufficient process or system memory to complete the request.
- SS$_IVCHAN
Unknown connection specified or invalid connection handle.
- SS$_IVMODE
Attempted to use a connection from a more privileged access mode than the mode in which it was opened.
- SS$_LINKDISCON
An Incoming disconnect event is in progress.
- SS$_SYNCH
If synchronous mode was requested at connection time, this return value indicates that completion has already occurred and the AST routine, if specified, will not be called.
- SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
Too many arguments were specified.
- SS$_WRONGSTATE
Connection is in the wrong state for the request.
$ICC_TRANSMITW
Transmit and Wait for Intra-Cluster Communications (ICC) — Sends a single message over a connection. The $ICC_TRANSMITW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller when the underlying transport layer has released use of the Transmit buffer. This does not mean that the data has been received by the partner application. For asynchronous completion, use the $ICC_TRANSMIT service. The $ICC_TRANSMIT service returns to the caller as soon as the transmission request has been queued to the transport layer, without waiting for notification that the transport layer has released control of the data buffer. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_TRANSMITW
conn_handle ,ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,send_buf ,send_lenC Prototype
sys$icc_transmitw
(unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc *ios_icc,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char *send_buf,
unsigned int send_len);$IDTOASC
Translate Identifier to Identifier Name — Translates the specified identifier value to its identifier name. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$IDTOASC id ,[namlen] ,[nambuf] ,[resid] ,[attrib] ,[contxt]C Prototype
int sys$idtoasc
(unsigned int id, unsigned short int *namlen, void *nambuf,
unsigned int *resid, unsigned int *attrib, unsigned int *contxt);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | rights_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Binary identifier value translated by $IDTOASC. The id argument is a
longword containing the binary value of the identifier. To determine the identifier
names of all identifiers in the rights database, you specify id
as –1 and call $IDTOASC repeatedly until it returns the status code SS$_NOSUCHID.
The identifiers are returned in alphabetical order.
| OpenVMS usage: | word_unsigned |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Number of characters in the identifier name translated by $IDTOASC. The
namlen argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and
Integrity server systems) of a word containing the length of the identifier name written
to nambuf.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Identifier name text string returned when $IDTOASC completes the translation. The
nambuf argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and
Integrity server systems) of a descriptor pointing to the buffer in which the identifier
name is written.
| OpenVMS usage: | rights_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Identifier value of the identifier name returned in nambuf. The
resid argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and
Integrity server systems) of a longword containing the 32-bit code of the
identifier.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Mask of attributes associated with the identifier returned in
resid. The attrib argument is the 32-
or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of a longword containing the
attribute mask.
|
Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC |
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the process rights list using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST. |
|
KGB$V_NAME_HIDDEN |
Allows holders of an identifier to have it translated – either from binary to ASCII or vice versa – but prevents unauthorized users from translating the identifier. |
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS |
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem attribute. |
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE |
Allows holders of an identifier to charge disk space to the identifier. It is used only for file objects. |
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM |
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in the subsystem. |
| OpenVMS usage: | context |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Context value used when repeatedly calling $IDTOASC. The contxt
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of a
longword used while $IDTOASC searches for all identifiers. The context value must be
initialized to the value 0, and the resulting context of each call to $IDTOASC must be
presented to each subsequent call. After contxt is passed to
$IDTOASC, you must not modify its value.
Description
The Translate Identifier to Identifier Name service translates the specified binary identifier value to an identifier name. While the primary purpose of this service is to translate the specified identifier to its name, you can also use it to find all identifiers in the rights database. Owner or read access to the rights database is required. To determine all the identifiers, call $IDTOASC repeatedly until it returns the status code SS$_NOSUCHID. When SS$_NOSUCHID is returned, $IDTOASC has returned all the identifiers, cleared the context value, and deallocated the record stream.
If you complete your calls to $IDTOASC before SS$_NOSUCHID is returned, use $FINISH_RDB to clear the context value and deallocate the record stream.
When you use wildcards with this service, the records are returned in identifier name order.
Required Access or Privileges
None, unless the id argument is NAME_HIDDEN, in which case you must
hold the identifier or have read access to the rights list.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CHECK_ACCESS, $CHKPRO, $CREATE_RDB, $ERAPAT, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $FORMAT_ACL, $FORMAT_AUDIT, $GET_SECURITY, $GRANTID, $HASH_PASSWORD, $MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT, $MTACCESS, $PARSE_ACL, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID, $SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
namlen,nambuf,resid,attrib, orcontxtargument cannot be written by the caller.- SS$_INSFMEM
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights database.
- SS$_IVCHAN
The contents of the context longword are not valid.
- SS$_IVIDENT
The specified identifier is of invalid format.
- SS$_NOIOCHAN
No more rights database context streams are available.
- SS$_NORIGHTSDB
The rights database does not exist.
- SS$_NOSUCHID
The specified identifier name does not exist in the rights database, or the entire rights database has been searched if the ID is –1.
Because the rights database is an indexed file that you access with OpenVMS RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes, refer to the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Set IEEE Floating-Point Control Register — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, modifies IEEE floating-point state and, optionally, returns the previous value. The service provides the mechanism to set the specified state bits, to clear the specified state bits, and to swap one set of state bits for another.
Format
SYS$IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL [clrmsk] ,[setmsk] ,[prvmsk]C Prototype
int sys$ieee_set_fp_control
(struct _ieee *clrmsk, struct _ieee *setmsk, struct _ieee *prvmsk);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_quadword |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a quadword bit mask to be cleared in the IEEE floating-point control register.
|
Symbol |
Mask |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_INV |
2 |
Enable invalid operation exception |
|
IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_DZE |
4 |
Enable divide by 0 exception |
|
IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_OVF |
8 |
Enable overflow exception |
|
IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_UNF |
10 |
Enable underflow exception |
|
IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_INE |
20 |
Enable inexact exception |
|
IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_DNOE |
40 |
Enable denormal operand exception |
|
IEEE$M_MAP_DNZ |
2000 |
Denormal operands are mapped to 0.0 |
|
IEEE$M_MAP_UMZ |
4000 |
Underflow results are mapped to 0.0 |
|
IEEE$M_INHERIT |
8000 |
Inherit FP state on thread create |
|
IEEE$M_STATUS_INV |
20000 |
Invalid operation |
|
IEEE$M_STATUS_DZE |
40000 |
Divide by 0 |
|
IEEE$M_STATUS_OVF |
80000 |
Overflow |
|
IEEE$M_STATUS_UNF |
100000 |
Underflow |
|
IEEE$M_STATUS_INE |
200000 |
Inexact |
|
IEEE$M_STATUS_DNO |
400000 |
Denormal operand |
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_quadword |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a quadword bit mask to be set in the IEEE floating-point control register.
Table 3 shows the format of the IEEE floating-point control register.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_quadword |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a quadword to receive the previous value of the IEEE floating-point control register.
Description
The Set IEEE Floating-Point Control Register service updates the IEEE floating-point control register, maintained by the operating system, with the values supplied by the calling program.
If the
prvmskargument is specified, $IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL first reads the previous value of the IEEE floating-point control register.If the
clrmskargument is specified, $IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL then clears the specified bit masks in theclrmskargument.If the
setmskargument is specified, $IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL then sets the specified bit masks in thesetmskargument.
The
clrmskargument with the address of a quadword of all 1sThe
setmskargument with the address of a quadword that holds the new register valueThe
prvmskargument with the address of a quadword to save the old register value
| Location of Call | State Value | Scope of New State Value |
|---|---|---|
| Mainline | Determined by the compiler switches used when compiling the modules. | Change is in effect until this service is called again, with the exception of ASTs (see below). |
| Condition handler | The same as the state in effect when the condition occurs, unless the setting was changed by a previous condition handler. | Change is in effect until all remaining condition handlers have been called or this service is called again. |
| AST routine | Determined by the compiler switches used when compiling the modules, regardless of the state value in effect when the AST was triggered. | Change is in effect only until the AST completes or this service is called again. |
On Alpha systems, calling this routine changes the setting for ASTs as well as the mainline program.
Required Access or Privilege
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
- $IEEE_SET_PRECISION_MODE
- $IEEE_SET_ROUNDING_MODE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The specified argument cannot be read or cannot be written.
$IEEE_SET_PRECISION_MODE (Integrity servers Only)
Set IEEE Precision Mode — On Integrity server systems, modifies the IEEE precision mode and, optionally, returns the previous value.
Format
SYS$IEEE_SET_PRECISION_MODE new_value , [*prev_value]C Prototype
int sys$ieee_set_precision_mode (int new_value, int *prev_value);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | IEEE precision mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The new value can be one of the following:
| Symbol | Value | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| IEEE$C_PM_NO_CHANGE | -1 | No change. Just get previous value |
| IEEE$C_PM_SINGLE | 0 | Single Precision |
| IEEE$C_PM_DOUBLE | 2 | Double Precision |
| IEEE$C_PM_DOUBLE_EXTENDED | 3 | Double-Extended Precision |
| OpenVMS usage: | IEEE precision mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The previous value is a pointer to a return value that can be one of the last three items from the table showing new values.
Description
The initial precision mode and the scope of the modified precision mode differ depending on the location of the call to this routine, as shown in the following table.
| Location of Call | Initial Precision Mode | Scope of New Precision Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Mainline | Determined by the compiler switches used when compiling the modules. | Change is in effect until this service is called again with the exception of ASTs (see below). |
| Condition handler | The same as the precision mode in effect when the condition occurs, unless the setting was changed by a previous condition handler. | Change is in effect until all remaining condition handlers have been called or this service is called again. |
| AST routine | Determined by the compiler switches used when compiling the modules, regardless of the precision in effect when the AST was triggered. | Change is in effect only until the AST completes or this service is called again. |
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quotas
None
Related Services
$IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL $IEEE_SET_ROUNDING_MODE
$IEEE_SET_ROUNDING_MODE (Integrity servers Only)
Set IEEE Rounding Mode — On Integrity server systems, modifies the IEEE rounding mode and, optionally, returns the previous value.
Format
SYS$IEEE_SET_ROUNDING_MODE new_value , [*prev_value]C Prototype
int sys$ieee_set_rounding_mode (int new_value, int *prev_value);,Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | IEEE rounding mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The new value can be one of the following:
| Symbol | Value | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| IEEE$C_RM_NO_CHANGE | -1 | No change. Just get previous value |
| IEEE$C_RM_NEAREST | 0 | Nearest (or even) |
| IEEE$C_RM_DOWN | 1 | -Infinity (down) |
| IEEE$C_RM_UP | 2 | +Infinity (up) |
| IEEE$C_RM_TRUNCATE | 3 | Zero (truncate/chop) |
| OpenVMS usage: | IEEE rounding mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The previous value is a pointer to a return value that can be one of the last four items from the table showing new values.
Description
The initial rounding mode and the scope of the modified rounding mode differ depending on the location of the call to this routine, as shown in the following table.
| Location of Call | Initial Rounding Mode | Scope of New Rounding Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Mainline | Determined by the compiler switches used when compiling the modules. | Change is in effect until this service is called again, with the exception of ASTs (see below). |
| Condition handler | The same as the rounding mode in effect when the condition occurs, unless the setting was changed by a previous condition handler. | Change is in effect until all remaining condition handlers have been called or this service is called again. |
| AST routine | Determined by the compiler switches used when compiling the modules, regardless of the rounding in effect when the AST was triggered. | Change is in effect only until the AST completes or this service is called again. |
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL $IEEE_SET_PRECISION_MODE
$INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Initialize System Alignment Fault Reporting — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, initializes system process alignment fault reporting. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT match_table ,buffer_size ,flagsC Prototype
int sys$init_sys_align_fault_report
(void *match_table, int buffer_size, unsigned int flags);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference |
Describes the system fault match table. The match_table argument is the
32-bit or 64-bit virtual address of an array of longwords describing the system fault
match table. The first longword is the number of match entries; the remaining longwords
are the match entries.
The match table is used to restrict the number of alignment faults reported. Each entry in the table is a bit mask divided into three groups: mode bits, program counter (PC) space bits, and virtual address (VA) space bits.
|
Bit Type |
Symbols | |
|---|---|---|
|
Mode bits |
AME$M_KERNEL_MODE |
Kernel mode |
|
AME$M_EXEC_MODE |
Executive mode | |
|
AME$M_SUPER_MODE |
Supervisor mode | |
|
AME$M_USER_MODE |
User mode | |
|
Program counter bits |
AME$M_USER_PC |
PC in User space |
|
AME$M_SYSTEM_PC |
PC in System space | |
|
Virtual address bits |
AME$M_SYSTEM_VA |
VA in System space |
|
AME$M_USER_VA_P0 |
VA in User P0 space | |
|
AME$M_USER_VA_P1 |
VA in User P1 space | |
|
AME$M_USER_VA_P2 |
VA in User P2 space |
The following diagram illustrates the data structure of the match table.
When an alignment fault occurs, a fault bit mask is created with one bit set in each group. The alignment fault handler then compares this fault bit mask against each entry in the match table. If the fault bit mask is a subset of an entry in the match table, the fault is reported.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | longword (signed) |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by value |
The number of bytes to allocate, from nonpaged pool, to save the alignment fault data. The
buffer you allocate must be sufficient to accommodate one data item of the size
specified in the flags argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Flag bit mask specifying options for the $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA operation.
If the flags argument is 0, data items of size AFR$K_VMS_LENGTH will be
returned. If the flags argument is AFR$M_USER_INFO, the user name
and image name are added to each data item and they are returned in a buffer of length
AFR$K_EXTENDED_LENGTH. If the user name and image name are not available, an empty
string is returned in the data item.
Description
The Initialize System Alignment Fault Reporting service initializes system alignment fault reporting.
System alignment faults must be written to a buffer. The following diagram illustrates the format in which system alignment fault data is saved in the buffer.
Only one user on a system can initialize system alignment fault reporting at any time. Subsequent calls will return SS$_AFR_ENABLED.
System alignment fault reporting is disabled when the program that called the service completes.
Required Access or Privileges
CMKRNL privilege is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT, $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The match table is not read accessible.
- SS$_AFR_ENABLED
The service was already called.
- SS$_BADPARAM
The
buffer_sizeargument is less than the minimum size required. If theflagsargument is 0, AFR$K_VMS_LENGTH + 32 is required. If theflagsargument is 1, AFR$K_EXTENDED_LENGTH + 32 is required.- SS$_NOPRIV
The caller does not have CMKRNL privilege.
$INIT_VOL
Initialize Volume — Formats a disk or magnetic tape volume and writes a label on the volume. At the end of initialization, the disk is empty except for the system files containing the structure information. All former contents of the volume are lost.
Format
SYS$INIT_VOL devnam, volnam [,itmlst]C Prototype
int sys$init_vol (void *devnam, void *volnam, void *itmlst);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Name of the device on which the volume is physically mounted. The descriptor must point to the device name, a character string of 1 to 64 characters. The device name can be a physical device name or a logical name; if it is a logical name, it must translate to a physical name.
The device does not have to be currently allocated; however, allocating the device before initializing it is recommended.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Identification to be encoded on the volume. The descriptor must point to the volume name, a character string of 1 to 12 characters. For a disk volume name, you can specify a maximum of 12 ANSI characters; for a magnetic tape volume name, you can specify a maximum of 6 ANSI “a” characters. Any valid ANSI “a” characters can be used; these include numbers, uppercase letters, and any one of the following nonalphanumeric characters:
! " % ' ( ) * + , - . / : ; < = >
VSI strongly recommends that a disk volume name consist of only alphanumeric characters, dollar signs ($), underscores (_), and hyphens (-).
| OpenVMS usage: | item_list_3 |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Item list specifying options that can be used when initializing the volume. The
itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors,
each of which describes one option. The list of item descriptors is terminated by a
longword of 0.
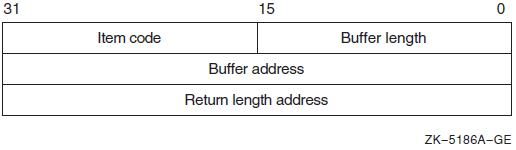
|
Descriptor Field |
Definition | |
|---|---|---|
|
Buffer length |
A word specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer that supplies the information $INIT_VOL needs to process the specific item code. The length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the item descriptor. | |
|
Item code |
A word containing an option for the initialize operation. These codes are defined by the $INITDEF macro. There are three types of item codes: | |
|
Boolean item code |
Boolean item codes specify a true or false value. The form INIT$_code specifies a true value and the form INIT$_NO_code specifies a false value. For Boolean item codes, the buffer length and buffer address fields of the item descriptor must be 0. | |
|
Symbolic value item code |
Symbolic value item codes specify one of a specified range of possible choices. The buffer length and buffer address fields of the item descriptor must be 0. | |
|
Input value item code |
Input value item codes specify a value to be used by $INIT_VOL. The buffer length and buffer address fields of the item descriptor must be nonzero. | |
|
Buffer address |
A longword containing the address of the buffer that supplies information to $INIT_VOL. | |
|
Return length address |
This field is not used. | |
Item Codes
INIT$_ACCESSED
An input item code that specifies the number of directories allowed in system space on the volume.
You must specify an integer between 0 and 255 in the input buffer. The default value is 3.
The INIT$_ACCESSED item code applies only to Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1 disks.
INIT$_BADBLOCKS_LBN
An input item code that enables $INIT_VOL to mark bad blocks on the volume; no data is written to those faulty areas. INIT$_BADBLOCKS_LBN specifies faulty areas on the volume by logical block number and block count.
The buffer from which $INIT_VOL reads the option information contains an array of quadwords containing information in the following format.
|
Field |
Symbol Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Logical block number |
INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_LBN |
Specifies the logical block number of the first block to be marked as allocated. |
|
Count |
INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_COUNT |
Specifies the number of blocks to be allocated. This range begins with the first block, as specified in INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_LBN. |
For example, if the input buffer contains the values 5 and 3, INIT_VOL starts at logical block number 5 and allocates 3 blocks.
The number of entries in the buffer is determined by the buffer length field in the item descriptor.
All media supplied by HP and supported on the operating system, except disks and TU58 cartridges, are factory formatted and contain bad block data. The Bad Block Locator utility (BAD) or the diagnostic formatter EVRAC can be used to refresh the bad block data or to construct it for the disks and TU58 cartridges. The INIT$_BADBLOCKS_LBN item code is necessary only to enter bad blocks that are not identified in the volume's bad block data. For more information, see the OpenVMS Bad Block Locator Utility Manual.
The INIT$_BADBLOCKS_LBN item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_BADBLOCKS_SEC
An input item code that specifies faulty areas on the volume by sector, track, cylinder, and block count. $INIT_VOL marks the bad blocks as allocated; no data is written to them.
The input buffer must contain an array of octawords containing information in the following format.
|
Field |
Symbol Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Sector |
INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_SECTOR |
Specifies the sector number of the first block to be marked as allocated. |
|
Count |
INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_COUNT |
Specifies the number of blocks to be allocated. |
|
Track |
INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_TRACK |
Specifies the track number of the first block to be marked as allocated. |
|
Cylinder |
INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_CYLINDER |
Specifies the cylinder number of the first block to be marked as allocated. |
For example, if the input buffer contains the values 12, 3, 1, and 2, INIT_VOL starts at sector 12, track 1, cylinder 2, and allocates 3 blocks.
The number of entries in the buffer is determined by the buffer length field in the item descriptor.
All media supplied by HP and supported on the operating system, except disks and TU58 cartridges, are factory formatted and contain bad block data. The Bad Block Locator utility (BAD) or the diagnostic formatter EVRAC can be used to refresh the bad block data or to construct it for the disks and TU58 cartridges. The INIT$_BADBLOCKS_SEC item code is necessary only to enter bad blocks that are not identified in the volume's bad block data. For more information, see the OpenVMS Bad Block Locator Utility Manual.
The INIT$_BADBLOCKS_SEC item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_CLUSTERSIZE
volume size in blocks/(255 * 4096)
Disks that are 50,000 blocks or larger have a default cluster size of 16.
Disks smaller than 50,000 blocks have a default value of 1.
Note
This item code applies to ODS-5 disks as well as to ODS-2 disks. For more information, see the INITIALIZE command in the VSI OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
INIT$_COMPACTIONINIT$_NO_COMPACTION—Default
A Boolean item code that specifies whether data compaction should be performed when writing the volume.
The INIT$_COMPACTION item code applies only to TA90 drives.
INIT$_DENSITY
A symbolic item code that specifies the density value for magnetic tapes and diskettes.
For magnetic tape volumes, the INIT$_DENSITY item code specifies the density.
The DENSITY item code is dependent on the type of tape device. If a tape device is seen as capable of using the MT3 density codes the buffer for MNT$_DENSITY item code must contain a longword with one of the MT3 codes, as defined in SYS$LIBRARY:STARLET (MT3$K_TK50, MT3$K_3480, M53$K_DSDLT, MT3$K_AIT2 and so on). Refer to the MT3_SUPPORTED argument for $GETDVI.
INIT$K_DENSITY_800_BPI
INIT$K_DENSITY_1600_BPI
INIT$K_DENSITY_6250_BPI
The specified density value must be supported by the drive. If you do not specify a density item code for a blank magnetic tape, the system uses a default density of the highest value allowed by the tape drive. If the drive allows 6250, 1600, and 800 bpi operation, the default density is 6250. If the drive allows only 1600 and 800 bpi operation, the default density is 1600. If you do not specify a density item code for a magnetic tape that has been previously written, the system uses the previously set volume density.
INIT$K_DENSITY_SINGLE_DISK
INIT$K_DENSITY_DOUBLE_DISK
INIT$K_DENSITY_DD_DISK
INIT$K_DENSITY_HD_DISK
INIT$K_DENSITY_SINGLE_DISK
INIT$K_DENSITY_DOUBLE_DISK
INIT$K_DENSITY_DD_DISK
INIT$K_DENSITY_HD_DISK
RX23 diskettes – DD or HD density
RX33 diskettes – double density only
RX02 dual-density diskette drives – single or double density
If you do not specify a density item code for a disk, the system leaves the volume at the density at which it was last formatted. RX02 disks purchased from HP are formatted in single density.
INIT$_DIRECTORIES
An input item code that specifies the number of entries to preallocate for user directories. The input buffer must contain a longword value in the range of 16 to 16000. The default value is 16.
The INIT$_DIRECTORIES item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_ERASEINIT$_NO_ERASE—Default
ODS–2 disk volumes
ANSI magnetic tape volumes on magnetic tape devices that support the hardware erase function, for example, TU78 and MSCP magnetic tapes
For disk devices, this item code sets the ERASE volume attribute, causing each file on the volume to be erased when it is deleted.
INIT$_ERASE_ON_DELETE
A Boolean item code that sets the HM2$V_ERASE bit. The volume is marked so that when files are deleted, the blocks that they formerly occupied are erased. See the DCL command SET VOLUME/ERASE for more information.
INIT$_ERASE_ON_INIT
A Boolean item code that specifies whether to perform the data security erase (DSE) operation immediately.
INIT$_EXTENSION
An input item code that specifies, by the number of blocks, the default extension size for all files on the volume. The extension default is used when a file increases to a size greater than its initial default allocation during an update. For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 disks, the buffer must contain a longword value in the range 0 to 65535. For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1 disks, the input buffer must contain a longword value in the range of 0 to 255. The default value is 5 for both Structure Level 1 and Structure Level 2 disks.
No default extension for the file has been set
No default extension for the process has been set using the SET RMS command
Note
This item code applies to ODS-5 disks as well as to ODS-2 disks. For more information, see the INITIALIZE command in the VSI OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
INIT$_FPROT
An input item code that specifies the default protection applied to all files on the volume. The input buffer must contain a longword protection mask that contains four 4-bit fields. Each field grants or denies read, write, create, and delete access to a category of users. Cleared bits grant access; set bits deny access.
The INIT$_FPROT item code applies only to Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1 disks and is ignored if it is used on an OpenVMS system. OpenVMS systems use the default file extension set by the DCL command SET PROTECTION/DEFAULT.
INIT$_HEADERS
An input item code that specifies the number of file headers to be allocated for the index file. The input buffer must contain a longword value within the range of 16 to the value set by the INIT$_MAXFILES item code. The default value is 16.
The INIT$_HEADERS item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_GPT—Default on Integrity serversINIT$_NO_GPT—Default on Alpha
A Boolean item code that specifies whether or not to create a Global Universal ID (GUID) Partition Table (GPT) structure.
INIT$_HIGHWATER—DefaultINIT$_NO_HIGHWATER
A Boolean item code that sets the file highwater mark (FHM) volume attribute, which guarantees that users cannot read data that they have not written.
INIT$_NO_HIGHWATER disables FHM for a volume.
The INIT$_HIGHWATER and INIT$_NO_HIGHWATER item codes apply only to Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 disks.
INIT$_HOMEBLOCKS
INIT$K_HOMEBLOCKS_GEOMETRY
Causes the homeblocks to be placed at separate locations on disk, to protect against failure of a disk block. Placement depends on the reported geometry of the disk.
INIT$K_HOMEBLOCKS_FIXED
Causes the homeblocks to be placed at separate fixed locations on the disk; this is the default. Placement is independent of the reported geometry of the disk. This caters for disks that report different geometries according to the type of controller to which they are attached.
INIT$K_HOMEBLOCKS_CONTIGUOUS
Causes the homeblocks to be placed contiguously at the start of the disk. This allows container file systems to maximize the amount of contiguous space on the disk, when used with the INIT$_INDEX_BEGINNING item code.
Note
This item code applies to ODS-5 disks as well as to ODS-2 disks. For more information, see the INITIALIZE command in the VSI OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
INIT$_INDEX_BEGINNING
A symbolic item code that places the index file for the volume's directory structure at the beginning of the volume. By default, the index is placed in the middle of the volume.
When issuing calls to $INIT_VOL, using this item code in conjunction with INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK results in an error. If you specify both item codes from DCL, INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK takes precedence.
This item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK
An input item code that specifies the location of the index file for the volume's directory structure by logical block number. The input buffer must contain a longword value specifying the logical block number of the first block of the index file. By default, the index is placed in the middle of the volume.
When issuing calls to $INIT_VOL, using this item code with INIT$_INDEX_BEGINNING, INIT$_INDEX_MIDDLE, or INIT$_INDEX_END results in an error. From DCL, if you specify INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK with INIT$_INDEX_BEGINNING, INIT$_INDEX_MIDDLE, or INIT$_INDEX_END, then INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK takes precedence.
The INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_INDEX_END
A symbolic item code that places the index file for the volume's directory structure at the end of the volume. The default is to place the index in the middle of the volume.
When issuing calls to $INIT_VOL, using this item code with INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK results in an error. If you specify both item codes from DCL, INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK takes precedence.
This item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_INDEX_MIDDLE
A symbolic item code that places the index file for the volume's directory structure in the middle of the volume. This is the default location for the index.
When issuing calls to $INIT_VOL, using this item code with INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK results in an error. If you specify both item codes from DCL, INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK takes precedence.
This item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_INTERCHANGE
An input item code that specifies that the magnetic tape ANSI VOL1 volume label is to be used for interchange in a heterogeneous vendor environment. On OpenVMS, this item code overrides creation of the ANSI VOL2 volume label, which contains security attributes specific to OpenVMS systems.
For more information about the INIT$_INTERCHANGE item code and about magnetic tape labeling and tape interchange, see the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
INIT$_LABEL_ACCESS
An input item code that specifies the character to be written in the volume accessibility field of the ANSI volume label VOL1 on an ANSI magnetic tape. Any valid ANSI “a” characters can be used; these include numbers, uppercase letters, and any one of the following nonalphanumeric characters:
! " % ' ( ) * + , - . / : ; < = >
If the magnetic tape was created on a version of the operating system that conforms to Version 3 of ANSI, this item code is used to override any character except an ASCII space.
If the magnetic tape conforms to an ANSI standard that is later than Version 3, this item code is used to override any character except an ASCII 1 character.
INIT$_LABEL_VOLO
An input item code that specifies the text that is written in the owner identifier field of the ANSI volume label VOL1 on an ANSI magnetic tape. The owner identifier field can contain up to 14 valid ANSI “a” characters.
INIT$_MAXFILES
volume size in blocks/cluster factor + 1
Once initialized, the maximum number of files can be increased only by reinitializing the volume.
volume size in blocks/(cluster factor + 1) * 2
The INIT$_MAXFILES item code applies only to disks.
Note
This item code applies to ODS-5 disks as well as to ODS-2 disks. For more information, see the INITIALIZE command in the VSI OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
INIT$_OVR_ACCESSINIT$_NO_OVR_ACCESS—Default
A Boolean item code that specifies whether to override any character in the accessibility field of the ANSI volume label VOL1 on an ANSI magnetic tape. For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
To specify INIT$_OVR_ACCESS, the caller must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
INIT$_OVR_EXPINIT$_NO_OVR_EXP—Default
A Boolean item code that specifies whether the caller writes to a magnetic tape that has not yet reached its expiration date. This item code applies only to the magnetic tapes that were created before VAX/VMS Version 4.0 and that use the D% format in the volume owner identifier field.
To specify INIT$_OVR_EXP, the caller must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
INIT$_OVR_VOLOINIT$_NO_OVR_VOLO—Default
A Boolean item code that allows the caller to override processing of the owner identifier field of the ANSI volume label VOL1 on an ANSI magnetic tape.
To specify INIT$_OVR_VOLO, the caller must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
INIT$_OWNER
An input item code that specifies the UIC that will own the volume. The input buffer must contain a longword value, which is the UIC. The default is the UIC of the caller.
For magnetic tapes, no UIC is written unless protection on the magnetic tape is specified. If the INIT$_VPROT item code is specified but the INIT$_OWNER item code is not specified, the UIC of the caller is assigned ownership of the volume.
INIT$_READCHECKINIT$_NO_READCHECK—Default
A Boolean item code that specifies whether data checking should be performed for all read operations on the volume. For more information about data checking, see the VSI OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
The INIT$_READCHECK item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_SIZE
An input item code that specifies the number of blocks allocated for a RAM disk with a device type of DT$_RAM_DISK. The input buffer must contain a longword value.
INIT$_SPECIAL_FILES—DefaultINIT$_NO_SPECIAL_FILES
Boolean item codes that control whether special files are enabled on the volume.
INIT$_STRUCTURE_LEVEL_1INIT$_STRUCTURE_LEVEL_2—Default
INIT$_READCHECK
INIT$_WRITECHECK
INIT$_CLUSTERSIZE
The default protection for a Structure Level 1 disk is full access to system, owner, and group users, and read access to all other users.
The INIT$_STRUCTURE_LEVEL_1 item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_USER_NAME
An input item code that specifies the user name that is associated with the volume. The input buffer must contain a character string from 1 to 12 alphanumeric characters, which is the user name. The default is the user name of the caller.
INIT$_VERIFIEDINIT$_NO_VERIFIED
A Boolean item code that indicates whether the disk contains bad block data. INIT$_NO_VERIFIED indicates that any bad block data on the disk should be ignored. For disks with 4096 blocks or more, the default is INIT$_VERIFIED.
Disks with fewer than 4096 blocks
DIGITAL Storage Architecture (DSA) devices
Disks that are not last-track devices
The INIT$_VERIFIED item codes apply only to disks.
INIT$_VOLUME_LIMIT
An input item code that specifies the maximum logical volume size. For more information, see the DCL command INITIALIZE/LIMIT.
INIT$_VPROT
An input item code that specifies the protection assigned to the volume. The input buffer must contain a longword protection mask that contains four 4-bit fields. Each field grants or denies read, write, create, and delete access to a category of users. Cleared bits grant access; set bits deny access. The following diagram depicts the structure of the protection mask.

The default is the default protection of the caller.
For magnetic tape, the protection code is written to a specific volume label. The system applies only read and write access restrictions; execute and delete access are ignored. Moreover, the system and the owner are always given read and write access to magnetic tapes, regardless of the protection mask specified.
When you specify a protection mask for a disk volume, access type E (execute) indicates create access.
For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 volumes, an initial security profile is created from the VOLUME.DEFAULT profile, with the owner and protection as currently defined for INITIALIZE.
You can use the $SET_SECURITY service to modify the security profile after the volume is initialized and mounted.
The caller needs read, write, or control access to the device.
INIT$_WINDOW
The INIT$_WINDOW item code specifies the number of mapping pointers to be allocated for file windows. The input buffer must contain a longword value in the range 7 to 80. The default is 7.
When a file is opened, the file system uses the mapping pointers to access the data in the file.
The INIT$_WINDOW item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_WRITECHECKINIT$_NO_WRITECHECK—Default
A Boolean item code that specifies whether data checking should be performed for all read operations on the volume. For more information about data checking, see the VSI OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
The INIT$_WRITECHECK item code applies only to disks.
Description
The Initialize Volume system service formats a disk or magnetic tape volume and writes a label on the volume. At the end of initialization, the disk is empty except for the system files containing the structure information. All former contents of the volume are lost.
A blank magnetic tape can sometimes cause unrecoverable errors when it is read. $INIT_VOL attempts to read the volume unless the following three conditions are in effect:
INIT$_OVR_ACCESS Boolean item code is specified.
INIT$_OVR_EXP Boolean item code is specified.
Caller has VOLPRO privilege.
If the caller has VOLPRO privilege, $INIT_VOL initializes a disk without reading the ownership information; otherwise, the ownership of the volume is checked.
A blank disk or a diskette with an incorrect format can sometimes cause a fatal drive error. Such a diskette can be initialized successfully by specifying the INIT$_DENSITY item code to format the diskette.
Required Access or Privileges
To initialize a particular volume, the caller must either have volume protection (VOLPRO) privilege or the volume must be one of the following:
Blank disk or magnetic tape; that is, a volume that has never been written
Disk that is owned by the caller's UIC or by the UIC [0,0]
Magnetic tape that allows write access to the caller's UIC or that was not protected when it was initialized
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SET_SECURITY, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The item list or an address specified in the item list cannot be accessed.
- SS$_BADPARAM
A buffer length of 0 was specified with a nonzero item code or an illegal item code was specified.
- SS$_IVSSRQ
A concurrent call to SYS$INIT_VOL is already active for the process.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The caller does not have sufficient privilege to initialize the volume.
- SS$_NOSUCHDEV
The specified device does not exist on the host system.
- INIT$_ALLOCFAIL
Index file allocation failure.
- INIT$_BADACCESSED
Value for INIT$_ACCESSED item code out of range.
- INIT$_BADBLOCKS
Invalid syntax in bad block list.
- INIT$_BADCLUSTER
Value for INIT$_CLUSTER_SIZE item code out of range.
- INIT$_BADDENS
Invalid value for INIT$_DENSITY item code.
- INIT$_BADDIRECTORIES
Value for INIT$_DIRECTORIES item code out of range.
- INIT$_BADEXTENSION
Value for INIT$_EXTENSION item code out of range.
- INIT$_BADHEADERS
Value for INIT$_HEADER item code out of range.
- INIT$_BADMAXFILES
Value for INIT$_MAXFILES item code out of range.
- INIT$_BADOWNID
Invalid value for owner ID.
- INIT$_BADRANGE
Bad block address not on volume.
- INIT$_BADVOL1
Bad VOL1 ANSI label.
- INIT$_BADVOLACC
Invalid value for INIT$_LABEL_ACCESS item code.
- INIT$_BADVOLLBL
Invalid value for ANSI tape volume label.
- INIT$_BADWINDOWS
Value for INIT$_WINDOWS item code out of range.
- INIT$_BLKZERO
Block 0 is bad—volume not bootable.
- INIT$_CLUSTER
Unsuitable cluster factor.
- INIT$_CONFQUAL
Conflicting options were specified.
- INIT$_DIAGPACK
Disk is a diagnostic pack.
- INIT$_ERASEFAIL
Volume not completely erased.
- INIT$_FACTBAD
Cannot read factory bad block data.
- INIT$_ILLOPT
Item codes not appropriate for the device were specified.
- INIT$_INDEX
Invalid index file position.
- INIT$_LARGECNT
Disk too large to be supported.
- INIT$_MAXBAD
Bad block table overflow.
- INIT$_MTLBLLONG
Magnetic tape label specified is longer than 6 characters.
- INIT$_MTLBLNONA
Magnetic tape label specified contains non-ANSI "a" characters.
- INIT$_NOBADDATA
Bad block data not found on volume.
- INIT$_NONLOCAL
Device is not a local device.
- INIT$_NOTRAN
Logical name cannot be translated.
- INIT$_NOTSTRUC1
Options not available with Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1.
- INIT$_UNKDEV
Unknown device type.
$IO_CLEANUP (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Clean Up Fast I/O — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, returns all resources allocated by $IO_SETUP. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$IO_CLEANUP fandleC Prototype
int sys$io_cleanup (unsigned __int64 fandl);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | fandle |
| type: | 64-bit integer (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
A fandle, passed by value, returned by a previous call to $IO_SETUP.
Description
The Clean Up Fast I/O system service returns various internal resources allocated by the $IO_SETUP system service. Buffer objects passed to $IO_SETUP cannot be deleted until every $IO_SETUP call has had a corresponding $IO_CLEANUP call.
Image rundown executes any required $IO_CLEANUP operations on behalf of the process.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$IO_PERFORM(W), $IO_SETUP
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_BADFANDLE
Argument was not a valid
fandle.- SS$_BUSY
The fandle cannot be cleaned up because an I/O is in progress. Reissue the call to $IO_CLEANUP after the I/O has finished.
$IO_FASTPATH (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Control Fast Path Devices — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, provides the ability to control the set of Fast Path devices and their assignment to CPUs enabled for Fast Path use.
Format
SYS$IO_FASTPATH
efn, cpu_mask,function_code, [iosb], [astadr], [astprm] [,[mask_length]]C Prototype
int sys$io_fastpath
(unsigned int efn, UINT32_PQ cpu_mask, int function_code,
struct_iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params),
__int64 astprm, ...);)Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | integer |
| type: | longword bit mask (unsigned) |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of the event flag to be set when the IO_FASTPATH(W) operation completes. The
efn argument is a longword containing the number of the event
flag.
| OpenVMS usage: | bitmap |
| type: | quadword bitmap |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The cpu_mask argument specifies a set of CPUs to be operated
upon.
| OpenVMS usage: | integer |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by value |
The function_code specifies the operation to be performed.
Note that there is currently only one function code:
FP$K_BALANCE_PORTS - Distribute Fast Path ports across CPUs.
| OpenVMS usage: | integer |
| type: | longword length |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by value |
The mask_length specifies the length of the cpu_mask bitmap in
bytes. If the mask_length is not supplied or is specified as
zero, a length of 4 bytes is used.
Description
The $IO_FASTPATH system service performs operations on the set of Fast Path devices and CPUs enabled for Fast Path use. The $IO_FASTPATHW system service completes synchronously. That is, it returns after the operation is complete.
The FP$K_BALANCE_PORTS function code specifies that the system service is to distribute
the set of system assignable Fast Path ports across the intersection of a caller-supplied
set of candidate CPUs (cpu_mask) and the current set of usable CPUs.
Usable CPUs are the intersection of the set of CPUs both enabled for Fast Path use by
IO$_PREFERRED_CPUS and whose current state is RUN.
The service does this by:
Eliminating all CPUs not in the set of usable CPUs from the set of candidate CPUs.
Restoring any user assigned ports that are not currently on the user's preferred CPU to the user's preferred CPU, if that CPU is in the set of usable CPUs.
Spreading the system assignable Fast Path ports, and any Fast Path ports whose user preferred CPU is unavailable, evenly across the set of usable candidate CPUs.
If the primary CPU is in the set of usable candidate CPUs, the distribution will be biased against the primary CPU in that a port will only be assigned to the primary after ports have been assigned to each of the other usable candidate CPUs.
Required Access or Privileges
PHYS_IO
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GETDVI, $QIO
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Unsupported value for cpu_mask.
- SS$_ILLIOFUNC
Illegal function code.
$IO_FASTPATHW
Control Fast Path Devices — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, performs operations on the set of Fast Path devices and CPUs enabled for Fast Path use. The $IO_FASTPATHW system service is functionally equivalent to the $IO_FASTPATH service except that it completes synchronously. That is, it returns after the operation is complete.
Format
SYS$IO_FASTPATHW
efn, cpu_mask, function_code, [iosb], [astadr], [astprm],
[,[mask_length]]C Prototype
int sys$io_fastpathw
(unsigned int efn, UINT32_PQ cpu_mask, int function_code,
struct_iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(_ _unknown_params),
_ _int64 astprm, ...);)$IO_PERFORM (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Perform Fast I/O — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, starts the Fast I/O operation. The $IO_PERFORM service completes asynchronously. For synchronous completion, use the Perform Fast I/O and Wait ($IO_PERFORMW) service. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$IO_PERFORM fandle ,chan ,iosadr ,bufadr ,buflen ,devdataC Prototype
int sys$io_perform
(unsigned __int64 fandl, unsigned short int chan, struct _iosa *iosadr,
void *bufadr, unsigned __int64 buflen, unsigned __int64 devdata);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | fandle |
| type: | 64-bit integer (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
A fandle returned by a previous call to $IO_SETUP.
| OpenVMS usage: | channel |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by value |
Software I/O channel number.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | address |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Address of the I/O Status Area (IOSA). This value cannot be 0; that is, an IOSA is required.
The iosadr must be aligned to a quadword boundary.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | address |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The process buffer address. Must be aligned on a 512-byte boundary.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | 64-bit integer |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The byte count for the I/O. The buflen argument must be a multiple of
512 bytes. Drivers have further limitations on the maximum size of an I/O
request.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | pointer or integer |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
A hardware integer passed unchanged to the driver. For disk devices, this is the media address for the transfer; that is, the virtual block number (VBN) for virtual I/O functions or the logical block number (LBN) for logical I/O functions. This argument is ignored for tape devices.
For drivers with complex parameters, devdata would be the address of a
descriptor or buffer specific to the device and function and would be documented with
the driver.
Description
The Perform Fast I/O system service initiates an I/O operation on the
channel number specified by the chan argument. The bytes
specified by the buflen argument are transferred between the
location (devdata) on the device driver and the user's buffer
starting at the process buffer address (bufadr). The byte count
is read or written according to the function code previously specified in the $IO_SETUP
call associated with the fandle argument.
Upon completion, the I/O status is written to the IOSA starting at the location specified by
iosadr, and an AST is delivered to the
astadr address supplied in the $IO_SETUP call associated with
fandle. The IOSA address is passed to the AST as the AST
parameter.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$IO_CLEANUP, $IO_SETUP, $IO_PERFORMW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_BADBUFADR
The data buffer does not reside within the bounds of the data buffer object for the fandle.
- SS$_BADIOSADR
The IOSA does not reside within the bounds of the IOSA buffer object for this fandle.
- SS$_FANDLEBUSY
The operation using this fandle is already in progress.
- SS$_IVCHAN
An invalid channel number was specified; that is, a channel number of 0 or a number larger than the number of channels available.
- SS$_UNALIGNED
The buffer specified by
bufadroriosadris not properly aligned.- SS$_WRONGACMODE
The request is invalid because the
fandlewas created from a more privileged access mode, or the channel was assigned from a more privileged access mode.
Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block
The VSI OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual lists these device-specific condition values for each device.
$IO_PERFORMW (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Perform Fast I/O and Wait — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, starts a Fast I/O operation. The $IO_PERFORMW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller after performing the Fast I/O operation. In all other respects, $IO_PERFORMW is identical to $IO_PERFORM. For all other information about the IO_PERFORMW service, see the description of $IO_PERFORM in this manual.
Format
SYS$IO_PERFORMW fandle ,chan ,iosadr ,bufadr ,buflen ,devdataC Prototype
int sys$io_performw
(unsigned __int64 fandl, unsigned short int chan, struct _iosa *iosadr,
void *bufadr, unsigned __int64 buflen, unsigned __int64 devdata);$IO_SETUP (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Set Up Fast I/O — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, allocates resources for Fast I/O. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$IO_SETUP func ,bufobj ,iosobj ,astadr ,flags ,return_fandleC Prototype
int sys$io_setup
(unsigned int func, struct _generic_64 *bufobj,
struct _generic_64 *iosobj, void (*astadr)(struct _iosa *),
unsigned int flags, unsigned __int64 *return_fandle);
Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | function_code |
| type: | longword |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
IO$_READVBLK
IO$_WRITEVBLK
IO$_READLBLK
IO$_WRITELBLK
Various function modifiers are supported, depending on the device and driver. Disk drivers support IO$M_NOVCACHE and IO$M_DATACHECK. Some tape devices support IO$M_REVERSE. Illegal modifiers are detected by the $IO_PERFORM(W) service.
| OpenVMS usage: | buffer object |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Handle describing the buffer object that contains the user's buffer. This identifier cannot be 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | object handle |
| type: | vector longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Buffer object handle describing the buffer object that contains the I/O Status Area (IOSA).
This might or might not be the same identifier as the bufobj
argument. This identifier cannot be 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Completion AST routine address (0, if none). There is no AST parameter
argument. When the AST routine is called, the AST parameter will be the address of the
IOSA for the operation. Applications can store data in the IOSA at offset
IOSA$IH_CONTEXT.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | 64-bit integer (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
flags argument is a bit vector in which each bit
corresponds to a flag. Flags are defined in the module IOSADEF. The following table
describes the flags that are valid for the $IO_SETUP service:|
Flag |
Description |
|---|---|
|
FIO$M_EXPEDITE |
This is a high priority I/O; that is, it is to be given preferential treatment by the I/O subsystem. Use of this bit requires ALTPRI or PHY_IO privilege. |
|
FIO$M_AST_NOFLOAT |
The AST procedure does not use, or call any procedure that uses, any floating-point registers. This is a performance option. If set, AST delivery will neither save nor restore floating-point registers. Caution: Use of floating-point registers when FIO$M_AST_NOFLOAT has been specified can cause unpredictable, difficult to detect, error conditions. |
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for future OpenVMS
use and should be specified as 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | fandle |
| type: | 64-bit integer (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Address of an aligned quadword to receive the handle for this I/O operation.
Description
The Set Up Fast I/O system service allocates and initializes a number of internal objects based on the parameters supplied. Because these objects are then ready for use when a subsequent $IO_PERFORM or $IO_PERFORMW is issued, the I/O operation will require less CPU time and fewer multiprocessor steps.
Required Privileges
If you use the flags argument FIO$M_EXPEDITE, a process must have
ALTPRI or PHY_IO privilege.
Required Quota
Byte count
Related Services
$IO_CLEANUP, $IO_PERFORM(W)
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The fandle does not have 8 bytes of writability, or the two buffer objects do not have 8 bytes of readability each.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Invalid flags options specified.
- SS$_EXBUFOBJLM
Buffer object cannot be created because it would bring the total number of buffer object pages above the systemwide limit MAXBOBMEM.
- SS$_ILLBUFOBJ
The buffer object is not valid.
- SS$_ILLIOFUNC
The function code is not valid.
- SS$_ILLMODIFIER
The I/O function modifier is not permitted.
- SS$_INSFMEM
There is no pool available from which to create a fandle vector, or the fandle vector is already full and an attempted expansion failed.
- SS$_INSFSPTS
Insufficient system page table entries.
- SS$_IVSTSFLG
The specified status flag is invalid.
- SS$_NOBUFOBJID
The process attempted to create a buffer object from user mode but was not holding required rights identifier VMS$BUFFER_OBJECT_USER.
- SS$_NOPRIV
Valid flag options were specified but from user mode.
- SS$_PAGNOTWRITE
A page within the address range is not writable.
- SS$_PAGOWNVIO
Page owner violation. The pages could not be put into the buffer object because the access mode associated with the call to $IO_SETUP was less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages. See $CREATE_BUFOBJ_64 for additional information.
- SS$_UNALIGNED
The I/O Status Area (IOSA) or data buffer is not aligned on a quadword boundary.
$JOIN_RM
JoinResourceManager — Adds a new Resource Manager (RM) participant to a transaction.
Format
SYS$JOIN_RM
[efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,rm_id
[,[tid] ,[part_name] ,[rm_context] ,[timout] ,[bid] ]C Prototype
int sys$join_rm
(unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int rm_id,...);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
flags argument
is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to an option flag. The $DDTMDEF
macro defines symbolic names for these option flags described in Table 4.
All undefined bits must be 0. If this argument is omitted, no flags are used.| Flag Name | Description |
|---|---|
| DDTM$M_COORDINATOR | Set this flag to specify that the new RM participant is to be a coordinator of the transaction on this node. |
| DDTM$M_SYNC | Specifies successful synchronous completion by returning SS$_SYNCH. When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the AST routine is not called, the event flag is not set, and the I/O status block is not filled in. |
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned section.
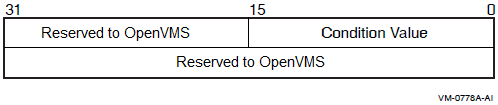
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure entry mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The AST routine that is executed when the service completes, if SS$_NORMAL is
returned in R0. The astadr argument is the address of the entry
mask of this routine. The routine is executed in the same access mode as that of the
caller of the $JOIN_RM service.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The AST parameter that is passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | identifier |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The identifier of the RMI with which the new RM participant is associated. This identifies:
Types of event that are to be reported to the new RM participant.
Event handler to which these event reports are to be delivered, and the access mode in which its ASTs are to be fired.
Minimum access mode that the new RM participant must be in to acknowledge one of these event reports by calling $ACK_EVENT.
Whether or not the DECdtm transaction manager may log information about the new RM participant.
| OpenVMS usage: | trans_id |
| type: | octaword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The identifier (TID) of the transaction to which the new RM participant is to be added.
If this argument is omitted (the default) or its value is zero, $JOIN_RM adds an RM participant to the default transaction of the calling process.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
The name of the new RM participant.
Used by recoverable resource managers to specify the RM participant to use in a subsequent call to $GETDTI or $SETDTI during recovery.
This argument has no effect if the RMI is volatile. If this argument is omitted (the default) or its value is zero, the name of the new RM participant is the same as that of the RMI with which it is associated.
The string passed in this argument can be no longer than 32 characters.
To ensure smooth operation in a mixed-network environment, refer to the chapter entitled Managing DECdtm Services in the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, for information on defining node names.
| OpenVMS usage: | userarg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The context associated with the new RM participant. This is passed in the event reports subsequently delivered to the new RM participant.
If this argument is omitted (the default) or is zero, the context associated with the new RM participant is the same as that of the RMI with which it is associated.
| OpenVMS usage: | date_time |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Reserved to OpenVMS.
| OpenVMS usage: | branch_id |
| type: | octaword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The identifier of an authorized branch (BID) that may be added to the transaction by
a subsequent call to $START_BRANCH on the same node as that of the RMI. This argument is
ignored if the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag is clear in the flags
argument. The call to $START_BRANCH should specify the node of the RMI for the
tm_name argument.
Description
Adds a new RM participant to the specified transaction. The new RM participant is associated with the RMI whose identifier is passed in the
rm_idargument.Introduces a new transaction to DECdtm if the new RM participant is a coordinator and the specified transaction is unknown to DECdtm.
Authorizes a new branch of the transaction if the new RM participant is a coordinator.
Preconditions for the successful completion of $JOIN_RM are:
Unless the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag is set, the calling process must contain at least one branch of the specified transaction.
The calling process must contain the specified RMI.
The caller must not be in a less privileged mode than the access mode of the specified RMI.
If the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag is set, either the calling process must have the SYSPRV privilege, or the caller must be in executive or kernel mode.
If the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag is set, the specified RMI must not be volatile. That is, the DDTM$M_VOLATILE flag must not have been set on the call to the $DECLARE_RM that created it.
The access mode of the specified RMI must not be less privileged than that of the specified transaction in this process.
$JOIN_RM can fail for various reasons, including:
Preconditions were not met.
The DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag was set, but no
bidargument was supplied.
When $JOIN_RM completes successfully, a new RM participant running in the calling process is added to the transaction. This RM participant is associated with the specified RMI.
The DECdtm transaction manager will report to the new RM participant the types of event specified in the call to $DECLARE_RM that created the RMI with which it is associated. Note however that events of type prepare, one-phase commit, and commit are never reported to RM participants that set the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag on the call to $JOIN_RM.
If the call to $DECLARE_RM requested prepare and one-phase commit events, and the $JOIN_RM call does not set the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag, the new RM participant is entitled to a vote on the outcome of the transaction.
If the $JOIN_RM call sets the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag, then the new RM participant is expected to initiate commit or abort processing by a call to $TRANS_EVENT. No events of type prepare, one-phase commit, or commit are delivered to the RM participant.
Events of type abort are reported to the RM participant.
The new RM participant is removed from the transaction when the first of the following conditions is met:
On successful completion of a call to $ACK_EVENT that acknowledges an event report delivered to that RM participant, if the event and its acknowledgment were one of those listed in the following table:
Event Acknowledgment (report_reply) Abort SS$_FORGET Commit SS$_FORGET or SS$_REMEMBER Prepare SS$_FORGET One-phase commit SS$_NORMAL or SS$_VETO On completion of a successful call to $TRANS_EVENT that specifies a commit or abort event, if the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag is set.
When a commit or abort event occurs, and no associated event report is delivered to the RM participant.
On successful completion of a call to $FORGET_RM that deletes the RMI with which it is associated.
When the current process terminates (normally or abnormally).
When the current image terminates (normally or abnormally).
If the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag is set:
A new branch is authorized for the transaction and its identifier is returned in the octaword that the
bidargument points to. $JOIN_RM uses the $CREATE_UID system service to generate the BID. No other call to $ADD_BRANCH, $JOIN_RM, or $CREATE_UID on any other node ever returns the same BID value.The transaction cannot commit until the new branch has been started by a matching call to $START_BRANCH. (See the description of $START_BRANCH for the definition of a matching call to $START_BRANCH.)
If the transaction is not already known to this process, then the transaction is introduced to this process with an access mode equal to the access mode of the caller. (See the description of $START_TRANS for a definition of the access mode of a transaction.)
There is also a wait form of the service, $JOIN_RMW.
Required Privileges
If the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag is set, then either the calling process must have the SYSPRV privilege or the caller must be in executive or kernel mode.
Required Quotas
BYTLM, ASTLM
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW, $CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW, $END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW, $GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW, $START_TRANS, $START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
If returned in R0, the request was successfully queued. If returned in the I/O status block, the service completed successfully.
- SS$_SYNCH
The service completed successfully and synchronously (returned only if the DDTM$M_SYNC flag is set).
- SS$_ACCVIO
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
- SS$_BADPARAM
The options flags were invalid, the specified
tidwas invalid, or DTM$M_COORDINATOR set but nobidsupplied.- SS$_EXASTLM
The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
The job buffered I/O byte limit quota (BYTLM) was exceeded.
- SS$_ILLEFC
The event flag number was invalid.
- SS$_INSFARGS
A required argument was missing.
- SS$_INSFMEM
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
- SS$_INVBUFLEN
The string passed in the
part_nameargument was too long.- SS$_NOSYSPRIV
The DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag was set and the caller was in user or supervisor mode but the calling process did not have the SYSPRV privilege.
- SS$_NOCURTID
An attempt was made to add a new participant to the default transaction (the
tidargument was zero or omitted) but the calling process did not have a default transaction.- SS$_NOSUCHTID
The DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag was clear and the calling process did not contain any branches in the transaction.
- SS$_NOSUCHRM
The calling process did not contain the specified RMI.
- SS$_WRONGACMODE
The caller was in a less privileged access mode than that of the RMI.
- SS$_WRONGSTATE
- The transaction was in the wrong state for the attempted operation because either:
An abort event had occurred for the transaction.
A call to $END_TRANS to end the transaction was in progress and it is too late to add a new RM participant to the transaction.
$JOIN_RMW
Join Resource Manager and Wait — Adds a new Resource Manager (RM) participant to a transaction. $JOIN_RMW always waits for the request to complete before returning to the caller. Other than this, it is identical to $JOIN_RM.
Format
SYS$JOIN_RMW
[efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,rm_id
[,[tid] ,[part_name] ,[rm_context] ,[timout] ,[bid] ]C Prototype
int sys$join_rmw
(unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int rm_id,...);$LCKPAG
Lock Pages in Memory — Locks a page or range of pages in memory. The specified virtual pages are forced into the working set and then locked in memory. A locked page is not swapped out of memory if the working set of the process is swapped out. These pages are not candidates for page replacement and in this sense are locked in the working set as well.
Format
SYS$LCKPAG inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode]C Prototype
int sys$lckpag
(struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr,
unsigned int acmode);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the range of pages to be locked. The
inadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array
containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses. Only the
virtual page number portion of each virtual address is used; the low-order
byte-within-page bits are ignored.
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Starting and ending process virtual addresses of the pages that $LCKPAG actually locked. The
retadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array
containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode to be associated with the pages to be locked. The acmode
argument is a longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines the four
access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. For the $LCKPAG service to complete successfully, the resultant access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the access mode already associated with the pages to be locked.
Description
The Lock Pages in Memory service locks a page or range of pages in memory. The specified virtual pages are forced into the working set and then locked in memory. A locked page is not swapped out of memory if the working set of the process is swapped out. These pages are not candidates for page replacement and in this sense are locked in the working set as well.
If more than one page is being locked and you need to determine specifically which pages were previously locked, the pages should be locked one at a time.
If an error occurs while the $LCKPAG service is locking pages, the return array, if requested, indicates the pages that were successfully locked before the error occurred. If no pages are locked, both longwords in the return address array contain the value –1.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, if you are attempting to lock executable code, you should issue multiple $LCKPAG calls: one to lock the code pages and others to lock the linkage section references into these pages.
Required Access or Privileges
The calling process must have PSWAPM privilege to lock pages into memory.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
You can unlock pages locked in memory with the Unlock Pages from Memory ($ULKPAG) service. Locked pages are automatically unlocked at image exit.
For more information, see the chapter on memory management in the VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were previously unlocked.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages was previously locked.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The input array cannot be read; the output array cannot be written; the page in the specified range is inaccessible or nonexistent; or an attempt to lock pages was made by a caller whose access mode is less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages.
- SS$_LCKPAGFUL
The system-defined maximum limit on the number of pages that can be locked in memory has been reached.
- SS$_LDWSETFUL
The locked working set is full. If any more pages are locked, not enough dynamic pages will be available to continue execution.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The process does not have the privilege to lock pages in memory.
- SS$_PAGOWNVIO
The pages could not be locked because the access mode associated with the call to $LCKPAG was less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages that were to be locked.
$LCKPAG_64 (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Lock Pages in Memory — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, locks a range of pages in memory. The specified virtual pages are forced into the working set and then locked in memory. A locked page is not swapped out of memory if the working set of the process is swapped out. These pages are not candidates for page replacement and, in this sense, are locked in the working set as well. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$LCKPAG_64
start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,return_va_64 ,return_length_64C Prototype
int sys$lckpag_64
(void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode,
void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address of the pages to be locked. The specified virtual address will be rounded down to a CPU-specific page boundary.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Length of the virtual address space to be locked. The specified length will be rounded up to a CPU-specific page boundary so that it includes all CPU-specific pages in the requested range.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode associated with the pages to be locked. The acmode argument
is a longword containing the access mode.
|
Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
PSL$C_KERNEL |
Kernel |
|
1 |
PSL$C_EXEC |
Executive |
|
2 |
PSL$C_SUPER |
Supervisor |
|
3 |
PSL$C_USER |
User |
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. For the $LCKPAG_64 service to complete successfully, the resultant access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the access mode already associated with the pages to be locked.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the pages locked in memory. The
return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of
a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns the virtual address.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns the length of the virtual address range locked in bytes.
Description
The Lock Pages in Memory service locks a range of pages in memory. The specified virtual pages are forced into the working set and then locked in memory. A locked page is not swapped out of memory if the working set of the process is swapped out. These pages are not candidates for page replacement and, in this sense, are locked in the working set as well.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments. If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned address
and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully locked before the error
occurred. If no pages were locked, the return_va_64 argument will
contain the value -1, and a value cannot be returned in the memory
location pointed to by the return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
A process must have PSWAPM privilege to call the $LCKPAG_64 service.
Required Quota
None.
Related Services
$LCKPAG, $ULKPAG, $ULKPAG_64
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were previously unlocked.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages was previously locked in the working set.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
return_va_64argument or thereturn_length_64argument cannot be written by the caller, or an attempt was made to lock pages by a caller whose access mode is less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages.- SS$_LCKPAGFUL
The system-defined maximum limit on the number of pages that can be locked in memory has been reached.
- SS$_LKWSETFUL
The locked working set is full. If any more pages are locked, not enough dynamic pages will be available to continue execution.
- SS$_NOPSWAPM
The process does not have the privilege to lock pages in memory.
- SS$_PAGOWNVIO
The pages could not be locked because the access mode associated with the call to $LCKPAG_64 was less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages that were to be locked.
$LKWSET
Lock Pages in Working Set — Locks a range of pages in the working set; if the pages are not already in the working set, it brings them in and locks them. A page locked in the working set does not become a candidate for replacement.
Format
SYS$LKWSET inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode]C Prototype
int sys$lkwset
(struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr,
unsigned int acmode);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the range of pages to be locked in the
working set. The inadr argument is the address of a 2-longword
array containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses. Only the
virtual page number portion of each virtual address is used; the low-order
byte-within-page bits are ignored.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, if the first address in the 2-longword array is within an image mapped to your process, the entire image specified by the address is locked in the working set.
Be sure to check calls to the SYS$LKWSET and SYS$LKWSET_64 system services for correct arguments. This affects only process-based code running above IPL2. Compiler and linker differences might cause your program layout to change from Alpha, resulting in incorrectly calculated starting and ending addresses for calls to SYS$LKWSET and SYS$LKWSET_64. Calling these services with incorrect arguments and then executing this code above IPL2 could cause PGFIPLHI bugchecks. Note that SYS$LKWSET and SYS$LKWSET_64 automatically lock linker-generated short data sections associated with code sections locked in the working set.
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Starting and ending process virtual addresses of the range of pages actually locked by
$LKWSET. The retadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array
containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, if the inadr argument
specifies an address within an image mapped to your process,
retadr specifies only one range of pages locked in the
working set. Many ranges of pages might be locked.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode to be associated with the pages to be locked. The acmode
argument is a longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines the four
access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. For the $LKWSET service to complete successfully, the resultant access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the access mode already associated with the pages to be locked.
Description
The Lock Pages in Working Set service locks a range of pages in the working set; if the pages are not already in the working set, it brings them in and locks them. A page locked in the working set does not become a candidate for replacement.
If more than one page is being locked and you need to determine specifically which pages were previously locked, the pages should be locked one at a time.
If an error occurs while the $LKWSET service is locking pages, the return array, if requested, indicates the pages that were successfully locked before the error occurred. If no pages are locked, both longwords in the return address array contain the value –1.
Global pages with write access cannot be locked into the working set.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, if the first address specified to SYS$LKWSET is within an image mapped to your process, a success status indicates that the entire image containing the specified address is locked in the working set. This behavior helps to ensure that privileged processes entering kernel mode and raising IPL higher than IPL 2 do not access an invalid page and cause a PGFIPLHI bugcheck. The system keeps a count of the number of times each image within your process is locked in the working set. This count is maintained so that calls to SYS$ULWSET unlock the image only when it has been called the same number of times as SYS$LKWSET.
If an attempt to lock an image in the working set returns SS$_LKWSETFUL, you might consider moving all kernel mode code within the image to a separate, smaller sharable image. Otherwise, you might consider increasing the working set quota of the process.
The LIBRTL routine LIB$LOCK_IMAGE and LIB$UNLOCK_IMAGE are preferable to SYS$LKWSET and SYS$ULKWSET for locking code and related data in the working set. For more information about locking images in the working set, see the LIBRTL manual and the descriptions of LIB$LOCK_IMAGE and LIB$UNLOCK_IMAGE.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
You can unlock pages locked in the working set with the Unlock Page from Working Set ($ULWSET) service.
For more information, see the chapter on memory management in the VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were previously unlocked. The entire image might have been locked in the working set.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages was previously locked in the working set. If the image has been locked in the working set, the count of times the image has been locked in the working set has been incremented.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The input address array cannot be read; the output address array cannot be written; a page in the specified range is inaccessible or nonexistent; or an attempt was made to lock pages by a caller whose access mode is less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages. If the image is being locked in the working set, the image is too large to be entirely locked in the working set.
- SS$_LKWSETFUL
The locked working set is full. If any more pages are locked, not enough dynamic pages will be available to continue execution.
- SS$_NOPRIV
A page in the specified range is in the system address space, or a global page with write access was specified.
- SS$_PAGOWNVIO
The pages could not be locked because the access mode associated with the call to $LKWSET was less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages that were to be locked.
$LKWSET_64 (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Lock Pages in Working Set — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, locks a range of virtual addresses in the working set; if the pages are not already in the working set, the service brings them in and locks them. A page locked in the working set does not become a candidate for replacement. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$LKWSET_64
start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,return_va_64 ,return_length_64C Prototype
int sys$lkwset_64
(void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode,
void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address of the pages to be locked in the working set. The specified virtual address will be rounded down to a CPU-specific page boundary.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Length of the virtual address space to be locked in the working set. The specified length will be rounded up to a CPU-specific page boundary so that it includes all CPU-specific pages in the requested range.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode associated with the pages to be locked. The acmode argument
is a longword containing the access mode.
|
Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
PSL$C_KERNEL |
Kernel |
|
1 |
PSL$C_EXEC |
Executive |
|
2 |
PSL$C_SUPER |
Supervisor |
|
3 |
PSL$C_USER |
User |
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. For the $LKWSET_64 service to complete successfully, the resultant access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the access mode already associated with the pages to be locked.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the pages locked in the working set. The
return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of
a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns the virtual address.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the virtual address range locked in the working set. The
return_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns the length of the
virtual address range in bytes.
Description
The Lock Pages in Working Set service locks a range of pages in the working set; if the pages are not already in the working set, it brings them in and locks them. A page locked in the working set does not become a candidate for replacement.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments. If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned address
and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully locked before the error
occurred. If no pages were locked, the return_va_64 argument will
contain the value -1, and a value cannot be returned in the memory
location pointed to by the return_length_64 argument.
Global pages with write access cannot be locked into the working set.
Be sure to check calls to the SYS$LKWSET and SYS$LKWSET_64 system services for correct arguments. This affects only process-based code running above IPL2. Compiler and linker differences might cause your program layout to change from Alpha, resulting in incorrectly calculated starting and ending addresses for calls to SYS$LKWSET and SYS$LKWSET_64. Calling these services with incorrect arguments and then executing this code above IPL2 could cause PGFIPLHI bugchecks. Note that SYS$LKWSET and SYS$LKWSET_64 automatically lock linker-generated short data sections associated with code sections locked in the working set.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, if the first address specified to SYS$LKWSET_64 is within an image mapped to your process, a success status indicates that the entire image containing the specified address is locked in the working set. This behavior helps to ensure that privileged processes entering kernel mode and raising IPL higher than IPL 2 do not access an invalid page and cause a PGFIPLHI bugcheck. The system keeps a count of the number of times each image within your process is locked in the working set. This count is maintained so that calls to SYS$ULWSET_64 unlock the image only when it has been called the same number of times as SYS$LKWSET_64.
If an attempt to lock an image in the working set returns SS$_LKWSETFUL, you might consider moving all kernel mode code within the image to a separate, smaller sharable image. Otherwise, you might consider increasing the working set quota of the process.
The LIBRTL routine LIB$LOCK_IMAGE and LIB$UNLOCK_IMAGE are preferable to SYS$LKWSET_64 and SYS$ULKWSET_64 for locking code and related data in the working set. For more information about locking images in the working set, see the LIBRTL manual and the descriptions of LIB$LOCK_IMAGE and LIB$UNLOCK_IMAGE.
Required Privileges
None.
Required Quota
None.
Related Services
$LKWSET, $ULWSET, $ULWSET_64
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were previously unlocked. The entire image might have been locked in the working set.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages was previously locked in the working set. If the image has been locked in the working set, the count of times the image has been locked in the working set has been incremented.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
return_va_64orreturn_length_64argument cannot be written by the caller, or an attempt was made to lock pages by a caller whose access mode is less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages.- SS$_LKWSETFUL
The locked working set is full. If any more pages are locked, not enough dynamic pages will be available to continue execution. If the image is being locked in the working set, the image is too large to be entirely locked in the working set.
- SS$_NOPRIV
No privilege; global pages with write access cannot be locked into the working set.
- SS$_PAGNOTINREG
A page in the specified range is not within the specified region.
- SS$_PAGOWNVIO
The pages could not be locked because the access mode associated with the call to $LKWSET_64 was less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages that were to be locked.
$MGBLSC
Map Global Section — Establishes a correspondence between pages (maps) in the virtual address space of the process and physical pages occupied by a global section.
Format
SYS$MGBLSC
inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode] ,[flags] ,gsdnam ,[ident] ,[relpag]C Prototype
int sys$mgblsc
(struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr,
unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, void *gsdnam,
struct _secid *ident, unsigned int relpag);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Starting and ending virtual addresses into which the section is to be mapped. The
inadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array
containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses. Only the
virtual page number portion of each virtual address is used to specify which pages are
to be mapped; the low-order byte-within-page bits are ignored for this purpose.
The interpretation of the inadr argument depends on the setting
of SEC$M_EXPREG in the flags argument and on whether you are
using an Alpha or an Integrity servers system. These system types are discussed
separately in this section.
Alpha and Integrity servers System Usage
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, if you do not set the
SEC$M_EXPREG flag, the inadr argument specifies the starting and
ending virtual addresses of the region to be mapped. Addresses in system space are not
allowed. The addresses must be aligned on CPU-specific pages; no rounding to
CPU-specific pages occurs. The lower address of the inadr
argument must be on a CPU-specific page boundary and the higher address of the
inadr argument must be 1 less than a CPU-specific boundary,
thus forming a range, from lowest to highest, of address bytes. You can use the
SYI$_PAGE_SIZE item code in the $GETSYI system service to set the
inadr argument to the proper values. You do this to avoid
programming errors that might arise because of incorrect programming assumptions about
page sizes.
inadr argument is used only to indicate
the desired region: the program region (P0) or the control region (P1).Caution
Mapping into the P1 region is generally discouraged, but, if done, must be executed with extreme care. Since the user stack is mapped in P1, it is possible that references to the user stack might inadvertently read or write the pages mapped with $CRMPSC.
When the SEC$M_EXPREG flag is set, the second inadr longword is
ignored, while bit 30 (the second most significant bit) of the first
inadr longword is used to determine the region of choice. If
the bit is clear, P0 is chosen; if the bit is set, P1 is chosen. On Alpha and Integrity
server systems, bit 31 (the most significant bit) of the first
inadr longword must be 0. To ensure
compatibility between Alpha and Integrity server systems when you choose a region, VSI
recommends that you specify, for the first inadr longword, any
virtual address in the desired region.
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Starting and ending process virtual addresses into which the section was actually mapped by
$MGBLSC. The retadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array
containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, the retadr argument returns the
starting and ending addresses of the usable range of
addresses. This might differ from the total amount mapped. The
retadr argument is required when the
relpag argument is specified. If the section being mapped
does not completely fill the last page used to map the section, the
retadr argument indicates the highest address that actually
maps the section. If the relpag argument is used to specify an
offset into the section, the retadr argument reflects the
offset.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode to be associated with the pages mapped into the process virtual address space. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access mode. The
$PSLDEF macro defines symbols for the four access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Flag mask specifying options for the operation. The flags argument is a
longword bit vector wherein a bit when set specifies the corresponding option.
flags argument by specifying the symbolic names of each
desired option in a logical OR operation. The following table describes each flag option.|
Flag Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
SEC$M_WRT |
Map the section with read/write access. By default, the section is mapped with read-only access. If SEC$M_WRT is specified and the section is not copy-on-reference, write access is required. |
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL |
Map a system global section. By default, the section is a group global section. |
|
SEC$M_EXPREG |
Map the section into the first available virtual address
range. By default, the section is mapped into the range
specified by the See the |
|
SEC$M_UNCACHED |
Flag that must be set when a PFN-mapped section is created if this section must be treated as uncached memory. Flag is ignored on Alpha systems; it applies only to Integrity server systems. |
| OpenVMS usage: | section_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gsdnam argument is the address of a
character string descriptor pointing to this name string.
For group global sections, the operating system interprets the group UIC as part of the global section name; thus, the names of global sections are unique to UIC groups. Further, all global section names are implicitly qualified by their identification fields.
You can specify any name from 1 to 43 characters. All processes mapping to the same global section must specify the same name. Note that the name is case sensitive.
Use of characters valid in logical names is strongly encouraged. Valid values include alphanumeric characters, the dollar sign ($), and the underscore (_). If the name string begins with an underscore (_), the underscore is stripped and the resultant string is considered to be the actual name. Use of the colon (:) is not permitted.
Names are first subject to a logical name translation, after the application of the prefix GBL$ to the name. If the result translates, it is used as the name of the section. If the resulting name does not translate, the name specified by the caller is used as the name of the section.
Additional information on logical name translations and on section name processing is available in the VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
| OpenVMS usage: | section_id |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section and, for processes
mapping to an existing global section, the criteria for matching the identification. The
ident argument is the address of a quadword structure
containing three fields.
|
Value/Name |
Match Criteria |
|---|---|
|
0 SEC$K_MATALL |
Match all versions of the section. |
|
1 SEC$K_MATEQU |
Match only if major and minor identifications match. |
|
2 SEC$K_MATLEQ |
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor identification of the global section. |
The version number is in the second longword and contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits.
If you do not specify ident or specify it as the value 0 (the default),
the version number and match control fields default to the value 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Relative page number within the section of the first page to be mapped. The
relpag argument is a longword containing this number.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, the relpag argument is
interpreted as an index into the section file, measured in pagelets for a file-backed
section or CPU-specific pages for a PFN-mapped section.
On Alpha, Integrity servers systems, if you do not specify
relpag or specify it as the value 0 (the default), the global
section is mapped beginning with the first virtual block in a file-backed section or the
first CPU-specific page in a PFN-mapped section.
Description
The Map Global Section service establishes a correspondence between pages (maps) in the virtual address space of the process and physical pages occupied by a global section. The protection mask specified at the time the global section is created determines the type of access (for example, read/write or read only) that a particular process has to the section.
When $MGBLSC maps a global section, it adds pages to the virtual address space of the process. The section is mapped from a low address to a high address, whether the section is mapped in the program or control region.
If an error occurs during the mapping of a global section, the return address array, if specified, indicates the pages that were successfully mapped when the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, both longwords of the return address array contain the value –1.
Required Access or Privileges
Read access is required. If the SEC$M_WRT flag is specified, write access is required.
Required Quota
The working set quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to accommodate the increased size of the virtual address space when the $MGBLSC service maps a section.
If the section pages are copy-on-reference, the process must also have sufficient paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA).
This system service causes the working set of the calling process to be adjusted to the size specified by the working set quota (WSQUOTA). If the working set size of the process is less than quota, the working set size is increased; if the working set size of the process is greater than quota, the working set size is decreased.
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC, $UPDSECW
For more information, see the chapter on memory management in the VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The input address array, the global section name or name descriptor, or the section identification field cannot be read by the caller; or the return address array cannot be written by the caller.
- SS$_ENDOFFILE
The starting virtual block number specified is beyond the logical end-of-file.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
The process exceeded its paging file quota, creating copy-on-reference pages.
- SS$_INSFWSL
The working set limit of the process is not large enough to accommodate the increased virtual address space.
- SS$_INVARG
Invalid argument specified to service. Common sources are the incorrect specification of
relpagor the values in theinadrarray.- SS$_IVLOGNAM
The global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43 characters.
- SS$_IVSECFLG
You set a reserved flag.
- SS$_IVSECIDCTL
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The file protection mask specified when the global section was created prohibits the type of access requested by the caller; or a page in the input address range is in the system address space.
- SS$_NOSHPTS
The region ID of a shared page-table region was specified.
- SS$_NOSUCHSEC
The specified global section does not exist.
- SS$_PAGOWNVIO
A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more privileged access mode.
- SS$_SECREFOVF
The maximum number of references for a global section has been reached (2,147,483,647).
- SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
Logical name translation of the
gsdnamstring exceeded the allowed depth.- SS$_VA_IN_USE
The existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated with a buffer object.
- SS$_VASFULL
The virtual address space of the process is full; no space is available in the page tables for the pages created to contain the mapped global section.
$MGBLSC_64 (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Map to Global Section — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, establishes a correspondence between pages in the virtual address space of the process and the pages occupied by a global disk file, page file, or demand-zero section and can map to a demand-zero section with shared page tables. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$MGBLSC_64
gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,region_id_64 ,section_offset_64 ,length_64
,acmode ,flags ,return_va_64 ,return_length_64 [,start_va_64]C Prototype
int sys$mgblsc_64
(void *gsdnam_64, struct _secid *ident_64,
struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, unsigned __int64 section_offset_64,
unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags,
void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64,...);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | section_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument is the 32- or
64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32-bit or 64-bit string descriptor
pointing to this name string.
You can specify any name from 1 to 43 characters. All processes mapping to the same global section must specify the same name. Note that the name is case sensitive.
Use of characters valid in logical names is strongly encouraged. Valid values include alphanumeric characters, the dollar sign ($), and the underscore (_). If the name string begins with an underscore (_), the underscore is stripped and the resultant string is considered to be the actual name. Use of the colon (:) is not permitted.
Names are first subject to a logical name translation, after the application of the prefix GBL$ to the name. If the result translates, it is used as the name of the section. If the resulting name does not translate, the name specified by the caller is used as the name of the section.
Additional information on logical name translations and on section name processing is available in the VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
| OpenVMS usage: | section_id |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section. The
ident_64 argument is a quadword containing three fields. The
ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a
naturally aligned quadword that contains the identification value.
The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order two bits.
|
Value |
Symbolic Name |
Match Criteria |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
SEC$K_MATALL |
Match all versions of the section. |
|
1 |
SEC$K_MATEQU |
Match only if major and minor identifications match. |
|
2 |
SEC$K_MATLEQ |
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor identification of the global section. |
If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0, the version number and match
control fields default to 0.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a section is created, processes that specify a version number when mapping cannot access the global section.
| OpenVMS usage: | region identifier |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to map the global section. The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three default regions in P0, P1, and P2 space.
|
Symbol |
Region |
|---|---|
|
VA$C_P0 |
Program region |
|
VA$C_P1 |
Control region |
|
VA$C_P2 |
64-bit program region |
Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can be specified.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte offset |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Offset into the global section at which to start mapping into the process's virtual address space.
If a map to a global disk file section is being requested, the
section_offset_64 argument specifies an even multiple of disk
blocks. If a map to a global page file or demand-zero section is being requested, the
section_offset_64 argument specifies an even multiple of
CPU-specific pages. If zero is specified, the global section is mapped beginning with
the first page of the section.
If the region_id_64 argument specifies a shared page table region,
section_offset_64 must be an even multiple of pages mapped by
a page table page.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Length, in bytes, of the desired mapping of the global disk file section.
If a map to a global section is being requested, the
length_64 argument must specify an even multiple of disk blocks. If a map to a global page file or demand-zero section is being requested, the
length_64 argument must specify an even multiple of CPU-specific pages. If zero is specified, the size of the disk file is used.
If a shared page-table region is specified by the region_id_64
argument, length_64 must be an even multiple of the number of
bytes that can be mapped by a CPU-specific page-table page or must include the last page
within the memory-resident global section.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the mapping. This is also the
read access mode and, if the SEC$M_WRT flag is specified, the write access mode. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
|
Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
PSL$C_KERNEL |
Kernel |
|
1 |
PSL$C_EXEC |
Executive |
|
2 |
PSL$C_SUPER |
Supervisor |
|
3 |
PSL$C_USER |
User |
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create mode associated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. The condition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is less privileged than the create mode for the region.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Flag mask specifying options for the operation. The flags argument is a
longword bit vector in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and the
SECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct the
flags argument by performing a logical OR operation on the
symbol names for all desired flags.
|
Flag |
Description |
|---|---|
|
SEC$M_EXPREG |
Pages are mapped into the first available space at the current end of the specified region. If /ALLOCATE was specified when the memory-resident global section was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, virtually aligned addresses after the first available space are chosen for the mapping. It the |
|
SEC$M_GBL |
Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. |
|
SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP |
Pages cannot overmap existing address space. |
|
SEC$M_SHMGS |
On OpenVMS Galaxy systems, create a shared-memory global section. |
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL |
The global section map is a system global section. By default, the section is a group global section. |
|
SEC$M_WRT |
Map the section with read/write access. |
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for future OpenVMS use and should be specified as 0. The condition value SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an attempt is made to use the SEC$M_PAGFIL flag, which applies only to the creation of a page-file backed section.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The process virtual address into which the global disk or page file section was mapped. The address.
Upon successful completion of this service, if the section_offset_64
argument was specified, the virtual address returned in the
return_va_64 argument reflects the offset into the global
section mapped such that the virtual address returned cannot be aligned on a
CPU-specific page boundary. The virtual address returned will always be on an even
virtual disk block boundary.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the usable virtual address range mapped. The
return_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns the length of the
virtual address range mapped in bytes.
Upon successful completion of this service, the value in the
return_length_64 argument might differ from the total amount
of virtual address space mapped. The value in the return_va_64
argument plus the value in the return_length_64 argument
indicates the address of the first byte beyond the end of the mapping of the global disk
file section.
If the value in the section_offset_64 argument plus the value in the
length_64 argument did not specify to map the entire global
section, this byte can be located at an even virtual disk block boundary within the last
page of the mapping.
If the section being mapped does not completely fill the last page used to represent the global disk file section, this byte can be mapped into your address space; however, it is not backed up by the disk file.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address to which to map the global section. The specified virtual address
must be a CPU-specific page-aligned address. If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, the
start_va_64 argument must not be specified or must be
specified as 0. If SEC$M_EXPREG is set and the start_va_64
argument is nonzero, the condition value SS$_IVSECFLG is returned.
If the region_id_64 argument specifies a shared page-table region,
start_va_64 must be aligned to a CPU-specific page-table page
boundary.
Description
The Map to Global Section service establishes a correspondence between pages in the virtual address space of the process and pages occupied by a global disk file, page file, or memory-resident demand-zero secton. This service adds pages to the virtual address space of the process.
If a global disk file or page file backed section is being mapped, invalid page table entries are placed in the process page table.
If a memory-resident global section is being mapped, global pages are not charged against the process's working set quota when the virtual memory is referenced and the global pages are not charged against the process's pagefile quota.
If the memory-resident global section was not registered in the Reserved Memory Registry or /NOALLOCATE was specified when the global section was registered, invalid page table entries are placed in the process page table.
If the memory-resident global section was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry and /ALLOCATE was specified when the memory-resident global section was registered, valid page table entries are placed in the process page tables.
If a global disk file or page file backed section is being mapped and the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set, the first free virtual address within the specified region is used to start mapping to the global section.
Specify a shared page table region in the
region_id_64argument.Specify SEC$M_WRT in the
flagsargument.Set the flag SEC$M_EXPREG or provide a CPU-specific page-table page-aligned virtual address in the
start_va_64argument.Specify a CPU-specific page-table page-aligned value for the
section_offset_64argument or zero.Specify a value for the
map_length_64 argumentthat is an even multiple of bytes mapped by a CPU-specific page-table page, or include the last page of the section or zero.
See the description of $CREATE_REGION_64 for information about calculating virtual addresses that are aligned to a CPU-specific page table page boundary.
|
Global Section Created with Shared Page Tables |
Shared Page-Table Region Specified by
|
Type of Page Tables Used in Mapping |
|---|---|---|
|
No |
No |
Private |
|
No |
Yes |
Private |
|
Yes |
No |
Private |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Shared |
In general, if the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set, the first free virtual address within the specified region is used to map to the global section.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set, a memory-resident global section is being mapped and
the region_id_64 argument indicates a shared page-table region,
the first free virtual address within the specified region is rounded up to a
CPU-specific page-table page boundary and used to map to the global section.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set and the /ALLOCATE qualifier was specified with the SYSMAN command RESERVED_MEMORY ADD for the memory-resident global section, the first free virtual address within the specified region is rounded up to the same virtual alignment as the physical alignment of the preallocated pages and used to map to the global section. Granularity hints are set appropriately for each process private page-table entry (PTE).
In general, if the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is clear, the virtual address in the
start_va_64 argument is used to map to the global
section.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is clear and a memory-resident global section is being
mapped, the value specified in the start_va_64 argument can
determine if the mapping is possible and if granularity hints are used in the private
page tables. If a shared page-table region is specified by the
region_id_64 argument, the virtual address specified by the
start_va_64 argument must be on an even CPU-specific
page-table page boundary or an error is returned by this service. If the
region_id_64 argument does not specify a shared page-table
region and the /ALLOCATE qualifier was specified with the SYSMAN command RESERVED_MEMORY
ADD for this global section, granularity hints are used only if the virtual alignment of
start_va_64 is appropriate for the use of granularity
hints:
On Alpha systems, granularity hints mean multiples of pages, regardless of page size. The multiples 8, 64, and 512 pages are architected.
On Integrity server systems, OpenVMS initially supports page sizes of 64KB, 256KB, and 4MB instead of granularity hints. Additional pages sizes will be supported in the future.
Whenever granularity hints are being used within the mapping of a memory-resident
global section, if the length_64 argument is not an exact
multiple of the alignment factor, lower granularity hints factors are used as
appropriate at the higher addressed portion of the global section. If the
section_offset_64 argument is specified, a lower granularity
hint factor can be used throughout the mapping of the global section to match the
physical alignment of the first page mapped.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned address and
returned length indicate the pages that were successfully mapped before the error
occurred. If no pages were mapped, the return_va_64 argument
contains the value –1.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
If private page tables are used to map to the global section, the working set limit quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to accommodate the increased size of the process page tables required by the increase in virtual address space when the section is mapped.
If private page tables are used to map to a memory-resident global section, the pagefile quota (PGFLQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to accommodate the increased size of the process page tables required by the increase in virtual address space.
If the process is mapping to a global copy-on-reference section, the pagefile quota (PGFLQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to accommodate the increased size of the virtual address space.
Related Services
$CREATE_GDZRO, $CREATE_GFILE, $CREATE_GPFILE, $CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC_GDZRO_64, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64, $DELETE_REGION_64, $DELTVA_64, $LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64, $MGBLSC, $MGBLSC_GPFN_64, $PURGE_WS, $ULKPAG_64, $ULWSET_64, $UPDSEC_64, $UPDSEC_64W
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
gs_name_64argument cannot be read by the caller, or thereturn_va_64argument or thereturn_length_64argument cannot be written by the caller.- SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA
The process's page file quota is not large enough to accommodate the increased virtual address space.
- SS$_GBLSEC_MISMATCH
Global section type mismatch. The specified global section was found; however, it is not a global disk-file, page-file, or demand-zero section.
- SS$_INSFWSL
The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the increased virtual address space.
- SS$_IVACMODE
The specified access mode is greater than PSL$_USER or the caller's mode is less privileged than the create mode associated with the region. Or, if a shared page table region is specified by the
region_id_64argument, theacmodeargument does not match the access mode of the shared PTEs.- SS$_IVLOGNAM
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43 characters.
- SS$_IVREGID
An invalid region ID was specified.
- SS$_IVSECFLG
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags was specified.
- SS$_IVSECIDCTL
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
- SS$_LEN_NOTBLKMULT
The
length_64argument is not a multiple of virtual disk blocks if a map to a global section was requested (SEC$M_PAGFIL is clear in the flags argument).- SS$_LEN_NOTPAGMULT
The
length_64argument is not a multiple of CPU-specific pages and a map to a global page file section was requested.- SS$_NOSHPTS
The region ID of a shared page-table region was specified, and a global section was specified that is not a memory-resident demand-zero section.
- SS$_NOSHPTS
The region ID of a shared page table region was specified.
- SS$_NOSUCHSEC
The specified global section does not exist.
- SS$_OFF_NOTPAGALGN
The
section_offset_64argument is not CPU-specific page aligned if a map to a global page-file or demand-zero section is requested. Or, if a shared page table region is specified by theregion_id_64argument, thesection_offset_64argument is not CPU-specific page-table page aligned.- SS$_OFFSET_TOO_BIG
The
section_offset_64argument specified is beyond the logical end-of-file.- SS$_PAGNOTINREG
A page in the specified input address range is not within the specified region.
- SS$_PAGOWNVIO
A page in the specified input address range already exists and cannot be deleted because it is owned by a more privileged access mode.
- SS$_PROTVIO
The file protection mask specified when the global section was created prohibits the type of access requested by the caller.
- SS$_REGISFULL
The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the region for the pages created to contain the mapped section.
- SS$_SECREFOVF
The maximum number of references for a global section has been reached (2,147,483,647).
- SS$_SECTBLFUL
There are no entries available in the system global section table.
- SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
The logical name translation of the
gs_name_64argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10.- SS$_VA_IN_USE
A page in the specified input address range is already mapped and the flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or a page in the specified input address range is in another region, in system space, or inaccessible; or, the existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated with a buffer object.
- SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN
The
start_va_64argument is not CPU-specific page aligned. Or, if a shared page table region is specified by theregion_id_64argument, thestart_va_64argument is not CPU-specific page-table page aligned.- SS$_NOWRTACC
The specified global section is not copy-on-reference and does not allow write access.
$MGBLSC_GPFN_64 (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Map Global Page Frame Section — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, establishes a correspondence between pages in the virtual address space of the process and the pages occupied by a global page frame section. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$MGBLSC_GPFN_64
gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,region_id_64 ,relative_page ,page_count ,acmode
,flags ,return_va_64 ,return_length_64 [,start_va_64]C Prototype
int sys$mgblsc_gpfn_64
(void *gsdnam_64, struct _secid *ident_64,
struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, unsigned int relative_page,
unsigned int page_count, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags,
void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64,...);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | section_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor pointing to this name
string.
You can specify any name from 1 to 43 characters. All processes mapping to the same global section must specify the same name. Note that the name is case sensitive.
Use of characters valid in logical names is strongly encouraged. Valid values include alphanumeric characters, the dollar sign ($), and the underscore (_). If the name string begins with an underscore (_), the underscore is stripped and the resultant string is considered to be the actual name. Use of the colon (:) is not permitted.
Names are first subject to a logical name translation, after the application of the prefix GBL$ to the name. If the result translates, it is used as the name of the section. If the resulting name does not translate, the name specified by the caller is used as the name of the section.
Additional information on logical name translations and on section name processing is available in the VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
| OpenVMS usage: | section_id |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section. The
ident_64 argument is a quadword containing three fields. The
ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a
naturally aligned quadword that contains the identification value.
|
Value |
Symbolic Name |
Match Criteria |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
SEC$K_MATALL |
Match all versions of the section. |
|
1 |
SEC$K_MATEQU |
Match only if major and minor identifications match. |
|
2 |
SEC$K_MATLEQ |
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor identification of the global section. |
If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0, the version number and match
control fields default to 0.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a section is created, processes that specify a version number when mapping cannot access the global section.
| OpenVMS usage: | region identifier |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
|
Symbol |
Region |
|---|---|
|
VA$C_P0 |
Program region |
|
VA$C_P1 |
Control region |
|
VA$C_P2 |
64-bit program region |
Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can be specified.
| OpenVMS usage: | CPU-specific page count |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Relative CPU-specific page number within the global section to start mapping.
| OpenVMS usage: | CPU-specific page count |
| type: | longword (unsigned) on Alpha, quadword (unsigned) on Integrity servers |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Length of mapping in CPU-specific pages. If zero is specified, the global page frame section is mapped to the end of the section.
| OpenVMS usage: | access-mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode to be associated with the pages mapped into the process virtual address space. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access mode. The
$PSLDEF macro defines symbols for the four access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create mode associated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. The condition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is less privileged than the create mode for the region.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Flag mask specifying options for the operation. The flags argument is a
longword bit vector in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and the
SECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct the
flags argument by performing a logical OR operation on the
symbol names for all desired flags.
|
Flag |
Description |
|---|---|
|
SEC$M_ARGS64 | Indicates that all parameters, specifically
start_pfn and
page_count, are passed as 64-bit numbers.
This flag is ignored on OpenVMS Alpha but must be set on Integrity
server systems. If the flag is not set on Integrity servers, the
error code SS$_IVSECFLG is returned. |
|
SEC$M_GBL |
Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. |
|
SEC$M_EXPREG |
Map the section into the first available space at the current
end of the specified region. If this flag is specified, the
|
|
SEC$M_PERM |
Pages are permanent. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. |
|
SEC$M_PFNMAP |
Pages form a page frame section. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. |
|
SEC$M_PAGFIL |
Pages form a global page-file section. SEC$M_PAGFIL also implies SEC$M_WRT and SEC$M_DZRO. |
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL |
Map a system global section. By default, the section is a group global section. |
|
SEC$M_UNCACHED |
Flag accepted but ignored on Integrity server systems. The cached/uncached characteristic is stored as a section attribute, and the system uses this attribute when the section is mapped. Refer to this flag in the documentation of the SYS$CREATE_GPFN system service. |
|
SEC$M_WRT |
Map the section with read/write access. By default, the section is mapped with read-only access. If SEC$M_WRT is specified, write access is required. |
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for future OpenVMS
use and should be specified as 0. The condition value SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any
undefined bits are set or if an illegal combination of flags is set.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address into which the global page frame section was mapped. The
return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of
a naturally aligned quadword that contains the virtual address.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the $MGBLSC_GPFN_64 service returns the length of the virtual address range in bytes.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address to map the global section. The specified virtual address must be
a CPU-specified page-aligned address. If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, the
start_va_64 argument must not be specified or must be
specified as 0. If SEC$M_EXPREG is set and the start_va_64
argument is nonzero, the condition value SS$_IVSECFLG is returned.
Always refer to the return_va_64 and
return_length_64 arguments to determine the range of virtual
addresses mapped.
Description
The Map Global Page Frame Section service establishes a correspondence between pages in the virtual address space of the process and pages occupied by a global page frame section. It adds pages to the virtual address space of the process.
Pages mapped to a global page frame section are not included in or charged against the process's working set; they are always valid. Do not lock these pages in the working set by using $LKWSET; this can result in a machine check if they are in I/O space.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned address and returned
length indicate the pages that were successfully mapped before the error occurred. If no
pages were mapped, the return_va_64 argument will contain the
value -1, and a value cannot be returned in the memory location
pointed to by the return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
Read access is required. If the SEC$M_WRT flag is specified, write access is required.
Required Quota
The working set quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to accommodate the increased length of the process page table required by the increase in virtual address space.
The page file quota (PAGFLQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to accommodate the increased number of process page tables required by the increase in virtual address space. (Note that this service can return the SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA.)
Related Services
$CREATE_GPFN, $CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64, $DELTVA_64, $MGBLSC, $MGBLSC_64
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
gs_name_64argument cannot be read by the caller, or thereturn_va_64orreturn_length_64argument cannot be written by the caller.- SS$_GBLSEC_MISMATCH
Global section type mismatch. The specified global section was found; however, it is not a global page frame section.
- SS$_ILLRELPAG
The specified relative page argument is either larger than the highest page number within the section or is not a valid 32-bit physical page frame number.
- SS$_INSFWSL
The working set limit of the process is not large enough to accommodate the increased virtual address space.
- SS$_IVACMODE
The caller's mode is less privileged than the create mode associated with the region.
- SS$_IVLOGNAM
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43 characters.
- SS$_IVREGID
Invalid region ID specified.
- SS$_IVSECFLG
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags was specified.
- SS$_IVSECIDCTL
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
- SS$_NOSUCHSEC
The specified global section does not exist.
- SS$_NOWRTACC
The specified global section is not copy-on-reference and does not allow write access.
- SS$_PROTVIO
The file protection mask specified when the global section was created prohibits the type of access requested by the caller.
- SS$_PAGNOTINREG
A page in the specified range is not within the specified region.
- SS$_PAGOWNVIO
A page in the specified range already exists and cannot be deleted because it is owned by a more privileged access mode than that of the caller.
- SS$_REGISFULL
The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the region for the pages created to contain the mapped global section.
- SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
The logical name translation of the
gs_name_64argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10.- SS$_VA_IN_USE
The existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated with a buffer object.
- SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN
The
start_va_64argument is not CPU-specific page aligned.
$MOD_HOLDER
Modify Holder Record in Rights Database — Modifies the specified holder record of the target identifier in the rights database.
Format
SYS$MOD_HOLDER id ,holder ,[set_attrib] ,[clr_attrib]C Prototype
int sys$mod_holder
(unsigned int id, struct _generic_64 *holder, unsigned int set_attrib,
unsigned int clr_attrib);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | rights_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Binary value of target identifier whose holder record is modified when $MOD_HOLDER completes
execution. The id argument is a longword containing the
identifier value.
| OpenVMS usage: | rights_holder |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Identifier of holder being modified when $MOD_HOLDER completes execution. The
holder argument is the address of a quadword containing the UIC identifier of the holder in the first longword and the value of 0 in the second longword.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Bit mask of attributes to be enabled for the identifier when $MOD_HOLDER completes execution.
The set_attrib argument is a longword containing the attribute
mask.
The attributes actually enabled are the intersection of those specified and the attributes of the identifier. If you specify the same attribute in
set_attrib and
clr_attrib, the attribute is enabled.
|
Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC |
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the process rights list by using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST. |
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS |
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem attribute. |
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE |
Allows the holder to charge resources, such as disk blocks, to the identifier. |
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM |
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in the subsystem. |
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Bit mask of attributes to be disabled for the identifier when $MOD_HOLDER completes execution.
The clr_attrib argument is a longword containing the attribute
mask.
If you specify the same attribute in set_attrib and
clr_attrib, the attribute is enabled.
|
Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC |
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the process rights list by using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST. |
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS |
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem attribute. |
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE |
Allows the holder to charge resources, such as disk blocks, to the identifier. |
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM |
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in the subsystem. |
Description
The Modify Holder Record in Rights Database service modifies the specified holder record in the rights database. Identifier attributes can be added or removed.
When you specify both the
set_attrib and
clr_attrib arguments, the attribute is cleared first. Thus, if you specify the same attribute bit with each argument, the result is that the bit is set.
Required Access or Privileges
Write access to the rights database is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CREATE_RDB, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $GET_SECURITY, $GRANTID, $IDTOASC, $MOD_IDENT, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID, $SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
holderargument cannot be read by the caller.- SS$_BADPARAM
The specified attributes contain invalid attribute flags.
- SS$_INSFMEM
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights database.
- SS$_IVIDENT
The specified identifier or holder identifier is of invalid format.
- SS$_NOSUCHID
The specified identifier does not exist in the rights database, or the specified holder identifier does not exist in the rights database.
- RMS$_PRV
The user does not have write access to the rights database.
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes, refer to the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$MOD_IDENT
Modify Identifier in Rights Database — Modifies the specified identifier record in the rights database.
Format
SYS$MOD_IDENT id ,[set_attrib] ,[clr_attrib] ,[new_name] ,[new_value]C Prototype
int sys$mod_ident
(unsigned int id, unsigned int set_attrib, unsigned int clr_attrib,
void *new_name, unsigned int new_value);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | rights_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Binary value of identifier whose identifier record is modified when $MOD_IDENT completes
execution. The id argument is a longword containing the
identifier value.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Bit mask of attributes to be enabled for the identifier when $MOD_IDENT completes execution.
The set_attrib argument is a longword containing the attribute
mask.
The attributes actually enabled are the intersection of those specified and the attributes of
the identifier. If you specify the same attribute in set_attrib
and clr_attrib, the attribute is enabled.
|
Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC |
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the process rights list by using the DCL command SET_RIGHTS_LIST. |
|
KGB$V_HOLDER_HIDDEN |
Prevents someone from getting a list of users who hold an identifier, unless they own the identifier themselves. |
|
KGB$V_NAME_HIDDEN |
Allows holders of an identifier to have it translated – either from binary to ASCII or vice versa – but prevents unauthorized users from translating the identifier. |
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS |
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem attribute. |
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE |
Allows holders of an identifier to charge disk space to the identifier. It is used only for file objects. |
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM |
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in the subsystem. |
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Bit mask of attributes to be disabled for the identifier when $MOD_IDENT completes execution.
The clr_attrib argument is a longword containing the attribute
mask.
If you specify the same attribute in set_attrib and
clr_attrib, the attribute is enabled.
|
Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC |
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the process rights list by using the DCL command SET_RIGHTS_LIST. |
|
KGB$V_HOLDER_HIDDEN |
Prevents someone from getting a list of users who hold an identifier, unless they own the identifier themselves. |
|
KGB$V_NAME_HIDDEN |
Allows holders of an identifier to have it translated – either from binary to ASCII or vice versa – but prevents unauthorized users from translating the identifier. |
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS |
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem attribute. |
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE |
Allows holders of an identifier to charge disk space to the identifier. It is used only for file objects. |
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM |
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in the subsystem. |
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor—fixed-length string descriptor |
New name to be given to the specified identifier. The new_name argument
is the address of the descriptor pointing to the identifier name string.
An identifier name consists of 1 to 31 alphanumeric characters, including dollar signs ($) and underscores (_), and must contain at least one nonnumeric character. Any lowercase characters specified are automatically converted to uppercase.
| OpenVMS usage: | rights_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
New value to be assigned to the specified identifier. The new_value
argument is a longword containing the binary value of the specified identifier. When the
identifier value is changed, $MOD_IDENT also changes the value of the identifier in all
of the holder records in which the specified identifier appears.
Description
The Modify Identifier in Rights Database service modifies the specified identifier record in
the rights database. Identifier attributes can be added or removed. The identifier name
or value can be changed. When you specify both the set_attrib and
clr_attrib arguments, the attribute is cleared first. Thus,
if you specify the same attribute bit with each argument, the result is that the bit is
set.
Required Access or Privileges
Write access to the rights database is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CREATE_RDB, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $GRANTID, $IDTOASC, $MOD_HOLDER, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_NOSUCHID
The specified identifier does not exist in the rights database.
- SS$_BADPARAM
The specified attributes contain invalid attribute flags.
- SS$_DUPIDENT
The specified identifier value already exists.
- SS$_DUPLNAM
The specified identifier name already exists in the rights database.
- SS$_INSFMEM
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights database.
- SS$_IVIDENT
The specified identifier is of invalid format.
- RMS$_PRV
The user does not have write access to the rights database.
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes, refer to the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$MOUNT
Mount Volume — Mounts a tape, disk volume, or volume set and specifies options for the mount operation.
Format
SYS$MOUNT itmlstC Prototype
int sys$mount (void *itmlst);Argument
| OpenVMS usage: | item_list_3 |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Item list specifying options for the mount operation. The itmlst
argument is the address of a list of item descriptors, each of which specifies an option and
provides the information needed to perform the operation.
The item list must include at least one device item descriptor and is terminated by a longword value of 0.
The following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor.

|
Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Buffer length |
A word specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer that supplies the information $MOUNT needs to process the specified item code. The required length of the buffer depends on the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of the buffer length is too small, $MOUNT truncates the data. |
|
Item code |
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code that specifies an option for the MOUNT operation. The $MNTDEF macro defines these codes. |
|
Buffer address |
A longword containing the address of the buffer that supplies information to $MOUNT. |
|
Return length address |
This field is not used. |
Item Codes
MNT$_ACCESSED
The MNT$_ACCESSED item code specifies the number of directories that will be in use, concurrently, on the volume. The buffer must contain a longword integer value in the range 0 to 255. This value overrides the number of directories specified when the volume was initialized. To specify MNT$_ACCESSED, the caller must have OPER privilege. The MNT$_ACCESSED item code applies only to disks.
MNT$_BLOCKSIZE
The MNT$_BLOCKSIZE item code specifies the default block size for tape volumes. The buffer must contain a longword integer value in the range 20 to 65,532 bytes for OpenVMS RMS operations or 10 to 65,534 bytes for operations that do not use RMS. The MNT$_BLOCKSIZE item code applies only to tapes.
If you do not specify MNT$_BLOCKSIZE, the default block size is 2048 bytes for Files-11 tape volumes and 512 bytes for foreign and unlabeled tapes.
You must specify MNT$_BLOCKSIZE when mounting (1) tapes that do not have ANSI HDR2 labels, (2) tapes to which data will be written from compatibility mode, and (3) tapes that are to contain records whose size is larger than the default value.
MNT$_COMMENT
The MNT$_COMMENT item code specifies text to be associated with an operator request. The buffer must contain a character string of no more than 78 characters. This text will be printed on the operator's console if an operator request is issued for the device being mounted.
MNT$_DATA
Specifies the Extended File Cache (XFC) to be enabled on the disk. To specify MNT$_DATA, you require OPER privilege. This is the default unless the NOQUOTA, NOFILEID, NOEXTENT, and WRITETHROUGH qualifiers are all specified with the MOUNT command.
MNT$_DENSITY
The MNT$_DENSITY item code specifies
the density at which data is to be written to a foreign or unlabeled tape. The DENSITY item code supplied is dependent on the type of tape device. If a tape device is capable of using the MT3 density codes, the buffer for the MNT$DENSITY item code must contain a longword with one of the MT3 codes, as defined in SYS$LIBRARY:STARLET (MT3$K_TK50, MT3$K_3480, MT3$K_SDLT, MT3$K_AIT2, and so on). Refer to the MT3_SUPPORTED argument for $GETDVI.
If the device does not support MT3 densities, the buffer must contain a longword value that specifies one of the following legal densities: 800 bpi, 1600 bpi, or 6250 bpi.
The specified density will be used only if ( 1 ) the tape is foreign or unlabeled and (2) the first operation is a write.
MNT$_DEVNAM
The MNT$_DEVNAM item code specifies the name of the device to be mounted. The buffer must contain a character string of from 1 to 64 characters, which is the device name. The device name can be a physical device name or a logical name; if it is a logical name, it must translate to a physical device name.
The MNT$_DEVNAM item code must appear at least once in an item list, and it can appear more than once. It appears more than once when a volume set is being mounted, because, in this case, one device is being mounted for each volume in the volume set.
MNT$_EXTENSION
The MNT$_EXTENSION item code specifies the number of blocks by which files will be extended. The buffer must contain a longword value in the range 0 to 65,535. The MNT$_EXTENSION item code applies only to disks.
MNT$_EXTENT
The MNT$_EXTENT item code specifies the size of the extent cache in units of extent pointers. The buffer must contain a longword value, which specifies this size. To specify MNT$_EXTENT, you need OPER privilege. The value 0 (the default) disables caching. The MNT$_EXTENT item code applies only to disks.
MNT$_FILEID
The MNT$_FILEID item code specifies the size of the file-ID cache in units of file numbers. The buffer must contain a longword value, which specifies this size. To specify MNT$_FILEID, you need OPER privilege. The value 1 disables caching. The MNT$_FILEID item code applies only to disks.
MNT$_FLAGS
The MNT$_FLAGS item code specifies a 2-longword bit vector wherein each bit specifies an option for the mount operation. The buffer must contain a quadword, which is the bit vector.
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
MNT$M_CLUSTER |
The volume is to be mounted for clusterwide access; that is, every OpenVMS Cluster node can access the volume. $MOUNT mounts the volume first on the caller's node and then on every other node in the existing cluster. Only system or group volumes can be mounted clusterwide. If you do not specify MNT$M_GROUP or MNT$M_SYSTEM, $MOUNT mounts the volume as a system volume, provided the caller has SYSNAM privilege. To mount a group volume clusterwide, the caller must have GRPNAM privilege. To mount a system volume clusterwide, the caller must have SYSNAM privilege. MNT$M_CLUSTER has no effect if the system is not a member of a cluster. MNT$M_CLUSTER applies only to disks. |
|
MNT$M_FOREIGN |
The volume is to be mounted as a foreign volume; a foreign volume is not Files-11 structured. If you specify MNT$M_FOREIGN, the following item codes can each appear in the item list only once: the caller must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege. |
|
MNT$M_GROUP |
The logical name for the volume to be mounted is entered in the group logical name table, and the volume is made accessible to other users with the same UIC group number as that of the calling process. To specify MNT$M_GROUP, the caller must have GRPNAM privilege. MNT$M_GROUP applies only to disks. |
|
MNT$M_INCLUDE |
Automatically reconstructs a shadow set to the state it was in before the shadow set was dissolved (due to dismounting or system failure). Use this option to mount a shadow set or a volume set of shadow sets. You must specify the exact name of the original virtual unit and the device name of at least one of the shadow set members. The shadowing software reads the shadow set membership information from the named device to determine the membership of the original shadow set. You can include the MNT$M_INCLUDE option in executable images to have a shadow set reconstructed. Using MNT$M_INCLUDE prevents your having to manually reinstate shadow sets after they have been dismounted. If you do not select this option, $MOUNT does not automatically reconstruct the former shadow set. |
|
MNT$M_INIT_CONT |
Additional volumes in the volume set are to be initialized without operator intervention. $MOUNT initializes new volumes with the protections specified for the first magnetic tape of the volume set and creates unique volume label names for up to 99 volumes in a volume set. |
|
If MNT$M_INIT_CONT is specified, you must allocate multiple magnetic tape drives to the volume set. If $MOUNT switches to a drive that has no magnetic tape loaded or has the wrong magnetic tape loaded or if $MOUNT tries to read a magnetic tape that is not loaded, it notifies the operator to load the correct magnetic tape. $MOUNT will dismount and unload volumes as soon as they have been read or written. The operator can load the next volume in the volume set before the current reel of the volume set reaches the end of the magnetic tape. | |
|
If writing to the volume set, $MOUNT automatically (1) switches to the next magnetic tape drive, (2) initializes that magnetic tape with the same volume name and protection as specified in the volume labels of the first volume in the set, and (3) notifies the operator that the switch has occurred. If reading the volume set, $MOUNT generates the label for the next volume in the volume set and reads that volume. | |
|
The label name that $MOUNT generates for each additional volume in the volume set consists of six characters: the first four characters are the same as the first four characters of the label name of the previous volume; the fifth and sixth characters represent the number of the volume in the volume set. MNT$M_INIT_CONT applies only to magnetic tapes. | |
|
MNT$M_MESSAGE |
Messages will be sent to the caller's SYS$OUTPUT device. |
|
MNT$M_MINICOPY_OPTIONAL |
$MOUNT fails if minicopy has not been enabled on the disk. |
|
MNT$M_MULTI_VOL |
Specifies, for foreign or unlabeled magnetic tapes, that subsequent volumes can be processed by overriding MOUNT's access checks. You can use this option when a utility that supports multivolume magnetic tape sets needs to process subsequent volumes, and these volumes do not contain labels that MOUNT can interpret. You need VOLPRO privilege to specify the MNT$M_MULTI_VOL option. MNT$M_MULTI_VOL can only be used with the MNT$M_FOREIGN option. VSI recommends the use of this qualifier only when it is not possible to alter the utility to explicitly perform MOUNT and DISMOUNT operations on each reel in the set. |
|
MNT$M_NOASSIST |
$MOUNT does not request operator assistance if errors are encountered during the mount operation. If not specified, $MOUNT requests operator assistance to recover from some error conditions. |
|
MNT$M_NOAUTO |
Automatic volume labeling (AVL) and automatic volume recognition (AVR) are to be disabled. If MNT$M_NOAUTO is specified, the operator must enter commands from the console to process each additional volume in a volume set. When a volume is finished processing, the operator specifies the drive on which the next volume is loaded and the label name of the next volume. You might want to use MNT$M_NOAUTO to disable AVL and AVR when not reading a volume set sequentially. You can enable AVL and AVR by specifying MNT$M_INIT_CONT. MNT$M_NOAUTO applies only to magnetic tapes. |
|
MNT$M_NOCACHE |
All caching associated with the volume is turned off. Specifying MNT$M_NOCACHE is equivalent to (1) specifying MNT$M_WRITETHRU, (2) specifying a value of 1 for the item descriptor MNT$_FILEID, and (3) specifying a value of 0 for the item descriptors MNT$M_EXTENT and MNT$M_QUOTA. |
|
MNT$M_NOCOPY |
Disables full copy operations on all physical devices being mounted or added to a shadow set. This option provides you with the opportunity to confirm the states of all of the devices or members of a shadow set before proceeding with any full copy operation. This prevents any accidental loss of data that could occur if an unintended device is added to the shadow set. If you do not select this option, $MOUNT automatically overwrites the data on shadow set members that are not current. When you select this option, a $MOUNT operation fails if any of the specified potential shadow set members require full copy operations. |
|
MNT$M_NODISKQ |
Disk quotas are not to be enforced for the volume to be mounted. If not specified, disk quotas are enforced. To specify MNT$M_NODISKQ, the caller must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege. MNT$M_NODISKQ applies only to disks. |
|
MNT$M_NOHDR3 |
ANSI HDR3 and HDR4 labels are not to be written to magnetic tapes as they are mounted. If not specified, ANSI HDR3 and HDR4 labels are written to all tapes. Use MNT$M_NOHDR3 when writing to volumes that will be read by a system, such as the RT-11 system, which does not process HDR3 and HDR4 labels correctly. MNT$M_NOHDR3 applies only to tapes. |
|
MNT$M_NOLABEL |
The volume is to be mounted as a foreign volume; a foreign volume is not Files-11 structured. If you specify MNT$M_NOLABEL, the following item codes can each appear in the item list only once: MNT$_DEVNAM, MNT$_VOLNAM, and MNT$_LOGNAM. To specify MNT$M_NOLABEL, the caller must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege. |
|
MNT$M_NOMNTVER |
The volume is not marked as a candidate for automatic mount verification. If not specified, the volume is marked as a candidate for mount verification. |
|
MNT$M_NOREBUILD |
The volume to be mounted should be returned to active use immediately, without performing a rebuild operation. This flag defers the disk rebuild operation, so that the volume to be mounted is returned to active use immediately. A rebuild operation can consume a considerable amount of time, depending on the number of files on the volume and on the number of different file owners (if quotas are in use). The volume can be rebuilt later with the DCL command SET VOLUME/REBUILD to recover the free space; for more information, see the VSI OpenVMS DCL Dictionary. If a disk volume is improperly dismounted, for example, during a system failure, it must be rebuilt to recover any caching limits that were enabled on the volume at the time of the dismount. By default, $MOUNT attempts to rebuild. When mounting a volume set, you must mount all members of the set to reclaim all available free space. MNT$M_NOREBUILD applies only to disks. |
|
MNT$M_NOUNLOAD |
The volume to be mounted is not to be unloaded when it is dismounted. Specifying MNT$M_NOUNLOAD causes the volume to remain loaded when it is dismounted unless the dismount explicitly requests that the volume be unloaded. |
|
MNT$M_NOWRITE |
The volume to be mounted is software write locked. If not specified, the volume is assumed to have read and write access. |
|
MNT$M_OVR_ACCESS |
If the installation allows, this option overrides any character in the accessibility
field of the volume. The necessity of this option is defined by the installation. That is,
each installation has the option of specifying a routine that the magnetic tape file system
will use to process this field. By default, the operating system provides a routine that
checks this field in the following manner:
To specify MNT$M_OVR_ACCESS, the caller must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege. MNT$M_OVR_ACCESS applies only to tapes. |
|
MNT$M_OVR_EXP |
A tape that has not yet reached its expiration date can be overwritten. To specify MNT$M_OVR_EXP, the caller must own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege. |
|
MNT$M_OVR_IDENT |
You can mount the volume without specifying the volume name (by using the MNT$_VOLNAM item code). If specified, the following options must not be specified: MNT$M_CLUSTER, MNT$M_GROUP, MNT$M_SHARE, and MNT$M_SYSTEM. |
|
MNT$M_OVR_LOCK |
The software write lock that occurs when a volume has a corrupted storage bit mask can be overridden. |
|
MNT$M_OVR_SETID |
Checks on the volume set identification are not to be performed when subsequent reels in the volume set are mounted. MNT$M_OVR_SETID applies only to tapes. |
|
MNT$M_OVR_SHAMEM |
Allows you to mount former shadow set members outside of the shadow set. If you do not specify this option, $MOUNT automatically mounts the volume write-locked to prevent accidental deletion of data. To specify this option, you must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege. When you use this option, the shadow set generation number is erased from the volume. If you then remount the volume in the former shadow set, $MOUNT considers it an unrelated volume and marks it for a full copy operation. |
|
MNT$M_OVR_VOLO |
The volume label's owner identifier field is not to be processed. $MOUNT reads volume owner and protection information from the volume owner field of the volume labels. The operating system requires that you specify MNT$M_OVR_VOLO to process magnetic tapes when all of the following conditions exist: (1) the volume was created on an operating system other than OpenVMS; (2) the volume was initialized with a protection specified; and (3) the volume conforms to the Version 3 ANSI label standard. To specify MNT$M_OVR_VOLO, the caller must either have VOLPRO privilege or own the volume. MNT$M_OVR_VOLO applies only to tapes. |
|
MNT$M_READCHECK |
Read checks are to be performed following all read operations. |
|
MNT$M_REQUIRE_MEMBERS |
Controls whether every physical device specified with the MEMBERS /SHADOW qualifier must be accessible when the MOUNT command is issued in order for the $MOUNT system service to take effect. |
|
MNT$M_SHARE |
Volume is to be mounted shared and is therefore accessible to other users. MNT$M_SHARE applies only to disks. If the volume was previously mounted shared by another user and MNT$M_SHARE is specified in the current call, all other options specified in the current call are ignored. If the caller allocated the device and specified MNT$M_SHARE in the call to $MOUNT, $MOUNT will deallocate the device so that other users can access the volume. |
|
MNT$M_SYSTEM |
The logical name for the volume to be mounted is entered in the system logical name table, and the volume is made accessible to all other users, provided that UIC-based protection allows access to the volume. To specify MNT$M_SYSTEM, the caller must have SYSNAM privilege. MNT$M_SYSTEM applies only to disks. |
|
MNT$M_TAPE_DATA_WRITE |
Enables the tape controller's write cache for this device. Enabling the write cache improves data throughput for write operations. By default, the tape controller's write cache is disabled for the device. This option applies only to tape systems that support a write cache. |
|
MNT$M_VERIFY_LABEL |
Requires that any member to be added to the shadow set have a volume label of SCRATCH_DISK. This helps ensure that the wrong disk is not added to a shadow set. If you plan to use VERIFY_LABEL, you must first assign the disk to a label. You can do this either by initializing the disk to be added to the set with the label SCRATCH_DISK, or by specifying the label for the disk with the SET VOLUME/LABEL command. |
|
MNT$M_WRITECHECK |
Write checks are to be performed after all write operations. |
|
MNT$M_WRITETHRU |
Disables the deferred write feature for file headers. By default this feature is enabled, which improves the performance of the applications, such as PATHWORKS, that use it. The deferred write feature is not available on Files-11 ODS-1 volumes. |
|
MNT2$M_CDROM |
Mounts a volume assuming the media to be ISO 9660 (or High Sierra) formatted. |
|
MNT2$M_COMPACTION |
Enables data compaction for those magnetic tapes that support data compaction (TA90, TA91, and others). |
|
MNT2$M_DISKQ |
Controls whether quotas are to be enforced on the specified disk volume. |
|
MNT2$_DSI |
Enables XAR permissions Owner and Group for XARs containing Digital System Identifiers (DSI). For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual. |
|
MNT2$_INCLUDE |
Automatically reconstructs a former shadow set to the way it was before the shadow set was dissolved. Applicable only if you have the volume shadowing option. For more information, see VSI OpenVMS Volume Shadowing Guide. |
|
MNT2$M_NOCOMPACTION |
Forces the density to no compaction for those magnetic tapes that support data compaction (TA90, TA91, and others). |
|
MNT2$_OVR_LIMITED_SEARCH |
For disk type devices that do not provide for bad-block revectoring, it is possible that the Files-11 homeblock has been placed numerous I/Os from the start of the volume. To decrease the failover time when accessing media which does not contain a valid Files-11 homeblock, a limited-search algorithm was implemented. This switch overrides the limited-search algorithm so that the entire volume will be searched for a valid Files-11 homeblock. |
|
MNT2$M_OVR_NOFE |
This bit mask is set to override those SCSI devices that do not support forced error functionality. By overriding those SCSI devices not supporting forced error capabilities, MNT2$M_OVR_NOFE enables those devices to be mounted. Otherwise, the shadowing code would report to $MOUNT that the device does not support forced error, and the device would not be mounted. |
|
MNT2$_OVR_SECURITY |
Enables you to continue mounting a volume if an error is returned because the volume has an invalid SECURITY.SYS file. You must have the VOLPRO privilege or own the volume to use this keyword. |
|
MNT2$M_SUBSYSTEM |
Enables the processing of protected subsystem identifiers on the volume. By default, subsystem identifiers are ignored on all but the system disk. Requires SECURITY privilege. |
|
MNT2$M_XAR |
Enables enforcement of the extended record attribute (XAR) access controls. For more information about XAR, see the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual. |
MNT$_LIMIT
The MNT$_LIMIT item code specifies the maximum amount of free space in the extent cache. The buffer must contain a longword value, which specifies the amount of free space in units of tenths of a percent of the disk's total free space. The MNT$_LIMIT item code applies only to disks.
MNT$_LOGNAM
The MNT$_LOGNAM item code specifies a logical name for the volume; this logical name is equated to the device name specified by the first MNT$_DEVNAM item code. The buffer must contain a character string from 1 to 64 characters, which is the logical name.
Unless you specify MNT$M_GROUP or MNT$M_SYSTEM, the logical name is entered in the process logical name table.
MNT$_NODATA
Specifies whether the XFC is to be disabled on the disk. This value is the default, when you specify NOQUOTA, NOFILEID, NOEXTENT, or WRITETHROUGH qualifier with the MOUNT command.
MNT$_OWNER
The MNT$_OWNER item code specifies the UIC to be assigned ownership of the volume. The buffer must contain a longword octal value, which is the UIC. If the volume is Files-11 structured, the specified value overrides the ownership recorded on the volume. You need either VOLPRO privilege or ownership of the volume to assign a UIC to a Files-11 structured volume.
MNT$_PROCESSOR
For magnetic tapes and Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1 disks, MNT$_PROCESSOR specifies the name of the ancillary control process (ACP) that is to process the volume. The specified ACP overrides the default ACP associated with the device.
For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 disks, MNT$_PROCESSOR controls block cache allocation.
To specify MNT$_PROCESSOR, the caller must have OPER privilege.
|
String |
Description |
|---|---|
|
UNIQUE |
For magnetic tapes and Files-11 Structure Level 1 disks, UNIQUE specifies that $MOUNT create a new process to execute a copy of the default ACP image associated with the device specified by the MNT$_DEVNAM item code. For Files-11 Structure Level 2 disks, UNIQUE allocates a separate block cache. |
|
ddcu |
For magnetic tapes and Files-11 Structure Level 1 disks, ddcu specifies that $MOUNT use the ACP process currently being used by the device ddcu. The device specified must be in the format ddcu, for example, DRA3. For Files-11 Structure Level 1 disks, ddcu specifies that $MOUNT take the block allocation from the specified device. |
|
filespec |
Specifies that $MOUNT create a new process to execute the ACP image with the file specification filespec. Wildcard characters are not allowed in the file specification. The file must be in the disk and directory specified by the logical name SYS$SYSTEM. This operation requires CMKRNL privilege. |
MNT$_QUOTA
The MNT$_QUOTA item code specifies the size of the quota record cache in units of quota records. The buffer must contain a longword value, which is this size. To specify MNT$_QUOTA, you need OPER privilege. The value 0 disables caching. The MNT$_QUOTA item code applies only to disks.
MNT$_RECORDSIZ
The MNT$_RECORDSIZ item code specifies the number of characters in each record and is used with MNT$_BLOCKSIZE to specify the data formats for foreign volumes. The buffer must contain a longword value less than or equal to the block size. The MNT$_RECORDSIZ item code applies only to tapes.
If you do not specify MNT$_RECORDSIZ, the record size is assumed to be equal to the block size.
MNT$_SHAMEM
The MNT$_SHAMEM item code specifies the name of a physical device to be mounted into a shadow set. The MNT$_SHAMEM descriptor is a 1- to 64-character string containing the device name. The string can be a physical device name or a logical name; if it is a logical name, it must translate to a physical device name. An item list must contain at least one item descriptor specifying a member; this item descriptor must appear after the MNT$_SHANAM item descriptor.
Volume Shadowing for OpenVMS automatically performs a copy or a merge operation, if necessary, when it mounts the disk into the shadow set.
MNT$_SHANAM
The MNT$_SHANAM item code specifies the name of the virtual unit to be mounted. The buffer is a 1- to 64-character string containing the device name. The virtual unit name can be a logical name; if it is a logical name, it must translate to a virtual unit name.
Because every shadow set is represented by a virtual unit, you must include at least one MNT$_SHANAM item descriptor in the item list that you pass to $MOUNT to create and mount the shadow set. If you are mounting a volume set containing more than one shadow set, you must include one MNT$_SHANAM item descriptor for each virtual unit included in the volume set.
The relative position of the item descriptors in the item list determines the membership of the shadow set. That is, it indicates which members should be bound to a specific virtual unit to form the shadow set. You must first specify the virtual unit by using the MNT$_SHANAM item code. Then, you can specify any number of members that are to be represented by that virtual unit by using one of the following item codes: MNT$_SHAMEM, MNT$_SHAMEM_COPY, or MNT$_SHAMEM_MGCOPY. If you specify one shadow set and want to specify a second, specify a second virtual unit item descriptor. The members you specify subsequently are bound to the shadow set represented by the virtual unit specified in the second virtual unit item descriptor.
MNT$_UCS
The MNT$_UCS item code specifies a descriptor containing a Universal Character Sequence (UCS) defined by ISO 2022 and used when mounting an ISO 9660 CD-ROM. For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
MNT$_UNDEFINED_FAT
The MNT$_UNDEFINED_FAT item code specifies the default file attributes to be used for the records on ISO 9660 media for which no record format has been specified.
The buffer contains a 32-bit structure that defines a file's record format, record attributes, and maximum record size.
The following diagram depicts the structure of the Undefined File Attributes buffer.
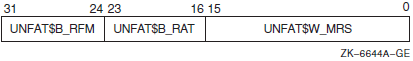
|
Buffer Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
UNFAT$W_MRS |
Maximum record size; specifies the maximum record size for all records in a file: 0 to 32767. Applies only to FIXED or STREAM formats. |
|
UNFAT$B_RAT |
Record attributes; specifies the attributes for all records in a file: NONE, CR, FTN, PRN, NOBKS. Applies only to non-STREAM record formats. |
|
UNFAT$B_RFM |
Record format; specifies the format for all records in a file: FIXED, VARIABLE, STREAM, STREAM_LF, STREAM_CR, LSB_VARIABLE, or MST_VARIABLE. |
MNT$_VOLNAM
|
Device Type |
Number of Characters in Label |
|---|---|
|
Magnetic tape |
0–6 |
|
Files-11 disk |
1–12 |
|
ISO 9660 disk |
1–32 |
The MNT$_VOLNAM item code can appear more than once in an item list; it appears more than once when a volume set is being mounted because, in this case, one volume name is given to each volume in the volume set.
When a disk volume set is being mounted, you must specify MNT$_DEVNAM and MNT$_VOLNAM once for each volume of the volume set. The $MOUNT service mounts the volume specified by the first MNT$_VOLNAM item code on the device specified by the first MNT$_DEVNAM item code in the item list; it mounts the volume specified by the second MNT$_VOLNAM code on the device specified by the second MNT$_DEVNAM code, and so on for all specified volumes and devices. Thus, there must be an equal number of these two item codes in the item list.
When a tape volume set is being mounted, the number of MNT$_DEVNAM item codes specified need not be equal to the number of MNT$_VOLNAM item codes specified, because more than one volume can be mounted on the same device.
MNT$_VOLSET
The MNT$_VOLSET item code specifies the name of a volume set. The buffer must contain a character string from 1 to 12 alphanumeric characters, which is the volume set name.
An ISO 9660 volume set name can be from 1 to 128 characters in length.
Volume set names must be unique in the first 12 characters. In addition, if the first 12 characters of the volume set name are the same as the first 12 characters of any volume label, a lock manager deadlock will occur. To avoid this problem, you must override either the volume label (by using the MNT$_VOLNAM item code) or the volume set name (by using the MNT$_VOLSET item code).
When you specify MNT$_VOLSET, volumes specified by the MNT$_VOLNAM item code are bound into a new volume set or added to an existing volume set, depending on whether the name specified by MNT$_VOLSET is a new or already existing name.
When you specify MNT$_VOLSET to add volumes to an existing volume set, the root volume (RVN1) must either (1) already be mounted or (2) be specified first (by the MNT$_DEVNAM and MNT$_VOLNAM item codes) in the item list.
When you specify MNT$_VOLSET to create a new volume set, the first volume specified (by the MNT$_DEVNAM and MNT$_VOLNAM item codes) in the item list becomes the root volume.
MNT$_VPROT
The MNT$_VPROT item code specifies the protection to be assigned to the volume. The buffer must contain a longword protection mask, which specifies the four types of access allowed to the four categories of user.
The protection mask consists of four 4-bit fields. Each field grants or denies read, write, logical, and physical access to a category of users. Cleared bits grant access; set bits deny access. The following diagram depicts the structure of the protection mask.
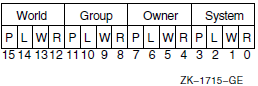
If you do not specify MNT$_VPROT or specify it as the value 0, the volume receives the protection that it was assigned when it was initialized. To specify MNT$_VPROT for a Files-11 structured volume, the caller must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
MNT$_WINDOW
The MNT$_WINDOW item code specifies the number of mapping pointers to be allocated for file windows. The buffer must contain a longword value in the range 7 to 80. This value overrides the default value that was applied when the volume was initialized. The MNT$_WINDOW item code applies only to disks.
When a file is opened, the file system uses the mapping pointers to access the data in the file. To specify MNT$_WINDOW, you need OPER privilege.
Description
The Mount Volume service mounts a tape, disk volume, or volume set and specifies options for the mount operation.
When a subprocess mounts a private volume without explicitly allocating the device, the master process of the job becomes the owner of this device. This provision is necessary because the subprocess can be deleted and the volume should remain privately mounted for this job.
When a subprocess explicitly allocates a device and then mounts a private volume on this device, this subprocess retains the device ownership. In this case, only subprocesses of the device owner, and processes with SHARE privilege, have access to the device.
Nonpaged pool
Paged pool
When $MOUNT mounts a disk volume, the logical name DISK$volume-label is always created. If you specify a logical name in the mount request that is different from DISK$volume-label, there will be two logical names associated with the device.
If the logical name of a volume is in a process-private table, then the name is not deleted when the volume is dismounted.
Required Access or Privileges
To mount a volume on a device, you must have read or control access to that device.
To mount a particular volume, the caller must either own or have privilege to access the specified volume or volumes. The privileges required depend on the operation and are listed with the item codes that specify the operation.
The calling process must have TMPMBX or PRMMBX privilege to perform an operator-assisted mount.
SECURITY privilege is required to enable protected subsystems.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The item list or an address specified in the item list cannot be accessed.
- SS$_BADPARAM
A buffer length of 0 was specified with a nonzero item code; an illegal item code was specified; or no device was specified.
- SS$_NOGRPNAM
The caller does not have GRPNAM privilege.
- SS$_NOHOMEBLK
Files-11 home block not found on volume.
- SS$_NOOPER
The caller does not have the required OPER privilege.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The caller does not have sufficient privilege to access a specified volume.
- SS$_NOSUCHDEV
The specified device does not exist on the host system.
- SS$_NOSYSNAM
The caller does not have SYSNAM privilege.
The $MOUNT service can also return a condition value that is specific to the Mount utility. The symbolic definition macro $MOUNDEF defines these condition values.
$MTACCESS
Magnetic Tape Accessibility — Allows installations to provide their own routine to interpret and output the accessibility field in the VOL1 and HDR1 labels of an ANSI labeled magnetic tape.
Format
SYS$MTACCESS
lblnam ,[uic] ,[std_version] ,[access_char] ,[access_spec] ,typeC Prototype
int sys$mtaccess
(unsigned int *lblnam, unsigned int uic, unsigned int std_version,
unsigned int access_char, unsigned int access_spec,
unsigned int type);
Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
ANSI label to be processed. The lblnam argument is the address of a
longword containing the label. On input, the label passed is either the VOL1 or HDR1
label read from the magnetic tape; on output of labels, the value of this field is 0.
The type of label passed is determined by type.
| OpenVMS usage: | uic |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
UIC of the user performing the operation. The
uic argument is a longword containing the UIC.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Decimal equivalent of the ANSI standard version read from the VOL1 label. The
std_version argument is a longword containing the standard
version number.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Accessibility character specified by the user. The access_char argument
is a byte containing the accessibility character used for the output of labels.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
access_char was specified by the user. The
access_spec argument is a byte containing one of the
following values.|
Value |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
MTA$K_CHARVALID |
Yes |
|
MTA$K_NOCHAR |
No |
This argument is used only for the output of labels.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
type argument is a byte
containing one of the following values.|
Value |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
MTA$K_INVOL1 |
Input a VOL1 label |
|
MTA$K_INHDR1 |
Input a HDR1 label |
|
MTA$K_OUTVOL1 |
Output a VOL1 label |
|
MTA$K_OUTHDR1 |
Output a HDR1 label |
Description
The Magnetic Tape Accessibility service allows installations to provide their own routine to interpret and output the accessibility field in the VOL1 and HDR1 labels of ANSI labeled magnetic tapes. The installation can override the default routine by providing an MTACCESS.EXE executive loaded image.
The default installation routine first checks the ANSI standard version of the label. For magnetic tapes with a version number of 3 or less, the routine outputs either a blank or the character you specified. On input of these magnetic tapes, the routine checks for a blank and returns the value SS$_FILACCERR if the field is not blank.
For magnetic tapes with a version number greater than 3, the routine outputs either the character specified by the
access_char argument or an ASCII 1 if no character was specified. On input of these magnetic tapes, the routine checks for a blank. If the field is blank, R0 is set to 0. In that case, you are given full access and protection is not checked. If the field contains an ASCII 1, and the VOL1 Implementation Identifier field contains the system code, R0 is set to SS$_NORMAL. In that case, the protection is checked.
If the field is not blank and does not contain an ASCII 1, R0 is set to SS$_FILACCERR, which forces you to override accessibility checking and allows the magnetic tape file system to check protection.
|
Contents of R0 |
Result |
|---|---|
|
SS$_NORMAL |
Check the protection on the magnetic tape. |
|
0 |
Give the user full access. Protection is not checked. |
|
SS$_FILACCERR |
Check for explicit override, then check protection. |
Note that the default accessibility routine does not output SS$_NOVOLACC or SS$_NOFILACC. These statuses are included for the installation's use, and the magnetic tape file system handles these cases.
The magnetic tape file system calls $MTACCESS to process the accessibility field in the VOL1 and HDR1 labels. After a call to the system service, the magnetic tape file system checks that the installation did not move the magnetic tape. If the magnetic tape was moved, the magnetic tape file system completes the current operation with an SS$_TAPEPOSLOST error. Finally, it processes the remainder of the label according to the status returned by $MTACCESS.
Required Access or Privileges
Because accessibility is an installation-provided routine, the operating system cannot determine which users have the authority to override the processing of this field. However, the magnetic tape file system allows only operator class users to deal with blank magnetic tapes so that a user must have both OPER and VOLPRO privileges to initialize or mount blank magnetic tapes.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CHECK_ACCESS, $CHKPRO, $CREATE_RDB, $ERAPAT, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $FORMAT_ACL, $FORMAT_AUDIT, $GET_SECURITY, $GRANTID, $HASH_PASSWORD, $IDTOASC, $MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT, $PARSE_ACL, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID, $SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_FILACCERR
The accessibility characteristic in the HDR1 label is not blank and you cannot access the file without overriding the field.
- SS$_NOFILACC
The user has no access to the file.
- SS$_NOVOLACC
The user has no access to the volume.
$NUMTIM
Convert Binary Time to Numeric Time — Converts an absolute or delta time from 64-bit system time format to binary integer date and time values. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$NUMTIM timbuf ,[timadr]C Prototype
int sys$numtim
(unsigned short int timbuf [7], struct _generic_64 *timadr);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | vector_word_unsigned |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Buffer into which $NUMTIM writes the converted date and time. The
timbuf argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and
Integrity server systems) of a 7-word structure.
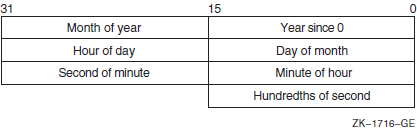
If the timadr argument specifies a delta time, $NUMTIM returns the
value 0 in the year since 0 and month of year fields. It returns in the day of month
field the number of days specified by the delta time.
| OpenVMS usage: | date_time |
| type: | quadword |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The 64-bit time value to be converted. The timadr argument is the 32-
or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of a quadword containing this
time. A positive-time value represents an absolute time, while a negative time value
indicates a delta time.
If you do not specify
timadr, $NUMTIM returns the current system time.
If timadr specifies the value 0, $NUMTIM returns the base date
(November 17, 1858).
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The 64-bit time value cannot be read by the caller, or the buffer cannot be written by the caller.
- SS$_IVTIME
The specified delta time is equal to or greater than 10,000 days.
$NUMUTC
Convert UTC Time to Numeric Components — Converts an absolute 128-bit binary time into its numeric components. The numeric components are returned in local time. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$NUMUTC timbuf ,[utcadr]C Prototype
int sys$numutc (unsigned short int timbuf [13], unsigned int *utcadr [4]);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | vector_word_unsigned |
| type: | word |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Buffer into which $NUMUTC writes the converted date and time. The
timbuf argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and
Integrity server systems) of a 13-word structure containing time, inaccuracy of time,
and time differential factor. The time differential factor encoded in the 128-bit buffer
is used to convert the UTC to its numerical components. Negative values in the
inaccuracy field indicate an infinite inaccuracy.
The following diagram depicts the fields in this structure:
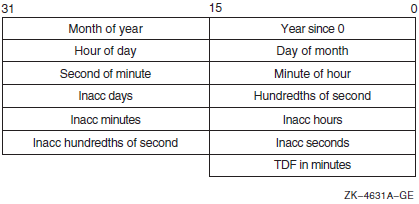
| OpenVMS usage: | coordinated universal time |
| type: | utc_date_time |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The 128-bit UTC time value to be converted.
The utcadr argument is optional; if it is not used, $NUMUTC will use
the current time.
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_INVTIME
The 128-bit UTC time is not valid.
$NXTVOL
Next Volume — The Next Volume service allows you to process the next tape volume in a multiple volume set. This service applies only to files on magnetic tape volumes. For additional information about this service, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$OPEN
Opens File — The Open service makes an existing file available for processing by your program. The Open service specifies the type of record access to be used and determines whether the file can be shared. The Open service also performs an implicit Display service. For additional information about this service, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$PARSE
Analyze File Specification String — The Parse service analyzes the file specification string and fills in various NAM block fields. For additional information about this service, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$PARSE_ACL
Parse Access Control List Entry — Parses the specified text string and converts it to the binary representation for an access control entry (ACE).
Format
SYS$PARSE_ACL aclstr ,aclent ,[errpos] ,[accnam] ,[nullarg]C Prototype
int sys$parse_acl
(void *aclstr, void *aclent, unsigned short int *errpos, void *accnam,
int (*routin)(void));Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor—fixed-length string descriptor |
Formatted ACE that is parsed when $PARSE_ACL completes execution. The
aclstr argument is the address of a string descriptor
pointing to the text string to be parsed.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor—fixed-length string descriptor |
Description of the ACE that is parsed when $PARSE_ACL completes execution. The
aclent argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to
the buffer in which the ACE is written. The first byte of the buffer contains the length
of the ACE; the second byte contains a value that identifies the type of ACE, which in
turn defines the format of the ACE. For information about the ACE types and their
associated formats, see $FORMAT_ACL system service documentation.
| OpenVMS usage: | word_unsigned |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Number of characters from aclstr processed by $PARSE_ACL. The
errpos argument is the address of a word that receives the
number of characters actually processed by the service. If the service fails, this count
points to the failing point in the string.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_bit_names |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Names of the bits in the access mask when $PARSE_ACL is executing. The
accnam argument is the address of an array of 32 quadword
descriptors that define the names of the bits in the access mask. Each element points to
the name of a bit. The first element names bit 0, the second element names bit 1, and so
on.
accnam, the following names
are used.|
Bit |
Name |
|---|---|
|
Bit 0 |
READ |
|
Bit 1 |
WRITE |
|
Bit 2 |
EXECUTE |
|
Bit 3 |
DELETE |
|
Bit 4 |
CONTROL |
|
Bit 5 |
BIT_5 |
|
Bit 6 |
BIT_6 |
|
. | |
|
Bit 31 |
BIT_31 |
| OpenVMS usage: | null_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to OpenVMS.
Description
The Parse Access Control List Entry service parses the specified text string and converts it to the binary representation for an access control entry (ACE).
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CHECK_ACCESS, $CHKPRO, $CREATE_RDB, $ERAPAT, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $FORMAT_ACL, $FORMAT_AUDIT, $GET_SECURITY, $GRANTID, $HASH_PASSWORD, $IDTOASC, $MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT, $MTACCESS, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID, $SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The string or its descriptor cannot be read by the caller; the buffer descriptor cannot be read by the caller; the buffer cannot be written by the caller; or the buffer is too small to hold the ACL entry.
- SS$_IVACL
The format of the access control list entry is not valid.
- SS$_NOSUCHID
The specified identifier does not exist in the rights database.
$PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Disable Alignment Fault Reporting — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, disables user process alignment fault reporting.
Format
SYS$PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORTC Prototype
int sys$perm_dis_align_fault_report (void);Arguments
None.
Description
The Disable Alignment Fault Reporting service disables user process alignment fault reporting.
See the description of the $PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT service for an example of a program that can be used to enable and disable user process alignment fault reporting.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT, $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
$PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Report Alignment Fault — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, initializes user process alignment fault reporting.
Format
SYS$PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULTC Prototype
int sys$perm_report_align_fault (void);Arguments
None.
Description
The Report Alignment Fault service allows the user to permanently enable user process alignment fault reporting for all subsequent images.
This service reports alignment faults only in exception mode. For more information about reporting modes, see the $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service.
Image alignment fault reporting takes precedence over process alignment fault reporting. That is, if both image and process alignment fault reporting are enabled, faults are reported to the image first.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
Example
/**********************************************************************/ /* */ /* SET_ALIGN_REPORT.C */ /* */ /* This program can be used to permanently turn on and off */ /* alignment fault reporting for a process. After creating the */ /* executable, do: */ /* */ /* $ align :== $dir:set_align_report.exe */ /* $ align on */ /* $ run program ! will generate align faults on screen */ /* $ align off */ /* $ run program ! will not generate align faults */ /* */ /**********************************************************************/ #include <stdio> #include <ctype> #include <ssdef> /* alignment fault reporting system services */ extern sys$perm_report_align_fault(), sys$perm_dis_align_fault_report(); main(argc, argv) int argc; char *argv[]; { int status; /* check arguments */ if (argc < 2) { printf ("Insufficient arguments\n"); return (40); } /* check if the argument is on or off */ if ((strcmp ("ON", argv[1]) == 0) || (strcmp ("on", argv[1]) == 0)) /* on, turn alignment fault reporting on for this process */ status = sys$perm_report_align_fault (); else if ((strcmp ("OFF", argv[1]) == 0) || (strcmp ("off", argv[1]) == 0)) /* off, turn alignment fault reporting off for this process */ status = sys$perm_dis_align_fault_report (); else return (SS$_BADPARAM); /* return status */ return (status); }
This example shows a program that can be used to enable and disable alignment fault reporting for a process.
$PERSONA_ASSUME (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Assume Persona — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, allows an OpenVMS thread to assume the identity of another persona.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_ASSUME persona ,[flags], [previous], [acmode]C Prototype
int sys$persona_assume
(unsigned int *persona, unsigned int flags, unsigned int *previous,
unsigned int acmode);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | persona |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword in which the persona identification handle is expected.
If the value passed is ISS$C_ID_NATURAL, then the state of the calling thread is returned to the natural persona.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Ignored.
| OpenVMS usage: | persona |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword into which the persona identification handle of the currently active persona being replaced is written.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode to be considered when assuming a persona. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. Only equal or more privileged access modes can use this persona.
Description
This service establishes the specified persona as the active security profile and returns the persona identification handle of the persona that was active at the point in which the call to this service was made.
On image exit, the natural persona is assumed and all nonpermanent personae are deleted.
The arguments are validated against the caller's mode, so an invalid argument can cause an access violation to be signaled.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully; the desired access is granted.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Access violation.
- SS$_INSFARG
Certain required arguments were not specified.
- SS$_IVMODE
The caller cannot create a persona that is more privileged than the caller.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The operation requires IMPERSONATE privilege.
- SS$_PERSONANONGRATA
Invalid persona argument.
$PERSONA_CLONE (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Clone Persona — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, creates a copy of an existing persona
within the context of the current process. The service returns the assigned persona
identification for the new persona in the persona argument. This
persona can be assumed using the $PERSONA_ASSUME service.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_CLONE persona ,[input]C Prototype
int sys$persona_clone (unsigned int *persona, unsigned int *input);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | persona |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword into which the persona identification handle is written.
| OpenVMS usage: | persona |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword containing the persona identification of the persona to be cloned. If this argument is 0, null, or absent, the currently active persona is cloned.
Description
The Clone Persona service creates a copy of an existing persona within the context of
the current process. The service returns the assigned persona identification for the new
persona in the persona argument. This persona can be assumed using
the $PERSONA_ASSUME service.
On image exit, the natural persona is assumed and all nonpermanent personae are deleted.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Access violation.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
The caller lacks sufficient quota to allocate a new persona.
- SS$_INSFMEM
Insufficient memory.
- SS$_IVMODE
The caller cannot create a persona that is more privileged than the caller.
- SS$_PERSONANONGRATA
The persona ID supplied was invalid.
$PERSONA_CREATE (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Create Persona — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, creates a persona that can be assumed using the $PERSONA_ASSUME service.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_CREATE persona ,[usrnam] ,[flags], [usrpro], [itmlst]C Prototype
int sys$persona_create
(unsigned int *persona, void *usrnam, unsigned int flags,
unsigned int *usrpro, unsigned int *itmlst);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | persona |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword into which the persona identification handle is written.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor - fixed-length descriptor |
Name of the user to be impersonated. The usrnam argument is the
address of a descriptor pointing to a character string containing the user name. The
string can contain a maximum of 32 alphanumeric characters.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The $ISSDEF macro defines these codes:
ISS$V_CREATE_AUTHPRIV - This bit is used to create a persona with the privilege fields set to the authorized privileges of the specified user.
ISS$V_CREATE_DEFPRIV - This bit is used for backward compatibility with the previous implementation of personae. This bit is accepted but not processed, as it describes the default behavior of the service.
ISS$V_NOACCESS - Tells $PERSONA_CREATE not to access the SYSUAF file. Only valid in exec or kernel mode.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | opaque byte stream |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Buffer containing an encoded security profile. The usrpro
argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a buffer that contains encoded
security profile data. This profile can be created by calling the
SYS$CREATE_USER_PROFILE system service.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: | item_list_3 |
| type: | longword |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Attributes describing modifications to the security profile. The
itmlst argument is the address of an item_list defining
changes to be made to the specified user profile.
Item Codes
This section lists the ISS$ item codes and definitions.
ISS$_WORKPRIV
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the working privileges for the new persona as a quadword value.
ISS$_MODE
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the access mode of the new persona as a longword value. The mode cannot be more privileged than that of the caller.
ISS$_FLAGS
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the flags field of the new persona as a longword bit mask. The following bits are currently defined for this field:
ISS$V_PERMANENT - Mark this persona as permanent. It will survive image activations/deactivations.
ISS$V_SECAUDIT - Always audit this persona's operations.
ISS$V_DEBIT - Debit and credit the process BYTLM/BYTCNT for this persona. (This flag is always set for user mode persona.)
ISS$_RIGHTS_INDEX
The index indicates into which rights chain the rights are placed. Values for the index are: ISS$M_ENABLED_PERSONA, ISS$M_ENABLED_SYSTEM, ISS$M_ENABLED_INSTALLED, ISS$M_ENABLED_SUBSYSTEM, and ISS$M_ENABLED_TEMPORARY. All subsequent rights item packets use the index until a new ISS$_RIGHTS_INDEX item changes the index. If a rights index is not specified, the rights item packets will use the PERSONA chain as the default. Rights item packets include: ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS, ISS$_RIGHTS, ISS$_ADD_AUTHRIGHTS, and ISS$_ADD_RIGHTS.
ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS (Reserved to OpenVMS)
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the user authorized rights of the new persona as a list of quadword values. Any existing authorized rights will be overwritten. By default, the rights will be placed in the PERSONA rights chain. See ISS$_RIGHTS_INDEX for more information on specifying different indexes.
ISS$_RIGHTS
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the user rights of the new persona as a list of quadword (paired longword) values. Any existing authorized rights will be overwritten. By default, the rights will be placed in the PERSONA rights chain. See ISS$_RIGHTS_INDEX for more information on specifying different indexes. The format of the list is the same as ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS.
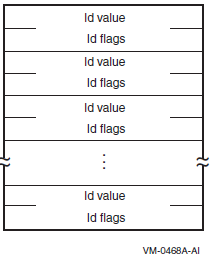
ISS$_USERNAME
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the user name of the new persona as a 32-byte character string.
ISS$_ACCOUNT
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the account of the new persona as a 32-byte character string.
ISS$_NOAUDIT
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the No Audit field of the new persona as a longword value.
ISS$_UIC
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the UIC of the new persona as a longword value.
ISS$_AUTHPRIV
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the authorized privileges for the new persona as a quadword value.
ISS$_PERMPRIV
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the permanent privileges for the new persona as a quadword value.
ISS$_IMAGE_WORKPRIV
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the image working privileges for the new persona as a quadword value.
ISS$_ENABLED
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the Rights Enable field of the new persona as a longword bit mask. These bits correspond to the indices of the different rights chains. By setting the bit in the ENABLED field, the corresponding rightslist chain will be enabled, and its rights will be included in all rights checks. Valid bits are: ISS$V_ENABLED_PERSONA, ISS$V_ENABLED_SUBSYSTEM, ISS$V_ENABLED_IMAGE, ISS$V_ENABLED_SYSTEM, and ISS$V_ENABLED_TEMPORARY.
ISS$_ADD_AUTHRIGHTS
$PERSONA_CREATE adds the rights to the current list of authorized rights. $PERSONA_CREATE expects the same format as that outlined in ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS. By default, the rights will be placed in the PERSONA rights chain. See ISS$_RIGHTS_INDEX for more information on specifying different indexes.
ISS$_ADD_RIGHTS
$PERSONA_CREATE adds the rights to the current list of rights. $PERSONA_CREATE expects the same format as that outlined in ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS. By default, the rights will be placed in the PERSONA rights chain. See ISS$_RIGHTS_INDEX for more information on specifying different indexes.
Description
When you call this service, you can specify either the usrnam
or usrpro argument, but not both. The required information
specifying the OpenVMS user is read from either the User Authorization File (UAF) and
rights database or the usrpro buffer and is stored in system
memory. Any modifications specified in the itmlst are then
applied to complete the new persona. A persona identification handle that refers to the
created persona is returned in the persona argument. This service creates a default VMS
extension for the persona.
It is possible to call $PERSONA_CREATE in any mode. To call $PERSONA_CREATE in kernel
mode, the calling sequence is different. Only the usrpro argument
is valid (usrnam cannot be used because kernel mode access to the
SYSUAF file is not allowed), and it is necessary to set the PSB$M_NOACESS value in the
flags.
No changes are made to the caller's thread as a result of calling $PERSONA_CREATE.
The arguments are validated against the caller's mode, so an invalid argument can cause an access violation to be signaled.
Required Access or Privileges
All calls to $PERSONA_CREATE require IMPERSONATE privilege and read access to the system authorization database.
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
personaargument cannot be written by the caller.- SS$_NOPRIV
The operation requires IMPERSONATE privilege.
- SS$_INSFMEM
Insufficient memory.
- SS$_USERDISABLED
User name disabled.
- SS$_IVMODE
The caller cannot create a persona that is more privileged than the caller.
- SS$_INSFARG
Certain required arguments were not specified.
- SS$_BADPARAM
The value of at least one of the arguments is incorrect.
- SS$_BADCHECKSUM
The buffer specified by
usrprois not valid.- SS$_BADBUFLEN
The buffer length for data within the
usrprooritmlstwas invalid.- SS$_BADITMCOD
At least one argument in the item code is invalid.
- SS$_INVARG
An incorrect combination of arguments was specified.
- SS$_INVSECDOMAIN
The buffer specified by usrpro contains data that originated outside the local security domain.
Any condition value returned by the $LKWSET, $GETUAI, or $FIND_HELD service can also be returned.
$PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Create Persona Extension — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, creates an extension on the current persona. A persona extension is a mechanism to attach support for additional security credentials.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION persona ,extensionID ,buffer ,length ,flags
C Prototype
int sys$persona_create_extension
(unsigned int *persona, unsigned int *extensionID, void *buffer,
unsigned int *length, unsigned int *flags);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | persona |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword containing the persona identification to which $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION attaches a new persona extension.
Two special values for persona are also permitted: 0, which
means the current persona, and -1, which means the process' natural persona is
used.
| OpenVMS usage: | extension_ID |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword containing the extension identification (EID) for which the registered CREATE routine will be called to create a new persona extension block.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a buffer containing data to be used in creating the persona extension data structure. The interpretation of the data within this buffer is the responsibility of the extension create routine. For example, this data could be a Type-Length-Value (TLV) structure containing fields in the extension data structure. Specifying this buffer is optional; a caller who does not want to supply a buffer should specify an address of zero (0).
| OpenVMS usage: | size |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword containing the size, in bytes, of the
buffer argument. Specifying length is
optional; a caller who does not want to supply a length should specify an address of
zero (0). Specifying a buffer without a length is the same as not specifying a
buffer.
| OpenVMS usage: | flags |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Flag mask specifying the options to be employed when the persona extension is created. Specifying flags is optional; a caller who does not want to supply flags should specify an address of zero (0).
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
| PXB$V_PRIMARY_EXTENSION | This extension is recorded as the persona's primary extension. If a persona already has a primary extension, the error SS$_UNSUPPORTED is returned and the extension is not created. The primary extension is returned when the persona is queried for its "Primary Extension." There is no other meaning for this value. |
Description
This service creates an extension by calling the registered Extension Create routine for the specified extension and by attaching it to the persona represented by the persona argument.
When a return fails, no persona extension is created.
A VMS extension is already associated with every persona. An attempt to create a VMS extension using this service returns SS$_DUPLNAM.
Required Access or Privileges
This service requires that the caller have the IMPERSONATE privilege enabled or be in exec or kernel mode.
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
A buffer or return address specified in the item list cannot be read.
- SS$_BADITMCOD
The item list contains an invalid identifier code.
- SS$_BADPARAM
An invalid parameter was specified.
- SS$_DUPLNAM
The persona already has an extension of this type.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
The caller lacks sufficient quota to allocate a new persona.
- SS$_NOIMPERSONATE
The caller does not have the privilege to extend its original identity/persona.
- SS$_NOSUCHEXT
The extension requested does not exist on the system.
- SS$_PERSONANONGRATA
The persona ID supplied was invalid.
- SS$_UNSUPPORTED
An unsupported request was made; check the PRIMARY_EXTENSION flags bit.
$PERSONA_DELEGATE (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Delegate Persona to a Server Process — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, delegates or assigns the currently active persona to another process.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_DELEGATE serverPID ,persona ,inputC Prototype
int sys$persona_delegate
(unsigned int *serverPID, unsigned int *persona, unsigned int *input);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | process_ID |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword containing the extended process identification (PID) of the server process to which $PERSONA_DELEGATE grants the current persona.
| OpenVMS usage: | persona |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword containing the identification that the $PERSONA_RESERVE service reserved in the server's process for this client's persona.
| OpenVMS usage: | persona |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword containing the persona identification that describes which
persona is delegated to the server. If the input argument is zero
(0) or null, or if the input value is zero (0), the current persona is delegated. If the
input value is -1, then the natural persona of the process is delegated.
Description
This service delegates or assigns either the specified persona or the currently active persona to another process. The server process must have reserved a persona slot for the current process to use by calling $PERSONA_RESERVE before calling this service.
The delegation of persona is only supported for processes residing on the same node in the cluster. When a return fails, the persona is not delegated.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The arguments cannot be read by the service.
- SS$_BADPARAM
An invalid parameter was specified.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
The caller lacks sufficient quota to allocate a new persona.
- SS$_NONEXPR
The process specified does not exist.
- SS$_PERSONANONGRATA
The persona ID supplied was invalid.
$PERSONA_DELETE
Delete Persona — Deletes a persona created using the $PERSONA_CREATE, the $PERSONA_CLONE, or the $PERSONA_RESERVE service.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_DELETE personaC Prototype
int sys$persona_delete (unsigned int *persona);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | persona |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword in which the persona identification handle is expected.
Description
The PERSONA_DELETE service frees the resources used by the persona. No changes to the caller's process are made as a result of calling $PERSONA_DELETE.
The persona argument is validated against the caller's mode, so
an invalid argument can cause an access violation to be signaled.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully
- SS$_ACCVIO
Access violation.
- SS$_PERSONADELPEND
Persona is in use; delete pending on release.
- SS$_NODELPERMANENT
Permanent personae cannot be deleted.
$PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Delete Persona Extension — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, deletes an extension attached to a persona.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION persona ,extensionID
C Prototype
int sys$persona_delete_extension (unsigned int *persona, unsigned int *extensionID);
Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | persona |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword containing the persona identification for which $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION calls the registered Extension Delete function.
| OpenVMS usage: | extension_ID |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword containing the extension identification (EID) for which the registered DELETE routine is called in order to delete a persona extension block from the specified persona.
Description
This service deletes an extension data structure by calling the registered Extension Delete routine for the specified extension.
When a return fails, the persona extension is not deleted.
The VMS extension associated with each persona cannot be deleted. An attempt to delete that extension returns SS$_UNSUPPORTED.
Required Access or Privileges
This service requires that the caller have the IMPERSONATE privilege enabled or be in exec or kernel mode.
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_BADPARAM
An invalid parameter was specified.
- SS$_NOIMPERSONATE
The caller does not have the privilege to delete pieces of the thread's original identity/persona.
- SS$_NOSUCHEXT
The extension specified does not exist in the persona.
- SS$_PERSONANONGRATA
The persona ID supplied was invalid.
- SS$_UNSUPPORTED
The specified extension cannot be deleted.
$PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Translates an Extension Name — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, translates a text name of an extension (for example, VMS or NT) into an extension identification (EID) that can be used in other persona-related system services.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP extensionName ,extensionIDC Prototype
int sys$persona_extension_lookup
(void *extensionName, unsigned int *extensionID);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | extension_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor – fixed-length descriptor |
Address of a character string descriptor pointing to the name of the extension being looked up.
| OpenVMS usage: | extension_ID |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword into which the value of the extension identification (EID) returned by the service is written.
Description
This service translates a text name of an extension into an extension identification (EID) that can be used in other persona-related system services.
There are currently two extension names: VMS and NT.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The string descriptor supplied in the
extensionNameargument cannot be read by the service.- SS$_BADPARAM
An invalid argument was specified.
- SS$_NOSUCHEXT
The supplied
extensionNamedoes not exist on this system.
$PERSONA_FIND (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Find Persona with Characteristics — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, enables the caller to find the personae within a process that have certain attributes or settings.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_FIND persona ,itmlst ,contxtC Prototype
int sys$persona_find
(unsigned int *persona, void *itmlst, unsigned int *contxt);Arguments
persona
| OpenVMS usage: | persona |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword into which the persona identification that matches all of the items present in the item list is written.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: | item_list_3 |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Attributes specifying which information about the persona is to be compared. The
itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors,
each describing an item of information or an item list processing directive. The list of
item descriptors is terminated by a longword value of 0.

The following table lists the item descriptor fields and their definitions:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Buffer length | A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer in which $PERSONA_FIND is to locate the information. The length of the buffer depends on the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too small, $PERSONA_FIND fails the comparison. |
| Item code | A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of information $PERSONA_FIND is to test, or specifying a directive for processing subsequent items. The $ISSDEF macro defines these codes. Each item code is described in the Description section. |
| Buffer address | A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer in which $PERSONA_FIND locates the information used for the comparison. |
| Return length address | An unused longword containing the user-supplied address of a word into which the system service writes the length in bytes of the information it returned. This longword is unused for PERSONA_FIND. |
| OpenVMS usage: | context |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Context value used when repeatedly calling $PERSONA_FIND. The
contxt argument is the address of a longword used while
$PERSONA_FIND searches for all personae that match the criteria. The context value must be
initialized to zero, and the resulting context of each call to $PERSONA_FIND must be
presented to each subsequent call. After contxt is passed to
$PERSONA_FIND, you must not modify its value.
Description
This service enables the caller to find the personae within a process that have certain attributes or settings.
A persona identification is returned only if all the items specified in the item list match those in the persona and its extensions.
The item list cannot be changed between context-saved calls. Results are unpredictable if the item list is changed between calls.
Repeated calls to $PERSONA_FIND return subsequent matching personae. When the service returns SS$_NOMOREPROC, there are no more personae to examine.
OpenVMS Persona Item Codes
| Item Code | Use? | Size (bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISS$_USERNAME | Q,M,F | 32 | OpenVMS user name as text string |
| ISS$_ACCOUNT | Q,M,F | 32 | OpenVMS account name as text string |
| ISS$_DOMAIN | Q,F | 32 | OpenVMS SCSNODE as text string as obtained from $GETJPI's nodename |
| ISS$_PRINCIPAL | Q,F | 64 | OpenVMS user name as text string |
| ISS$_EXTENSION | Q,F | 32 | The text string VMS |
| ISS$_WORKPRIV | Q,M | 8 | Working privilege mask |
| ISS$_WORKCLASS | Q,M | Varying | Working classification |
| ISS$_RIGHTS | Q | Varying | Enabled list of rights identifiers |
| ISS$_NOAUDIT | Q,M | 4 | No audit counter---0 means audits disabled |
| ISS$_UIC | Q,M,F | 4 | Current UIC |
| ISS$_AUTHPRIV | Q,M | 8 | Authorized privilege mask |
| ISS$_PERMPRIV | Q,M | 8 | Permanent privilege mask |
| ISS$_IMAGE_WORKPRIV | Q,M | 8 | Image working privilege mask |
| ISS$_ENABLED | Q | 4 | Mask of enabled rights chains |
| ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS | Q | Varying | Authorized list of rights identifiers |
| ISS$_MINCLASS | Q | Varying | Minimum classification |
| ISS$_MAXCLASS | Q | Varying | Maximum classification |
Required Access or Privileges
The caller may require extension-specific privileges to search on some data items. The Persona Item Codes section lists the privileges that are needed.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The item list cannot be read by the caller.
- SS$_BADPARAM
An invalid parameter was specified.
- SS$_BADITMCOD
The item list contains an invalid item code.
- SS$_BADCONTEXT
The context value is invalid.
- SS$_NOIMPERSONATE
The caller does not have the privilege to obtain information about the specified personae.
- SS$_NOMOREPROC
There are no more personae to check.
- SS$_NOSUCHEXT
The extension requested does not exist on the system.
$PERSONA_MODIFY (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Modify Persona Data — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, sets attribute values for a persona.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_MODIFY persona ,itmlstC Prototype
int sys$persona_modify (unsigned int *persona, void *itmlst);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | persona |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword containing the persona identification for which this service is to set information.
| OpenVMS usage: | item_list_3 |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Attributes specifying which information in the persona is to be modified. The
itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors,
each describing an item of information or an item list processing directive. The list of
item descriptors is terminated by a longword value of 0.

The following table lists the item descriptor fields and their definitions:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Buffer length | A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer from which $PERSONA_MODIFY is to get information. |
| Item code | A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of information $PERSONA_MODIFY is to change, or specifying a directive for processing subsequent items. The $ISSDEF macro defines these codes. Each item code is described in the Description section. |
| Buffer address | A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer from which $PERSONA_MODIFY is to get the information. |
| Return length address | This field is ignored on a call to PERSONA_MODIFY. |
Description
The Modify Persona Data service sets attribute values for a persona.
OpenVMS Persona Item Codes
| Item Code | Use? | Size (bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISS$_USERNAME | Q,M,F | 32 | OpenVMS user name as text string |
| ISS$_ACCOUNT | Q,M,F | 32 | OpenVMS account name as text string |
| ISS$_DOMAIN | Q,F | 32 | OpenVMS SCSNODE as text string as obtained from $GETJPI's nodename |
| ISS$_PRINCIPAL | Q,F | 64 | OpenVMS user name as text string |
| ISS$_EXTENSION | Q,F | 32 | The text string VMS |
| ISS$_WORKPRIV | Q,M | 8 | Working privilege mask |
| ISS$_WORKCLASS | Q,M | Varying | Working classification |
| ISS$_RIGHTS | Q | Varying | Enabled list of rights identifiers |
| ISS$_NOAUDIT | Q,M | 4 | No audit counter---0 means audits disabled |
| ISS$_UIC | Q,M,F | 4 | Current UIC |
| ISS$_AUTHPRIV | Q,M | 8 | Authorized privilege mask |
| ISS$_PERMPRIV | Q,M | 8 | Permanent privilege mask |
| ISS$_IMAGE_WORKPRIV | Q,M | 8 | Image working privilege mask |
| ISS$_ENABLED | Q | 4 | Mask of enabled rights chains |
| ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS | Q | Varying | Authorized list of rights identifiers |
| ISS$_MINCLASS | Q | Varying | Minimum classification |
| ISS$_MAXCLASS | Q | Varying | Maximum classification |
Required Access or Privileges
This service requires that the caller have the IMPERSONATE privilege enabled or be in exec or kernel mode.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The item list cannot be read by the caller, or the buffer cannot be read by the caller.
- SS$_BADPARAM
An invalid parameter was specified.
- SS$_BADITMCOD
The item list contains an invalid item code.
- SS$_NOIMPERSONATE
The caller does not have the privilege to obtain information about the specified personae.
- SS$_NOSUCHEXT
The extension requested does not exist on the system.
- SS$_PERSONANONGRATA
The persona ID supplied was invalid. This service may also return status codes associated with the various extension routines.
$PERSONA_QUERY (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Query for Persona Data — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, retrieves attribute values from a persona (and accompanying extensions).
Format
SYS$PERSONA_QUERY persona ,itmlstC Prototype
int sys$persona_query (unsigned int *persona, void *itmlst);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | persona |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword into which the persona identification handle is written.
Two special values for persona are also permitted: 0, which
means use the current persona, and -1, which means use the process' natural
persona.
| OpenVMS usage: | item_list_3 |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Attributes describing which information about the persona is to be returned. The
itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors,
each of which describes an item of information or an item list processing directive. The
list of item descriptors is terminated by a longword value of 0.

The following table lists the item field descriptors and their definitions:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Buffer length | A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer into which $PERSONA_QUERY writes the information. The length of the buffer depends on the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too small, $PERSONA_QUERY truncates the data. If the buffer length is specified as 0, the service does not return any data in the buffer; instead, the service returns the size of buffer required to contain the data in the Return Length address. This allows run-time determination of the size of buffer needed to hold the requested information. |
| Item code | A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of information $PERSONA_QUERY is to return, or specifying a directive for processing subsequent items. The $ISSDEF macro defines these codes. Each item code is described in the Description section. |
| Buffer address | A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer into which $PERSONA_QUERY writes the information. |
| Return length address | A longword containing the user-supplied address of a word into which the service writes the length in bytes of the information it returned. If the buffer length field is zero (0), then you must specify a return length address. |
Description
The Query for Persona Data service returns the requested items in the buffers supplied.
OpenVMS Persona Item Codes
| Item Code | Use? | Size (bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISS$_USERNAME | Q,M,F | 32 | OpenVMS user name as text string |
| ISS$_ACCOUNT | Q,M,F | 32 | OpenVMS account name as text string |
| ISS$_DOMAIN | Q,F | 32 | OpenVMS SCSNODE as text string as obtained from $GETJPI's nodename |
| ISS$_PRINCIPAL | Q,F | 64 | OpenVMS user name as text string |
| ISS$_EXTENSION | Q,F | 32 | The text string VMS |
| ISS$_WORKPRIV | Q,M | 8 | Working privilege mask |
| ISS$_WORKCLASS | Q,M | Varying | Working classification |
| ISS$_RIGHTS | Q | Varying | Enabled list of rights identifiers |
| ISS$_NOAUDIT | Q,M | 4 | No audit counter---0 means audits disabled |
| ISS$_UIC | Q,M,F | 4 | Current UIC |
| ISS$_AUTHPRIV | Q,M | 8 | Authorized privilege mask |
| ISS$_PERMPRIV | Q,M | 8 | Permanent privilege mask |
| ISS$_IMAGE_WORKPRIV | Q,M | 8 | Image working privilege mask |
| ISS$_ENABLED | Q | 4 | Mask of enabled rights chains |
| ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS | Q | Varying | Authorized list of rights identifiers |
| ISS$_MINCLASS | Q | Varying | Minimum classification |
| ISS$_MAXCLASS | Q | Varying | Maximum classification |
Common Item Codes
| Item Code | Use? | Size (bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISS$_COMMON_USERNAME | Q | varying | User name as text string |
| ISS$_COMMON_ACCOUNT | Q | varying | Account name as text string |
| ISS$_COMMON_FLAGS | Q | 4 | Flags as a longword |
| ISS$_DOMAIN | Q | varying | Domain name as text string |
| ISS$_COMMON_PRINCIPAL | Q | varying | Principal name as text string |
| ISS$_EXTENSION | Q | 32 | Extension name as text string |
| ISS$_DOI | Q | 8 | Domain Of Interpretation quadword |
General Persona Item Codes
| Item Code | Use? | Size (bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISS$_SWITCH_EXTENSION | Q,M | 4 | Extension ID to be used for subsequent item code processing |
| ISS$_FLAGS | Q,M | 4 | Various flags (ISS$_FLAG_PERMANENT) |
| ISS$_MODE | Q | 4 | Persona creation mode (user, supervisor, exec, or kernel) |
| ISS$_UID | Q | 16 | UID assigned when persona created |
| ISS$_PERSONA_ID | Q | 4 | Persona ID of this PSB |
| ISS$_PRIMARY_EXTENSION | Q,M | 4 | Extension id of primary authenticator |
| ISS$_EXTENSION_COUNT | Q | 4 | Count of extensions attached to persona |
| ISS$_EXTENSION_ARRAY | Q | varying | Array of longwords containing extension ids of all extensions attached to persona |
NT Persona Item Codes
| Item Code | Use? | Size (bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISS$_NT_PRINCIPAL | Q,F | varying | Principal name as text string |
| ISS$_NT_TOKEN_USERNAME | Q,F | varying | NT user name as text string |
| ISS$_NT_TOKEN_DOMAINNAME | Q,F | varying | NT domain as text string |
| ISS$_EXTENSION | Q,F | varying | The text string "NT" |
| ISS$_NT_FLAGS | Q,M | 4 | Various flags |
| ISS$_NT_USER_REFCOUNT | Q,M | 4 | NT-Specific User Field |
| ISS$_NT_CREDENTIALS | Q,M | varying | All Token and Security info |
| ISS$_NT_NT_OWF_PASSWORD | Q,M | varying | NT Password |
| ISS$_NT_LM_OWF_PASSWORD | Q,M | varying | LM Password |
|
ISS$_NT_TOKEN_ | Q,F | 16 | User's session key |
| ISS$_NT_TOKEN_LMSESSIONKEY | Q,F | 8 | LM session key |
Required Access or Privileges
No privileges are required to call this service.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The item list cannot be read by the caller, or the buffer length or buffer cannot be written by the caller.
- SS$_BADPARAM
An invalid parameter was specified.
- SS$_BADITMCOD
The item list contains an invalid item code.
- SS$_NOSUCHEXT
The extension requested does not exist on the system.
- SS$_PERSONANONGRATA
The persona ID supplied is invalid.
$PERSONA_RESERVE (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Reserve Persona Slot — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, reserves a persona ID in the server's persona table to be filled in by the $PERSONA_DELEGATE system service.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_RESERVE clientPID ,personaC Prototype
int sys$persona_reserve (unsigned int *clientPID, unsigned int *persona);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | process_ID |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword containing the External Process Identification (EPID) of the client process for which the server is reserving the slot.
| OpenVMS usage: | persona |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a longword into which the persona identification is written. This service sets aside the identification for the client's to-be-delegated persona.
Description
This service reserves a persona identifier slot within the current process for a specific client process to use in delegating its persona to this process. A reserved persona slot can be deleted by a call to the $PERSONA_DELETE service. When a return fails, no persona slot has been reserved for the client process.
The delegation of persona is only supported for processes residing on the same node of a cluster.
Required Access or Privileges
IMPERSONATE
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The item list cannot be read by the caller.
- SS$_BADPARAM
An invalid parameter was specified.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
The caller lacks sufficient quota to allocate a new persona.
- SS$_NONEXPR
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process identification was specified.
$POWER_CONTROL
Power Control — Manipulates the platform's power and performance settings to the value specified in the power_setting parameter. This applies to the entire system just as though commanded through the Integrated Lights-Out (iLO) web interface.
Format
SYS$POWER_CONTROL power_setting, current_valueC Prototype
int sys$power_control
unsigned __int64 power_setting, unsigned __int64 *current_value;Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | quadword_unsigned |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 64-bit value |
A quadword value to specify the new power or performance setting.
| OpenVMS usage: | quadword_unsigned |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 64-bit value |
The address of a quadword for the service to return the current setting (optional).
Description
Power control on Integrity servers comprises power saving strategies and a means of commanding a strategy to be used. The various means of commanding include iLO web interface, Insight Power Manager (IPM), and EFI command line.
Regardless of the interface used (iLO web interface, IPM, or EFI command line), iLO commanding can specify one of the following four states:
Operate at the highest possible performance ("High Performance Mode")
Operate using the least possible power ("Low Power Mode")
Operate using some efficient compromise between power and performance ("Efficiency Mode")
Give power control over to some OS-defined method ("OS Control")
"OS Control Mode", including platforms which have no iLO power commands, is implemented on OpenVMS by the system service $POWER_CONTROL.
This service can be used on all Integrity server platforms.
Power Setting—Enumerated values are as follows:
POWER$C_HIGHEST_PERF---Similar to the iLO 'highest performance' command
POWER$C_LOWEST_POWER---Similar to the iLO 'lowest power' command
POWER$C_EFFICIENCY---Similar to the iLO 'efficiency' command
Previous Value (Optional)---Returns the previous power control state.
Additional values can be added to provide finer control than is possible with the iLO command, but they are not implemented initially.
Required Access or Privileges
This service requires WORLD privilege.
Related Quota
None
Related Services
None
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The requested action is performed.
- SS$_WRONGSTATE
The platform power state is not set to OS control.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The address specified by current_value is not writable.
- SS$_BADPARAM
The value of power_setting is not a legal value.
- SS$_NOWORLD
The user does not have the WORLD privilege, which is required to use this service.
$PROCESS_AFFINITY (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Modify Process Affinity — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, allows modification of the CPU affinity set for a specified kernel thread. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$PROCESS_AFFINITY
[pidadr], [prcnam], [select_mask], [modify_mask], [prev_mask],
[flags] [,[mask_length]]C Prototype
int sys$process_affinity
(unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, struct _generic_64 *select_mask,
struct _generic_64 *modify_mask, struct _generic_64 *prev_mask,
struct _generic_64 *flags,...);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Process identification (PID) of a kernel thread whose affinity mask is to be modified or returned. The
pidadr argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a longword that contains the PID.
Process selection is made through a combination of the
pidadr and
prcnam arguments. If neither are specified or if both have a zero value, the service operations are made to the user affinity mask of the current kernel thread of the calling process. The
pidadr argument takes precedence over the
prcnam argument in any circumstances where both are supplied in the service call.
| OpenVMS usage: | process_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Process name of the process whose affinity mask is to be modified or returned. The
prcnam argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a character string descriptor pointing to the process name string. A process can be identified with a 1- to 15-character string. The service operations are made to the user affinity mask of the initial thread of the specified process.
If pidadr and prcnam are both specified, then
pidadr is modified or returned and
prcnam is ignored. If neither argument is specified, then the
context of the current kernel thread of the calling process is modified or
returned.
| OpenVMS usage: | bitmap |
| type: | quadword bitmap |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The select_mask argument specifies which bits of the specified
process's affinity mask are to be modified. The select_mask
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword bit vector wherein a bit, when set,
specifies that the corresponding CPU position in the mask is to be modified.
| OpenVMS usage: | bitmap |
| type: | quadword bitmap |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Mask specifying the settings for those explicit affinities selected in the
select_mask argument. The modify_mask
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword bit vector wherein a bit, when set,
specifies that the corresponding CPU is to be added to the specified process affinity
set; when clear, the corresponding CPU is to be removed from the specified process
affinity set.
To add a specific CPU to the affinity mask set, that bit position must be set in both
select_mask and modify_mask. To remove
a specific CPU from the affinity mask set, that bit position must be set in
select_mask and clear in
modify_mask.
The constant CAP$K_ALL_CPU_ADD, when specified in modify_mask,
indicates that all CPUs specified in select_mask are to be added
to the affinity mask set. The constant CAP$K_ALL_CPU_REMOVE indicates that all CPUs in
select_mask are to be removed from the affinity mask
set.
| OpenVMS usage: | bitmap |
| type: | quadword bitmap |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Previous CPU affinity mask for the specified kernel thread before execution of this call to
$PROCESS_AFFINITY. The prev_mask argument is the 32- or 64-bit
address of a quadword into which $PROCESS_AFFINITY writes the previous explicit affinity
bitmap.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_quadword |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Options selected for affinity modification. The
flags argument is a quadword bit vector wherein a bit corresponds to an option. Only the bits specified below are used; the remainder of the quadword bits are reserved and must be 0.
Each option (bit) has a symbolic name, which the $CAPDEF macro defines. The
flags argument is constructed by performing a logical OR
operation using the symbolic names of each desired option.
|
Symbolic Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
CAP$M_FLAG_PERMANENT |
Indicates whether to modify the permanent process affinities
in addition to the current image copy. If CAP$M_FLAG_PERMANENT
is set, then both the permanent and current affinities are
modified. If the flag bit is clear or
This bit also determines which of the affinity masks are
returned in |
|
CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU |
Determines whether the kernel thread can be left in a
non-runnable state under some circumstances. No operation of
this service will allow a transition from a runnable to blocked
state; however, if the kernel thread is already at a blocked
state, this bit determines whether the result of the operation
must leave it runnable. If CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU is set or
|
|
CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU_ACTIVE |
Indicates whether a check is made to verify that all CPUs in the select mask that are about to be selected for affinity binding are in the active set. This does not apply to CPUs that are about to be cleared from the current affinity set. Unlike CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU where only a single CPU has to be valid for the condition to pass, CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU_ACTIVE requires that all CPUs in the selected set must pass the criteria. |
|
CAP$M_PURGE_WS_IF_NEW_RAD |
Causes the working set of the process to be purged if the choice of affinity results in a change to the home RAD of the process. |
| OpenVMS usage: | bitmap |
| type: | quadword bitmap |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The mask_length specifies the length in bytes of each of the
three bitmaps: select_mask, modify_mask,
prev_mask. If mask_length is not
supplied or specified as zero, a length of 8 bytes is used.
The correct value for mask_length is determined by the number
of supported CPUs on the system. You can compute the number of bytes needed for the
bitmap as follows: Use the $GETSYI system service with an item code of SYI$_MAX_CPUS to
find the minimum number of bits needed, round this number up to a multiple of 64, and
divide the result by 8.
Description
The Modify Process Affinity system service, based on the arguments
select_mask and modify_mask, adds or
removes CPUs from the specified kernel thread's affinity mask sets. If specified, the
previous affinity mask is returned in prev_mask. With the
modify_mask argument, multiple CPUs can be added or removed
from the process affinity mask set in the same system service call.
Adding a specific CPU to the process affinity mask indicates that the kernel thread is able to execute only on that CPU or on the others specified in the mask. Affinity scheduling takes effect as soon as the affinity mask becomes nonzero, limiting the CPU selection for the kernel thread to what is specified and available. Thread selection and execution is still subject to standard capability requirements, but only the affinity CPU set is considered when looking for an available site. When the affinity mask is cleared, all CPUs are again considered available and affinity is deactivated.
Either
modify_mask or
prev_mask, or both, must be specified as arguments. If
modify_mask is specified, then
select_mask must be specified as an argument. If
modify_mask is not specified, then no modifications are made to the affinity mask for the specified kernel thread. In this case,
select_mask is ignored. If
prev_mask is not specified, then no previous mask is returned.
No service changes will be allowed if the specified kernel thread will transition from a
runnable to blocked state. The CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU bit in the
flags argument requires that the final thread state be
runnable regardless of previous state; otherwise, interim changes that maintain a
blocked state are allowed if the thread is already in one.
Required Privileges
- ALTPRI—To modify any process with a matching UIC
- ALTPRI and GROUP—To modify any process in the same UIC group
- ALTPRI and WORLD—To modify any process
- None—To retrieve the state of itself or any process with a matching UIC
- GROUP—To retrieve the state of any process in the same UIC group
- WORLD—To retrieve the state of any process
Related Services
$CPU_CAPABILITIES $PROCESS_CAPABILITIES
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_BADPARAM
One of more arguments has an invalid value.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more arguments.
- SS$_NOPRIV
Insufficient privilege for attempted operation.
- SS$_NOSUCHTHREAD
The specified kernel thread does not exist.
- SS$_NONEXPR
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process identification was specified.
- SS$_IVLOGNAM
The process name string has a length of 0 or has more than 15 characters.
- SS$_CPUCAP
No CPU can run the specified process with new affinities.
- SS$_INSFARG
Fewer than the required number of arguments were specified or no operation was specified.
$PROCESS_CAPABILITIES (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Modify Process User Capabilities — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, allows modification of the user capability set for a specified kernel thread, or for the global user capability process default. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$PROCESS_CAPABILITIES
[pidadr] [,prcnam] [,select_mask] [,modify_mask] [,prev_mask] [,flags]C Prototype
int sys$process_capabilities
(unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, struct _generic_64 *select_mask,
struct _generic_64 *modify_mask, struct _generic_64 *prev_mask,
struct _generic_64 *flags);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Process identification (PID) of a kernel thread whose user capability mask is to be modified or returned. The
pidadr argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a longword that contains the PID.
Process selection is made through a combination of the
pidadr and
prcnam arguments. If neither are specified or if both have a zero value, the service operations are made to the user capability mask of the current kernel thread of the calling process. The
pidadr argument takes precedence over the
prcnam argument where both are supplied in the service call.
If the constant CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY is specified in flags, then the
user portion of the default process user capability mask is modified or returned
instead, regardless of the values specified in pidadr.
| OpenVMS usage: | process_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Process name of the process whose user capability mask is to be modified or returned. The
prcnam argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a character
string descriptor pointing to the process name string. A process can be identified with
a 1- to 15-character string. The service operations are made to the user capability mask
of the initial thread of the specified process.
You can use the
prcnam argument only if the process identified by the descriptor has the same UIC group number as the calling process. To obtain information about processes in other groups, the
pidadr argument must be used.
If pidadr and prcnam are both specified, then
prcnam is ignored. If neither argument is specified, then the
context of the current kernel thread of the calling process is modified or
returned.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_quadword |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Mask specifying which bits of the specified process' user capability mask are to be modified.
The select_mask argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a
quadword bit vector wherein a bit, when set, specifies that the corresponding user
capability is to be modified.
The individual user capability bits in select_mask can be referenced by
their symbolic bit constant names, CAP$M_USER1 through CAP$M_USER16. These constants
(not zero-relative) specify the position in the mask quadword that corresponds to the
bit name. Multiple capabilities can be selected by ORing together the appropriate bits.
Alternatively, the constant CAP$K_ALL_USER, when specified as the
select_mask argument, selects all user capabilities.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_quadword |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Mask specifying the settings for those capabilities selected in the
select_mask argument. The modify_mask
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword bit vector wherein a bit, when set,
specifies that the corresponding user capability is to be added to the specified kernel
thread; when clear, the corresponding user capability is to be removed.
The symbolic bit constants CAP$M_USER1 through CAP$M_USER16 can be used to modify the appropriate bit position in
modify_mask. Multiple capabilities can be modified by ORing together the appropriate bits.
To add a specific user capability to a kernel thread, that bit position must be set in both
select_mask and modify_mask. To remove
a specific user capability from a kernel thread, that bit position must be set in
select_mask and clear in
modify_mask.
The symbolic constant CAP$K_ALL_USER_ADD, when specified in
modify_mask, indicates that all capabilities specified in
select_mask are to be added to the appropriate capability
set. The symbolic constant CAP$K_ALL_USER_REMOVE indicates that all specified
capabilities are to be removed from the set.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_quadword |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Previous user capability mask for the specified process or thread before execution of this
call to $PROCESS_CAPABILITIES. The prev_mask argument is the 32-
or 64-bit address of a quadword into which $PROCESS_CAPABILITIES writes the previous bit
mask. If CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY is set in the flags argument,
then prev_mask will contain the user portion of the global
default capability mask.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_quadword |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Options selected for the user capability modification. The flags
argument is a quadword bit vector wherein a bit corresponds to an option. Only the bits
specified below are used; the remainder of the quadword bits are reserved and must be
zero.
Each option (bit) has a symbolic name, defined by the $CAPDEF macro. The
flags argument is constructed by performing a logical OR
operation using the symbolic names of each desired option.
|
Symbolic Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY |
Indicates that the specified operations are to be performed on
the global context cell instead of on a specific kernel thread.
This bit supersedes any individual kernel thread specified in
|
|
CAP$M_FLAG_PERMANENT |
Indicates whether to modify the permanent user process
capabilities in addition to the current image copy. If
CAP$M_FLAG_PERMANENT is set, then both the permanent and current
user process capabilities are modified. If this bit is clear or
This bit also determines which of the capability masks are
returned in |
|
CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU |
Determines whether the kernel thread can be left in a
non-runnable state under some circumstances. No operation of
this service will allow a transition from runnable to blocked
state; however, if the kernel thread is already at a blocked
state, this bit determines whether the result of the operation
must leave it runnable. If CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU is set or
|
|
CAP$M_PURGE_WS_IF_NEW_RAD |
Causes the working set of the process to be purged if the choice of capability results in a change to the home RAD of the process. |
Description
The Modify Process User Capabilities system service, based on the arguments
select_mask and
modify_mask, adds or removes user capabilities for the specified kernel thread. If specified, the previous capability mask is returned in
prev_mask. With the
modify_mask argument, multiple user capabilities for a kernel thread can be added or removed in the same system service call.
Either
modify_mask or
prev_mask, or both, must be specified as arguments. If
modify_mask is specified, then
select_mask must be specified as an argument. If
modify_mask is not specified, then no modifications are made to the user capability mask for the specified kernel thread. In this case,
select_mask is ignored. If
prev_mask is not specified, then no previous mask is returned.
No service changes will be allowed if the specified kernel thread will transition from a runnable to blocked state. The CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU bit in the
flags argument requires that the final thread state be runnable regardless of previous state; otherwise, interim changes that maintain a blocked state are allowed if the thread is already in one.
If the symbolic bit constant CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY is set in the
flags argument, the user capability modifications or the mask
read requests are made only to the global initialization cell regardless of what process
selections values are specified in the pidadr and
prcnam arguments.
Required Access or Privileges
- ALTPRI—To modify any process with a matching UIC
- ALTPRI and GROUP—To modify any process in the same UIC group
- ALTPRI and WORLD—To modify any process
- None—To retrieve the state of itself or any process with a matching UIC
- GROUP–To retrieve the state of any process in the same UIC group
- WORLD—To retrieve the state of any process
Related Services
$CPU_CAPABILITIES
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_BADPARAM
One of more arguments has an invalid value.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more arguments.
- SS$_NOSUCHTHREAD
The specified kernel thread does not exist.
- SS$_NONEXPR
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process identification was specified.
- SS$_IVLOGNAM
The process name string has a length of 0 or more than 15 characters.
- SS$_NOPRIV
Insufficient privilege for attempted operation.
- SS$_CPUCAP
No CPU can run the specified process with new capabilities.
- SS$_INSFARG
Fewer than the required number of arguments were specified or no operation was specified.
$PROCESS_SCAN
Process Scan — Creates and initializes a process context that is used by $GETJPI to scan processes on the local system or across the nodes in an OpenVMS Cluster system. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$PROCESS_SCAN pidctx [,itmlst]C Prototype
int sys$process_scan (unsigned int *pidctx, void *itmlst);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Context value supplied by $PROCESS_SCAN to be used as the
pidadr argument of $GETJPI. The pidctx
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of a
longword that is to receive the process context longword. This longword normally
contains 0 or a previous context. If it contains a previous context, the old context is
deleted. If it contains a value other than 0 or a previous context, the old value is
ignored.
| OpenVMS usage: | 32-bit item_list_3 or 64-bit item_list_64b |
| type: | longword (unsigned) for 32-bit; quadword (unsigned) for 64-bit |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Item list specifying selection criteria to be used by the scan or to control the scan.
The itmlst argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and
Integrity server systems) of a list of item descriptors, each of which describes one
selection criterion or control option. Within each selection criterion you can include
several item entries. An item list in 32-bit format is terminated by a longword of 0; an
item list in 64-bit format is terminated by a quadword of 0. All items in an item list
must be of the same format—either 32-bit or 64-bit.
The information in the item list is passed to the item descriptor in one of two ways. If the item descriptor can always hold the actual value of the selection criterion, the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor and the buffer length is specified as 0. If the item descriptor points to the actual value of the selection criterion, the address of the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor and you must specify the buffer length for the selection criterion. Each item code description specifies whether the information is passed by value or by reference.
The following diagram depicts the format of a 32-bit item descriptor that passes the selection criterion as a value:
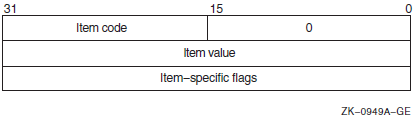
The following diagram depicts the format of a 64-bit item descriptor that passes the selection criterion as a value.
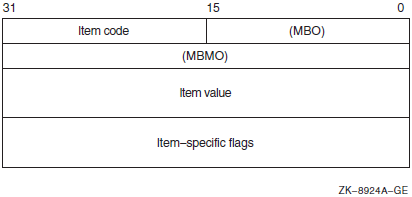
The following diagram depicts the format of a 32-bit item descriptor that passes the selection criterion by reference.

The following diagram depicts the format of a 64-bit item descriptor that passes the selection criterion by reference.
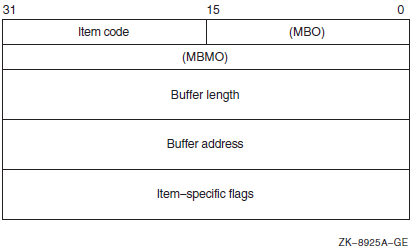
|
Descriptor Field |
Definition | |
|---|---|---|
|
Buffer length |
Buffer length is specified in a different way for the two types of item descriptors. | |
|
Character string or reference descriptors: |
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer from which $PROCESS_SCAN retrieves a selection criterion. The length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the item descriptor. | |
|
Immediate value descriptors: |
The length of the buffer is always specified as 0. | |
|
Item code |
A word containing the selection criterion. These codes are defined by the $PSCANDEF macro. Each item code is described after this list of descriptor fields. | |
|
Item value |
A longword containing the actual value of the selection criterion. When you specify an item code that is passed by value, $PROCESS_SCAN searches for the actual value contained in the item list. See the description of the buffer address field for information about item codes that are passed by reference. | |
|
Buffer address |
A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer from which $PROCESS_SCAN retrieves information needed by the scan. When you specify an item code that is passed by reference, $PROCESS_SCAN uses the address as a pointer to the actual value. See the description of the item value field for information about item codes that are passed by value. | |
|
Item-specific flags |
A longword that contains flags to help control selection information. Item-specific flags, for example EQL or NEQ, are used to specify how the value specified in the item descriptor is compared to the process value. These flags are defined by the $PSCANDEF macro. Some flags are common to multiple item codes; other flags are specific to an individual item code. See the description of each item code to determine which flags are used. For item codes that describe bit masks or character strings, these flags control how the bit mask or character string is compared with that in the process. By default, they are compared for equality. For item codes that describe integers, these flags specify an arithmetic comparison of an integer item with the process attribute. For example, a PSCAN$M_GTR selection specifying the value 4 for the item code PSCAN$_PRIB finds only the processes with a base priority above 4. Without one of these flags, the comparison is for equality. | |
|
MBO |
Must be 1. | |
|
MBMO |
Must be –1. | |
Item Codes
PSCAN$_ACCOUNT
When you specify PSCAN$_ACCOUNT, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the account field.
If the string supplied in the item descriptor is shorter than the account field, the string is blank-padded for the comparison unless the item-specific flag PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH is present.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is passed by reference. The length of the buffer is placed in the first word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is placed in the second longword.
Although the current length of the account field is 8 bytes, the PSCAN$_ACCOUNT buffer can be up to 64 bytes in length. If the buffer length is 0 or greater than 64, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
PSCAN$_AUTHPRI
When you specify PSCAN$_AUTHPRI, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the authorized base priority field.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_CURPRIV
When you specify PSCAN$_CURPRIV, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the current privilege field. Privilege bits are defined by the $PRVDEF macro.
Because the bit mask information is too long to be passed by value, the information is passed by reference. The privilege buffer must be exactly 8 bytes, otherwise the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_GETJPI_BUFFER_SIZE
When you specify PSCAN$_GETJPI_BUFFER_SIZE, you determine the size of a buffer to be used by $GETJPI to process multiple requests in a single message. Using this item code can greatly improve the performance of scans on remote nodes, because fewer messages are needed. This item code is ignored during scans on the local node.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0. The buffer is allocated by $PROCESS_SCAN; you do not have to allocate a buffer.
If you use PSCAN$_GETJPI_BUFFER_SIZE with $PROCESS_SCAN, all calls to $GETJPI using the context established by $PROCESS_SCAN must request the same item code information. Because $GETJPI locates information for more than one process at a time, it is not possible to change the item codes or the length of the buffers used in the $GETJPI item list. $GETJPI checks each call and returns the error SS$_BADPARAM if an attempt is made to change the item list during a buffered process scan. However, the buffer addresses can be changed between $GETJPI calls.
Because the locating and buffering of information by $GETJPI is transparent to a calling program, you are not required to change the way $GETJPI is called when you use this item code.
The $GETJPI buffer uses the process quota BYTLM. If the buffer is too large for the process quota, $GETJPI (not $PROCESS_SCAN) returns the error SS$_EXBYTLM. If the buffer specified is not large enough to contain the data for at least one process, $GETJPI returns the error SS$_BADPARAM.
No item-specific flags are used with PSCAN$_GETJPI_BUFFER_SIZE.
PSCAN$_GRP
When you specify PSCAN$_GRP, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the UIC group number.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. Because the value of the group number is a word, the high-order word of the value is ignored. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_HW_MODEL
When you specify PSCAN$_HW_MODEL, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the specified CPU hardware model number.
The hardware model number is an integer, such as VAX$K_V8840. The VAX$ symbols are defined by the $VAXDEF macro.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_HW_NAME
When you specify PSCAN$_HW_NAME, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the specified CPU hardware name, such as VAX-11/780, VAX 8800, or VAXstation II/GPX.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is passed by reference. The length of the selection value is placed in the first word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is placed in the second longword.
The PSCAN$_HW_NAME buffer can be up to 128 bytes in length. If the buffer length is 0 or greater than 128, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_JOBPRCCNT
When you specify PSCAN$_JOBPRCCNT, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the subprocess count for the job (the count of all subprocesses in the job tree).
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_JOBTYPE
|
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
JPI$K_LOCAL |
Local interactive process |
|
JPI$K_DIALUP |
Interactive process accessed by a modem line |
|
JPI$K_REMOTE |
Interactive process accessed by using SET HOST |
|
JPI$K_BATCH |
Batch process |
|
JPI$K_NETWORK |
Noninteractive network process |
|
JPI$K_DETACHED |
Detached process |
These values are defined by the $JPIDEF macro. Note that values checked by PSCAN$_JOBTYPE are similar to PSCAN$_MODE values.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_KT_COUNT
When you specify PSCAN$_KT_COUNT, $PROCESS_SCAN uses the current count of kernel threads for the process as a selection criteria. The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5
PSCAN$_MASTER_PID
When you specify PSCAN$_MASTER_PID, $GETJPI returns information about processes that are descendants of the specified parent process. The master process is the first process created in the job tree. The PSCAN$_OWNER item is similar, but the owner process is the process that created the target process (the owner process might itself be a subprocess). Although all jobs in a job tree must have the same master, they can have different owners.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_MEM
When you specify PSCAN$_MEM, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the UIC member number.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. Because the value of the member number is a word, the high-order word of the value is ignored. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_MODE
|
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
JPI$K_INTERACTIVE |
Interactive process |
|
JPI$K_BATCH |
Batch job |
|
JPI$K_NETWORK |
Noninteractive network job |
|
JPI$K_OTHER |
Detached and other process |
These values are defined by the $JPIDEF macro. Note that values checked by PSCAN$_MODE are similar to PSCAN$_JOBTYPE values.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_MULTITHREAD
When you specify PSCAN$_MULTITHREAD, $PROCESS_SCAN uses the maximum count of kernel threads for the process as a selection criteria. The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_NODE_CSID
When you specify PSCAN$_NODE_CSID, $GETJPI returns information about processes on the specified nodes. To scan all nodes in an OpenVMS Cluster system, you specify a CSID of 0 and the item-specific flag PSCAN$M_NEQ.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_NODENAME
When you specify PSCAN$_NODENAME, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the specified node names.
To scan all of the nodes in an OpenVMS Cluster system, specify the node name using an asterisk wildcard (*) and the PSCAN$M_WILDCARD item-specific flag.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is passed by reference. The length of the selection value is placed in the first word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is placed in the second longword.
Although the current length of the node name is 6 bytes, the PSCAN$_NODENAME buffer can be up to 64 bytes in length. If the buffer length is 0 or greater than 64, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_OWNER
When you specify PSCAN$_OWNER, $GETJPI returns information about processes that are immediate descendants of the specified process. The PSCAN$_MASTER_PID item is similar, but the owner process is the process that created the target process (the owner process might itself be a subprocess). Although all jobs in a job tree must have the same master, they can have different owners.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_PRCCNT
When you specify PSCAN$_PRCCNT, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the subprocess count (the count of all immediate descendants of a given process). The PSCAN$_JOBPRCCNT item code is similar, except that JOBPRCCNT is the count of all subprocesses in a job.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_PRCNAM
When you specify PSCAN$_PRCNAM, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the specified process names.
The process name string is blank-padded for the comparison unless the item-specific flag PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH is present.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is passed by reference. The length of the selection value is placed in the first word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is placed in the second longword.
Although the current length of the process name field is 15 bytes, the PSCAN$_PRCNAM buffer can be up to 64 bytes in length. If the buffer length is 0 or greater than 64, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_PRI
When you specify PSCAN$_PRI, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match current priority. Note that the current priority of a process can be temporarily increased as a result of system events such as the completion of I/O.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_PRIB
When you specify PSCAN$_PRIB, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match base priority.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_STATE
When you specify PSCAN$_STATE, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the specified process state. State values, for example SCH$C_COM and SCH$C_PFW, are defined by the $STATEDEF macro.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_STS
When you specify PSCAN$_STS, $GETJPI returns information that matches the current status mask. Without any item-specific flags, the match is for a process mask that is equal to the pattern. Status bits, for example PCB$V_ASTPEN or PCB$V_PSWAPM, are defined by the $PCBDEF macro.
This bit mask item code uses an immediate value descriptor; the selection value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_TERMINAL
When you specify PSCAN$_TERMINAL, $GETJPI returns information that matches the specified terminal names. The terminal name string is blank-padded for the comparison unless the item-specific flag PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH is present.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is passed by reference. The length of the selection value is placed in the first word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is placed in the second longword.
Although the current length of the terminal name field is 8 bytes, the PSCAN$_TERMINAL buffer can be up to 64 bytes in length. If the buffer length is 0 or greater than 64, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_UIC
When you specify PSCAN$_UIC, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the UIC identifier. To convert an alphanumeric identifier name to the internal identifier, use the $ASCTOID system service before calling $PROCESS_SCAN.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
PSCAN$_USERNAME
When you specify PSCAN$_USERNAME, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the specified user name.
The user name string is blank-padded for the comparison unless the item-specific flag PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH is present.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is passed by reference. The length of the selection value is placed in the first word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is placed in the second longword.
Although the current length of the user name field is 12 bytes, the PSCAN$_USERNAME buffer can be up to 64 bytes in length. If the buffer length is 0 or greater than 64, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table 5.
Item-Specific Flags
|
Item-Specific Flag |
Description |
Common to the Following $PROCESS_SCAN Item Codes |
|---|---|---|
|
PSCAN$M_BIT_ALL |
All bits set in pattern set in target |
_CURPRIV |
|
PSCAN$M_BIT_ANY |
Any bit set in pattern set in target |
_STS |
|
PSCAN$M_CASE_BLIND |
Match without regard to case of letters |
_ACCOUNT |
|
PSCAN$M_EQL |
Match value exactly (the default) |
All except _BUFFER_SIZE |
|
PSCAN$M_GEQ |
Match if value is greater than or equal to |
_AUTHPRI |
|
PSCAN$M_GTR |
Match if value is greater than |
_GRP |
|
PSCAN$M_LEQ |
Match if value is less than or equal to |
_JOBPRCCNT |
|
PSCAN$M_LSS |
Match if value is less than |
_PRI |
|
_PRIB | ||
|
PSCAN$M_NEQ |
Match if value is not equal |
All except _BUFFER_SIZE |
|
PSCAN$M_OR |
Match this value or the next value |
All except _BUFFER_SIZE |
|
PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH |
Match on leading substring |
_HW_NAME |
|
PSCAN$M_WILDCARD |
Match a wildcard pattern |
_NODENAME _PRCNAM _TERMINAL _USERNAME |
PSCAN$M_BIT_ALL
If the PSCAN$M_BIT_ALL flag is used, all bits set in the pattern mask specified by the item descriptor must also be set in the process mask. Other bits in the process mask can also be set.
For item codes that describe bit masks, such as privilege masks and status words, this flag controls how the pattern bit mask specified by the item descriptor is compared with that in the process. By default, the bit masks are compared for equality.
The PSCAN$M_BIT_ALL flag is used only with bit masks.
PSCAN$M_BIT_ANY
If the PSCAN$M_BIT_ANY flag is used, a match occurs if any bit in the pattern mask is also set in the process mask.
For item codes that describe bit masks, such as privilege masks and status words, this flag controls how the pattern bit mask specified by the item descriptor is compared with that in the process. By default, the bit masks are compared for equality.
The PSCAN$M_BIT_ANY flag is used only with bit masks.
PSCAN$M_CASE_BLIND
When you specify PSCAN$M_CASE_BLIND to compare the character string specified by the item descriptor with the character string value from the process, $PROCESS_SCAN does not distinguish between uppercase and lowercase letters.
The PSCAN$M_CASE_BLIND flag is used only with character-string item codes. The PSCAN$M_CASE_BLIND flag can be specified with either the PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH flag or the PSCAN$M_WILDCARD flag.
PSCAN$M_EQL
When you specify PSCAN$M_EQL, $PROCESS_SCAN compares the value specified by the item descriptor with the value from the process to see if there is an exact match.
PSCAN$M_EQL and PSCAN$M_NEQ are used with bit masks, character strings, and integers to control how the item is interpreted. Only one of the flags can be specified; if more than one of these flags is used, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned. If you want to specify that bits not set in the pattern mask must not be set in the process mask, use PSCAN$M_EQL.
PSCAN$M_GEQ
When you specify PSCAN$M_GEQ, $PROCESS_SCAN selects a process if the value from the process is greater than or equal to the value specified by the item descriptor.
PSCAN$M_GEQ, PSCAN$M_GTR, PSCAN$M_LEQ, and PSCAN$M_LSS are used with integer item codes only. Only one of these four flags can be specified; if more than one of these flags is used, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned.
PSCAN$M_GTR
When you specify PSCAN$M_GTR, $PROCESS_SCAN selects a process if the value from the process is greater than the value specified by the item descriptor.
PSCAN$M_GEQ, PSCAN$M_GTR, PSCAN$M_LEQ, and PSCAN$M_LSS are used with integer item codes only. Only one of these four flags can be specified; if more than one of these flags is used, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned.
PSCAN$M_LEQ
When you specify PSCAN$M_LEQ, $PROCESS_SCAN selects a process if the value from the process is less than or equal to the value specified by the item descriptor.
PSCAN$M_GEQ, PSCAN$M_GTR, PSCAN$M_LEQ, and PSCAN$M_LSS are used with integer item codes only. Only one of these four flags can be specified; if more than one of these flags is used, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned.
PSCAN$M_LSS
When you specify PSCAN$M_LSS, $PROCESS_SCAN selects a process if the value from the process is less than the value specified by the item descriptor.
PSCAN$M_GEQ, PSCAN$M_GTR, PSCAN$M_LEQ, and PSCAN$M_LSS are used with integer item codes only. Only one of these four flags can be specified; if more than one of these flags is used, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned.
PSCAN$M_NEQ
When you specify PSCAN$M_NEQ, $PROCESS_SCAN selects a process if the value from the process is not equal to the value specified by the item descriptor.
PSCAN$M_EQL and PSCAN$M_NEQ are used with bit masks, character strings, and integers to control how the item is interpreted. Only one of the flags can be specified; if more than one of these flags is used, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned.
PSCAN$M_OR
When you specify PSCAN$M_OR, $PROCESS_SCAN selects processes whose values match the current item descriptor or the next item descriptor. The next item descriptor must have the same item code as the item descriptor with the PSCAN$M_OR flag. Multiple items are chained together; all except the last item descriptor must have the PSCAN$M_OR flag.
The PSCAN$M_OR flag can be specified with any other flag and can be used with bit masks, character strings, and integers. If the PSCAN$M_OR flag is used between different item codes, or if it is missing between identical item codes, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned.
PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH
When you specify PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH, $PROCESS_SCAN compares the character string specified in the item descriptor to the leading characters of the requested process value.
For example, to find all process names that start with the letters AB, use the string AB with the PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH flag. If you do not specify the PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH flag, the search looks for a process with the 2-character process name AB.
The PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH flag also allows either the PSCAN$M_EQL or the PSCAN$M_NEQ flag to be specified. If you specify PSCAN$M_NEQ, the service matches those names that do not begin with the specified character string.
The PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH flag is used only with character string item codes. The PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH flag cannot be specified with the PSCAN$M_WILDCARD flag; if both of these flags are used, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned.
PSCAN$M_WILDCARD
When you specify PSCAN$M_WILDCARD, the character string specified by the item descriptor is assumed to be a wildcard pattern. Acceptable wildcard characters are the asterisk (*), which allows the match to substitute any number of character in place of the asterisk, and the percent sign (%), which allows the match to substitute any one character in place of the percent sign. For example, if you want to search for all process names that begin with the letter A and end with the string ER, use the string A*ER with the PSCAN$M_WILDCARD flag. If the PSCAN$M_WILDCARD flag is not specified, the search looks for the 4-character process name A*ER.
Only one of the flags PSCAN$M_EQL, PSCAN$M_NEQ, PSCAN$M_BIT_ALL, PSCAN$M_BIT_ANY can be specified
PSCAN$M_CASE_BLIND item-specific flag also allows either the PSCAN$M_EQL or the PSCAN$M_NEQ flag to be specified
Only one of the flags PSCAN$M_EQL and PSCAN$M_WILD_CARD can be specified
Description
The Process Scan system service creates and initializes a process context that is used by $GETJPI to scan processes on the local system or across the nodes in an OpenVMS Cluster system. An item list is used to specify selection criteria to obtain information about specific processes, for example, all processes owned by one user or all batch processes.
The output of the $PROCESS_SCAN service is a process context longword named
pidctx. This process context is then provided to $GETJPI as the
pidadr argument. The process context provided by $PROCESS_SCAN enables $GETJPI to search for processes across the nodes in an OpenVMS Cluster system and to select processes that match certain selection criteria.
The process context consumes process dynamic memory. This memory is deallocated when the end of the context is reached. For example, when the $GETJPI service returns SS$_NOMOREPROC or when $PROCESS_SCAN is called again with the same
pidctx longword, the dynamic memory is deallocated. If you anticipate that a scan might be interrupted before it runs out of processes, $PROCESS_SCAN should be called a second time (without an
itmlst argument) to release the memory. Dynamic memory is automatically released when the current image terminates.
$PROCESS_SCAN copies the item list and user buffers to the allocated dynamic memory. This means that the item lists and user buffers can be deallocated or reused immediately; they are not referenced during the calls to $GETJPI.
The item codes referenced by $PROCESS_SCAN are found in data structures that are always resident in the system, primarily the process control block (PCB) and the job information block (JIB). A scan of processes never forces a process that is swapped out of memory to be brought into memory to read nonresident information.
See the $GETJPI service for a C program example that uses the $PROCESS_SCAN service.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
See the description for the PSCAN$_GETJPI_BUFFER_SIZE item.
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND, $WAKE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
pidctxargument cannot be written by the caller; the item list cannot be read by the caller; or a buffer for a reference descriptor cannot be read.- SS$_BADPARAM
The item list contains an invalid item identifier, or an invalid combination of item-specific flags is present. Or, an item list containing both 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries was found.
- SS$_IVBUFLEN
The buffer length field is invalid. For immediate value descriptors, the buffer length must be 0. For reference descriptors, the buffer length cannot be 0 or longer than the maximum for the specified item code. This error is also returned if the total length of the item list plus the length of all of the buffer fields is too large to process.
- SS$_IVSSRQ
The
pidctxargument was not supplied, or the item list is improperly formed (for example, multiple occurrences of a given item code were interspersed with other item codes).
$PURGWS
Purge Working Set — Removes a specified range of pages from the current working set of the calling process to make room for pages required by a new program segment.
Format
SYS$PURGWS inadrC Prototype
int sys$purgws (struct _va_range *inadr);Argument
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the range of pages to be purged. The
inadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array
containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses. The addresses
are adjusted up or down to fall on CPU-specific page boundaries. Only the virtual page
number portion of each virtual address is used; the low-order byte-within-page bits are
ignored.
Description
The Purge Working Set service removes a specified range of pages from the current working set of the calling process to make room for pages required by a new program segment; however, the Adjust Working Set Limit ($ADJWSL) service is the preferred mechanism for controlling a process's use of physical memory resources.
The $PURGWS service locates pages within the specified range and removes them if they are in the working set.
If the starting and ending virtual addresses are the same, only that single page is purged.
To purge the entire working set, specify a range of pages from 0 through 7FFFFFFF; in this case, the image continues to execute and pages are faulted back into the working set as they are needed. If you exceed this range, the service returns SS$_NOPRIV. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, use the $PURGE_WS service to specify a larger page range.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET, $MGBLSC, $PURGE_WS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC, $UPDSECW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The input address array cannot be read by the caller.
- SS$_NOPRIV
A page in the specified range is in the system address space.
$PURGE_WS (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Purge Working Set — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, removes a specified range of pages from the current working set of the calling process to make room for pages required by a new program segment. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$PURGE_WS start_va_64 ,length_64C Prototype
int sys$purge_ws (void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address of the pages to be purged from the working set. The specified virtual address will be rounded down to a CPU-specific page boundary.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Length of the virtual address space to be purged from the working set. The specified length will be rounded up to a CPU-specific page boundary so that it includes all CPU-specific pages in the requested range.
Description
The Purge Working Set service removes a specified range of pages from the current working set of the calling process to make room for pages required by a new program segment. However, the Adjust Working Set Limit ($ADJWSL) service is the preferred mechanism for controlling a process's use of physical memory resources.
The $PURGE_WS service locates pages within the specified range and removes them if they are in the working set. To purge the entire working set, specify a range of pages from 0 through FFFFFFFF.FFFFFFFF (or to the highest possible process private virtual address, available from $GETJPI); in this case, the image continues to execute, and pages are faulted back into the working set.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADJWSL, $LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64, $PURGWS, $ULKPAG_64, $ULWSET_64
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
$PUT
Inserts Record — The Put service inserts a record into a file. For additional information about this service, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual
$PUTMSG
Put Message — Writes informational and error messages to processes. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses. Note that the return value from *actrtn is checked to determine whether or not the message is output.
Format
SYS$PUTMSG msgvec ,[actrtn] ,[facnam] ,[actprm]C Prototype
int sys$putmsg
(void *msgvec, void (*actrtn)(__unknown_params), void *facnam,
unsigned __int64 actprm);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | cntrlblk |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Message argument vector specifying the message or messages to be written and options that
$PUTMSG is to use in writing the message or messages. The msgvec argument
is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of the message
vector.
The message vector consists of one longword followed by one or more message descriptors, one descriptor per message. The following diagram depicts the contents of the first longword:
|
Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Argument count |
This word-length field specifies the total number of longwords in the message vector, not including the first longword (of which it is a part). |
|
Default message options |
This word-length field specifies which message component or components are to be written. The default message options field is a word-length bit vector wherein a bit, when set, specifies that the corresponding message component is to be written. For a description of each of these components, refer to the Description section. |
|
Bit |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
Include message text Do not include message text |
|
1 |
|
Include mnemonic name for message text Do not include mnemonic name for message text |
|
2 |
|
Include severity level indicator Do not include severity level indicator |
|
3 |
|
Include facility prefix Do not include facility prefix |
Bits 4 through 15 must be 0.
You can override the default setting specified by the default message options field for any or all messages by specifying different options in the new message options field of any subsequent message descriptor. When you specify new message options, the options it specifies become the new default settings for all remaining messages until you specify new message options again.
The $PUTMSG service passes the default message options field to the $GETMSG service as the
flags argument.
If you specify the default message options field as 0, the default message options for the process are used; you can set the process default message options by using the DCL command SET MESSAGE.
The Description section shows the format that $PUTMSG uses to write these message components.
Message Descriptors
Following the first longword of the message vector are one or more message descriptors. A message descriptor can have one of four possible formats, depending on the type of message it describes. There are four types of messages:
User-supplied
System
OpenVMS RMS
System exception
The following diagrams depict the message descriptors for each type of message.

|
Message Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Message code |
Longword value that uniquely identifies the message. The Description section discusses the message code; the VSI OpenVMS Command Definition, Librarian, and Message Utilities Manual explains how to create message codes. |
|
FAO parameter count |
Word-length value specifying the number of longword $FAO parameters that follow in the message descriptor. The number of $FAO parameters needed depends on the $FAO directives used in the message text; some $FAO directives require one or more parameters, while some directives require none. |
|
New message options |
Word-length bit vector specifying new message options for the current message. The contents and format of this field are identical to that of the default message options field. |
|
FAO parameter |
Longword value used by an $FAO directive appearing in the message text. The $FAO parameters listed in the message descriptor must appear in the order in which they will be used by the $FAO directives in the message text. |

|
Message Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Message code |
Longword value that uniquely identifies the message. The facility number field in the message code identifies the facility associated with the message. A system message has a facility number of 0. You cannot specify the FAO parameter count, new message options, and FAO parameter fields. Each longword following the message identification field in the message vector will be interpreted as another message identification. |

|
Message Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Message code |
Longword value that uniquely identifies the message. The |
|
RMS status value |
Longword containing an STV for use by an RMS message that has an associated STV value. The $PUTMSG service uses the STV value as an $FAO parameter or as another message identification, depending on the RMS message identified by the message identification field. If the RMS message does not have an associated STV, $PUTMSG ignores the STV longword in the message descriptor. |

|
Message Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Message code |
Longword value that uniquely identifies the message. The facility number field in the message code identifies the facility associated with the message. A system exception message has a facility number of 0. You cannot specify the FAO parameter count and new message options fields. The longword or longwords following the message code field in the message vector will be interpreted as $FAO parameters. |
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, 64-bit message vectors can be used for applications that require them. A 64-bit message vector begins with the same argument count longword as the 32-bit message vector. After the argument count longword is another longword containing the value SS$_SIGNAL64, which signals that a 64-bit message vector follows. Subsequent message vector elements have a layout analogous to 32-bit message vectors but are 64-bits wide.
The $PUTMSG service accepts either the 32-bit or the 64-bit form of the message vector on Alpha systems.
| OpenVMS usage: | procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
User-supplied action routine to be executed during message processing. The
actrtn argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity
server systems) of this routine.
Note that the first argument passed to the action routine is the address of a character
string descriptor pointing to the message text; the parameter specified by
actprm is the second.
The action routine receives control after a message is formatted but before it is actually written to the user.
The completion code in general register R0 from the action routine indicates whether the message should be written. If the low-order bit of R0 is set (1), then the message will be written. If the low-order bit is cleared (0), then the message will not be written.
If you do not specify actrtn or specify it as 0 (the default), no
action routine executes.
Because $PUTMSG writes messages only to SYS$ERROR and SYS$OUTPUT, an action routine is useful when output must be directed to, for example, a file.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Facility prefix to be used in the first or only message written by $PUTMSG. The
facnam argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity
server systems) of a character string descriptor pointing to this facility prefix.
If you do not specify facnam, $PUTMSG uses the default facility
prefix associated with the message.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Parameter to be passed to the action routine. The actprm argument is
a longword value containing this parameter. If you do not specify actprm,
no parameter is passed.
Description
In the operating system, a message is identified by a longword value, which is called the message code. To construct a message code, you specify values for its four fields, using the Message utility. The following diagram depicts the longword message code.
Thus, each message has a unique longword value associated with it: its message code. You can give this longword value a symbolic name using the Message utility. Such a symbolic name is called the message symbol.
The Message utility describes how to construct a message symbol according to the conventions for operating system messages. Basically, the message symbol has two parts: (1) a facility prefix, which is an abbreviation of the name of the facility with which the message is associated, and (2) a mnemonic name for the message text, which serves to hint at the nature of the message. These two parts are separated by an underscore character (_) in the case of a user-constructed message and by a dollar sign/underscore ($_) in the case of system messages.
The message components written by $PUTMSG are derived both from the message code and from the message symbol. For additional information about both the message code and the message symbol, refer to the VSI OpenVMS Command Definition, Librarian, and Message Utilities Manual.
%FACILITY-L-IDENT, message textwhere:
|
% |
Is the prefix used for the first message written. The hyphen (-) is the prefix used for the remaining messages. |
|
FACILITY |
Is the facility prefix taken from the message symbol. This facility prefix can be
overridden by a facility prefix specified in the |
|
L |
Is the severity level indicator. The severity level indicator is taken from the message code. |
|
IDENT |
Is a mnemonic name for the message text, taken from the message symbol. |
|
message text |
Is the message text specified in the message source file. |
The $PUTMSG service does not check the length of the argument list and therefore cannot return the SS$_INSFARG (insufficient arguments) condition value. Be sure you specify the required number of arguments.
If an error occurs while $PUTMSG calls the Formatted ASCII Output ($FAO) service, $FAO parameters specified in the message vector do not appear in the output.
You cannot call the $PUTMSG service from kernel mode.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
Example
#include <ssdef.h>
#include <rmsdef.h>
#include <starlet.h>
main()
{
int msgvec[] = {3, /* Arg count and message flags */
SS$_ABORT, /* Message code */
RMS$_FNF, /* RMS Message code */
0}; /* RMS Status value */
return (sys$putmsg(msgvec)); /* Generate message */
} $QIO
Queue I/O Request — Queues an I/O request to a channel associated with a device. This service completes asynchronously; for synchronous completion, use the Queue I/O Request and Wait ($QIOW) service. For additional information about system service completion, see the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$QIO
[efn] ,chan ,func ,[iosb] ,[astadr] ,[astprm]
,[p1] ,[p2] ,[p3] ,[p4] ,[p5] ,[p6]C Prototype
int sys$qio
(unsigned int efn, unsigned short int chan, unsigned int func,
struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params),
__int64 astprm, void *p1, __int64 p2, __int64 p3, __int64 p4,
__int64 p5, __int64 p6);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Event flag that $QIO is to set when the I/O operation completes. The
efn argument is a longword value containing the number of the
event flag; however, $QIO uses only the low-order byte.
If you do not specify efn, event flag 0 is used.
When $QIO begins execution, it clears the specified event flag or event flag 0 if
efn was not specified.
The specified event flag is set if the service terminates without queuing an I/O request.
| OpenVMS usage: | channel |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
I/O channel assigned to the device to which the request is directed. The
chan argument is a word value containing the number of the
I/O channel; however, $QIO uses only the low-order word.
Specifying an invalid value for the chan argument will result in either
SS$_IVCHAN or SS$_IVIDENT being returned.
| OpenVMS usage: | function_code |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Device-specific function codes and function modifiers specifying the operation to be
performed. The func argument is a longword containing the
function code.
Each device has its own function codes and function modifiers. For complete information about the function codes and function modifiers that apply to the particular device to which the I/O operation is to be directed, refer to the VSI OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
I/O status block to receive the final completion status of the I/O operation. The
iosb argument is the address of the quadword I/O status
block. The following diagram depicts the structure of the I/O status block.
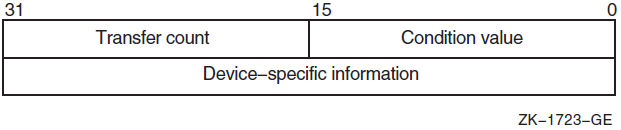
|
Status Block Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Condition value |
Word-length condition value that $QIO returns when the I/O operation actually completes. |
|
Transfer count |
Number of bytes of data transferred in the I/O operation. For information about how specific devices handle this field of the I/O status block, refer to the VSI OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual. |
|
Device-specific information |
Contents of this field vary depending on the specific device and on the specified function code. For information on how specific devices handle this field of the I/O status block, refer to the VSI OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual. |
When $QIO begins execution, it clears the quadword I/O status block if the
iosb argument is specified.
If you are using an event flag to signal the completion of the service, you can test the I/O status block for a condition value to be sure that the event flag was not set by an event other than service completion.
If you are using the $SYNCH service to synchronize completion of the service, the I/O status block is a required argument for $SYNCH.
The condition value returned in R0 and the condition value returned in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of the call to the $QIO service. The condition value returned in R0 gives you information about the success or failure of the service call itself; the condition value returned in the I/O status block gives you information about the success or failure of the service operation. Therefore, to accurately assess the success or failure of the call to $QIO, you must first check the condition value returned in R0. If R0 contains a successful value, then you must check the condition value in the I/O status block.
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
AST service routine to be executed when the I/O completes. The astadr
argument is the address of the AST routine.
The AST routine executes at the access mode of the caller of $QIO.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | quadword unsigned (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 64-bit value (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine. On Alpha and Integrity server systems,
the astprm argument is a quadword value containing the AST
parameter.
| OpenVMS usage: | varying_arg |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference or by 64-bit value, depending on the I/O function (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Optional device-specific and function-specific I/O request parameters. For example, the
p1 parameter usually specifies a buffer by reference. Other
parameters, such as the buffer size, disk block number, or carriage control are often
passed by value.
For more information about these parameters, see the VSI OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
Description
The Queue I/O Request service operates only on assigned I/O channels and only from access modes that are equal to or more privileged than the access mode from which the original channel assignment was made.
The $QIO service uses system dynamic memory to construct a database to queue the I/O request and might require additional memory depending on the queued device.
For $QIO, you can synchronize completion (1) by specifying the
astadr argument to have an AST routine execute when the I/O
completes or (2) by calling the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service to await
completion of the I/O operation. The $QIOW service completes synchronously, and it is
the best choice when synchronous completion is required.
For information about how to use the $QIO service for network operations, refer to the VSI OpenVMS DECnet Networking Manual.
Required Access or Privileges
LOG_IO or PHY_IO is required, depending upon the device type and the requested operation. DIAGNOSE is required to issue a $QIO with an associated diagnostic buffer. In addition, read or write access is generally required for the device. For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
Required Quota
The process's quota for buffered I/O limit (BIOLM) or direct I/O limit (DIOLM)
The process's buffered I/O byte count (BYTLM) quota
The process's AST limit (ASTLM) quota, if an AST service routine is specified
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR, $IO_CLEANUP, $IO_PERFORM, $IO_SETUP
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully. The I/O request was successfully queued.
- SS$_ABORT
A network logical link was broken.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Either the I/O status block cannot be written by the caller, or the parameters for device-dependent function codes are specified incorrectly.
- SS$_CONNECFAIL
The connection to a network object timed out or failed.
- SS$_DEVOFFLINE
The specified device is off line and not currently available for use.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
The process has (1) exceeded its AST limit (ASTLM) quota, (2) exceeded its buffered I/O byte count (BYTLM) quota, (3) exceeded its buffered I/O limit (BIOLM) quota, (4) exceeded its direct I/O limit (DIOLM) quota, or (5) requested a buffered I/O transfer smaller than the buffered byte count quota limit (BYTLM), but when added to other current buffer requests, the buffered I/O byte count quota was exceeded.
- SS$_FILALRACC
A logical link is already accessed on the channel (that is, a previous connect on the channel).
- SS$_FILEFULL
File full; allocation failure. An attempt to extend a file will exceed the maximum supported size of the file. For ODS-2 and ODS-5 disks, this is 2 TB (4,294,967,295 blocks). Reduce the size of the extend request. If the difference between the maximum file size and the current file is less than the cluster size, the file cannot be extended.
- SS$_ILLEFC
You specified an illegal event flag number.
- SS$_INSFMEM
The system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the service.
- SS$_INVLOGIN
The access control information was invalid at the remote node.
- SS$_IVCHAN
You specified an invalid channel number, that is, a channel number of 0, or you failed to specify a channel number.
- SS$_IVIDENT
You specified a channel number greater than the number of channels assigned for the process.
- SS$_IVDEVNAM
The NCB has an invalid format or content.
- SS$_LINKABORT
The network partner task aborted the logical link.
- SS$_LINKDISCON
The network partner task disconnected the logical link.
- SS$_LINKEXIT
The network partner task was started, but exited before confirming the logical link (that is, $ASSIGN to SYS$NET).
- SS$_NOLINKS
No logical links are available. The maximum number of logical links as set for the executor MAXIMUM LINKS parameter was exceeded.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The specified channel does not exist or was assigned from a more privileged access mode, or the process does not have the necessary privileges to perform the specified functions on the device associated with the specified channel.
- SS$_NOSUCHNODE
The specified node is unknown.
- SS$_NOSUCHOBJ
The network object number is unknown at the remote node; or for a TASK= connect, the named DCL command procedure file cannot be found at the remote node.
- SS$_NOSUCHUSER
The remote node could not recognize the login information supplied with the connection request.
- SS$_NOT64DEVFUNC
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this fatal condition value is returned under the following circumstances: (1) The caller has specified a 64-bit virtual address in the P1 device dependent parameter but the device driver does not support 64-bit addresses with the requested I/O function. (2) The caller has specified a 64-bit address for a diagnostic buffer but the device driver does not support 64-bit addresses for diagnostic buffers. (3) Some device drivers might also return this condition value when 64-bit buffer addresses are passed using the P2 through P6 parameters and the driver does not support a 64-bit address with the requested I/O function.
- SS$_PATHLOST
The path to the network partner task node was lost.
- SS$_PROTOCOL
A network protocol error occurred. This error is most likely due to a network software error.
- SS$_REJECT
The network object rejected the connection.
- SS$_REMRSRC
The link could not be established because system resources at the remote node were insufficient.
- SS$_SHUT
The local or remote node is no longer accepting connections.
- SS$_THIRDPARTY
The logical link was terminated by a third party (for example, the system manager).
- SS$_TOOMUCHDATA
The task specified too much optional or interrupt data.
- SS$_UNASEFC
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified event flag.
- SS$_UNREACHABLE
The remote node is currently unreachable.
- SS$_UNSUPPORTED
Unsupported operation or function. An attempt has been made to create a contiguous file with a size greater than the supported maximum. For ODS-2 and ODS-5 disks, this value is 1,073,741,824 blocks. Reduce the size of the request when creating such a file.
Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block
Device-specific condition values; the VSI OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual lists these condition values for each device.
$QIOW
Queue I/O Request and Wait — The Queue I/O Request and Wait service queues an I/O request to a channel associated with a device.
Format
SYS$QIOW
[efn] ,chan ,func ,[iosb] ,[astadr] ,[astprm]
,[p1] ,[p2] ,[p3] ,[p4] ,[p5] ,[p6]C Prototype
int sys$qiow
(unsigned int efn, unsigned short int chan, unsigned int func,
struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params),
__int64 astprm, void *p1, __int64 p2, __int64 p3,
__int64 p4, __int64 p5, __int64 p6);Description
The $QIOW service completes synchronously; however, VSI recommends that you use an IOSB with this service to avoid premature completion.
For asynchronous completion, use the Queue I/O Request ($QIO) service.
In all other respects, $QIOW is identical to $QIO. For more information about $QIOW, refer to the description of $QIO.
For additional information about system service completion, refer to the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
$READ
Retrieves Bytes from File — The Read service retrieves a specified number of bytes from a file (beginning on a block boundary) and transfers them to memory. A Read service using block I/O can be performed on any file organization. For additional information about this service, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$READEF
Read Event Flags — Returns the current status of all 32 event flags in a local or common event flag cluster and indicates whether the specified event flag is set or clear. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$READEF efn ,stateC Prototype
int sys$readef (unsigned int efn, unsigned int *state);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of any event flag in the cluster whose status is to be returned. The
efn argument is a longword containing this number; however,
$READEF uses only the low-order byte. Specifying an event flag within a cluster requests
that $READEF return the status of all event flags in that cluster.
There are two local event flag clusters, which are local to the process: cluster 0 and cluster 1. Cluster 0 contains event flag numbers 0 to 31, and cluster 1 contains event flag numbers 32 to 63.
There are two common event flag clusters: cluster 2 and cluster 3. Cluster 2 contains event flag numbers 64 to 95, and cluster 3 contains event flag numbers 96 to 127.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
State of all event flags in the specified cluster. The state argument
is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of a longword into
which $READEF writes the state (set or clear) of the 32 event flags in the
cluster.
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully. The specified event flag is clear. Note that this is also the same value as SS$_NORMAL.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully. The specified event flag is set. Note that while the message id is the same as SS$_ACCVIO, the severity bits are different.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The longword that is to receive the current state of all event flags in the cluster cannot be written by the caller.
- SS$_ILLEFC
You specified an illegal event flag number.
- SS$_UNASEFC
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified event flag.
$REGISTRY (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Interface to the OpenVMS Registry Database — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, interface to the OpenVMS Registry database server. The $REGISTRY service allows you to query, update, and set keys, subkeys, and values in the OpenVMS Registry database. The $REGISTRY service supports both asynchronous and synchronous operations. For asynchronous completion, use the Registry ($REGISTRY) system service. For synchronous completion, use the Registry and Wait ($REGISTRYW) system service. The $REGISTRYW system service is identical to the $REGISTRY system service, except that $REGISTRYW returns to the caller after the system completes the requested operation. For additional information about system service completion, see the Synchronize ($SYNCH) system service. This system service is 64-bit compatible.
Format
SYS$REGISTRY
[efn] ,func ,0 ,itmlst ,[iosb or iosa_64] [,astadr or astadr_64]
[,astprm or astprm_64] [,timeout]C Prototype
int sys$registry
(unsigned int efn, unsigned int func, void *, void *itmlst,
struct _iosb *iosb, ...);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of the event flag to be used by $REGISTRY. If you do not specify the event flag, the system defaults to event flag 0. The event flag is initially cleared by $REGISTRY and then set when the operation completes.
| OpenVMS usage: | function_code |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Function code specifying the action that $REGISTRY is to perform. The
func argument is a longword containing this function code. The
function code can contain function modifiers. For more information on function modifiers,
see the Function Modifiers section.
A single call to $REGISTRY can specify only one function code. All function codes
require additional information to be passed in the call with the
itmlst argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | 32-bit item_list_3 or 64-bit item_list_64b |
| type: | longword (unsigned) for 32-bit; quadword (unsigned) for 64-bit |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Item list supplying information that the system will use to perform the function
specified by the func argument.
The itmlst argument is the address of the item list. The item
list consists of one or more sets of item descriptors. Each descriptor is either an
item_list_3 or item_list_64b format.
Some function codes allow you to specify multiple operations in a single call. In this case, you must place the REG$_SEPARATOR item code between each set of item codes. Each request, separated by a REG$_SEPARATOR item code, can contain the item codes in any order.
You can specify item codes as either input or output parameters. Input parameters modify functions, set context, or describe the information to be returned. Output parameters return the requested information.
For item_list_3 lists, you must terminate the list with a longword of 0. For item_list_64b lists, you must terminate the list with a quadword of 0.
item_list_3 descriptor:
item_list_64b descriptor: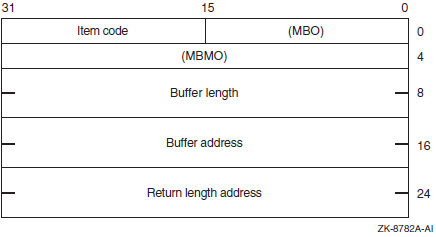
| Descriptor Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| Buffer length | A word that specifies the length of the buffer. The buffer either supplies information to be used by $REGISTRY, or receives information from $REGISTRY. The required length of the buffer varies, depending on the item code specified. Each item code description specifies the required length. |
| Item code | A word containing a symbolic code that describes the type of information currently in the buffer or that is returned in the buffer. The buffer address field points to the location of the buffer. |
| Buffer address | A longword that contains the address of the buffer that specifies or receives the information. |
| Return length address | A longword that contains the address of a word that specifies the actual length in bytes of the information returned by $REGISTRY. The information resides in a buffer identified by the buffer address field. The field applies to output item list entries only, and must be 0 (zero) for input entries. If the return length address is 0, it is ignored. |
| OpenVMS usage: | status_block |
| type: | buffer |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Status block to receive the final completion status and information of the $REGISTRY operation.
If multiple operations are requested for a function code, the value returned in
iosb is either SS$_NORMAL or SS$_REGERROR.
A more specific return status for each operation is returned in the REG$_RETURNSTATUS item code (if specified).
iosb argument is the address of the $REGISTRY status block:
When $REGISTRY begins execution, it clears the quadword I/O status block if you specify the iosb argument.
Although the iosb argument is optional, VSI strongly recommends
that you specify it for the following reasons:
If you are using an event flag to signal the completion of the service, you can test the I/O status block for a condition value to be sure that the event flag was not set by an event other than service completion.
If you are using the $SYNCH system service to synchronize completion of the service, the I/O status block is a required argument for $SYNCH.
The condition value returned in R0 and the condition value returned in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of the call to the $REGISTRY service. The condition value returned in R0 provides information about the success or failure of the service call itself; the condition value returned in the I/O status block provides information about the success or failure of the service operation.
To assess the success or failure of the call to $REGISTRY accurately, you must first check the condition value returned in R0. If R0 contains a successful value, you must check the condition value in the I/O status block.
| Descriptor Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| Status | A longword specifying the final status of the $REGISTRY service. If you
request multiple operations for a function code, the system returns either
SS$_NORMAL or SS$_REGERROR to iosb. This field is set
to 0 (zero) when the operation begins. |
| Reserved | A reserved longword. |
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
AST service routine to be executed when $REGISTRY completes. The
astadr argument is the address of this routine. If you specify
astadr, the AST routine executes at the same access mode as the
caller of the $REGISTRY service.
If the $REGISTRY service is not called successfully (that is, if it returns an error immediately), the AST routine is not executed.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine specified by the
astadr argument. The astprm argument
specifies this longword parameter.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Timeout value specifies the number of seconds allotted to $REGISTRY to perform the request. If the Registry server does not complete the request within the time you allot, $REGISTRY returns REG$_NORESPONSE.
Function Codes
Table 6 provides a summary of valid function codes, a brief description of their function, and the OpenVMS Registry rights identifier required to perform the function.
You can find a detailed description of each item code in the Item Codes section.
| Function Code | Identifier | Description |
|---|---|---|
| REG$FC_CLOSE_KEY | REG$LOOKUP | Closes an open key or subkey. |
| REG$FC_CREATE_KEY | REG$UPDATE | Creates (and opens) a subkey. |
| REG$FC_DELETE_KEY | REG$UPDATE | Removes a subkey from a key. |
| REG$FC_DELETE_VALUE | REG$UPDATE | Removes a value from a key. |
| REG$FC_ENUM_KEY | REG$LOOKUP | Lists (enumerates) the subkeys of a key. |
| REG$FC_ENUM_VALUE | REG$LOOKUP | Lists (enumerates) the values of a key. |
| REG$FC_FLUSH_KEY | REG$UPDATE | Ensures that all information for the key is backed to disk. |
| REG$FC_MODIFY_KEY | REG$UPDATE | Modifies a key. |
| REG$FC_MODIFY_TREE_KEY | REG$UPDATE | Modifies a key and all its subkeys. |
|
REG$FC_NOTIFY_CHANGE_ | REG$UPDATE | Notifies when a key or value has changed. |
| REG$FC_OPEN_KEY | REG$LOOKUP | Opens a key or subkey. |
| REG$FC_QUERY_KEY | REG$LOOKUP | Fetches information about a key. |
| REG$FC_QUERY_VALUE | REG$LOOKUP | Fetches information about a value. |
| REG$FC_SEARCH_TREE_DATA | REG$LOOKUP | Searches the value data of key and its subkeys. |
| REG$FC_SEARCH_TREE_KEY | REG$LOOKUP | Searches the names of a key and its subkeys. |
| REG$FC_SEARCH_TREE_VALUE | REG$LOOKUP | Searches the values of a key and its subkeys. |
| REG$FC_SET_VALUE | REG$UPDATE | Changes the data associated with a value name. |
REG$FC_CLOSE_KEY
This request releases the open resources of the specified key. If REG$_KEYID indicates a predefined key, the system ignores the action and returns success.
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
REG$FC_CREATE_KEY
If the key does not exist, this request creates a new subkey under the key specified by REG$_KEYID. If the key does exist, the system does not modify it.
If you specify the REG$_KEYRESULT item code, the system opens the specified subkey.
The system returns the result in the REG$_DISPOSITION item code buffer.
Using this function code, you can group multiple requests into a single call to the $REGISTRY service. To use the multiple-request feature, you must use the REG$_SEPARATOR item code to indicate the end of the set of item codes for the current request and that there is another request to process.
To set a value for a key, call the $REGISTRY service with the REG$FC_SET_VALUE function code.
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_CACHEACTION | No | Input |
| REG$_CLASSNAME | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_DISPOSITION | No | Output |
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_KEYRESULT | No | Output |
| REG$_LINKPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_LINKTYPE | No | Input |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
| REG$_SECACCESS | No | Input |
| REG$_SECURITYPOLICY | No | Input |
| REG$_SEPARATOR | No | n/a |
| REG$_SUBKEYNAME | Yes | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_VOLATILE | No | Input |
Note
If you do not specify the REG$_CACHEACTION item code, the new key is created with the same cache action value as the parent key. The same rule applies to the REG$_VOLATILE and REG$_SECURITYPOLICY item codes.
REG$FC_DELETE_KEY
This request removes the specified subkey and its values from the OpenVMS Registry database. If the specified key has subkeys, the key is not deleted. You must delete the subkeys first.
Using this function code, you can group multiple requests into a single call to the $REGISTRY service. If you use this multiple-request feature, use the REG$_SEPARATOR item code to indicate the end of the set of item codes for the current request and that there is another request to process.
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_KEYPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
| REG$_SEPARATOR | No | n/a |
| REG$_SUBKEYNAME | Yes | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
REG$FC_DELETE_VALUE
This request deletes the specified value from the key.
Using this function code, you can group multiple requests into a single call to the $REGISTRY service. If you use this multiple-request feature, use the REG$_SEPARATOR item code to indicate the end of the set of item codes for the current request and that there is another request to process.
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_KEYPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
| REG$_SEPARATOR | No | n/a |
| REG$_VALUENAME | Yes | Input |
REG$FC_ENUM_KEY
This request retrieves information about one subkey of the key. You identify the subkey in the REG$_SUBKEYINDEX item code.
To enumerate all the key's subkeys, the application must call the $REGISTRY service repeatedly using the REG$FC_ENUM_KEY function code. Begin with a REG$_SUBKEYINDEX of zero, then increment the count until the request returns a REG$_NOMOREITEMS error.
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_CACHEACTION | No | Output |
| REG$_CLASSNAME | No | Output (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_KEYPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_LASTWRITE | No | Output |
| REG$_LINKCOUNT | No | Output |
| REG$_LINKPATH | No | Output (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_LINKTYPE | No | Output |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
| REG$_SECURITYPOLICY | No | Output |
| REG$_SUBKEYINDEX | Yes | Input |
| REG$_SUBKEYNAME | No | Output (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_VOLATILE | No | Output |
REG$FC_ENUM_VALUE
This request retrieves information about a value of the specified key identifier. The value to retrieve is identified in the REG$_VALUEINDEX item code.
To enumerate all a key's values, the application must call the $REGISTRY service repeatedly using the REG$FC_ENUM_VALUE function code. Begin with a REG$_VALUEINDEX of zero, then increment the count until the request returns a REG$_NOMOREITEMS error.
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_DATAFLAGS | No | Output |
| REG$_DATATYPE | No | Output |
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_KEYPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
| REG$_VALUEDATA | No | Output |
| REG$_VALUEDATASIZE | No | Output |
| REG$_VALUEINDEX | Yes | Input |
| REG$_VALUENAME | No | Output |
| REG$_VOLATILE | No | Output |
REG$FC_FLUSH_KEY
This request writes all the information about a specified key to disk.
This request returns only after the operation is complete and all attributes of the key have been written to the OpenVMS Registry database.
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_KEYPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
REG$FC_MODIFY_KEY
This request modifies a specified key's attributes.
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_CACHEACTION | No | Input |
| REG$_CLASSNAME | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_KEYPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_LINKPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_LINKTYPE | No | Input |
| REG$_NEWNAME | No | Input |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
| REG$_SECURITYPOLICY | No | Input |
To remove the link from the specified key, enter a REG$_LINKPATH item code with an address of zero. You cannot add a link to a key that has either values or subkeys (or both).
REG$FC_MODIFY_TREE_KEY
This request modifies a specified key and all its subkey attributes. No link will be followed or modified.
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_CACHEACTION | No | Input |
| REG$_CLASSNAME | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_KEYPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
| REG$_SECURITYPOLICY | No | Input |
REG$FC_NOTIFY_CHANGE_KEY_VALUE
This request notifies the calling process when a specified key or any of its subkeys has changed. That is, the requested function waits for the specified condition before returning.
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_FLAGSUBKEY | Yes | Input |
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_KEYPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_NOTIFYFILTER | Yes | Input |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
REG$FC_OPEN_KEY
This request opens the specified key. If you do not specify a subkey, the system opens the key specified in REG$_KEYID.
If REG$_KEYID specifies a key other than a predefined key, the system opens the key again (duplicates the key).
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_KEYRESULT | Yes | Output |
| REG$_KEYPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
| REG$_SECACCESS | Yes | Input |
| REG$_SUBKEYNAME | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
REG$FC_QUERY_KEY
This request retrieves attributes about a specified key.
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_CACHEACTION | No | Output |
| REG$_CLASSNAME | No | Output (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_CLASSNAMEMAX | No | Output |
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_KEYPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_LASTWRITE | No | Output |
| REG$_LINKCOUNT | No | Output |
| REG$_LINKPATH | No | Output (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_LINKTYPE | No | Output |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
| REG$_SECURITYPOLICY | No | Output |
| REG$_SUBKEYNAMEMAX | No | Output |
| REG$_SUBKEYSNUMBER | Yes | Output |
| REG$_VALUEDATAMAX | No | Output |
| REG$_VALUENAMEMAX | No | Output |
| REG$_VALUENUMBER | No | Output |
| REG$_VOLATILE | No | Output |
REG$FC_QUERY_VALUE
This request retrieves the type, data flags, and data for the specified value name.
Using this function code, you can group multiple requests into a single call to the $REGISTRY service.
If you use this multiple-request feature, use the REG$_SEPARATOR item code to indicate the end of the set of item codes for the current request and that there is another request to process.
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_DATAFLAGS | No | Output |
| REG$_DATATYPE | No | Output |
| REG$_KEYPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_LINKCOUNT | No | Output |
| REG$_LINKPATH | No | Output (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_LINKTYPE | No | Output |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
| REG$_SEPARATOR | No | n/a |
| REG$_VALUEDATA | No | Output |
| REG$_VALUEDATASIZE | No | Output |
| REG$_VALUENAME | Yes | Input |
| REG$_VOLATILE | No | Output |
REG$FC_SEARCH_TREE_DATA
This request scans a specified key and all its descendants for a match with a specified set of data information.
The set of data information can be either the REG$_DATAFLAGS item code, or the pair REG$_DATATYPE and REG$_VALUEDATA item codes, or all three item codes.
The REG$_FLAGOPCODE item code specifies how the REG$_DATAFLAGS item code should be matched against the database. (See the item codes description for more information about the REG$_FLAGOPCODE item code.)
Every time the system finds a match, it appends the path name relative to the specified key to the REG$_PATHBUFFER item code. A Unicode null character is used to separate the value path names.
If the buffer supplied by the application is not big enough to hold all the value
path names found, the system returns the SS$_BUFFEROVF error message in the
iosb argument, and the length required to complete the
operation successfully is returned in the REG$_REQLENGTH item (if specified).
Use the ellipsis (...) wildcard to match zero or more subkeys in the REG$_KEYPATH item code.
(For example, Hardware\...\disks finds all the paths that start with the Hardware subkey and end with the disk subkey, with zero or more subkeys in between.)
Use the asterisk (*) wildcard to match an entire subkey or a portion of a subkey in the REG$_KEYPATH item code.
Use the percent (%) wildcard to match one character in a key name in the REG$_KEYPATH item code.
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_DATAFLAGS | No | Input |
| REG$_DATATYPE | No | Input |
| REG$_FLAGOPCODE | No | Input |
| REG$_KEYPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_PATHBUFFER | Yes | Output |
| REG$_REQLENGTH | No | Output |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
| REG$_VALUEDATA | No | Input |
REG$FC_SEARCH_TREE_KEY
This request scans a specified key and all its descendants for a specified key path.
For this function code, a valid key path is a Unicode string that can include the ellipsis (...), asterisk (*), or percent (%) wildcard character, but that cannot start with the backslash character (\).
Use the ellipsis (...) wildcard to match zero or more subkeys in the REG$_KEYPATH item code. (For example, Hardware\...\disks finds all the paths that start with the Hardware subkey and end with the disk subkey, with zero or more subkeys in between.)
Use the asterisk (*) wildcard to match an entire subkey or a portion of a subkey in the REG$_KEYPATH item code.
Use the percent (%) wildcard to match one character in a key name in the REG$_KEYPATH item code.
hardware\system\*\disk%%
Every time the system finds a match, the system appends its path name relative to the specified key identifier to the REG$_PATHBUFFER item code. A Unicode null character (4 bytes) separates the subkey path names.
If the buffer supplied by the application is not big enough to contain all the subkey
path names found, the system returns the SS$_BUFFEROVF error message in the
iosb argument, and the system returns the required length to
complete the operation successfully in the REG$_REQLENGTH item (if specified).
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_KEYPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_PATHBUFFER | Yes | Output |
| REG$_REQLENGTH | No | Output |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
REG$FC_SEARCH_TREE_VALUE
This request scans a specified key and all its descendants for a specified value name.
For this function code a valid key name is a Unicode string that can include the ellipsis (...), asterisk (*), or percent (%) wildcard character, but cannot start with the backslash character (\).
Use the ellipsis (...) wildcard to match zero or more subkeys in the REG$_KEYPATH item code. (For example, Hardware\...\disks finds all the paths that start with the Hardware subkey and end with the disk subkey, with zero or more subkeys in between.)
Use the asterisk (*) wildcard to match an entire subkey or a portion of a subkey in the REG$_KEYPATH item code.
Use the percent (%) wildcard to match one character in a key name in the REG$_KEYPATH item code.
hardware\system\...
For this function code, a valid name is a Unicode string that can include the asterisk (*) and percent (%) wildcard characters.
Every time the system finds a match, the system appends its path name relative to the specified key identifier to the REG$_PATHBUFFER item code. A Unicode null character (4 bytes) separates the subkey path names.
If the buffer supplied by the application is not big enough to contain all the subkey
path names found, the system returns the SS$_BUFFEROVF error message in the
iosb argument, and the system returns the required length to
complete the operation successfully in the REG$_REQLENGTH item (if specified).
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_KEYPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_PATHBUFFER | Yes | Output |
| REG$_REQLENGTH | No | Output |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
| REG$_VALUENAME | Yes | Input |
REG$FC_SET_VALUE
This request sets value and type information for a specified key.
Using this function code, you can group multiple requests into a single call to the $REGISTRY service.
If you use this multiple-request feature, use the REG$_SEPARATOR item code to indicate the end of the set of item codes for the current request and that there is another request to process.
When a value is set to a link, the system validates the link unless you specify the REG$M_IGNORE_LINKS function code modifier.
| Item Code | Required | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_DATAFLAGS | No | Input |
| REG$_DATATYPE | No | Input |
| REG$_KEYID | Yes | Input |
| REG$_KEYPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_LINKPATH | No | Input (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_LINKTYPE | No | Input |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | No | Output |
| REG$_SEPARATOR | No | n/a |
| REG$_VALUEDATA | No | Input |
| REG$_VALUENAME | No | Input |
Item Codes
Table 7 provides
a summary of item codes that are valid as an item descriptor in the
itmlst argument. The table lists the item codes, input/output
usage, and data types.
| Item Code | Input/Output | Data Type |
|---|---|---|
| REG$_CACHEACTION | Input, output | Longword |
| REG$_CLASSNAME | Input, output | (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_CLASSNAMEMAX | Output | Longword |
| REG$_DATAFLAGS | Input, output | Quadword |
| REG$_DATATYPE | Input, output | Longword |
| REG$_DISPOSITION | Output | Longword |
| REG$_FLAGOPCODE | Input | Longword |
| REG$_FLAGSUBKEY | Input | Longword |
| REG$_KEYID | Input, output | Longword |
| REG$_KEYPATH | Input | (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_KEYRESULT | Output | Longword |
| REG$_LASTWRITE | Output | Quadword |
| REG$_LINKCOUNT | Output | Longword |
| REG$_LINKPATH | Input, output | (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_LINKTYPE | Input, output | Longword |
| REG$_NEWNAME | Input | Unicode string |
| REG$_NOTIFYFILTER | Input | Longword |
| REG$_PATHBUFFER | Output | Buffer |
| REG$_REQLENGTH | Output | Longword |
| REG$_RETURNSTATUS | Output | Longword |
| REG$_SECACCESS | Input | Longword |
| REG$_SECURITYPOLICY | Input, output | Longword |
| REG$_SEPARATOR | n/a | None |
| REG$_SUBKEYINDEX | Input | Longword |
| REG$_SUBKEYNAME | Input, output | (Pointer to Unicode string. Unicode character is 4 bytes long.) |
| REG$_SUBKEYNAMEMAX | Output | Longword |
| REG$_SUBKEYSNUMBER | Output | Longword |
| REG$_VALUEDATA | Input, output | Buffer |
| REG$_VALUEDATAMAX | Output | Longword |
| REG$_VALUEDATASIZE | Output | Longword |
| REG$_VALUEINDEX | Input | Longword |
| REG$_VALUENAME | Input, output | Unicode string |
| REG$_VALUENAMEMAX | Output | Longword |
| REG$_VALUENUMBER | Output | Longword |
| REG$_VOLATILE | Input, output | Longword |
REG$_CACHEACTION
The REG$_CACHEACTION item code is an input item code. It is a longword flag that specifies whether the information on a specified object should be written to disk immediately. It takes one of the following values:
| Cache Value | Description |
|---|---|
| REG$K_WRITEBEHIND | Write information about the specified object written to disk at a later time (default). |
| REG$K_WRITETHRU | Write information about the specified object to disk immediately. |
Note
If you do not specify this item code, the value or key inherits its value from the parent object. By default, the entry points (REG$_HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT, REG$_HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, and REG$_HKEY_USERS) are set with a value equal to that of REG$K_WRITEBEHIND.
REG$_CLASSNAME
The REG$_CLASSNAME item code is, depending on the function code, either an input or output item code.
The class name is an information field for a key. The type of an object is an example of a class name. It can be composed of any string of Unicode characters. A Unicode character is 4 bytes long.
REG$_CLASSNAMEMAX
The REG$_CLASSNAMEMAX item code is an output item code. It receives the length, in bytes, of the longest string specifying a subkey class name.
REG$_DATAFLAGS
Depending on the function code, the REG$_DATAFLAGS item code is either an input or output item code. It is a 64-bit application-dependent value data flag.
REG$_DATATYPE
Depending on the function code, the REG$_DATATYPE item code is either an input or output item code.
It is a longword that either specifies the type of information to be stored as a value data or receives the type of information of a specified value data component.
| Type code | Description |
|---|---|
| REG$K_BINARY | Binary data |
| REG$K_DWORD | A 32-bit number |
| REG$K_EXPAND_SZ | A string of Unicode characters |
| REG$K_MULTI_SZ | A concatenated array of REG$K_SZ strings |
| REG$K_NONE | No defined value type (default) |
| REG$K_QWORD | A 64-bit number |
| REG$K_SZ | A null-terminated Unicode string |
Note
The difference between REG$K_EXPAND_SZ and REG$K_SZ:
A string is a set of characters usually in human-readable form. Many value entries in the OpenVMS Registry are written using a string (REG_SZ) or an expandable string (REG_EXPAND_SZ) format.
An expandable string is usually human-readable text, but it can also include a variable that will be replaced when the string is called by an application.
For example, on a Windows NT system, in the value entry %SystemRoot%\System32\Bootok.exe, %SystemRoot% is the expandable portion of the variable. This part is replaced with the actual location of the directory that contains the Windows NT system files.
REG$_DISPOSITION
The REG$_DISPOSITION item code is an output item code. It is a longword and takes one of the following values:
| Disposition value | Description |
|---|---|
| REG$K_CREATENEWKEY | The key did not exist and was created. |
| REG$K_OPENEXISTINGKEY | The key existed and was opened. |
REG$_FLAGOPCODE
The REG$_FLAGOPCODE item code is an input item code. It is a longword flag that indicates how the REG$_DATAFLAGS input item code should be matched against the data flags field in the OpenVMS Registry database. It takes one of the following values:
| Operator code options | Description |
|---|---|
| REG$K_ANY | The data field in the OpenVMS Registry database must contain at least one of the flags in the REG$_DATAFLAGS input item code. |
| REG$K_EXACTMATCH | The REG$_DATAFLAGS input item code must match exactly the data flags field in the OpenVMS Registry database. |
| REG$K_EXCLUDE | The data flags field in the OpenVMS Registry database must not contain the flags in the REG$_DATAFLAGS input item code. |
| REG$K_INCLUDE | The data flags field in the OpenVMS Registry database must contain, at a minimum, the flags in the REG$_DATAFLAGS input item code. |
| REG$K_NOTANY | The data field in the OpenVMS Registry database must not contain any of the flags in the REG$_DATAFLAGS input item code. |
REG$_FLAGSUBKEY
The REG$_FLAGSUBKEY item code is an input item code. It is a longword Boolean field that indicates the following:
If set to 1, report changes in a specified key and any of its subkeys.
If set to 0, report changes to a specified key only.
REG$_KEYID
The REG$_KEYID item code is an input item code. It is a longword that contains the key identifier.
REG$_KEYRESULT
The REG$_KEYRESULT item code is an output item code. It is a longword that receives a key identifier. The key identifier can be passed to other Registry calls using the REG$_KEYID item code.
REG$_KEYPATH
The REG$_KEYPATH item code is an input item code. It is a string of Unicode characters that specifies a key path. A Unicode character is 4 bytes long.
REG$_LASTWRITE
The REG$_LASTWRITE item code is an output item code. It is a quadword representation of absolute time that receives the time a specified key was last written to (including changes to its values).
REG$_LINKCOUNT
The REG$_LINKCOUNT item code is an output item code. It is longword count of the number of symbolic links that refer to the item.
REG$_LINKPATH
The REG$_LINKPATH item code is, depending on the function code, either an input or an output item code. It is a string of Unicode characters that specifies the key path to which a specified key is linked. A Unicode character is 4 bytes long.
REG$_LINKTYPE
The REG$_LINKTYPE item code is, depending on the function code, either an input or an output item code. It is longword type that indicates the link type.
| Link Type | Description |
|---|---|
| REG$K_NONE | No link (default) |
| REG$K_SYMBOLICLINK | Symbolic (logical) link |
REG$_NEWNAME
The REG$_NEWNAME item code is a string of Unicode characters that specifies the new name of the key.
REG$_NOTIFYFILTER
The REG$_NOTIFYFILTER item code is an input item code. It is a longword mask that specifies which changes to the specified key and its subkeys and values to report. It takes any combination of the following values:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| REG$M_CHANGEATTRIBUTES | An attribute change of the specified key or its subkeys. |
| REG$M_CHANGELASTSET | Changes to the last write time of the specified key or its subkeys. |
| REG$M_CHANGENAME | A key name change, including creation and deletion, of the specified key or its subkeys. |
Note
The system report changes to subkeys of the specified key only if the REG$_FLAGSUBKEY item code is set to 1.
REG$_PATHBUFFER
The REG$_PATHBUFFER item code is an output item code. It is a buffer that receives a set of either key paths or value paths, separated by a null Unicode character (4 bytes long). (The third longword of the item descriptor contains the number of bytes written to the buffer.)
REG$_REQLENGTH
The REG$_REQLENGTH item code is an output item code. It is a longword that receives the required buffer size (in bytes) to complete the operation successfully.
REG$_RETURNSTATUS
The REG$_RETURNSTATUS item code is an output item code. It is a longword that receives the final completion status for a specified operation. For more information, see the Condition Values Returned section.
REG$_SECACCESS
The REG$_SECACCESS item code is an input item code. It is a longword mask that specifies the desired security access for the new key. It takes any combination of the following values:
| Security access mask | Description |
|---|---|
| REG$M_ALLACCESS |
A combination of the following access values:
|
| REG$M_CREATELINK | Allows creation of a symbolic link. |
| REG$M_CREATESUBKEY | Allows creation of subkeys. |
| REG$M_ENUMSUBKEYS | Allows enumeration of subkeys. |
| REG$M_EXECUTE | Allows read access. |
| REG$M_NOTIFY | Allows change notification. |
| REG$M_QUERYVALUE | Allows queries of subkey data. |
| REG$M_READ |
A combination of the following access values:
|
| REG$M_SETVALUE | Allows setting of values and data. |
| REG$M_WRITE |
A combination of the following access values:
|
REG$_SECURITYPOLICY
The REG$_SECURITYPOLICY item code is an input item code. It is a longword that specifies the security policy to enforce for the key.
| Policy Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| REG$K_POLICY_NT_40 | Access is required to the first key and the requested key (default). |
REG$_SEPARATOR
The REG$_SEPARATOR item code is an empty item code that provides a separator between sets of item codes.
Using this item code, you can group multiple requests into a single call to the $REGISTRY service. If you use this multiple-request feature, use the REG$_SEPARATOR item code to indicate the end of the set of item codes for the current request and that there is another request to process.
REG$_SUBKEYINDEX
The REG$_SUBKEYINDEX item code is an input item code. It is a longword that specifies the index of the subkey to retrieve.
REG$_SUBKEYNAME
The REG$_SUBKEYNAME item code is an input item code. It is a string of Unicode characters that specifies the name of a subkey. A Unicode character is 4 bytes long.
REG$_SUBKEYNAMEMAX
The REG$_SUBKEYNAMEMAX item code is an output item code. It is a longword that receives the length (in characters) of a specified key's longest subkey name.
REG$_SUBKEYSNUMBER
The REG$_SUBKEYSNUMBER item code is an output item code. It is a longword that receives the number of subkeys contained in a specified key.
REG$_VALUEDATA
The REG$_VALUEDATA item code is, depending on the function code, either an input or output item code. It is a buffer that contains either the value data component to write to the OpenVMS Registry (input), or it receives a data value component from the OpenVMS Registry (output).
REG$_VALUEDATAMAX
The REG$_VALUEDATAMAX item code is an output item code. It is a longword that receives the length (in bytes) of the specified key's longest data component value.
REG$_VALUEDATASIZE
The REG$_VALUEDATASIZE item code is an output item code. It is used to specify the address and size of a buffer that receives the length, in bytes, of the value data. The buffer size should be 4 bytes.
REG$_VALUEINDEX
The REG$_VALUEINDEX item code is an input item code. It is a longword that specifies the index of the value to retrieve within a specified key. Note that the value index starts at zero and can be any value up to one less than the count returned by REG$_VALUENUMBER.
REG$_VALUENAME
The REG$_VALUENAME item code is, depending on the function code, either an input or an output item code. It is a string of Unicode characters that specifies the name of a value.
REG$_VALUENAMEMAX
The REG$_VALUENAMEMAX item code is an output item code. It is a longword that receives the length (in characters) of a specified key's longest value name.
REG$_VALUENUMBER
The REG$_VALUENUMBER item code is an output item code. It is a longword that receives the number of values contained in a specified key.
REG$_VOLATILE
The REG$_VOLATILE item code identifies the volatility of an item. As an output, it returns the volatility of the object. On OpenVMS, volatile keys and values are lost when all nodes running an OpenVMS Registry server are rebooted. (In a standalone system, volatile keys and values are lost when the system reboots.)
| Volatile Type | Description |
|---|---|
| REG$K_CLUSTER | The item is removed when the cluster reboots. |
| REG$K_NONE | The item is not volatile (default). |
Function Modifiers
You can optionally specify the high-order bits of a function code value with function modifiers. These individual bits can alter the operation of the function.
For example, you can specify the function modifier REG$M_CASE_SENSITIVE with the function REG$FC_CREATE_KEY. When you use the function and function modifier together, the data passed to the OpenVMS Registry is treated as case sensitive. The two values are written in VSI C as REG$M_CASE_SENSITIVE |REG$FC_CREATE_KEY.
The OpenVMS Registry function modifiers are defined in the header file REGDEF.H.
REG$M_CASE_SENSITIVE
Use case sensitive matching for keys and values.
REG$M_DISABLE_WILDCARDS
Treat wildcard characters as normal characters for this function.
REG$M_IGNORE_LINKS
Force the operation to not follow any symbolic links associated with a key or a value.
By default, if a key or value is symbolically linked to another key or value, the system follows all links so that the operation specified by the function code is performed on the linked key or value.
When you specify the REG$M_IGNORE_LINKS function modifier, the operation specified by the function code affects only the specified key or value, not the linked key or value.
By default, if a key or value has a symbolic link, it can not be deleted. If you specify the REG$M_IGNORE_LINKS function modifier, the system deletes the key or value.
REG$M_NOW
Write to disk immediately, regardless of the REG$_CACHEACTION item code value.
Description
The $REGISTRY service provides the means to create, delete and modify registry keys, key values, and key attributes.
The $REGISTRY service uses process P1 space to store handles to keys.
The $REGISTRY service must be called at IPL 0, and requires system dynamic memory to deliver AST requests.
Related Services
$REGISTRYW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Normal successful completion.
- SS$_ACCVIO
One of the arguments cannot be read/written.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Function code or one of the item list code is invalid.
- SS$_EXASTLM
Exceeded AST limit.
- SS$_INSFARG
Insufficient number of argument supplied.
- SS$_INSFP1POOL
Not enough process P1 space available.
- SS$_NOIMPERSONATE
The caller does not have the privilege to obtain information about the specified personae.
- SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
Too many arguments.
- REG$_ACCESSDENIED
Requested access to key is denied.
- REG$_IPLTOOHIGH
Callers above IPL 0 cannot call this service.
Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block
- SS$_NORMAL
Normal successful completion.
- SS$_ACCVIO
One of the arguments cannot be read/written.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Function code or one of the item list code is invalid.
- SS$_EXASTLM
Exceeded AST limit.
- SS$_INSFARG
Insufficient number of argument supplied.
- SS$_INSFP1POOL
Not enough process P1 space available.
- SS$_NOIMPERSONATE
The caller does not have the privilege to obtain information about the specified personae.
- SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
Too many arguments.
- REG$_ACCESSDENIED
Requested access to key is denied.
- REG$_BUFFEROVF
Buffer overflow.
- REG$_DBALREADYLOADED
Database is already loaded.
- REG$_DBNOTYETLOADED
Database is not yet loaded.
- REG$_EXQUOTA
Registry file quota or page file quota exceeded.
- REG$_HASLINK
Key has a link to another key.
- REG$_HAVESUBKEYS
Cannot delete a key with subkeys.
- REG$_INTERNERR
Registry internal error.
- REG$_INVCACHEACTION
Invalid cache action parameter.
- REG$_INVCREDENTIALS
NT credentials are not valid.
- REG$_INVDATA
Invalid data value.
- REG$_INVDATATYPE
Invalid data type parameter.
- REG$_INVFUNCCODE
Invalid function code.
- REG$_INVKEYFLAGS
Invalid key flags.
- REG$_INVKEYID
Key does not exist or invalid key ID was specified.
- REG$_INVKEYNAME
Invalid key name.
- REG$_INVLINK
Invalid link or link type.
- REG$_INVLINKPATH
Invalid link path.
- REG$_INVPARAM
Invalid parameter.
- REG$_INVPATH
Invalid key path.
- REG$_INVSECDESCRIPTOR
Invalid security descriptor.
- REG$_INVSECPOLICY
Invalid security policy parameter.
- REG$_INVVALNAME
Invalid value name.
- REG$_INVVOLROOTKEY
Cannot create a new file with a volatile root key.
- REG$_IPLTOOHIGH
Callers above IPL 0 cannot call this service.
- REG$_KEYCHANGED
Key or subkey has changed.
- REG$_KEYLOCKED
Key locked by another thread.
- REG$_KEYNAMEEXIST
Key name already exists.
- REG$_NOKEY
Specified key does not exist.
- REG$_NOMOREITEMS
No more items for specified key.
- REG$_NOPATHFOUND
Path not found.
- REG$_NORESPONSE
OpenVMS Registry server failed to respond within the allotted time period.
- REG$_NOTROOTKEY
Invalid root key index.
- REG$_NOTSUPPORTED
Function code, item code, or item value is not supported.
- REG$_NOVALUE
Specified value does not exist.
- REG$_REQRECEIVED
Received request for key change notification.
- REG$_RESERVED
Cannot delete or modify a reserved key or value.
- REG$_SECVIO
Violates the security access method specified when this key was last opened.
- REG$_STRINGTOOLONG
Input string too long.
- REG$_STRINGTRUNC
Output buffer is not large enough to contain the converted string.
- REG$_TOOMANYOPENKEY
Number of opened keys exceeds the limit.
- REG$_VALUEEXIST
Value already exists.
- REG$_VOLMISMATCH
Cannot create nonvolatile subkey for a volatile key.
This service can also return status values from the following system services: $CLREF, $SYNCH, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, and $PERSONA_QUERY.
$REGISTRYW (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Interface to the OpenVMS Registry Database and Wait — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, interface to the OpenVMS Registry database server. The $REGISTRY service supports both asynchronous and synchronous operations. For asynchronous completion, use the Registry ($REGISTRY) system service. For synchronous completion, use the Registry and Wait ($REGISTRYW) system service. The $REGISTRYW system service is identical to the $REGISTRY system service, except that $REGISTRYW returns to the caller after the system completes the requested operation. For additional information about system service completion, see the Synchronize ($SYNCH) system service. This system service is 64-bit compatible.
Format
SYS$REGISTRYW
[efn] ,func ,0 ,itmlst ,[iosb or iosa_64] [,astadr or astadr_64]
[,astprm or astprm_64] [,timeout]C Prototype
int sys$registryw
(unsigned int efn, unsigned int func, void *, void *itmlst,
struct _iosb *iosb, ...);$RELEASE
Unlocks Record — The Release service unlocks the record specified by the contents of the record file address (RAB$W_RFA) field of the RAB. For additional information about this service, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$RELEASE_GALAXY_LOCK (Alpha Only)
Release OpenVMS Galaxy Lock — Releases ownership of an OpenVMS Galaxy lock. Note that this system service is supported only in an OpenVMS Alpha Galaxy environment. For more information about programming with OpenVMS Galaxy system services, see the VSI OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
Format
SYS$RELEASE_GALAXY_LOCK handleC Prototype
int sys$release_galaxy_lock (unsigned __int64 lock_handle);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | galaxy lock handle |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | input by value |
The 64-bit lock handle that identifies the lock to be released. This value is returned by SYS$CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK.
Description
This service releases ownership of an OpenVMS Galaxy lock. Because a Galaxy lock can be acquired multiple times by the same owner (nested ownership), the lock is not released until the ownership count goes to zero. If the lock ownership is completely released and there are other threads waiting for the lock, they are released from their wait states.
Required Access or Privileges
Write access to lock.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ACQUIRE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE, $DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK, $DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE, $GET_GALAXY_LOCK_INFO, $GET_GALAXY_LOCK_SIZE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Normal completion.
- SS$_IVLOCKID
Invalid lock id.
- SS$_IVLOCKOP
Invalid lock operation.
- SS$_IVLOCKTBL
Invalid lock table.
$REMOVE
Deletes File Name — The Remove service deletes a file name from a directory. It is the reverse of the Enter service. For additional information about this service, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$REM_HOLDER
Remove Holder Record from Rights Database — Deletes the specified holder record from the target identifier's list of holders.
Format
SYS$REM_HOLDER id ,holderC Prototype
int sys$rem_holder (unsigned int id, struct _generic_64 *holder);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | rights_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Binary value of target identifier whose holder is deleted when $REM_HOLDER completes
execution. The id argument is a longword containing the
identifier value.
| OpenVMS usage: | rights_holder |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Identifier of holder being deleted when $REM_HOLDER completes execution. The
holder argument is the address of a quadword containing the
UIC identifier of the holder in the first longword and the value of 0 in the second
longword.
Description
The Remove Holder Record from Rights Database service removes the specified holder record from the target identifier's list of holders.
Required Access or Privileges
Write access to the rights database is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CREATE_RDB, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $GRANTID, $IDTOASC, $MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
holderargument cannot be read by the caller.- SS$_INSFMEM
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights database.
- SS$_IVIDENT
The specified identifier or holder identifier is of invalid format.
- SS$_NORIGHTSDB
The rights database does not exist.
- SS$_NOSUCHID
The specified identifier does not exist in the rights database, or the specified holder identifier does not exist in the rights database.
- RMS$_PRV
The user does not have write access to the rights database.
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes, refer to the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$REM_IDENT
Remove Identifier from Rights Database — Removes the specified identifier record and all its holder records (if any) from the rights database.
Format
SYS$REM_IDENT idC Prototype
int sys$rem_ident (unsigned int id);Argument
| OpenVMS usage: | rights_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Binary value of identifier deleted from rights database when $REM_IDENT completes execution.
The id argument is a longword containing the identifier
value.
Description
The Remove Identifier from Rights Database service removes from the rights database the specified identifier record, all its holder records (if any), and all records in identifiers that the deleted identifier held.
Required Access or Privileges
Write access to the rights database is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CREATE_RDB, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $GRANTID, $IDTOASC, $MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT, $REM_HOLDER, $REVOKID
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_INSFMEM
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights database.
- SS$_IVIDENT
The specified identifier is of invalid format.
- SS$_NORIGHTSDB
The rights database does not exist.
- SS$_NOSUCHID
The specified identifier does not exist in the rights database.
- RMS$_PRV
The user does not have write access to the rights database.
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes, refer to the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$RENAME
Rename File — You can use the Rename service to change the name, type, or version of a file, or to move a file to another directory by changing its directory specification. However, you cannot use this service to move a file to another device. For additional information about this service, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$RESCHED
Reschedule Process — Requests reschedule of a process.
Format
SYS$RESCHEDC Prototype
int sys$resched (void);Arguments
None.
Description
The Reschedule Process service requests that the set of runnable processes on the system be evaluated by their priority, with the potential result that the current process may be descheduled and requeued.
n to
voluntarily relinquish the remainder of its run quantum to another process of the same
priority. When the set of all runnable processes is evaluated, one of the following will occur:The process executing $RESCHED will be descheduled, while another process of equal or higher priority is selected to run. The descheduled process is placed at the end of its priority queue and all other processes at that priority will run before the process that called $RESCHED runs again. When the process does run again, $RESCHED completes and returns control to the application.
If, after the evaluation of all runnable processes, the process that executed $RESCHED remains the highest-priority runnable process, that process remains current and continues to run. In this case, $RESCHED returns immediately.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
None
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
$RESUME
Resume Process — Causes a process previously suspended by the Suspend Process ($SUSPND) service to resume execution or cancels the effect of a subsequent suspend request.
Format
SYS$RESUME [pidadr] ,[prcnam]C Prototype
int sys$resume (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Process identification (PID) of the process to be resumed. The pidadr
argument is the address of a longword containing the PID. The
pidadr argument can refer to a process running on the local
node or a process running on another node in the cluster.
You must specify the pidadr argument to delete processes in other UIC
groups.
| OpenVMS usage: | process_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the process to be resumed. The prcnam argument is the address
of a character string descriptor pointing to the process name.
A process running on the local node can be identified with a 1- to 15-character string. To identify a process on a particular node on a cluster, specify the full process name, which includes the node name as well as the process name. The full process name can contain up to 23 characters.
You can use the prcnam argument to resume only processes in the same
UIC group as the calling process, because process names are unique to UIC groups, and
the operating system uses the UIC group number of the calling process to interpret the
process name specified by the prcnam argument. You must use the
pidadr argument to delete processes in other UIC
groups.
Description
The Resume Process service (1) causes a process previously suspended by the Suspend Process ($SUSPND) service to resume execution or (2) cancels the effect of a subsequent suspend request.
If you specify neither the pidadr nor prcnam
argument, the resume request is issued on behalf of the calling process.
If the longword value at address pidadr is 0, the PID of the target
process is returned.
If one or more resume requests are issued for a process that is not suspended, a subsequent suspend request completes immediately; that is, the process is not suspended. No count of outstanding resume requests is maintained.
Required Access or Privileges
GROUP privilege to resume execution of a process in the same group unless the process has the same UIC as the calling process
WORLD privilege to resume execution of any process in the system
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER, $PROCESS_SCAN, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND, $WAKE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The process name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the caller, or the process identification cannot be written by the caller.
- SS$_INCOMPAT
The remote node is running an incompatible version of the operating system.
- SS$_IVLOGNAM
The specified process name has a length of 0 or has more than 15 characters.
- SS$_NONEXPR
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process identification was specified.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The process does not have the privilege to resume the execution of the specified process.
- SS$_NOSUCHNODE
The process name refers to a node that is not currently recognized as part of the cluster.
- SS$_REMRSRC
The remote node has insufficient resources to respond to the request. (Bring this error to the attention of your system manager.)
- SS$_UNREACHABLE
The remote node is a member of the cluster but is not accepting requests. (This is normal for a brief period early in the system boot process.)
$REVOKID
Revoke Identifier from Process — Removes the specified identifier from the rights list of the process or the system. If the identifier is listed as a holder of any other identifier, the appropriate holder records are also deleted.
Format
SYS$REVOKID
[pidadr] ,[prcnam] ,[id] ,[name] ,[prvatr]C Prototype
int sys$revokid
(unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, struct _generic_64 *id, void *name,
unsigned int *prvatr, unsigned int segment);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Process identification (PID) number of the process affected when $REVOKID completes execution.
The pidadr argument is the address of a longword containing the
PID of the process to be affected. You use –1 to indicate the system rights list.
When pidadr is passed, it is also returned; therefore, you must
pass it as a variable rather than a constant.
| OpenVMS usage: | process_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Process name on which $REVOKID operates. The prcnam argument is the
address of a character string descriptor containing the process name. The maximum length
of the name is 15 characters. Because the UIC group number is interpreted as part of the
process name, you must use pidadr to specify the rights list of a
process in a different group.
| OpenVMS usage: | rights_id |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Identifier and attributes to be removed when $REVOKID completes execution. The
id argument is the address of a quadword containing the
binary identifier code to be removed in the first longword and the attributes in the
second longword.
|
Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC |
Allows unprivileged holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the process rights database by using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST. |
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS |
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem attribute. |
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE |
Allows holders of an identifier to charge disk space to the identifier. It is used only for file objects. |
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM |
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in the subsystem. |
You must specify either id or name. Because the
id argument is returned as well as passed if you specify
name, you must pass it as a variable rather than a constant
in this case.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the identifier removed when $REVOKID completes execution. The
name argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to the
name of the identifier.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Attributes of the deleted identifier. The prvatr argument is the
address of a longword used to store the attributes of the identifier.
Description
The Revoke Identifier from Process service removes the specified identifier from the rights list of the process or the system. If the identifier is listed as a holder of any other identifier, the appropriate holder records are also deleted.
The result of passing the pidadr or the prcnam
argument, or both, to $REVOKID is summarized in the following table.
|
prcnam |
pidadr |
Result |
|---|---|---|
|
Omitted |
Omitted |
Current process ID is used; process ID is not returned. |
|
Omitted |
0 |
Current process ID is used; process ID is returned. |
|
Omitted |
Specified |
Specified process ID is used. |
|
Specified |
Omitted |
Specified process name is used; process ID is not returned. |
|
Specified |
0 |
Specified process name is used; process ID is returned. |
|
Specified |
Specified |
Specified process ID is used and process name is ignored. |
name or the id
argument, or both, to SYS$REVOKID is summarized in the following table.|
name |
id |
Result |
|---|---|---|
|
Omitted |
Omitted |
Illegal. The INSFARG condition value is returned. |
|
Omitted |
Specified |
Specified identifier value is used. |
|
Specified |
Omitted |
Specified identifier name is used; identifier value is not returned. |
|
Specified |
0 |
Specified identifier name is used; identifier value is returned. |
|
Specified |
Specified |
Specified identifier value is used and identifier name is ignored. |
Because the Revoke Identifier from Process service removes the specified identifier from the rights list of the process or the system, this service is meant for use by a privileged subsystem to alter the access rights profile of a user, based on installation policy. It is not meant for use by the general system user.
Required Access or Privileges
You need CMKRNL privilege to invoke this service. In addition, you need GROUP privilege to modify the rights list of a process in the same group as the calling process (unless the process has the same UIC as the calling process). You need WORLD privilege to modify the rights list of a process outside the caller's group. You need SYSNAM privilege to modify the system rights list.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CREATE_RDB, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $GRANTID, $IDTOASC, $MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully; the rights list did not contain the specified identifier.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully; the rights list already held the specified identifier.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
pidadrargument cannot be read or written;prcnamcannot be read;idcannot be read or written;namecannot be read; orprvatrcannot be written.- SS$_INSFARG
You did not specify either the
idor thenameargument.- SS$_INSFMEM
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights database.
- SS$_IVIDENT
The specified identifier name is invalid; the identifier name is longer than 31 characters, contains an illegal character, or does not contain at least one nonnumeric character.
- SS$_IVLOGNAM
You specified an invalid process name.
- SS$_NONEXPR
You specified a nonexistent process.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The caller does not have CMKRNL privilege or is not running in executive or kernel mode; or the caller lacks GROUP, WORLD, or SYSNAM privilege as required.
- SS$_NOSUCHID
The specified identifier name does not exist in the rights database. Note that the binary identifier, if given, is not validated against the rights database.
- SS$_NOSYSNAM
The operation requires SYSNAM privilege.
- SS$_RIGHTSFULL
The rights list of the process or system is full.
- RMS$_PRV
The user does not have read access to the rights database.
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes, refer to the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$REWIND
Sets to First Record — The Rewind service sets the context of a record stream to the first record in the file. RMS alters the context of the next record to indicate the first record as being the next record. For additional information about this service, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$RMSRUNDWN
RMS Rundown — Closes all files opened by OpenVMS RMS for the image or process and halts I/O activity. This routine performs a $CLOSE service for each file opened for processing.
Format
SYS$RMSRUNDWN buf-addr ,type-valueC Prototype
int sys$rmsrundwn ( void *buf-addr, unsigned char *type-value);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
A descriptor pointing to a 22-byte buffer that is to receive the device identification (16
bytes) and the file identification (6 bytes) of an improperly closed output file. The
buf-addr argument is the address of the descriptor that
points to the buffer.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte_unsigned |
| type: | byte (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
A single byte code that specifies the type of I/O rundown to be performed. The
type-value argument is the actual value used.
|
0 |
Rundown of image and indirect I/O for process permanent files. |
|
1 |
Rundown of image and process permanent files. The caller's mode must not be user. |
|
2 |
Abort RMS I/O. The caller's mode must be either executive or kernel (the system calls the I/O rundown control routine with this argument for process deletion). |
Description
The RMS Rundown service closes all files opened by OpenVMS RMS for the image or process and halts I/O activity. This routine performs a $CLOSE service for each file opened for processing. In addition to closing all files and terminating I/O activity, the I/O rundown control routine releases all locks held on records in shared files, clears buffers, and returns other resources allocated for file processing. You should continue to call the rundown control routine until you receive the success completion status code of RMS$_NORMAL.
Note that, prior to the execution of the $CLOSE service, the rundown control routine cancels all outstanding file operations specified in a File Access Block (FAB) or any QIO requests related to file operations (an Open, Create, or Extend service, for example). It also cancels any read/write requests to nondisk devices such as terminals or mailboxes prior to the execution of the $CLOSE service, resulting in possible loss of data. All read/write requests of disk I/O buffers, however, are allowed to complete, which guarantees that none of the data written to disk files will be lost.
There is no predefined macro of the form $RMSRUNDWN_G or $RMSRUNDWN_S to call this service.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CLOSE, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SETDDIR, $SETDFPROT, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
- RMS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- RMS$_CCF
The I/O rundown routine cannot close the file.
- RMS$_IAL
The argument list is invalid. An output file could not be closed successfully, and the user buffer could not be written.
$RPCC_64 (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Read 64-Bit Process Cycle Counter — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, returns a 64-bit, process-based, high-resolution time counter.
Format
SYS$RPCC_64C Prototype
uint64 sys$rpcc_64 ();Description
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, returns a 64-bit long version of the current process cycle counter.
On Alpha systems, this service must be called at least once within each wrap period of the least significant 32 bits of the counter.
For more information, see the RPCC() C-language built-in documentation and the RPCC instruction in the Alpha Architecture Handbook.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
$SCAN_INTRUSION
Scan Intrusion Database — Scans the intrusion database for suspects or intruders during a login attempt, audits login failures and updates records, or adds new records to the intrusion database.
Format
SYS$SCAN_INTRUSION
logfail_status ,failed_user ,job_type ,[source_terminal]
,[source_node] ,[source_user] ,[source_addr] ,[failed_password]
,[parent_user] ,[parent_id] ,[flags]
C Prototype
int sys$scan_intrusion
(unsigned int logfail_status, void *failed_user, unsigned int job_type,
void *source_terminal, void *source_node, void *source_user,
void *source_address, void *failed_password, void *parent_user,
unsigned int parent_id, unsigned int flags);
Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | status code |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Reason why the user's login attempt failed. The logfail_status argument
is a longword containing the login failure status code.
The logfail_status argument can contain any valid message code. For
example, the value of the logfail_status argument is
SS$_NOSUCHUSER if the user name the user entered does not exist on the system.
If the logfail_status argument contains a failure status, the service
performs a suspect scan. Here, the service searches the intrusion database for intruder
suspects as well as intruders. If the value of the logfail_status
argument is a successful message, such as SS$_NORMAL, the service scans the database
only for intruders. For more information about how the database works, see the
VSI OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string or item_list_3 |
| type: | character-coded text string or longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor or by reference |
If the CIA$M_ITEMLIST flag is FALSE:
This argument is the user name associated with the unsuccessful login attempt. The
failed_user argument is the address of a character-string
descriptor pointing to the failed user name.
A failed user name consists of 1 to 32 alphanumeric characters.
If the CIA$M_ITEMLIST flag is TRUE:
The failed_user argument is the address of a 32-bit item list.
If the item list is used, one item, the CIA$_FAILED_USERNAME item, must be present in
the item list.
failed_user argument:| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| CIA$_FAILED_USERNAME | Address of a buffer containing the failed user name. |
| CIA$_SCSNODE | Address of the 8-character null-padded SCS node name on which the intrusion happened. |
| CIA$_USER_DATA | Address of a 256-byte buffer, available for passing third party specified data. |
| OpenVMS usage: | job type |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Type of job that failed. The job_type argument is a longword indicating
the type of job that failed.
job_type argument:JPI$K_BATCH
JPI$K_DETACHED
JPI$K_DIALUP
JPI$K_LOCAL
JPI$K_NETWORK
JPI$K_REMOTE
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Source terminal where the login attempt is occurring. The
source_terminal argument is the address of a character-string
descriptor pointing to the device name of the terminal from which the login attempt
originates.
A source terminal device name consists of 1 to 64 alphanumeric characters, including underscores (_) and colons (:).
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the node from which the user's login attempt originates. The
source_node argument is the address of a character-string
descriptor pointing to the source node name string.
A source node name consists of 1 to 1024 characters. No specific characters, format, or case is required for a source node name string.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
User name associated with the login attempt. The source_user argument
is the address of a character-string descriptor pointing to the source user name
string.
A source user name consists of 1 to 32 alphanumeric characters, including dollar signs ($) and underscores (_).
| OpenVMS usage: | node address |
| type: | descriptor |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Source DECnet for OpenVMS address from which the login attempt originates. The
source_addr argument is the address of a descriptor
containing the source node address.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Password the user entered for the login attempt. The failed_password
argument is the address of a character-string descriptor pointing to the plaintext
password the user entered to log in.
A failed password is a password of 0 to 32 characters that did not allow the user to log in to the system. This argument is not stored in the intrusion database and is only used for auditing during break-in attempts.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Parent process name of the failed login. The parent_user argument is
the address of a character-string descriptor pointing to the parent process name of the
failed login process.
A parent process name consists of 1 to 15 characters. This argument should be specified only for failed spawn commands.
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Process identification of the parent process from which the login was attempted. The
parent_id argument is a longword containing the parent
process identification.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Operational instructions for the service. The flags argument is a
longword bit mask wherein each bit corresponds to an option.
|
Symbolic Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
CIA$M_NOAUDIT |
If set, this flag indicates that the service should instruct the security server to not audit the login failure or the break-in attempt. If the flag is set, you are expected to do your own auditing. |
|
CIA$M_IGNORE_RETURN |
Specifies that the service should not wait for the return status from the security server. No return status from the server's function will be returned to the caller. |
|
CIA$M_ITEMLIST |
If FALSE, the |
|
CIA$M_REAL_USERNAME |
If set, indicates that the user name passed as the failed user name is read and known to the system. |
|
CIA$M_SECONDARY_PASSWORD |
Indicates that the failed password passed to the service was the secondary password. If the flag is clear, the password is assumed to be the primary password. |
Description
Scans the intrusion database for intruders so that successful logins are evaded if the system is taking evasive action.
Adds login failures to the intrusion database.
Changes records in the intrusion database from suspects to intruders when the number of login failures by the specified user or from the specified source reaches the value of the LGI_BREAK_LIM system parameter.
Disables user accounts if the LGI_BRK_DISUSER flag is set and the number of login attempts on a real user has reached LGI_BRK_LIM.
Audits login failures or break-in attempts on behalf of the caller.
The information that $SCAN_INTRUSION stores in the intrusion database is based on the setting of the LGI_BRK_TERM system parameter and the information passed by the caller. For more information about how the intrusion database functions and the use of the LGI system parameters, see the VSI OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
Required Access or Privileges
$SCAN_INTRUSION requires the SECURITY privilege.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$DELETE_INTRUSION, $SHOW_INTRUSION
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
One or more of the arguments were not readable.
- SS$_BADBUFLEN
The length of one or more of the specified arguments is out of range.
- SS$_BADPARAM
An invalid flag was specified in the
flagsargument.- SS$_NOSECURITY
The caller does not have SECURITY privilege.
This service can also return any of the following messages passed from the security server:
- SECSRV$_INSUFINFO
Not enough information is supplied to form an intrusion record.
- SECSRV$_INTRUDER
An intruder matching the information passed to the service exists in the intrusion database.
- SECSRV$_NOMATCH
No intruders or suspects exist that match the information passed to the service.
- SECSRV$_SERVERNOTACTIVE
The security server is not currently active. Try the request again later.
- SECSRV$_SUSPECT
A suspect matching the information passed to the service exists in the intrusion database.
$SCHDWK
Schedule Wakeup — Schedules the awakening (restarting) of a process that has placed itself in a state of hibernation with the Hibernate ($HIBER) service.
Format
SYS$SCHDWK [pidadr] ,[prcnam] ,daytim ,[reptim]C Prototype
int sys$schdwk
(unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, struct _generic_64 *daytim,
struct _generic_64 *reptim);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Process identification (PID) of the process to be awakened. The pidadr
argument is the address of a longword containing the PID. The
pidadr argument can refer to a process running on the local
node or a process running on another node in the OpenVMS Cluster system.
You must specify the pidadr argument to awaken processes in other UIC
groups.
| OpenVMS usage: | process_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed length string descriptor |
Name of the process to be awakened. The prcnam is the address of a
character string descriptor pointing to the process name. A process running on the local
node can be identified with a string of from 1 to 15 characters.
To identify a process on a particular node on a cluster, specify the full process name, which includes the node name as well as the process name. The full process name can contain up to 23 characters.
You can use the prcnam argument to awaken only processes in the same
UIC group as the calling process because process names are unique to UIC groups, and the
operating system uses the UIC group number of the calling process to interpret the
process name specified by the prcnam argument. You must use the
pidadr argument to awaken processes in other UIC
groups.
| OpenVMS usage: | date_time |
| type: | quadword |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Time at which the process is to be awakened. The daytim argument is the
address of a quadword containing this time in the system 64-bit time format. A positive
time value specifies an absolute time at which the specified process is to be awakened.
A negative time value specifies an offset (delta time) from the current time.
| OpenVMS usage: | date_time |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Time interval at which the wakeup request is to be repeated. The reptim
argument is the address of a quadword containing this time interval. The time interval
must be expressed in delta time format.
The time interval specified cannot be less than 10 milliseconds; if it is, $SCHDWK automatically increases it to 10 milliseconds.
If you do not specify reptim, a default value of 0 is used, which
specifies that the wakeup request is not to be repeated.
Description
The Schedule Wakeup service schedules the awakening of a process that has placed itself in a state of hibernation with the Hibernate ($HIBER) service. A wakeup can be scheduled for a specified absolute time or for a delta time and can be repeated at fixed intervals.
If you specify neither the
pidadr nor the
prcnam argument, the wakeup request is issued on behalf of the calling process. If the longword value at address
pidadr is 0, the PID of the target process is returned.
$SCHDWK uses the system dynamic memory to allocate a timer queue entry.
If you issue one or more scheduled wakeup requests for a process that is not hibernating, a subsequent hibernate request by the target process completes immediately; that is, the process does not hibernate. No count of outstanding wakeup requests is maintained.
You can cancel scheduled wakeup requests that have not yet been processed by using the Cancel Wakeup ($CANWAK) service.
If a specified absolute time value has already passed and no repeat time is specified, the timer expires at the next clock cycle (within 10 milliseconds).
Required Access or Privileges
GROUP privilege to schedule wakeup requests for a process in the same group unless it has the same UIC
WORLD privilege to schedule wakeup requests for any other process in the system
Required Quota
This service uses the process's timer queue entries (TQELM) quota. If you specify an AST routine, the service uses the AST limit (ASTLM) quota of the calling process to schedule a wakeup request.
Related Services
$ASCTIM, $BINTIM, $CANTIM, $CANWAK, $GETTIM, $NUMTIM, $SETIME, $SETIMR
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The expiration time, repeat time, process name string, or string descriptor cannot be read by the caller, or the process identification cannot be written by the caller.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
The process has exceeded its AST limit quota.
- SS$_INCOMPAT
The remote node is running an incompatible version of the operating system.
- SS$_INSFMEM
The system dynamic memory is insufficient for allocating a timer queue entry.
- SS$_IVLOGNAM
The process name string has a length of 0 or has more than 15 characters.
- SS$_IVTIME
The specified delta repeat time is a positive value, or an absolute time plus delta repeat time is less than the current time.
- SS$_NONEXPR
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process identification was specified.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The process does not have the privilege to schedule a wakeup request for the specified process.
- SS$_NOSUCHNODE
The process name refers to a node that is not currently recognized as part of the OpenVMS Cluster system.
- SS$_REMRSRC
The remote node has insufficient resources to respond to the request. (Bring this error to the attention of your system manager.)
- SS$_UNREACHABLE
The remote node is a member of the cluster but is not accepting requests. (This is normal for a brief period early in the system boot process.)
$SCHED
Affect Process Scheduling — Affects process scheduling. This service is intended for use by a class scheduler process.
Format
SYS$SCHED func ,p1 ,p2 ,p3C Prototype
int sys$sched
(unsigned int func, unsigned int *p1, unsigned int *p2,
unsigned int *p3);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | function_code |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Function code specifying the action $SCHED is to perform. The func
argument is a longword containing this code.
See the Function Codes section for a list of valid function codes for $SCHED.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | varies |
| mechanism: | varies |
The meaning of the p1, p2, and
p3 arguments depends on the function code specified in the
func argument, and is defined in the Function Codes
section.
Function Codes
This section defines each of the $SCHED function codes and describes the values of the
p1 argument, p2 argument, and
p3 argument for each function.
CSH$_READ_ALL
When you specify CSH$_READ_ALL, $SCHED returns a buffer containing information, including an index, EPID, and priority, for all processes.
The format of the buffer is defined in the $CSHDEF macro and consists of a series of CSHP fields.
p1 argument,
p2 argument, and p3 argument values
for the CSH$_READ_ALL function code. |
Argument |
Access |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Read |
Address of the buffer. |
|
|
Write |
Address of the longword size of the buffer. |
|
|
Write |
Address of the longword size of the per-process entry. |
CSH$_READ_NEW
When you specify CSH$_READ_NEW, $SCHED returns a buffer containing information, including an index, EPID, and priority, for all processes for which a class assignment has not been made.
The format of the buffer is defined in the $CSHDEF macro and consists of a series of CSHP fields.
p1 argument,
p2 argument, and p3 argument values
for the CSH$_READ_NEW function code.|
Argument |
Access |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Read |
Address of the buffer. |
|
|
Write |
Address of the longword size of the buffer. |
|
|
Write |
Address of the longword size of the per-process entry. |
|
Buffer Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
CSHP$T_ACCOUNT |
Account string from the user authorization file (first eight characters). |
|
CSHP$L_CPUTIM |
Process CPU time used, in 10-millisecond ticks. |
|
CSHP$L_EPID |
Process ID (PID). If CSHP information is insufficient to determine the right class for a process, the PID can be used with the $GETJPI(W) system service to obtain additional detail. |
|
CSHP$W_PIX |
A unique integer assigned to the process for its duration. Applications might want to use this value to index arrays. |
|
CSHP$B_PRI |
Current process priority. |
|
CSHP$B_PRIB |
Base process priority. |
|
CSHP$L_STATUS |
Undefined; reserved to OpenVMS. |
CSH$_READ_QUANT
When you specify CSH$_READ_QUANT, $SCHED returns a buffer containing information about how many ticks are left for each class. Data is returned in a series of longwords, one longword per class, starting with class number 0.
p1 argument,
p2 argument, and p3 argument values
when specifying the CSH$_READ_QUANT function code.|
Argument |
Access |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Read |
Address of the buffer. |
|
|
Read |
Address of the longword size of the buffer. |
|
|
— |
Unused. |
CSH$_SET_ATTN_AST
Enables attention asynchronous system traps (ASTs).
p1 argument,
p2 argument, and p3 argument values
when specifying the CSH$_SET_ATTN_AST function code.|
Argument |
Access |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Read |
Address of an AST routine. |
|
|
Read |
Access mode to deliver AST. |
|
|
— |
Unused. |
CSH$_SET_CLASS
Places processes in classes with or without windfall capability. The caller supplies a buffer consisting of CSHC blocks.
|
Buffer Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
CSHC$L_EPID |
Process ID (PID) of the process to affect. |
|
CSHC$W_CLASS |
Class into which to place the process. Class 65535 (hexadecimal FFFF) has a special interpretation: the associated process is not to be class scheduled and will, therefore, never run out of class quantum. The largest class number is 8191. |
|
CSHC$W_WINDFALL |
Determines whether the process is to share windfall. A value of 1 permits the process to share windfall; a value of 0 prevents the process from sharing windfall. Values other than 0 and 1 are undefined and can cause unpredictable behavior in future releases of the operating system. |
p1 argument,
p2 argument, and p3 argument values
when specifying the CSH$_SET_CLASS function code.|
Argument |
Access |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Read |
Address of the buffer. |
|
|
Read |
Address of the longword size of the buffer. |
|
|
Read |
Address of the longword size of the entry used. Should be CSHC$K_LENGTH or equivalent. |
CSH$_SET_NEW
Indicates to the class scheduler that the next READ_NEW will return information about the calling process. This function should be used only in executive or kernel mode.
p1 argument,
p2 argument, and p3 argument values
when specifying the CSH$_SET_NEW function code.|
Argument |
Access |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
— |
Unused. |
|
|
Read |
PID (by value). |
|
|
— |
Unused. |
CSH$_SET_QUANT
Establishes class quantum and enables class scheduling. The caller supplies a buffer that allocates CPU ticks to classes, one longword per class, starting with class number 0. Class-scheduled processes will have their quantum deducted from the appropriate longword, and will be removed from execution if class quantum is decremented to 0.
p1 argument,
p2 argument, and p3 argument values
when specifying the CSH$_SET_QUANT function code.|
Argument |
Access |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Read |
Address of the buffer. |
|
|
Read |
Address of the longword size of buffer. |
|
|
— |
Unused. |
CSH$_SET_TIMEOUT
Establishes a nonstandard timeout. If the application does not issue a CSH$_SET_QUANT within the timeout period, all class scheduling is stopped and processes are returned to normal scheduling. The default value, 30 seconds, should be suitable for most circumstances.
p1 argument,
p2 argument, and p3 argument values
when specifying the CSH$_SET_TIMEOUT function code.|
Argument |
Access |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
— |
Unused. |
|
|
Read |
Time in seconds (by value). |
|
|
— |
Unused. |
Description
The Affect Process Scheduling service is used by class scheduler processes to affect scheduling.
Use the func argument to specify which action $SCHED is to
perform.
Required Access or Privileges
ALTPRI is required to affect processes. Group access is required to affect processes in the same UIC group. World access is required to affect processes in different UIC groups. SYSPRV is required to set the timeout value.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $SETPRI
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Buffer, length, or size locations not writeable.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Specified a class higher than currently defined, or an element size of 0 was specified.
- SS$_BUFFEROVF
Buffer is too small, only some data transferred.
- SS$_INCLASS
Returned if a process (specified by the input PID) already belongs to a scheduling class. This can happen if the process was previously class scheduled at login through the class scheduler permanent database file, or by issuing the command, SET PROCESS/SCHEDULING_CLASS="class_name".
- SS$_INSFMEM
System dynamic memory is insufficient to complete the service.
- SS$_NOSUCHUSER
Supplied PID is not valid.
$SEARCH
Scans Directory File — The Search service scans a directory file and fills in various NAM block fields. This service should be preceded by the Parse service, in order to initialize the NAM block appropriately. For additional information about this service, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$SETAST
Set AST Enable — Enables or disables the delivery of asynchronous system traps (ASTs) for the access mode from which the service call was issued.
Format
SYS$SETAST enbflgC Prototype
int sys$setast (char enbflg);Argument
| OpenVMS usage: | boolean |
| type: | byte (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Value specifying whether ASTs are to be enabled. The enbflg argument is
a byte containing this value. The value 1 enables AST delivery for the calling access
mode; the value 0 disables AST delivery.
Description
The Set AST Enable service enables or disables the delivery of ASTs for the access mode from which the service call was issued.
Required Access or Privileges
When an image is executing in user mode, ASTs are always enabled for more privileged access modes. If ASTs are disabled for a more privileged access mode, the operating system cannot deliver ASTs for less privileged access modes until ASTs are enabled once again for the more privileged access mode. Therefore, a process that has disabled ASTs for a more privileged access mode must reenable ASTs for that mode before returning to a less privileged access mode.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$DCLAST, $SETPRA
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully. AST delivery was previously disabled for the calling access mode.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully. AST delivery was previously enabled for the calling access mode.
$SETCLUEVT
Set Cluster Event — Establishes a request for notification when an OpenVMS Cluster configuration event occurs.
Format
SYS$SETCLUEVT event ,astadr ,[astprm] ,[acmode] ,[handle]C Prototype
int sys$setcluevt
(unsigned int event, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm,
unsigned int acmode, struct _generic_64 *handle);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | event_code |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Event code indicating the type of cluster configuration event for which an AST is to be
delivered. The event argument is a value indicating which type of
event is of interest.
|
Symbolic Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
CLUEVT$C_ADD |
One or more OpenVMS nodes have been added to the OpenVMS Cluster system. |
|
CLUEVT$C_REMOVE |
One or more OpenVMS nodes have been removed from the OpenVMS Cluster system. |
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Notification AST routine to receive control after a change in OpenVMS Cluster configuration occurs.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Optional AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine. The
astprm argument is a longword value containing the AST
parameter.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Optional access mode at which the configuration event AST is to execute. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
|
Symbol |
Access Mode |
|---|---|
|
PSL$C_KERNEL |
Kernel |
|
PSL$C_EXEC |
Executive |
|
PSL$C_SUPER |
Supervisor |
|
PSL$C_USER |
User |
The value of the access mode must not be more privileged than the access mode of the caller.
| OpenVMS usage: | identifier |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Optional identifier to receive a value that uniquely identifies this AST request. $SETCLUEVT sets this handle to a unique value so that it can later be used to identify the request in the $CLRCLUEVT and $TSTCLUEVT services.
Description
The Set Cluster Event service establishes a request for notification when a cluster configuration event occurs. The service establishes only one AST notification for a configuration event. To receive AST notification for all cluster configuration events, the $SETCLUEVT service must be reissued within the notification AST routine. The service will verify that the input parameters specify a valid request, allocate appropriate data structures to hold the request, and enqueue the request for notification.
You must specify an event type and an AST address. You can specify an AST parameter, the access mode, and an address into which to place the handle of this request.
If quotas are exceeded, an error identifying the specific quota will be returned. It is important to note that this routine will return an error and will not retry an attempt to get quota if quota is exhausted on the first attempt. See the Condition Values Returned section for types of errors that can be returned.
If the
astadrargument is omitted, SS$_BADPARAM will be returned.If the
eventargument is omitted or incorrectly specified, SS$_BADPARAM will be returned.If the access mode parameter is more privileged than the mode of the caller, the mode of the caller will be used.
If specified, the
handleargument must be readable and writable from the mode of the caller. SS$_ACCVIO is returned if this is not the case.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CLRCLUEVT, $TSTCLUEVT
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Unable to process parameters for improper use.
- SS$_BADPARAM
The event was improperly specified.
- SS$_EXASTLM
The process exceeded its quota for outstanding AST requests.
- SS$_INSFMEM
The system dynamic memory is insufficient to complete the service.
$SETDDIR
Set Default Directory — Allows you to read and change the default directory string for the process. Do not include any device or file name strings in the default directory string; include only the [DIR] syntax. Modify the device portion of the current default directory location through the specification of the SYS$DISK logical name. Redefine this logical name using either the $CRELNM system service or the LIB$SET_LOGICAL RTL routine.
Format
SYS$SETDDIR [new-dir-addr] ,[length-addr] ,[cur-dir-addr]C Prototype
int sys$setddir
(void *newdiraddr, unsigned short int *lengthaddr, void *curdiraddr);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor—fixed-length string descriptor |
A descriptor of the new default directory. The
new-dir-addr argument is the address of the descriptor that points to the buffer containing the new directory specification that RMS will use to set the new process-default directory. If the default directory is not to be changed, the value of the
new-dir-addr argument should be 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | word_unsigned |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
A word that is to receive the length of the current default directory. The
length-addr argument is the address of the word that will
receive the length. If you do not want this value returned, specify the value 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor—fixed-length string descriptor |
A descriptor of a buffer that is to receive the current default directory string. The
cur-dir-addr argument is the address of the descriptor that
points to the buffer area that is to receive the current directory string.
Description
The Set Default Directory service allows you to read and change the default directory string for the process. You should restore the previous default directory string to its original state unless you want the changed default directory string to last beyond the exit of your image. The new directory name string is checked for correct syntax.
There is no predefined macro of the form $SETDDIR_G or $SETDDIR_S to call this service.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, the Set Default Directory service attempts to replace the default directory string with a DID abbreviation if the length of the resulting default directory exceeds 255 characters. If this happens, then in addition to the normal syntax check, the entire path to that specification, including the device, is verified and must exist for the call to succeed.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
- RMS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- RMS$_DIR
The directory name contains an error.
- RMS$_IAL
The argument list is invalid.
$SETDFPROT
Set Default File Protection — Allows you to read and write the default file protection for the process.
Format
SYS$SETDFPROT [new-def-prot-addr] ,[cur-def-prot-addr]C Prototype
int sys$setdfprot
(unsigned short int *newdefprotaddr,
unsigned short int *curdefprotaddr);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | file_protection |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
A word that specifies the new default file protection specification. The
new-def-prot-addr argument is the address of the word that
specifies the desired protection. If you do not want the process-default file protection
to be changed, specify the value 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | file_protection |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
A word that is to receive the current default file protection specification. The
cur-def-prot-addr argument is the address of the word that
receives the current process-default protection. If you do not want the current default
file protection, specify the value 0.
Description
The Set Default File Protection service allows you to read and write the default file protection for the process. You should restore the old default file protection specification unless you want the changed default to last beyond the exit of your image.
There is no predefined macro of the form $SETDEFPROT_G or $SETDEFPROT_S to call this service.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $GET_SECURITY, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SET_SECURITY, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
- RMS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- RMS$_IAL
The argument list is invalid.
$SETDTI
Set Distributed Transaction Information — The Set Distributed Transaction Information service removes resource managers from transactions. It can also be used to modify transaction states.
Format
SYS$SETDTI
[efn], [flags], iosb, [astadr], [astprm], [contxt], func, itmlstC Prototype
int sys$setdti
(unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int *contxt,
unsigned short int *func, void *itmlst);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
flags argument
is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to an option flag. The $DDTMDEF
macro defines symbolic names for the option flag described in Table 8.
All undefined bits must be 0. If this argument is omitted, no flags are used.| Flag Name | Description |
|---|---|
| DDTM$M_SYNC | Specifies successful synchronous completion by returning SS$_SYNCH. When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the AST routine is not called, the event flag is not set, and the I/O status block is not filled in. |
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned section.

| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure entry mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The AST routine executed when the service completes, if SS$_NORMAL is returned in R0.
The astadr argument is the address of the entry mask of this
routine. The routine is executed in the same access mode as that of the caller of the
$SETDTI service.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The AST parameter passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | contxt |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Context value obtained from a call to $GETDTI. It implicitly specifies a node and transaction manager log identifier.
| OpenVMS usage: | function_code |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Function modifier that specifies the set operation to be performed. The
func argument is a longword value containing the function
code.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| DTI$K_DELETE_RM_NAME | Deletes the resource manager specified in
itmlst item DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION,
DTI$T_PART_NAME from the transaction specified by
DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION, DTI$T_TID. |
| DTI$K_DELETE_TRANSACTION | Deletes the transaction specified by itmlst
item DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION, DTI$T_TID. |
| DTI$K_MODIFY STATE | Modifies the transaction specified by itmlst
item DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION, DTI$T_TID, using the transaction state
specified in DTI$_B_STATE. |
| OpenVMS usage: | item_list_3 |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Item list specifying the transaction information that $SETDTI is to use. The
itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors,
each of which describes an item of information. The list of item descriptors is terminated
by a longword of 0. Each item descriptor in the item list acts as an input argument to
$SETDTI and as such is only required to be read only.
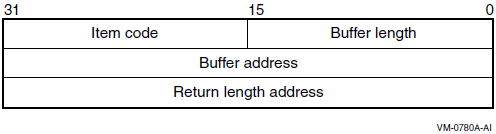
itmlst item descriptor fields:| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Buffer length | A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in bytes) of a buffer from which $SETDTI is to read the information. The length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too small, $SETDTI will return an error status. |
| Item code | A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the search item that $SETDTI is to use. The $DTIDEF macro defines these codes. Each item code is described in the Item Codes section. |
| Buffer address | A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer from which $SETDTI reads the item information. |
| Return length address | This longword that is not used in the item list as all items are read-only. |
Item Codes
DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION
When you specify DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION, $SETDTI uses the fields in the following
table to perform the $SETDTI call. Each function requires a specific set of fields from the
transaction record to perform its operation. If one or more of these fields is not present
or valid, then the $SETDTI call will fail. The fields required by each function are listed
in the func argument description.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| DTI$B_PART_NAME_LEN | A byte containing the length of the participant name field DTI$T_PART_NAME. |
| DTI$B_STATE | A byte containing the state of the transaction. Two states are valid: DTI$K_COMMITTED and DTI$K_ABORTED. |
| DTI$T_PART_NAME | A character field containing DTI$B_PART_NAME_LEN characters that specifies a resource manager name. To ensure smooth operation in a mixed-network environment, refer to the chapter entitled Managing DECdtm Services in the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, for information on defining node names. |
| DTI$T_PART_LOG_ID | Reserved to OpenVMS. |
| DTI$T_TID | A 16-byte field containing the transaction identifier. |
Description
The $SETDTI service can be used either to remove resource managers from transactions, or to modify transaction states.
The $SETDTI service removes resource managers from a single transaction or from all transactions when they no longer have any further interest in a transaction. A call to $SETDTI typically follows a call to $GETDTI that established a search context and returned the state of an unresolved transaction.
When a resource manager is recovering from a system failure it will use $GETDTI to return the state of all unresolved transactions. If the resource manager can recover the transaction, then it needs to be removed from the transaction in the same way it would have been removed had it been able to call $ACK_EVENT with the forget status before the system failure.
To remove a resource manager, $SETDTI uses the following fields from the
DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION item descriptor in the itmlst
argument:
Transaction Identifier (TID)
Resource Manager name
Resource Manager log identifier
This information, along with the search context, is used to remove the resource manager from the transaction. If the TID field is zero in the DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION item descriptor, then the resource manager will be removed from all committed transactions in which it was involved.
When searching for a resource manager, a comparison is made of the leftmost bytes in the transaction manager's log records. This feature enables multiple instances of resource manager classes to be removed from the transaction manager's log after performing a recovery.
The $SETDTI service can also be used to modify transaction states. It can perform two
state transitions: from prepared to committed, or from prepared to aborted. To modify
transaction states, $SETDTI uses the following fields from the DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION
item descriptor in the itmlst argument:
Transaction Identifier (TID)
Transaction state
To modify a transaction state, first modify the DTI$B_STATE field in the DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION item descriptor to either DTI$K_COMMITTED and DTI$K_ABORTED. Then specify the function code DTI$K_MODIFY_TRANSACTION to instruct $SETDTI to perform the state transition.
Note that because DECdtm uses a presumed abort protocol, changing the transaction state to aborted is the same as deleting the transaction.
SYSPRV privilege is required to retrieve or modify information about transactions with which the process is not currently associated.
In most cases, the search context remains valid across multiple calls to $SETDTI. That is, a call to $GETDTI may be followed by one or more calls to $SETDTI without the context becoming invalid. However, the search context is invalidated when a resource manager is deleted from all transactions by specifying a zero TID.
Required Privileges
SYSPRV is required to modify transactions with which the process is not currently associated.
Required Quotas
BYTLM, ASTLM
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW, $CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW, $END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW, $GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTIW, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW, $START_TRANS, $START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
If returned in R0, the request was successfully queued. If returned in the I/O status block, the service completed successfully.
- SS$_SYNCH
The service completed successfully and synchronously (returned only if the DDTM$M_SYNC flag is set).
- SS$_ACCVIO
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
- SS$_BADLOGVER
There was an invalid or unsupported log version.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Either the options flags were invalid or the
tidargument was omitted but thebidargument was not zero.- SS$_BADSTATE
There was an invalid transaction state in the ITMLST. Valid states are DTI$K_COMMITTED and DTI$K_ABORTED.
- SS$_BUGCHECK
A failure has occurred during the processing of the request.
- SS$_EXASTLM
The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded.
- SS$_ILLEFC
The event flag number was invalid.
- SS$_INSFARGS
A required argument was missing.
- SS$_INSFMEM
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
- SS$_INVLOG
The log format is invalid.
- SS$_NOSUCHFILE
The transaction manager log cannot be found.
- SS$_NOSUCHNODE
The subordinate DECnet node is unknown.
- SS$_NOSUCHPART
The participant is not part of the transaction.
- SS$_NOSUCHTID
The designated TID is unknown.
- SS$_NOSYSPRV
The caller does not have the SYSPRV privilege.
- SS$_PROTOCOL
There is a message protocol error.
- SS$_REMRSRC
There are insufficient resources at the remote node.
- SS$_UNREACHABLE
A superior node is unreachable.
$SETDTIW
Set Distributed Transaction Information and Wait — Sets the process current transaction and removes resource managers from transactions. $SETDTIW$ always waits for the request to complete before returning to the caller. Other than this, it is identical to $SETDTI.
Format
SYS$SETDTIW
[efn], [flags], iosb, [astadr], [astprm], [contxt], func, itmlstC Prototype
int sys$setdtiw
(unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int *contxt,
unsigned short int *func, void *itmlst);$SETEF
Set Event Flag — Sets an event flag in a local or common event flag cluster. The condition value returned by $SETEF indicates whether the specified flag was previously set or clear. After the event flag is set, processes waiting for the event flag to be set resume execution.
Format
SYS$SETEF efnC Prototype
int sys$setef (unsigned int efn);Argument
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of the event flag to be set. The efn argument is a longword
containing this number; however, $SETEF uses only the low-order byte.
Two local event flag clusters are local to the process: cluster 0 and cluster 1. Cluster 0 contains event flag numbers 0 to 31, and cluster 1 contains event flag numbers 32 to 63.
There are two common event flag clusters: cluster 2 and cluster 3. Cluster 2 contains event flag numbers 64 to 95, and cluster 3 contains event flag numbers 96 to 127.
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully. The specified event flag was previously 0.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully. The specified event flag was previously 1.
- SS$_ILLEFC
You specified an illegal event flag number.
- SS$_UNASEFC
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified event flag.
$SETEXV
Set Exception Vector — Assigns a condition handler address to the primary, secondary, or last chance exception vectors, or removes a previously assigned handler address from any of these three vectors.
Format
SYS$SETEXV [vector] ,[addres] ,[acmode] ,[prvhnd]C Prototype
int sys$setexv
(unsigned int vector, int (*addres)(__unknown_params),
unsigned int acmode, void *(*(prvhnd)));Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Vector for which a condition handler is to be established or removed. The
vector argument is a longword value. The value 0 (the
default) specifies the primary exception vector; the value 1, the secondary vector; and
the value 2, the last chance exception vector.
| OpenVMS usage: | procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Condition handler address to be established for the exception vector specified by the
vector argument. The addres argument
is a longword value containing the address of the condition handler routine.
If you do not specify addres or specify it as the value 0, the
condition handler address already established for the specified vector is removed; that
is, the contents of the longword vector is set to 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode for which the exception vector is to be modified. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access mode. The
$PSLDEF macro defines symbols for the four access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. Exception vectors for access modes more privileged than the caller's access mode cannot be modified.
| OpenVMS usage: | procedure value |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Previous condition handler address contained by the specified exception vector. The
prvhnd argument is the address of a longword into which
$SETEXV writes the handler's procedure value.
Description
The Set Exception Vector service (1) assigns a condition handler address to the primary, secondary, or last chance exception vectors or (2) removes a previously assigned handler address from any of these three vectors. A process cannot modify a vector associated with a more privileged access mode.
Using the call stack associated with each access mode. Each call frame includes a longword to contain the address of a condition handler associated with that frame.
Using the software exception vectors (by using $SETEXV) associated with each access mode. These vectors are set aside in the control region (P1 space) of the process.
The modular properties associated with the first method do not apply to the second. The software exception vectors are intended primarily for performance monitors and debuggers. For example, the primary exception vector and the last chance exception vector are used by the OpenVMS Debugger for user mode access, and DCL uses the last chance exception vector for supervisor mode access.
User mode exception vectors are canceled at image exit.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$DCLCMH, $UNWIND
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The longword to receive the previous contents of the vector cannot be written by the caller.
$SETFLT
Set Fault Characteristic on Pages — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, allows a process to change the fault characteristic on a page or range of pages.
Format
SYS$SETFLT inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode] ,fault_flagC Prototype
int sys$setflt
(struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr, unsigned int acmode,
unsigned int fault_flag);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the range of pages whose fault
characteristic is to be changed. The inadr argument is the
address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and ending process
virtual addresses.
Addresses are adjusted up or down to fall on CPU-specific page boundaries. Only the virtual page number portion of each virtual address is used; the low-order byte-within-page bits are ignored.
If the starting and ending virtual addresses are the same, the fault characteristic is changed for a single page.
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference—array reference or descriptor |
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the range of pages whose fault
characteristic was actually changed by $SETFLT. The retadr
argument is the address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and
ending process virtual addresses.
If an error occurs while the fault characteristic is being changed, $SETFLT writes
into retadr the range of pages that were successfully changed
before the error occurred. If no pages were affected before the error occurred, $SETFLT
writes the value --1 into each longword of the 2-longword array.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode associated with the call to $SETFLT. The acmode
argument is a longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines symbols for
the access modes.
The $SETFLT service uses whichever of the following two access modes is less
privileged: (1) the access mode specified by acmode or (2) the
access mode of the caller. To change the fault characteristic of any page in the
specified range, the resultant access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the
access mode of the owner of that page.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Flag mask specifying the request options. The fault_flag
argument is a longword bit vector in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $FLTDEF
macro and the FLTDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag.
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| FLT$M_NO_EXECUTE | Fault on execute access attempt |
| FLT$M_EXECUTABLE | Allow execute access |
If you specify the fault characteristic as the value 0, the characteristic defaults to no execute access.
Description
The Set Fault Characteristic on Pages service allows a process to change the fault characteristic on a page or range of pages.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CRETVA, $EXPREG, $SETPRT
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The input address array cannot be read by the caller; the output address array or the byte to receive the previous protection cannot be written by the caller; or an attempt was made to change the fault characteristic of a nonexistent page.
- SS$_BADPARAM
A bad
fault_flagargument was specified.- SS$_LENVIO
A page in the specified range is beyond the end of the program or control region.
- SS$_NOPRIV
A page in the specified range is in the system address space.
- SS$_PAGOWNVIO
The process attempted to change the fault characteristic on a page owned by a more privileged access mode.
$SETFLT_64
Set Fault Characteristic — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, allows a process to change the fault characteristic (for example, no execute) on a page or range of pages.
Format
$SETFLT_64
start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,fault_flag ,return_va_64
,return_length_64Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address of the range of pages whose fault characteristic is to be changed. The specified virtual address will be rounded down to a CPU-specific page boundary.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Length of the virtual address space whose fault characteristic is to be changed. The specified length will be rounded up to a CPU-specific page boundary so that it includes all CPU-specific pages in the requested range.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode associated with the call to $SETFLT_64. The acmode
argument is a longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines symbols for
the four access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. The calling process can modify pages only if those pages are owned by an access mode equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the calling process.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Flag mask specifying the request options. The fault_flag
argument is a longword bit vector in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $FLTDEF
macro and the FLTDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag.
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| FLT$M_NO_EXECUTE | Fault on execute access attempt |
| FLT$M_EXECUTABLE | Allow execute access |
If you specify the fault characteristic as the value 0, the characteristic defaults to no execute access.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the range of pages whose fault characteristics were actually changed.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference |
The length of the virtual address range whose fault characteristics were actually
changed. The return_length_64 argument is the 32-bit or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns the
length of the virtual address range in bytes.
Description
The Set Fault Characteristic service sets the fault characteristics (for example, no execute) for the specified range of pages, checking that the specified mode is at least as privileged as the owner of the page.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value might not be returned in the memory locations pointed to by
the return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned address and
returned length indicate the pages that were successfully changed before the error
occurred. If no pages were changed, the return_va_64 argument
will contain the value -1, and a value might not be
returned in the memory location pointed to by the
return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CRETVA_64, $EXPREG_64, $SETPRT_64
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
return_va_64orreturn_length_64argument cannot be written by the caller.- SS$_BADPARAM
A bad fault_flag argument was specified.
- SS$_LENVIO
A page in the specified range is beyond the length of virtual addresses within that region.
- SS$_NOSUCHPAG
An attempt was made to change the fault characteristic on a nonexistent page.
- SS$_PAGNOTINREG
A page in the specified range is not in process private address space.
- SS$_PAGOWNVIO
The process attempted to change the protection on a page owned by a more privileged access mode.
$SETIME
Set System Time — Changes the value of, or recalibrates, the system time. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$SETIME [timadr]C Prototype
int sys$setime (struct _generic_64 *timadr);Argument
| OpenVMS usage: | date_time |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
New absolute time value for the system time, specifying the number of 100-nanosecond
intervals since 00:00 o'clock, November 17, 1858. The timadr
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of a
quadword containing the new system time value. A negative (delta) time value is
invalid.
If you do not specify the value of timadr or specify it as 0,
$SETIME recalibrates the system time using the time-of-year clock.
Description
The Set System Time service (1) changes the value of or (2) recalibrates the system time which is defined by a quadword value that specifies the number of 100-nanosecond intervals since 00:00 o'clock, November 17, 1858.
System time is the reference used for nearly all timer-related software activities in the operating system. After changing or recalibrating the system clock, $SETIME updates the timer queue by adjusting each element in the timer queue by the difference between the previous system time and the new system time.
The $SETIME service saves the new time (for future bootstrap operations) in the system image SYS$LOADABLE_IMAGES:SYS$BASE_IMAGE.EXE on Alpha and Integrity server systems. To save the time, the service assigns a channel to the system boot device and calls $QIOW. You need the LOG_IO user privilege to perform this operation.
Required Access or Privileges
To set system time, the calling process must have OPER, LOG_IO, and SYSPRV privileges.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ASCTIM, $BINTIM, $CANTIM, $CANWAK, $GETTIM, $NUMTIM, $SCHDWK, $SETIMR
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The quadword that contains the new system time value cannot be read by the caller.
- SS$_IVTIME
The caller specified no time value or a negative time value and an invalid processor clock was found.
- SS$_NOIOCHAN
No I/O channel is available for assignment.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The process does not have the privileges to set the system time.
$SETIMR
Set Timer — Sets the timer to expire at a specified time. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$SETIMR [efn] ,daytim ,[astadr] ,[reqidt] ,[flags]C Prototype
int sys$setimr
(unsigned int efn, struct _generic_64 *daytim,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), unsigned __int64 reqidt,
unsigned int flags);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Event flag to be set when the timer expires. The efn argument is a
longword value containing the number of the event flag; however, $SETIMR uses only the
low-order byte. If you do not specify efn, event flag 0 is
used.
When $SETIMR first executes, it clears the specified event flag or event flag 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | date_time |
| type: | quadword |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Time at which the timer expires. The daytim argument is the 64-bit
address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of a quadword time value. A positive
time value specifies an absolute time at which the timer expires; a negative time value
specifies an offset (delta time) from the current time.
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
AST service routine that is to execute when the timer expires. The
astadr argument is the 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity
server systems) of the procedure value of this routine. If you do not specify the value
of astadr or specify it as 0 (the default), no AST routine
executes.
The AST routine, if specified, executes at the access mode of the caller.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | quadword |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Identification of the timer request. The reqidt argument is a
quadword value containing a number that uniquely identifies the timer
request. If you do not specify reqidt, the value 0 is
used.
To cancel a timer request, the identification of the timer request (as specified by
reqidt in $SETIMR) is passed to the Cancel Timer ($CANTIM) service (as the
reqidt argument).
If you want to cancel specific timer requests but not all timer requests, be sure to specify a nonzero value for
reqidt in the $SETIMR call; $CANTIM interprets an identification value of 0 as a request to cancel all timer requests.
You can specify unique values for
reqidt for each timer request or give the same value to related timer requests. This permits selective canceling of a single timer request, a group of related timer requests, or all timer requests.
If you specify the astadr argument in the $SETIMR call, the value
specified by the reqidt argument is passed as a parameter to the
AST routine. If the AST routine requires more than one parameter, specify an address for
the value of reqidt; the AST routine can then interpret that
address as the beginning of a list of parameters.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Longword of bit flags for the set timer operation. Currently, only bit 0 is used for the
flags argument. When the low bit (bit 0) is set, it indicates that this timer request should be in units of CPU time, rather than elapsed time. When bit 0 is clear (the default), the timer request is in units of elapsed time. The
flags argument is optional.
Description
The Set Timer service sets the timer to expire at a specified time. When the timer expires, an event flag is set and (optionally) an AST routine executes. This service requires dynamic memory and executes at the access mode of the caller, as does the AST routine if one is specified.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
This service uses the process's timer queue entries (TQELM) quota. If you specify an AST routine, the service uses the AST limit (ASTLM) quota of the process.
Related Services
$ASCTIM, $BINTIM, $CANTIM, $CANWAK, $GETTIM, $NUMTIM, $SCHDWK, $SETIME
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The expiration time cannot be read by the caller.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
The process exceeded its quota for timer entries or its AST limit quota; or the system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the request.
- SS$_ILLEFC
You specified an illegal event flag number.
- SS$_INSFMEM
The dynamic memory is insufficient for allocating a timer queue entry.
- SS$_UNASEFC
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified event flag.
$SETPRA
Set Power Recovery AST — Establishes a routine to receive control after a power recovery is detected.
Format
SYS$SETPRA astadr ,[acmode]C Prototype
int sys$setpra (int (*astadr)(__unknown_params), unsigned int acmode);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Power recovery AST routine to receive control when a power recovery is detected. The
astadr argument is the address of this routine.
If you specify
astadr as the value 0, an AST is not delivered to the process when a power recovery is detected.
The system passes one parameter to the specified AST routine. This parameter is a longword value containing the length of time that the power was off, expressed as the number of 1/100th-of-a-second intervals that have elapsed.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode at which the power recovery AST routine is to execute. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access mode. The
$PSLDEF macro defines symbols for the access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
Description
The Set Power Recovery AST service establishes a routine to receive control after a power recovery is detected.
You can specify only one power recovery AST routine for a process. The AST entry point address is cleared at image exit.
The entry and exit conventions for the power recovery AST routine are the same as for all AST service routines.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
One unit of quota is deducted from the process's ASTLM.
Related Services
$DCLAST, $SETAST
For more information, see the chapter on AST services in the VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
The process exceeded its quota for outstanding AST requests.
$SETPRI
Set Priority — Changes the base priority of the process. The base priority is used to determine the order in which executable processes are to run.
Format
SYS$SETPRI
[pidadr] ,[prcnam] ,pri ,[prvpri] ,[nullarg] ,[nullarg]C Prototype
int sys$setpri
(unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, unsigned int pri,
unsigned int *prvpri, unsigned int *pol, unsigned int *prvpol);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Process identification (PID) of the process whose priority is to be set. The
pidadr argument is the address of the PID. The
pidadr argument can refer to a process running on the local
node or a process running on another node in the cluster.
| OpenVMS usage: | process_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Process name of the process whose priority is to be changed. The prcnam
argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to the process
name.
A process running on the local node can be identified with a 1- to 15-character string. To identify a process on a particular node on a cluster, specify the full process name, which includes the node name as well as the process name. The full process name can contain up to 23 characters.
You can use the prcnam argument only on behalf of processes in the same
UIC group as the calling process. To set the priority for processes in other groups, you
must specify the pidadr argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
New base priority to be established for the process. The pri
argument is a longword value containing the new priority. Priorities that are not real
time are in the range 0 through 15; real-time priorities are in the range 16 through
31.
If the specified priority is higher than the base priority of the target process, and if the caller does not have ALTPRI privilege, then the base priority of the target process is used.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Base priority of the process before the call to $SETPRI. The prvpri
argument is the address of a longword into which $SETPRI writes the previous base
priority of the process.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, address of a longword containing the new scheduling policy for the process.
|
Symbol |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
JPI$K_DEFAULT_POLICY |
The normal scheduling policy. The priority interval for this
policy is defined as [0.. |
|
JPI$K_PSX_FIFO_POLICY |
POSIX FIFO scheduling policy. The priority interval for this
policy is defined as [ |
|
JPI$K_PSX_RR_POLICY |
POSIX round-robin policy. The priority interval for this
policy is defined as [ |
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, address of a longword into which the previous
scheduling policy for the process is written. If the policy
argument is null, no change in policy is requested and prvpol
returns the current policy.
SYI$_DEF_PRIO_MAX, SYI$_DEF_PRIO_MIN
SYI$_PSXFIFO_PRIO_MAX, SYI$_PSXFIFO_PRIO_MIN
SYI$_PSXRR_PRIO_MAX, SYI$_PSXRR_PRIO_MIN
See the Item Codes section of the $GETSYI service description for more information about these item codes.
| OpenVMS usage: | null_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to OpenVMS.
Description
The Set Priority service changes the base priority of the process or, optionally, changes the scheduling policy of the process. The base priority is used to determine the order in which executable processes are to run.
The basic scheduling discipline (FIFO, round-robin, and so forth).
The preemption/compensation rules by which a running process is descheduled in favor of another process and, ultimately, rescheduled.
The source and target processes are in the same job tree.
The source and target processes have the same UIC.
The source process has WORLD privilege enabled.
The source and target processes are in the same process group.
The value to which the priority of a process can be set can be subject to limitations. If the source has ALTPRI privilege enabled, the target can be set to any valid priority. Otherwise, the priority value specified by the source process is compared to the authorized priority of the target process and the smaller of the two values is used as the new base priority of the target process.
If you specify neither the
pidadr nor the
prcnam argument, $SETPRI sets the base priority of the calling process.
If the longword at address
pidadr is the value 0, the PID of the target process is returned.
The base priority of a process remains in effect until specifically changed or until the process is deleted.
To determine the priority set by the $SETPRI service, use the Get Job/Process Information ($GETJPI) service.
Required Access or Privileges
GROUP privilege to change the priority of a process in the same group, unless the target process has the same UIC as the calling process.
WORLD privilege to change the priority of any other process in the system.
ALTPRI privilege to set any process's priority to a value greater than the target process's initial base priority. If a process does not have ALTPRI privilege, the priority value specified by the source process is compared to the authorized priority of the target process and the smaller of the two values is used as the new base priority of the target process.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER, $PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND, $WAKE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The process name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the caller, or the process identification or previous priority longword cannot be written by the caller.
- SS$_ILLPOLICY
An invalid scheduling policy was specified.
- SS$_ILLPRIPOL
Setting the process to the specified priority and/or policy would result in an illegal policy/priority combination. The illegal combination can occur between the SETPRI policy and priority parameters themselves, or it can occur between either of the parameters and the current policy and/or priority of the target process.
- SS$_INCOMPAT
The remote node is running an incompatible version of the operating system.
- SS$_IVLOGNAM
The process name string has a length of 0 or has more than 15 characters.
- SS$_NONEXPR
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process identification was specified.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The process does not have the privilege to affect other processes.
- SS$_NOSUCHNODE
The process name refers to a node that is not currently recognized as part of the cluster.
- SS$_REMRSRC
The remote node has insufficient resources to respond to the request. (Bring this error to the attention of your system manager.)
- SS$_UNREACHABLE
The remote node is a member of the cluster but is not accepting requests. (This is normal for a brief period early in the system boot process.)
$SETPRN
Set Process Name — Allows a process to establish or to change its own process name.
Format
SYS$SETPRN [prcnam]C Prototype
int sys$setprn ( void *prcnam);Argument
| OpenVMS usage: | process_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor—fixed length string descriptor |
Process name to be given to the calling process. The prcnam argument is
the address of a character string descriptor pointing to a 1- to 15-character process
name string. If you do not specify prcnam, the calling process is
given no name.
Description
The Set Process Name service allows a process to establish or to change its own process name, which remains in effect until you change it (using $SETPRN) or until the process is deleted. Process names provide an identification mechanism for processes executing with the same group number. A process can also be identified by its process identification (PID).
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER, $PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND, $WAKE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The process name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the caller.
- SS$_DUPLNAM
The specified process name duplicates one already specified within that group.
- SS$_IVLOGNAM
The specified process name has a length of 0 or has more than 15 characters.
$SETPRT
Set Protection on Pages — Allows a process to change the protection on a page or range of pages.
Format
SYS$SETPRT inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode] ,prot ,[prvprt]C Prototype
int sys$setprt
(struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr, unsigned int acmode,
unsigned int prot, unsigned char *prvprt);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the range of pages whose protection is to be changed.
The inadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array
containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses.
Addresses are adjusted up or down to fall on CPU-specific page boundaries. Only the virtual page number portion of each virtual address is used; the low-order byte-within-page bits are ignored.
If the starting and ending virtual addresses are the same, the protection is changed for a single page.
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference—array reference or descriptor |
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the range of pages whose protection was actually
changed by $SETPRT. The retadr argument is the address of a
2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual
addresses.
If an error occurs while the protection is being changed, $SETPRT writes into
retadr the range of pages that were successfully changed
before the error occurred. If no pages were affected before the error occurred, $SETPRT
writes the value –1 into each longword of the 2-longword array.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode associated with the call to $SETPRT. The acmode argument is
a longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines symbols for the access
modes.
The $SETPRT service uses whichever of the following two access modes is least privileged:
(1) the access mode specified by acmode or
(2) the access mode of the caller. To change the protection of any page in the
specified range, the resultant access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the
access mode of the owner of that page.
| OpenVMS usage: | page_protection |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Page protection to be assigned to the specified pages. The prot
argument is a longword value containing the protection code. Only bits 0 to 3 are used;
bits 4 to 31 are ignored.
|
Symbol |
Description |
|---|---|
|
PRT$C_NA |
No access |
|
PRT$C_KR |
Kernel read only |
|
PRT$C_KW |
Kernel write |
|
PRT$C_ER |
Executive read only |
|
PRT$C_EW |
Executive write |
|
PRT$C_SR |
Supervisor read only |
|
PRT$C_SW |
Supervisor write |
|
PRT$C_UR |
User read only |
|
PRT$C_UW |
User write |
|
PRT$C_ERKW |
Executive read; kernel write |
|
PRT$C_SRKW |
Supervisor read; kernel write |
|
PRT$C_SREW |
Supervisor read; executive write |
|
PRT$C_URKW |
User read; kernel write |
|
PRT$C_UREW |
User read; executive write |
|
PRT$C_URSW |
User read; supervisor write |
OpenVMS Alpha and Integrity server systems convert PRT$C_NA to the next highest protection, kernel-read.
If you specify the protection as the value 0, the protection defaults to kernel read only.
| OpenVMS usage: | page_protection |
| type: | byte (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Protection previously assigned to the last page in the range. The
prvprt argument is the address of a byte into which $SETPRT
writes the protection of this page. The prvprt argument is useful
only when protection for a single page is being changed.
Description
The Set Protection on Pages service allows a process to change the protection on a page or range of pages.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
If a process changes the protection for any pages in a private section from read only to read/write, $SETPRT uses the paging file (PGFLQUOTA) quota of the process.
For pages in global sections, the new protection can alter only copy-on-reference pages.
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET, $MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC, $UPDSECW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The input address array cannot be read by the caller; the output address array or the byte to receive the previous protection cannot be written by the caller; or an attempt was made to change the protection of a nonexistent page.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
The process exceeded its paging file quota while changing a page in a read-only private section to a read/write page.
- SS$_IVPROTECT
The specified protection code has a numeric value of 1, less than 0, or greater than 15.
- SS$_LENVIO
A page in the specified range is beyond the end of the program or control region.
- SS$_NOPRIV
A page in the specified range is in the system address space; an attempt was made to change the protection of a valid global page, of an invalid global noncopy-on-reference page, or a PFN global or private page.
- SS$_PAGOWNVIO
The process attempted to change the protection on a page owned by a more privileged access mode.
$SETPRT_64 (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Set Protection on Pages — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, allows a process to change the protection on a page or range of pages. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$SETPRT_64
start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,prot ,return_va_64 ,return_length_64
,return_prot_64C Prototype
int sys$setprt_64
(void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode,
unsigned int prot, void *(*(return_va_64)),
unsigned __int64 *return_length_64, unsigned int *return_prot_64);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address of the range of pages whose protection is to be changed. The specified virtual address will be rounded down to a CPU-specific boundary.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Length of the virtual address space whose protection is to be changed. The specified length will be rounded up to a CPU-specific page boundary so that it includes all CPU-specific pages in the requested range.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode associated with the call to $SETPRT_64. The acmode argument
is a longword containing the access mode.
|
Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
PSL$C_KERNEL |
Kernel |
|
1 |
PSL$C_EXEC |
Executive |
|
2 |
PSL$C_SUPER |
Supervisor |
|
3 |
PSL$C_USER |
User |
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. To change the protection of any page in the specified range, the resultant access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the access mode of the owner of that page.
| OpenVMS usage: | page_protection |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Page protection to be assigned to the specified pages. The prot
argument is a longword value containing the protection code. Only bits 0 to 3 are used;
bits 4 to 31 are ignored.
The $PRTDEF macro for MACRO-32 and the include file PRTDEF.H for C define the symbolic names for the protection codes.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the range of pages whose protection was actually
changed. The return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns the virtual
address.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the virtual address range whose protection was actually changed. The
return_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns the length of the
virtual address range in bytes.
| OpenVMS usage: | page_protection |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Protection previously assigned to the last page in the range. The
return_prot_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address
of a naturally aligned longword into which $SETPRT_64 writes the protection of this
page. The return_prot_64 argument is useful only when protection
for a single page is being changed.
Description
The Set Protection on Pages service allows a process to change the protection on a page or range of pages. For pages in a global section, the new protection can alter only copy-on-reference pages.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64, return_length_64, and
return_prot arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned address and returned
length indicate the pages that were successfully changed before the error occurred. If
no pages were changed, the return_va_64 argument will contain the
value -1, and a value cannot be returned in the memory location
pointed to by the return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
If a process changes the protection for any pages in a private section from read-only to read/write, $SETPRT_64 uses the paging file (PGFLQUOTA) quota of the process.
Related Services
$CRETVA_64, $CRMPSC_FILE_64, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64, $EXPREG_64, $MGBLSC_64
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
return_va_64or thereturn_length_64argument cannot be written by the caller.- SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA
The process exceeded its paging file quota while changing a page in a read-only private section to a read/write page.
- SS$_IVPROTECT
The specified protection code has a numeric value of 1 or is greater than 15.
- SS$_LENVIO
A page in the specified range is not in process private address space.
- SS$_NOSUCHPAG
An attempt was made to change the protection on a nonexistent page.
- SS$_PAGNOTINREG
A page in the specified range is not within the specified region.
- SS$_PAGTYPVIO
A page in the specified range is not in process private address space.
- SS$_PAGOWNVIO
The process attempted to change the protection on a page owned by a more privileged access mode.
$SETPRV
Set Privileges — Enables or disables specified privileges for the calling process.
Format
SYS$SETPRV [enbflg] ,[prvadr] ,[prmflg] ,[prvprv]C Prototype
int sys$setprv
(char enbflg, struct _generic_64 *prvadr, char prmflg,
struct _generic_64 *prvprv);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | boolean |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Indicator specifying whether the specified privileges are to be enabled or disabled. The
enbflg argument is a longword value. The value 1 indicates that the privileges specified in the
prvadr argument are to be enabled. The value 0 (the default) indicates that the privileges are to be disabled.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_privileges |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Privileges to be enabled or disabled for the calling process. The
prvadr argument is the address of a quadword bit vector
wherein each bit corresponds to a privilege that is to be enabled or disabled.
|
Privilege |
Symbolic Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
ACNT |
PRV$M_ACNT |
Create processes for which no accounting is done |
|
ALLSPOOL |
PRV$M_ALLSPOOL |
Allocate a spooled device |
|
ALTPRI |
PRV$M_ALTPRI |
Set (alter) any process priority |
|
AUDIT |
PRV$V_AUDIT |
Generate audit records |
|
BUGCHK |
PRV$M_BUGCHK |
Make bugcheck error log entries |
|
BYPASS |
PRV$M_BYPASS |
Bypass all protection |
|
CMEXEC |
PRV$M_CMEXEC |
Change mode to executive |
|
CMKRNL |
PRV$M_CMKRNL |
Change mode to kernel |
|
DIAGNOSE |
PRV$M_DIAGNOSE |
Can diagnose devices |
|
DOWNGRADE |
PRV$V_DOWNGRADE |
Can downgrade classification |
|
EXQUOTA |
PRV$M_EXQUOTA |
Can exceed quotas |
|
GROUP |
PRV$M_GROUP |
Group process control |
|
GRPNAM |
PRV$M_GRPNAM |
Place name in group logical name table |
|
GRPPRV |
PRV$V_GRPPRV |
Group access by means of system protection field |
|
IMPERSONATE |
PRV$M_IMPERSONATE |
Create detached processes under another UIC |
|
IMPORT |
PRV$V_IMPORT |
Mount a nonlabeled tape volume |
|
LOG_IO |
PRV$M_LOG_IO |
Perform logical I/O operations |
|
MOUNT |
PRV$M_MOUNT |
Issue mount volume QIO |
|
NETMBX |
PRV$M_NETMBX |
Create a network device |
|
OPER |
PRV$M_OPER |
All operator privileges |
|
PFNMAP |
PRV$M_PFNMAP |
Map to section by physical page frame number |
|
PHY_IO |
PRV$M_PHY_IO |
Perform physical I/O operations |
|
PRMCEB |
PRV$M_PRMCEB |
Create permanent common event flag clusters |
|
PRMGBL |
PRV$M_PRMGBL |
Create permanent global sections |
|
PRMMBX |
PRV$M_PRMMBX |
Create permanent mailboxes |
|
PSWAPM |
PRV$M_PSWAPM |
Change process swap mode |
|
READALL |
PRV$V_READALL |
Possess read access to everything |
|
SECURITY |
PRV$V_SECURITY |
Can perform security functions |
|
SETPRV |
PRV$M_SETPRV |
Set any process privileges |
|
SHARE |
PRV$M_SHARE |
Can assign a channel to a nonshared device |
|
SHMEM |
PRV$M_SHMEM |
Allocate structures in memory shared by multiple processors |
|
SYSGBL |
PRV$M_SYSGBL |
Create system global sections |
|
SYSLCK |
PRV$M_SYSLCK |
Queue systemwide locks |
|
SYSNAM |
PRV$M_SYSNAM |
Place name in system logical name table |
|
SYSPRV |
PRV$M_SYSPRV |
Access files and other resources as if you have a system UIC |
|
TMPMBX |
PRV$M_TMPMBX |
Create temporary mailboxes |
|
UPGRADE |
PRV$V_UPGRADE |
Can upgrade classification |
|
VOLPRO |
PRV$M_VOLPRO |
Override volume protection |
|
WORLD |
PRV$M_WORLD |
World process control |
If you do not specify prvadr or assign it the value 0, the privileges
are not altered.
| OpenVMS usage: | boolean |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Indicator specifying whether the privileges are to be affected permanently or temporarily. The
prmflg argument is a longword value. The value 1 specifies
that the privileges are to be affected permanently, that is, until you change them again
by using $SETPRV or until the process is deleted. The value 0 (the default) specifies
that the privileges are to be affected temporarily, that is, until the current image
exits (at which time the permanently enabled privileges of the process will be
restored).
Setting the prmflg argument to nonzero changes privilege bits
in both the CURPRIV mask and the PROCPRIV mask.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_privileges |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Privileges previously possessed by the calling process. The prvprv
argument is the address of a quadword bit vector wherein each bit corresponds to a
privilege that was previously either enabled or disabled. If you do not specify
prvprv or assign it the value 0, the previous privilege mask
is not returned.
Description
The Set Privileges service enables or disables specified privileges for the calling process.
AUTHPRIV—Privileges that the process is authorized to enable, as designated by the system manager or the process creator. The AUTHPRIV mask never changes during the life of the process.
PROCPRIV—Privileges that are designated as permanently enabled for the process. The PROCPRIV mask can be modified by $SETPRV.
IMAGPRIV—Privileges with which the current image is installed.
CURPRIV—Privileges that are currently enabled. The CURPRIV mask can be modified by $SETPRV.
When a process is created, its AUTHPRIV, PROCPRIV, and CURPRIV masks have the same contents. Whenever a system service (other than $SETPRV) must check the process privileges, that service checks the CURPRIV mask.
When a process runs an installed image, the privileges with which that image was installed are enabled in the CURPRIV mask. When the installed image exits, the PROCPRIV mask is copied to the CURPRIV mask.
The $SETPRV service can set bits only in the CURPRIV and PROCPRIV mask, but $SETPRV checks the AUTHPRIV mask to see whether a process can set specified privilege bits in the CURPRIV or PROCPRIV masks. Consequently, a process can give itself the SETPRV privilege only if this privilege is enabled in the AUTHPRIV mask.
You can obtain each of a process's four privilege masks by calling the $GETJPI (Get Job/Process Information) service and specifying the desired privilege mask or masks as item codes in the
itmlst argument. You construct the item code for a privilege mask by prefixing the name of the privilege mask with the characters
JPI$_ (for example, JPI$_CURPRIV is the item code for the current privilege mask).
The DCL command SET PROCESS/PRIVILEGES also enables or disables specified privileges; refer to the VSI OpenVMS DCL Dictionary for details.
Required Access or Privileges
To set a privilege permanently, the calling process must be authorized to set the specified privilege, or the process must be executing in kernel or executive mode.
The calling process must be authorized to set the specified privilege.
The calling process must be executing in kernel or executive mode.
The image currently executing must be one that was installed with the specified privilege.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CMKRNL, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER, $PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETRWM, $SUSPND, $WAKE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully. All privileges were enabled or disabled as specified.
- SS$_NOTALLPRIV
The service completed successfully. Not all specified privileges were enabled; see the Description section for details.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The privilege mask cannot be read or the previous privilege mask cannot be written by the caller.
- SS$_IVSTSFLG
You specified a value other than 1 or 0 in either the
prmflgargument or theenblfgargument.
$SETRWM
Set Resource Wait Mode — Allows a process to specify what action system services should take when system resources required for their execution are unavailable. Disabling resource waiting should be performed with caution, as doing so can have unexpected effects on constituent sharable images and runtime libraries. Caution: Disabling resource waiting should be performed with caution, as doing so can have unexpected effects on constituent sharable images and runtime libraries.
Format
SYS$SETRWM [watflg]C Prototype
int sys$setrwm ( char watflg);Argument
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Indicator specifying whether system services should wait for required resources. The
watflg argument is a longword value. The value 0 (the
default) specifies that system services should wait until resources needed for their
execution become available. The value 1 specifies that system services should return
failure status immediately when resources needed for their execution are
unavailable.
The operating system enables resource wait mode for all processes. You can disable resource wait mode only by calling $SETRWM.
If resource wait mode is disabled, it remains disabled until it is explicitly reenabled or until the process is deleted.
Description
The Set Resource Wait Mode service allows a process to specify what action system services should take when system resources required for their execution are unavailable. When resource wait mode is enabled, system services wait for the required system resources to become available and then continue execution. When resource wait mode is disabled, system services return to the caller when required system resources are unavailable. The condition value returned by $SETRWM indicates whether resource wait mode was previously enabled or previously disabled.
System dynamic memory: nonpaged pool, lock manager dynamic memory?
UNIBUS adapter map registers
Direct I/O limit (DIOLM) quota
Buffered I/O limit (BIOLM) quota
Buffered I/O byte count limit (BYTLM) quota
Timer queue quota
Mailbox buffer quota
Insufficient pipe quota
Caution
Due to the process-wide implications of resource waiting, disabling resource waiting should be performed with caution.
Disabling resource wait mode can have unexpected effects on libraries or shareable images upon which your application may be directly or indirectly dependent. If resource waiting is disabled, these constituent libraries or shareable images may not perform as expected. It is possible that these constituent components are coded to assume resource waiting is enabled; therefore, they may not be coded to receive various quota-related errors such as SS$_EXQUOTA.
Note that you should have full control over the entire program context down to the system calls before disabling resource wait mode.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER, $PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SUSPND, $WAKE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully. Resource wait mode was previously enabled.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully. Resource wait mode was previously disabled.
$SETSHLV
Set Automatic Unshelving — Controls whether a process automatically unshelves files.
Format
SYS$SETSHLV [pidadr] ,[prcnam] ,[shlvflg]C Prototype
int sys$setshlv
(unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, unsigned int shlvflg);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Process identification (PID) of the process. The
pidadr argument is the address of the PID. The
pidadr argument can only refer to a process running on the local node. You cannot modify a process on a remote node.
You must specify the pidadr argument to modify a process whose UIC
group number is different from that of the calling process.
| OpenVMS usage: | process_name |
| type: | character–coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed length string descriptor |
Process name of the process. The prcnam argument is the address of a
character string descriptor pointing to the process name. You identify a process with a
1- to 15-character string.
You can only use the prcnam argument to modify a process in the same
UIC group as the calling process. To modify a process in another UIC group, you must
specify the pidadr argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Value specifying whether automatic unshelving is to be turned on or off. The
shlvflg argument is a longword containing this value. The
value 0 turns automatic unshelving on. The value 1 turns automatic unshelving
off.
Description
The Set Automatic Unshelving service controls whether a process automatically unshelves files.
The pidadr and prcnam default to the current
process. If the longword at address pidadr is 0, the PID of the
target process is returned.
The setting for automatic unshelving is inherited by subprocesses.
The DCL command SET PROCESS/[NO]AUTOUNSHELVE also controls automatic unshelving for a process; refer to the VSI OpenVMS DCL Dictionary for details.
Required Access or Privileges
GROUP privilege to modify a process in the same group, unless the target process has the same UIC as the calling process.
WORLD privilege to modify any process in the system.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GETJPI
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully. Automatic unshelving was previously on.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully. Automatic unshelving was previously off.
- SS$_ACCVIO
An argument was not accessible by the caller.
- SS$_BADPARAM
The
shlvflgargument was invalid.- SS$_IVLOGNAM
The
prcnamargument was invalid. The process name string had either 0 characters or more than 15 characters.- SS$_NONEXPR
The specified process did not exist, or the specified process identification was invalid.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The caller did not have the privilege to modify other processes.
- SS$_REMOTE_PROC
The specified process was not on the local node. The service cannot modify a process on a remote node.
$SETSTK
Set Stack Limits — Allows a process to change the size of its supervisor, executive, and kernel stacks by altering the values in the stack limit for a memory stack and base arrays held in P1 (per-process) space.
Format
SYS$SETSTK inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode]C Prototype
int sys$setstk
(struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr, unsigned int acmode);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Range of addresses that express the stack's new limits. The inadr
argument is the address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the address of the
top of the stack and the address of the base of the stack. Because stacks in P1 space
expand from high to low addresses, the address of the base of the stack must be greater
than the address of the top of the stack.
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Range of addresses that express the stack's previous limits. The retadr
argument is the address of a 2-longword array into which $SETSTK writes, in the first
longword, the previous address of the top of the stack and, in the second longword, the
previous address of the base of the stack.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode of the stack to be altered. The acmode argument is a
longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines symbols for the four
access modes. The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the
caller.
If acmode specifies user mode, $SETSTK performs no operation and
returns the SS$_NORMAL condition value.
Description
The Set Stack Limits service allows a process to change the size of its supervisor, executive, and kernel stacks by altering the values in the stack limit and base arrays held in P1 (per-process) space.
Required Access or Privileges
The calling process can adjust the size of stacks only for access modes that are equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the calling process.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET, $MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC, $UPDSECW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The input address array cannot be read by the caller; the input range is invalid; or the return address array cannot be written by the caller.
$SETSTK_64 (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Set Stack Limits — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, allows a process to change the size of its supervisor, executive, and kernel stacks by altering the values in the stack limit for a memory stack or a register stack and base arrays held in P1 (per-process) space.
Format
SYS$SETSTK_64
start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode, flags, prev_start_va, prev_lengthC Prototype
int sys$setstk_64
(void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode,
unsigned int flags, void ** prev_start_va_64,
unsigned __int64 * prev_length_64);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Lowest address in range of addresses that express the stack's new limits. For a memory stack, this address is the stack limit. For an Integrity servers register stack, this address is the stack base.
| OpenVMS usage: | length |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Length of the range of addresses that express the stack's new limits.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode of the stack to be altered. The acmode argument is
a longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines symbols for the four
access modes. The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the
caller.
If acmode specifies user mode, $SETSTK_64 performs no
operation and returns the SS$_NORMAL condition value.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
0 for memory stack (Alpha and Integrity servers VA$M_SETSTK_REGISTER for register stack (Integrity servers only)
The $VADEF macro and VADEF.H file define symbolic names for the
flags argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Lowest address in the range of addresses that express the stack's previous limits. For a memory stack, this address was the stack limit. For an Integrity servers register stack, this address was the stack base.
| OpenVMS usage: | length |
| type: | quadword |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Length of the range of addresses that express the stack's previous limits.
Description
The Set Stack Limits service allows a process to change the size of its supervisor, executive, and kernel stacks by altering the values in the stack limit and base arrays held in P1 (per-process) space. For Alpha, only the memory stack limits can be changed. The address range must be within 32-bit address space. For IA64, either the memory stack or register stack limits can be changed. The address range for the register stack can be in 64-bit address space.
Required Access or Privileges
The calling process can adjust the size of stacks only for access modes that are equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the calling process.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA_64, $DELTVA_64, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG_64, $LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64, $MGBLSC_64, $PURGWS, $SETPRT_64, $ULKPAG_64, $ULWSET_64, $UPDSEC_64, $UPDSECW_64
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The prev_start_va_64 or prev_length_64 argument cannot be written by the caller.
- SS$_LENVIO
Memory stack limits were specified in 64-bit address space. Only 32-bit addresses are supported for the memory stack limits.
$SETSWM
Set Process Swap Mode — Allows a process to control whether it can be swapped out of the balance set.
Format
SYS$SETSWM [swpflg]C Prototype
int sys$setswm (char swpflg);Argument
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Indicator specifying whether the process can be swapped. The swpflg
argument is a longword value. The value 0 (the default) enables process swap mode,
meaning the process can be swapped. The value 1 disables process swap mode, meaning the
process cannot be swapped.
Description
The Set Process Swap Mode service allows a process to control whether it can be swapped out of the balance set.
When the process swap mode is enabled, the process can be swapped out; when disabled, the process remains in the balance set until (1) process swap mode is reenabled or (2) the process is deleted.
The $SETSWM service returns a condition value indicating whether process swap mode was enabled or disabled prior to the call to $SETSWM.
Required Access or Privileges
To change its process swap mode, the calling process must have PSWAPM privilege.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET, $MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC, $UPDSECW
To lock some but not necessarily all process pages into the balance set, use the Lock Pages in Memory ($LCKPAG) service.
For more information, see the chapter on memory management in the VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully. The process was not previously locked in the balance set.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully. The process was previously locked in the balance set.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The process does not have the necessary PSWAPM privilege.
$SETUAI
Set User Authorization Information — Modifies the user authorization file (UAF) record for a specified user.
Format
SYS$SETUAI
[nullarg] ,[contxt] ,usrnam ,itmlst ,[nullarg] ,[nullarg] ,[nullarg]C Prototype
int sys$setuai
(unsigned int efn, unsigned int *contxt, void *usrnam, void *itmlst,
struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | null_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to OpenVMS.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
A longword used to maintain authorization file context. The contxt
argument is the address of a longword to receive a $SETUAI context value. On the initial
call, this longword should contain the value –1. On subsequent calls, the value of
the contxt argument from the previous call should be passed back
in.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor-fixed length string descriptor |
Name of the user whose UAF record is modified. The usrnam argument is
the address of a descriptor pointing to a character text string containing the user
name. The user name string can contain a maximum of 32 alphanumeric characters.
| OpenVMS usage: | item_list_3 |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Item list specifying which information from the specified UAF record is to be modified. The
itmlst argument is the address of a list of one or more item
descriptors, each of which specifies an item code. The item list is terminated by the
item code 0 or by the longword 0.
The following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor.

|
Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Buffer length |
A word specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer in which $SETUAI is to write the information. The length of the buffer varies, depending on the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor, and is given in the description of each item code. If the value of the buffer length field is too small, $SETUAI truncates the data. |
|
Item code |
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of information that $SETUAI is to set. The $UAIDEF macro defines these codes. |
|
Buffer address |
A longword address of the buffer that specifies the information to be set by $SETUAI. |
|
Return length address |
A longword containing the user-supplied address of a word in which $SETUAI writes the length in bytes of the information it actually set. |
UAI$_codenullarg
| OpenVMS usage: | nullarg |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Placeholding argument reserved to OpenVMS.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: | nullarg |
| type: | procedure entry mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Placeholding argument reserved to OpenVMS.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: | nullarg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to OpenVMS.
Item Codes
UAI$_ACCOUNT
When you specify UAI$_ACCOUNT, $SETUAI sets, as a blank-padded 32-character string, the account name of the user.
An account name can include up to 8 characters. Because the account name is a blank-filled string, however, the buffer length field of the item descriptor should specify 32 (bytes).
UAI$_ASTLM
When you specify UAI$_ASTLM, $SETUAI sets the AST queue limit.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_BATCH_ACCESS_P
When you specify UAI$_BATCH_ACCESS_P, $SETUAI sets, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which batch access is permitted for primary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m., to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_BATCH_ACCESS_S
When you specify UAI$_BATCH_ACCESS_S, $SETUAI sets, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which batch access is permitted for secondary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m., to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_BIOLM
When you specify UAI$_BIOLM, $SETUAI sets the buffered I/O count limit.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_BYTLM
When you specify UAI$_BYTLM, $SETUAI sets the buffered I/O byte limit.
Because the buffered I/O count limit is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_CLITABLES
When you specify UAI$_CLITABLES, $SETUAI sets, as a character string, the name of the user-defined CLI table for the account, if any.
Because the CLI table name can include up to 31 characters plus a size-byte prefix, the buffer length field of the item descriptor should specify 32 (bytes).
UAI$_CPUTIM
When you specify UAI$_CPUTIM, $SETUAI sets the maximum CPU time limit (per session) for the process in 10-millisecond units.
Because the maximum CPU time limit is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_DEFCLI
When you specify UAI$_DEFCLI, $SETUAI sets, as an OpenVMS RMS file name component, the name of the command language interpreter used to execute the specified batch job. The file specification set assumes the device name and directory SYS$SYSTEM and the file type .EXE.
Because a file name can include up to 31 characters plus a size-byte prefix, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 32 (bytes).
UAI$_DEFDEV
When you specify UAI$_DEFDEV, $SETUAI sets, as a 1- to 31-character string, the name of the default device.
Because the device name string can include up to 31 characters plus a size-byte prefix, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 32 (bytes).
UAI$_DEFDIR
When you specify UAI$_DEFDIR, $SETUAI sets, as a 1- to 63-character string, the name of the default directory.
Because the directory name string can include up to 63 characters plus a size-byte prefix, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 64 (bytes).
UAI$_DEF_PRIV
When you specify UAI$_DEF_PRIV, $SETUAI sets, as a quadword value, the default privileges for the user.
Because the default privileges are set as a quadword value, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
UAI$_DFWSCNT
When you specify UAI$_DFWSCNT, $SETUAI sets, pagelets (on Alpha and Integrity server systems), the default working set size.
Because the default working set size is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_DIALUP_ACCESS_P
When you specify UAI$_DIALUP_ACCESS_P, $SETUAI sets, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which dialup access is permitted for primary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m., to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_DIALUP_ACCESS_S
When you specify UAI$_DIALUP_ACCESS_S, $SETUAI sets, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which dialup access is permitted for secondary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m., to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_DIOLM
When you specify UAI$_DIOLM, $SETUAI sets the direct I/O count limit.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_ENCRYPT
|
Symbolic Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
UAI$C_AD_II |
Uses a CRC algorithm and returns a longword hash value. It was used in VAX/VMS releases prior to Version 2.0. |
|
UAI$C_PURDY |
Uses a Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a blank-padded user name and returns a quadword hash value. This algorithm was used during VAX/VMS Version 2.0 field test. |
|
UAI$C_PURDY_V |
Uses the Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a variable length user name and returns a quadword hash value. This algorithm was used in VMS releases prior to Version 5.4. |
|
UAI$C_PURDY_S |
Uses the Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a variable length user name and returns a quadword hash value. This is the current algorithm that the operating system uses for all new password changes. |
|
UAI$C_PREFERED_ALGORITHM |
Represents the latest encryption algorithm that the operating system uses to encrypt new passwords. Currently, it equates to UAI$C_PURDY_S. VSI recommends that you use this symbol in source modules. |
Because the encryption algorithm is a byte in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
UAI$_ENCRYPT2
- UAI$C_AD_II
- UAI$C_PURDY
- UAI$C_PURDY_V
- UAI$C_PURDY_S
- UAI$C_PREFERED_ALGORITHM
UAI$_ENQLM
When you specify UAI$_ENQLM, $SETUAI sets the lock queue limit.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_EXPIRATION
When you specify UAI$_EXPIRATION, $SETUAI sets, as a quadword absolute time value, the expiration date and time of the account.
Because the absolute time value is a quadword in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
UAI$_FILLM
When you specify UAI$_FILLM, $SETUAI sets the open file limit.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_FLAGS
When you specify UAI$_FLAGS, $SETUAI sets, as a longword bit vector, the various login flags set for the user.
|
Symbol |
Description |
|---|---|
|
UAI$V_AUDIT |
All actions are audited. |
|
UAI$V_AUTOLOGIN |
User can only log in to terminals defined by the Automatic Login facility (ALF). |
|
UAI$V_CAPTIVE |
User is restricted to captive account. |
|
UAI$V_DEFCLI |
User is restricted to default command interpreter. |
|
UAI$V_DISACNT |
User account is disabled. |
|
UAI$V_DISCTLY |
User cannot use Ctrl/Y. |
|
UAI$V_DISFORCE_PWD_CHANGE |
User will not be forced to change expired passwords at login. |
|
UAI$V_DISIMAGE |
User cannot issue the RUN or MCR commands or use the foreign command mechanism in DCL. |
|
UAI$V_DISMAIL |
Announcement of new mail is suppressed. |
|
UAI$V_DISPWDDIC |
Automatic checking of user-selected passwords against the system dictionary is disabled. |
|
UAI$V_DISPWDHIS |
Automatic checking of user-selected passwords against previously used passwords is disabled. |
|
UAI$V_DISPWDSYNCH |
When set, prevents synchronizing a user's SYSUAF.DAT password using an external authentication password (when UAI$V_EXTAUTH is set). |
|
UAI$V_DISRECONNECT |
User cannot reconnect to existing processes. |
|
UAI$V_DISREPORT |
User will not receive last login messages. |
|
UAI$V_DISWELCOME |
User will not receive the login welcome message. |
|
UAI$V_EXTAUTH |
User is considered externally authenticated by an external user ID and password and not by the SYSUAF user name and password. The SYSUAF record is still used for checking login restrictions and quotas and for creating the user's OpenVMS process profile. |
|
UAI$V_GENPWD |
User is required to use generated passwords. |
|
UAI$V_LOCKPWD |
SET PASSWORD command is disabled. |
|
UAI$V_MIGRATEPWD |
User's SYSUAF password was set using AUTHORIZE or SYS$SETUAI and is likely to be inconsistent with the user's external user password. If password migration is enabled, the system will attempt to update external authorization service the next time the user attempts a login. |
|
UAI$V_NOMAIL |
Mail delivery to user is disabled. |
|
UAI$V_PWD_EXPIRED |
Primary password is expired. |
|
UAI$V_PWD2_EXPIRED |
Secondary password is expired. |
|
UAI$V_PWDMIX |
Enables case-sensitive and extended-character passwords. After PWDMIX is specified, you can then use mixed-case and extended characters in passwords. Be aware that before the PWDMIX flag is enabled, the system stores passwords in all upper-case. Therefore, until you change passwords, you must enter your pre-PWDMIX passwords in upper-case. To change the password after PWDMIX is enabled:
|
|
UAI$V_RESTRICTED |
User is limited to operating under a restricted account. Clear the CAPTIVE flag (UAI$V_CAPTIVE), if set, before setting the RESTRICTED flag. (See the VSI OpenVMS Guide to System Security |
|
UAI$V_VMSAUTH |
When set, the user is allowed to authenticate with the SYSUAF.DAT user name and password (when UAI$V_EXTAUTH is set). |
UAI$_JTQUOTA
When you specify UAI$_JTQUOTA, $SETUAI sets the initial byte quota with which the jobwide logical name table is to be created.
Because this quota is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_LASTLOGIN_I
When you specify UAI$_LASTLOGIN_I, $SETUAI sets, as a quadword absolute time value, the date of the last interactive login.
UAI$_LASTLOGIN_N
When you specify UAI$_LASTLOGIN_N, $SETUAI sets, as a quadword absolute time value, the date of the last noninteractive login.
UAI$_LGICMD
When you specify UAI$_LGICMD, $SETUAI sets, as an OpenVMS RMS file specification, the name of the default login command file.
Because a file specification can include up to 63 characters plus a size-byte prefix, the buffer length field of the item descriptor should specify 64 (bytes).
UAI$_LOCAL_ACCESS_P
When you specify UAI$_LOCAL_ACCESS_P, $SETUAI sets, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which local interactive access is permitted for primary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m., to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_LOCAL_ACCESS_S
When you specify UAI$_LOCAL_ACCESS_S, $SETUAI sets, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which local interactive access is permitted for secondary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m., to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_LOGFAILS
When you specify UAI$_LOGFAILS, $SETUAI sets the count of login failures.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_MAXACCTJOBS
When you specify UAI$_MAXACCTJOBS, $SETUAI sets the maximum number of batch, interactive, and detached processes that can be active at one time for all users of the same account. The value 0 represents an unlimited number.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_MAXDETACH
When you specify UAI$_MAXDETACH, $SETUAI sets the detached process limit. The value 0 represents an unlimited number.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_MAXJOBS
When you specify UAI$_MAXJOBS, $SETUAI sets the active process limit. A value of 0 represents an unlimited number.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_NETWORK_ACCESS_P
When you specify UAI$_NETWORK_ACCESS_P, $SETUAI sets, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which network access is permitted for primary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m., to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_NETWORK_ACCESS_S
When you specify UAI$_NETWORK_ACCESS_S, $SETUAI sets, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which network access is permitted for secondary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m., to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_OWNER
When you specify UAI$_OWNER, $SETUAI sets, as a character string, the name of the owner of the account.
Because the owner name can include up to 31 characters plus a size-byte prefix, the buffer length field of the item descriptor should specify 32 (bytes).
UAI$_PASSWORD
When you specify UAI$_PASSWORD, $SETUAI sets the specified plaintext string as the primary password for the user and updates the primary password change date. You must have SYSPRV privilege to set passwords for any user account (including your own).
The UAI$_PASSWORD and UAI$_PASSWORD2 item codes provide the building blocks for designing a site-specific SET PASSWORD utility. Note that if you create such a utility, you should also set the LOCKPWD bit in the user authorization file (UAF) to prevent users from using the DCL command SET PASSWORD and to prevent the LOGINOUT process from forcing password changes. If you create a site-specific SET PASSWORD utility, install the utility with SYSPRV privilege.
You must adhere to the following guidelines when specifying a password with UAI$_PASSWORD or UAI$_PASSWORD2:
The password must meet the minimum password length defined for the user account.
The password cannot exceed 32 characters in length.
The password must be different from the previous password.
To clear the primary password, specify the value 0 in the buffer length field.
Note
If you specify UAI$_PASSWORD, the UAI$_PWD_DATE item is ignored. To use these two item codes, you must use them in two separate calls.
To generate a pre-expired password, follow the instructions in the "Description" section at the end of this system service documentation."
UAI$_PASSWORD2
Sets the specified plaintext string as the secondary password for the user and updates the secondary password change date. You must have SYSPRV privilege to set passwords for any user account (including your own).
Note
If you specify UAI$_PASSWORD2, the UAI$_PWD2_DATE item is ignored. To use these two item codes, you must use them in two separate calls.
To generate a pre-expired password, follow the instructions in the "Description" section at the end of this system service documentation.
UAI$_PBYTLM
When you specify UAI$_PBYTLM, $SETUAI Sets, in pagelets (on Alpha and Integrity server systems), the paging file quota.
Because the paging file quota is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_PGFLQUOTA
When you specify UAI$_PGFLQUOTA, $SETUAI sets, in pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets (on Alpha systems), the paging file quota.
Because the paging file quota is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_PRCCNT
When you specify UAI$_PRCCNT, $SETUAI sets the subprocess creation limit.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_PRI
When you specify UAI$_PRI, $SETUAI sets the default base priority.
Because this decimal number is a byte in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
UAI$_PRIMEDAYS
When you specify UAI$_PRIMEDAYS, $SETUAI sets, as a byte bit vector, the primary and secondary days of the week.
- UAI$V_MONDAY
- UAI$V_TUESDAY
- UAI$V_WEDNESDAY
- UAI$V_THURSDAY
- UAI$V_FRIDAY
- UAI$V_SATURDAY
- UAI$V_SUNDAY
UAI$_PRIV
When you specify UAI$_PRIV, $SETUAI sets, as a quadword value, the names of the privileges that the user holds.
Because the privileges are set as a quadword value, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
UAI$_PWD
When you specify UAI$_PWD, $SETUAI sets, as a quadword value, the hashed primary password of the user.
Because the hashed primary password is set as a quadword value, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
When you use $SETUAI to change the password on an account that has the UAI$V_EXTHAUTH flag set, the UAI$V_MIGRATEPWD flag is set automatically.
UAI$_PWD_DATE
When you specify UAI$_PWD_DATE, $SETUAI sets, as a quadword absolute time value, the date of the last password change.
Because this value is a quadword in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
Note
If you specify UAI$_PASSWORD, the UAI$_PWD_DATE item is ignored. To use these two item codes, you must use them in two separate calls.
To generate a pre-expired password, follow the instructions in the "Description" section at the end of this system service documentation.
UAI$_PWD_LENGTH
When you specify UAI$_PWD_LENGTH, $SETUAI sets the minimum password length.
Because this decimal number is a byte in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
UAI$_PWD_LIFETIME
When you specify UAI$_PWD_LIFETIME, $SETUAI sets, as a quadword delta time value, the password lifetime.
Because this value is a quadword in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
A quadword of 0 means that none of the password mechanisms will take effect.
UAI$_PWD2
When you specify UAI$_PWD2, $SETUAI sets, as a quadword value, the hashed secondary password of the user.
Because the hashed secondary password is set as a quadword value, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
UAI$_PWD2_DATE
When you specify UAI$_PWD2_DATE, $SETUAI sets, as a quadword absolute time value, the last date the secondary password was changed.
Because this value is a quadword in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
A value of –1 indicates that the password could be marked as preexpired.
UAI$_QUEPRI
When you specify UAI$_QUEPRI, $SETUAI sets the maximum job queue priority in the range 0 through 31.
Because this decimal number is a byte in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
UAI$_REMOTE_ACCESS_P
When you specify UAI$_REMOTE_ACCESS_P, $SETUAI sets, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which batch access is permitted for primary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m., to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_REMOTE_ACCESS_S
When you specify UAI$_REMOTE_ACCESS_S, $SETUAI sets, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which batch access is permitted for secondary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m., to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_SALT
When you specify UAI$_SALT, $SETUAI sets the salt field of the user's record to the value you provide. The salt value is used in the operating system hash algorithm to generate passwords. $SETUAI does not generate a new salt value for you.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
By copying the item codes UAI$_SALT, UAI$_ENCRYPT, UAI$_PWD, UAI$_PWD_DATE, and UAI$_FLAGS, a site-security administrator can construct a utility that propagates password changes throughout the network. Note, however, that VSI does not recommend using the same password on more than one node in a network.
UAI$_SHRFILLM
When you specify UAI$_SHRFILLM, $SETUAI sets the shared file limit.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_TQCNT
When you specify UAI$_TQCNT, $SETUAI sets the timer queue entry limit.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_UIC
When you specify UAI$_UIC, $SETUAI sets, as a longword, the user identification code (UIC). For the format of the UIC, see the VSI OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
UAI$_USER_DATA
When you specify UAI$_USER_DATA, $SETUAI sets up to 255 bytes of information in the user data area of the system user authorization file (SYSUAF). This is the supported method for modifying the user data area of the SYSUAF. VSI no longer supports direct user modification of the SYSUAF.
To clear all the information in the user data area of the SYSUAF, specify $SETUAI with a buffer length field of 0.
UAI$_WSEXTENT
When you specify UAI$_WSEXTENT, $SETUAI sets the working set extent, in pagelets (on Alpha and Integrity server systems), specified for the specified job or queue.
Because the working set extent is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_WSQUOTA
When you specify UAI$_WSQUOTA, $SETUAI sets the working set quota, in pagelets (on Alpha and Integrity server systems), for the specified user.
Because the working set quota is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
Description
The Set User Authorization Information service is used to modify the user authorization file (UAF) record for a specified user.
The UAI$V_PWD_EXPIRED should only be set when the bit UAI$V_DISFORCE_PWD_CHANGE is set in the user's SYSUAF record and the comparison between the UAI$_PWD_DATE and UAI$_PWD_LIFETIME indicates a password is past its valid life.
To generate a pre-expired password, first generate a new hashed password using $HASH_PASSWORD. Then make a call to $SETUAI using either UAI$_PASSWORD or UAI$_PASSWORD2, as appropriate. Finally, make a separate call to $SETUAI to set UAI$_PWD_DATE or UAI$_PWD_DATE2 to -1.
For information about login and password expiration, see the Description section of the $GETUAI system service.
Required Access or Privileges
BYPASS or SYSPRV—Allows modification of any record in the UAF (user authorization file).
GRPPRV—Allows modification of any record in the UAF whose UIC group matches that of the requester. Note, however, that you cannot change a UAF record whose UIC matches exactly the requester's UIC. Group managers with GRPPRV privilege are limited in the extent to which they can modify the UAF records of users in the same group; values such as privileges and quotas can be changed only if the modification does not exceed the values set in a group manager's UAF record.
No privilege—Does not allow access to any UAF record.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GETUAI
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The item list or input buffer cannot be read by the caller; or the return length buffer, output buffer, or status block cannot be written by the caller.
- SS$_BADPARAM
The function code is invalid; the item list contains an invalid item code; a buffer descriptor has an invalid length; or the reserved parameter has a nonzero value.
- SS$_NOGRPPRV
The user does not have the privileges required to modify the authorization information for other members of the UIC group.
- SS$_NOSYSPRV
The user does not have the privileges required to modify the authorization information associated with the user or for users outside of the user's UIC group.
- RMS$_RSZ
The UAF record is smaller than required; the caller's SYSUAF is likely corrupt.
This service can also return OpenVMS RMS status codes associated with operations on indexed files. For a description of RMS status codes that are returned by this service, refer to the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$SETUP_AVOID_PREEMPT
Setup for Process Preemption Avoidance — Performs initial setup for process preemption avoidance.
Format
SYS$SETUP_AVOID_PREEMPT enableC Prototype
int sys$setup_avoid_preempt (int enable);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Enables or disables preemption avoidance. If the
enable argument is set to 1, preemption avoidance is enabled; if 0, preemption avoidance is disabled.
Description
The Setup for Process Preemption Avoidance service is a kernel-mode initialization routine that locks the necessary internal data structures in memory so scheduling routines can access them above pageable IPL. A process or thread can then set or clear the indicator bit by calling the $AVOID_PREEMPT service.
In addition, if the process or thread has ALTPRI privilege, $SETUP_AVOID_PREEMPT sets a bit in the PKTA (a per-kernel-thread data area) to mark that the process or thread can prevent preemption by other processes or threads having the same base priority but not those that have a higher base priority.
Note that without ALTPRI, this service will still function successfully, but will only enable the $AVOID_PREEMPT service to avoid preemptions due to quantum end.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$AVOID_PREEMPT
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
Also, any values returned by the $LKWSET or $UNLKSET services.
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS
Set Default Transaction — Sets or clears the default transaction of the calling process.
Format
SYS$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS
[efn] ,[flags] ,iosb [,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[new_tid] ,[old_tid]]C Prototype
int sys$set_default_trans
(unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb *iosb,...);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
flags argument
is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to an option flag. The $DDTMDEF
macro defines symbolic names for the option flag, described in Table 11. All undefined bits must be 0. If
this argument is omitted, no flags are used.| Flag Name | Description |
|---|---|
| DDTM$M_SYNC | Specifies successful synchronous completion by returning SS$_SYNCH. When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the AST routine is not called, the event flag is not set, and the I/O status block is not filled in. |
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned section.

astadr
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure entry mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The AST routine executed when the service completes, if SS$_NORMAL is returned in R0.
The astadr argument is the address of the entry mask of this
routine. The routine is executed in the same access mode as that of the caller of the
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS service.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The AST parameter passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | trans_id |
| type: | octaword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The identifier (TID) of the new default transaction for the calling process. If this argument is zero (the default) or if it specifies a zero TID (an octaword of zeros), the service clears the default transaction of the calling process.
| OpenVMS usage: | trans_id |
| type: | octaword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
An octaword in which the service returns the identifier (TID) of the calling process' previous transaction (the one that was set or cleared by this call to $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS).
A zero TID is returned if the calling process did not have a default transaction prior to the call.
Description
The $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS system service:
Sets or clears the default transaction of the calling process.
If either the
new_tidargument passes the null value or thenew_tidargument is omitted or zero, then the default transaction of the calling process is cleared. Otherwise the default transaction of the calling process is set to the value passed in thenew_tidargument.Returns the identifier (TID) of the previous default transaction of the calling process (the one that was set or cleared by this call to $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS), if the
old_tidargument is not zero.
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS may fail for various reasons, including a call to $START_TRANS or $START_BRANCH that changes the default transaction of the calling process in progress.
Following a successful completion of $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS:
The calling process does not have a default transaction, if either the
new_tidargument passed the null value or thenew_tidargument was omitted or zero.The default transaction of the calling process is that passed in the
new_tidargument, if that argument was specified and its value was not zero.The identifier (TID) of the previous default transaction of the calling process is returned in the
old_tidargument, if that argument was not omitted.A null value is returned if the calling process did not previously have a default transaction.
There is also a wait form of the service, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quotas
ASTLM
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW, $CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW, $END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW, $GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW, $START_TRANS, $START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
If returned in R0, the request was successfully queued. If returned in the I/O status block, the service completed successfully.
- SS$_SYNCH
The service completed successfully and synchronously (returned only if the DDTM$M_SYNC flag is set).
- SS$_ACCVIO
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
- SS$_BADPARAM
The options flags were invalid.
- SS$_EXASTLM
The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded.
- SS$_ILLEFC
The event flag number was invalid.
- SS$_INSFARGS
A required argument was missing.
- SS$_INSFMEM
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
- SS$_WRONGSTATE
The default transaction was being changed at the time of the call.
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW
Set Default Transaction and Wait — Sets or clears the default transaction of the calling process. $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW always waits for the request to complete before returning to the caller. Other than this, it is identical to $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS.
Format
SYS$SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW
[efn] ,[flags] ,iosb [,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[new_tid] ,[old_tid]]C Prototype
int sys$set_default_transw
(unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb *iosb,...);$SET_DEVICE
Set Device Characteristics — Modifies the characteristics of a device or the paths used to access that device. For synchronous completion, use the Set Device Characteristics and Wait ($SET_DEVICEW) service. The $SET_DEVICEW service is identical to the $SET_DEVICE service, except that $SET_DEVICEW returns to the caller only after the requested action has taken effect. For additional information about system service completion, see the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
Format
SYS$SET_DEVICE
[efn] [,chan] [,devnam] ,itmlst [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm] [,nullarg]C Prototype
int sys$set_device
(unsigned int efn, unsigned short int chan, void *devnam, void *itmlst,
struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm,
struct_generic_64 *nullarg);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of the event flag to be set when $SET_DEVICE returns the requested
information. The efn argument is a longword containing this
number; however, $SET_DEVICE uses only the low-order byte.
Upon request initiation, $SET_DEVICE clears the specified event flag (or event flag 0
if efn was not specified). Then, when $SET_DEVICE returns the
requested information, it sets the specified event flag (or event flag 0).
| OpenVMS usage: | channel |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of the I/O channel assigned to the device about which information is desired.
The chan argument is a word containing this number.
To identify a device to $SET_DEVICE, you can specify either the
chan or devnam parameters, but you
should not specify both. If you specify both arguments, the chan
argument is used.
If you specify neither chan nor devnam,
$SET_DEVICE uses a default value of 0 for chan.
| OpenVMS usage: | device_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor-fixed-length string descriptor |
The name of the device about which $SET_DEVICE is to modify the characteristics or
path settings. The devnam argument is the address of a character
string descriptor pointing to this name string.
The device name string can be either a physical device name or a logical name. If the first character in the string is an underscore (_), the string is considered a physical device name; otherwise, the string is considered a logical name and logical name translation is performed until either a physical device name is found or the system default number of translations has been performed.
If the device name string contains a colon (:), the colon and the characters that follow it are ignored.
To identify a device to $SET_DEVICE, you can specify either the
chan or devnam argument, but you should
not specify both. If both arguments are specified, the chan
argument is used.
If you specify neither chan nor devnam,
$SET_DEVICE uses a default value of 0 for chan.
| OpenVMS usage: | item_list_3 |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Item list specifying which information about the device is to be returned. The
itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors,
each of which describes an item of information. The list of item descriptors is
terminated by a longword of 0.
Currently, $SET_DEVICE allows only one valid item list entry.

See the itmlst argument in the $GETDVI system service description
for information on the meaning of these fields in the item list.
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
I/O status block that is to receive the final completion status. The
iosb argument is the address of the quadword I/O status block.
See iosb in the $GETDVI system service description for more
information.
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
AST service routine to be executed when $SET_DEVICE completes. The
astadr argument is the address of this routine.
If you specify astadr, the AST routine executes at the same
access mode as the caller of the $SET_DEVICE service.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine specified by the
astadr argument. The astprm argument is
the longword parameter.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: | null_arg |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Placeholding argument reserved to OpenVMS and should be zero.
Item Codes
SDV$_MP_SWITCH_PATH
Forces an immediate I/O path switch for the specified device. The active path will be switched from the current I/O path to the path name specified in the buffer for this item code. Note that issuing $SET_DEVICE with SDV$_MP_SWITCH_PATH will initiate the process of switching the path. A delay may occur between when the service completes and when the path switch is complete. A synchronous version of this service, $SET_DEVICEW, is available that will wait until the path switch attempt is complete before returning to the caller.
The path name specified in this and the following item codes must be fully specified. It may be in either uppercase or lowercase, however the entire name must be specified.
The Return Length field in this and the following item codes should set to zero.
The SDVDEF macro contains these item codes.
SDV$_MP_DISABLE_PATH
Disables the path specified in the buffer for this item code so that it will no longer be considered as a switch candidate. Note that this does not apply to the current path, which cannot be disabled. The reasons one might want to disable a path include the following:
You know a specific path is broken or that a failover to that path will cause some members of the cluster to lose access.
To prevent automatic switching to a selected path while it is being serviced.
SDV$_MP_ENABLE_PATH
Reenables the path name specified in the buffer for this item code as a switch candidate.
Description
The Set Device service modifies the characteristics of devices or I/O paths that have been established to those devices. For Multipath, the service allows the user to switch the current I/O path to a different available path and to enable and disable paths from being used for I/O.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ASSIGN, $DASSGN, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DEVICE_PATH_SCAN, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The device name string descriptor, device name string, or
itmlstargument cannot be read; or the buffer or return length longword cannot be written.- SS$_BADPARAM
The item list contains an invalid item code, or the buffer length field in an item descriptor specified insufficient space for the return length information.
- SS$_DEVOFFLINE
The specified path is not available.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
Quota for pool has been exceeded.
- SS$_IVCHAN
You specified an invalid channel number, that is, a channel number larger than the number of channels.
- SS$_IVDEVNAM
The device name string contains invalid characters, or neither the
devnamnorchanargument was specified.- SS$_MPDEVBUSY
The specified path for this device is temporarily unavailable. This condition is quite rare; if this status is returned, the operation should be retried immediately, because the cause of the unavailability is very short-lived.
- SS$_MPDEVUSERDISABLE
The user has disabled the specified path for this device.
- SS$_NOOPER
Caller does not have OPER privileges.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The specified channel is not assigned or was assigned from a more privileged access mode.
- SS$_NOSUCHDEV
The specified device does not exist on the host system.
- SS$_NOSUCHPATH
The specified pathname does not exist on the host system.
- SS$_PATHAMBIG
The specified pathname is ambiguous for this device.
$SET_DEVICEW
Set Device Characteristics and Wait — Modifies the characteristics of a device or the paths used to access that device. The $SET_DEVICEW completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller only after the requested action has taken effect.
Format
SYS$SET_DEVICEW
[efn] [,chan] [,devnam] ,itmlst [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm] [,nullarg]C Prototype
int sys$set_devicew
(unsigned int efn, unsigned short int chan, void *devnam, void *itmlst,
struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm,
struct_generic_64 *nullarg);$SET_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Modify Process Implicit Affinity — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, controls or retrieves the activation state for the implicit affinity system capability of a specific kernel thread or of the global process default. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$SET_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY
[pidadr] [,prcnam] [,state] [,cpu_id] [,prev_mask]C Prototype
int sys$set_implicit_affinity
(unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, struct _generic_64 *state,
int cpu_id, struct _generic_64 *prev_mask);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Process identification (PID) of a kernel thread whose implicit affinity is to be modified or returned. The
pidadr argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a longword that contains the PID.
Process selection is made through a combination of the
pidadr and
prcnam arguments. If neither are specified or if both have a zero value, the service operations are made to the user capability mask of the current kernel thread of the current calling process. The
pidadr argument takes precedence over the
prcnam argument where both are supplied in the service call.
If the bit constant CAP$M_IMPLICIT_DEFAULT_ONLY is specified in the
state argument, then the implicit affinity state portion of
the default capability mask is modified or returned instead.
| OpenVMS usage: | process_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Process name of the process whose implicit affinity capability state is to be modified or
returned. The prcnam argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a
character string descriptor pointing to the process name string. A process can be
identified with a 1- to 15-character string. The service operations are made to the user
capability mask of the initial thread of the specified process.
If pidadr and prcnam are both specified, then
pidadr is modified or returned and
prcnam is ignored. If neither argument is specified, then the
context of the current kernel thread of the calling process is modified or
returned.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_quadword |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
State options that can be selected for the affected thread's implicit affinity. The
state argument is a pointer to a quadword bit vector wherein a bit corresponds to a requested state for the implicit affinity feature. Only the bits specified below are used; the remainder of the quadword bits are reserved.
Each option (bit) has a symbolic name, defined in the $CAPDEF macro. The
state argument is constructed by performing a logical OR
operation using the symbolic names of each desired option.
|
Symbolic Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
CAP$M_IMPLICIT_DEFAULT_ONLY |
Indicates the specified operations are to be performed on the
global cell instead of on a specific kernel thread. This bit
supersedes any individual kernel thread specified in
|
|
CAP$M_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY_SET |
Indicates that the implicit affinity capability bit is to be set for the specified kernel thread. This is mutually exclusive with CAP$M_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY_CLEAR. |
|
CAP$M_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY_CLEAR |
Indicates that the implicit affinity capability bit is to be cleared for the specified kernel thread. This is mutually exclusive with CAP$M_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY_SET. |
| OpenVMS usage: | longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Identifier of the CPU requested as the first CPU on which this kernel thread is to execute.
The cpu_id is a longword containing this number, which is in the
supported range of individual CPUs from 0 to SYI$_MAX_CPUS − 1.
If no explicit CPU is needed, specifying a value of −1 in this argument indicates the system is to select the initial association based on system dynamics and load balancing.
Note that, regardless of what explicit CPU is supplied to this argument, it will be taken only as a suggestion. This service will attempt to make the requested association, but it will be superseded by another CPU if the system dynamics are adversely affected by the operation.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_quadword |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Previous implicit affinity state mask for the specified kernel thread before execution of this
call to $SET_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY. The prev_mask argument is the 32-
or 64-bit address of a quadword into which $SET_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY writes a bit mask
specifying the implicit affinity state.
The current state of the kernel thread's current implicit affinity feature can be determined
by testing the returned mask with the symbolic bit definitions described for the
state argument. These bit definitions are found in the
$CAPDEF macro.
Description
The Modify Process Implicit Affinity system service modifies or returns the implicit affinity state for the specified kernel thread or from the system default process creation cell.
Setting a kernel thread's implicit affinity function indicates to the system that it is to schedule the process in ways that will maximize the cache and TB performance in the current symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) configuration. This might tend to bias the process towards specific CPUs more than the standard scheduling algorithm would normally have allowed.
Required Access or Privileges
- ALTPRI—To modify any process with a matching UIC
- ALTPRI and GROUP—To modify any process in the same UIC group
- ALTPRI and WORLD—To modify any process
- None—To retrieve the state of itself or any process with a matching UIC
- GROUP—To retrieve the state of any process in the same UIC group
- WORLD—To retrieve the state of any process
Related Services
$CPU_CAPABILITIES, $PROCESS_CAPABILITIES, $PROCESS_AFFINITY
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_BADPARAM
One or more arguments has an invalid value.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more arguments.
- SS$_NOSUCHTHREAD
The specified kernel thread does not exist.
- SS$_NONEXPR
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process identification was specified.
- SS$_IVLOGNAM
The process name string has a length of 0 or more than 15 characters.
- SS$_NOPRIV
Insufficient privilege for attempted operation.
- SS$_CPUCAP
No CPU can run the specified process with new capabilities.
- SS$_INSFARG
Fewer than the required number of arguments were specified or no operation was specified.
$SET_PROCESS_PROPERTIESW (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Sets Simple Value — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, sets a simple value associated with a process.
Format
SYS$SET_PROCESS_PROPERTIESW
mbz1 ,pidadr ,prcnam ,property ,value ,prev_value
[,bufsiz ,bufcnt ,flags]C Prototype
int sys$set_process_propertiesw
(mbz1, unsigned int *pidadr, unsigned int *prcnam,
unsigned int property, unsigned __int64 value,
unsigned __int64 *prev_value,...);Arguments
mbz1
Reserved for future OpenVMS use. Must be specified as 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Process identification (PID) of the process whose system service logging
characteristics are to be modified. The pidadr argument is the
address of the PID.
Supported only for use with PPROP$C_SS_LOG_ENABLE, PPROP$C_SS_LOG_DISABLE, and PPROP$C_SS_LOG_UNLOAD. Otherwise, must be specified as 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | process_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Process name of the process whose priority is to be changed. The
prcnam argument is the address of a character string
descriptor pointing to the process name. The process name can be 1 - 15 characters
long.
You can use the prcnam argument only on behalf of processes in
the same UIC group as the calling process. To affect system service logging for
processes in other groups, you must specify the pidadr
argument.
Supported only for use with PPROP$C_SS_LOG_ENABLE, PPROP$C_SS_LOG_DISABLE, and PPROP$C_SS_LOG_UNLOAD. Otherwise, must be specified as 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | integer |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
A constant that selects which property to set.
| Property Code | Description |
|---|---|
| PPROP$C_CASE_LOOKUP_TEMP |
The type of case lookup to use. This value is set for the life of the currently active image. This value reverts to the permanent case setting on image rundown. In the absence of an explicit case lookup specification in a user-provided NAML, RMS uses this value to determine the case setting for the current file operation. Valid values are PPROP$K_CASE_BLIND and PPROP$K_CASE_SENSITIVE. For additional information, see the VSI OpenVMS Guide to OpenVMS File Applications. |
| PPROP$C_CASE_LOOKUP_PERM |
The type of case lookup to use. This value is set for the life of the process or until the case is set agairundown. Setting this value affects only future activated images for this process. To change the case setting for the current active image, you must modify the PPROP$C_CASE_LOOKUP_TEMP setting. Valid values are PPROP$K_CASE_BLIND and PPROP$K_CASE_SENSITIVE. For additional information, see the VSI OpenVMS Guide to OpenVMS File Applications. |
| PPROP$C_SEARCH_SYMLINK_TEMP | Processes the active search mode. The value reverts to the permanent setting on image rundown. Valid values are PPROP$K_SEARCH_SYMLINK_NONE, PPROP$K_SEARCH_SYMLINK_ALL, and PROP$K_SEARCH_SYMLINK_NOELLIPS. |
| PPROP$C_SEARCH_SYMLINK_PERM | Processes the permanent search mode. This value is set for the life of the process. Changing this setting only changes the behavior of subsequently activated images. Valid values are PPROP$K_SEARCH_SYMLINK_NONE, PPROP$K_SEARCH_SYMLINK_ALL, and PROP$K_SEARCH_SYMLINK_NOELLIPS. |
| PPROP$C_DEADLOCK_WAIT | The per-process deadlock wait time (in 100-ns units). A value of zero resets and disables the per-process deadlock wait time and fallback to the systemwide deadlock wait time that comes from the system parameter DEADLOCK_WAIT. Valid values are in the range of 100000 (=10ms) and 10000000 (=1 s). If the value is too small, the per-process deadlock wait is set to 10 ms; if the value is too large, it is set to 1 s. |
| PPROP$C_HOME_RAD | The Resource Affinity Domain (RAD) to which the process is assigned. Newly mapped memory in the process will come from the home RAD of the process. Currently mapped memory will not move into the new home RAD unless $PURGWS is issued. Valid values are integers between 0 and the maximum RAD on the system. Valid home RADs must also contain either memory or CPUs. |
| PPROP$C_KERNEL_THREAD_LIMIT | Sets the process specific limit of the number of kernel threads that can be created. By default, this is controlled systemwide through the SYSGEN parameter MULTITHREAD. A value between 0 (use default) and the current setting of the MULTITHREAD parameter can be used. |
| PPROP$C_MEDDLE | Reserved for OpenVMS use. |
| PPROP$C_MEDDLE_ENABLE | Reserved for OpenVMS use. |
| PPROP$C_PARSE_STYLE_TEMP | The type of command parsing to use. This value is set only for the life of the image. The value reverts to the permanent style on image rundown. Valid values are PARSE_STYLE$C_TRADITIONAL and PARSE_STYLE$C_EXTENDED. |
| PPROP$C_PARSE_STYLE_PERM | The type of command parsing to use. This value is set for the life of the process unless the style is set again. Valid values are PARSE_STYLE$C_TRADITIONAL and PARSE_STYLE$C_EXTENDED. |
| PPROP$C_SS_LOG_DISABLE |
Stop logging system service requests for the current or specified
process. If logging was previously disabled, the value returned in
For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS System Analysis Tools Manual. |
| PPROP$C_SS_LOG_ENABLE |
Allocate log buffers and enable logging of system service requests
for the current or specified process. If logging was previously disabled,
the value returned in For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS System Analysis Tools Manual. |
| PPROP$C_SS_LOG_UNLOAD |
Stop logging system service requests for the current or specified
process and close the log file so that it can be analyzed. If logging was
previously disabled, the value returned in
For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS System Analysis Tools Manual. |
| PPROP$C_TOKEN | Controls the token size used by DCL. When the bit is clear (the default), traditional tokens are used, and each command token can hold up to 255 characters. When the bit is set, extended tokens are used; each command token can be up to 4000 characters. |
| PPROP$C_UNITS | Controls the process units. When the bit is clear (the default), all size-related numbers are displayed in blocks. When the bit is set, size-related numbers are converted to bytes. |
| OpenVMS usage: | integer |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by value |
A quadword value to which to set the property.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) address of a quadword value |
| access: | write |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The address of a quadword that will receive the previous value of the property.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The requested system service log buffer size in bytes. Supported only for use with PPROP$C_SS_LOG_ENABLE. If omitted, it defaults to 65,024 bytes. The maximum value is 65,024 bytes. The minimum value is 4096 bytes.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The requested number of system service log buffers. Supported only for use with PPROP$C_SS_LOG_ENABLE. If omitted, it defaults to 2. The maximum number of buffers is 6.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Flag mask specifying the enable logging request. The flags
argument is a longword bit vector in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The
$LOGTYPDEF macro and the LOGTYPDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag.
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| LOGTYP$M_ARGS | Log system service arguments. |
| LOGTYP$M_FILE | Write log information to a file. |
If you specify the flags argument as 0, the service defaults to
logging to a file and logging arguments.
If you specify LOGTYP$M_ARGS but lack privilege, service arguments are not logged.
Description
The $SET_PROCESS_PROPERTIESW system service sets a simple value associated with a process.
Generally, this service is used for changing process properties that have a maximum of a single quadword. You can change only one property at a time per call to this service.
Required Access or Privileges
To affect system service logging for another process, the calling process might need one of the following privileges:
GROUP privilege to affect a process in the same group, unless the target process has the same UIC as the calling process.
WORLD privilege to affect any process in the system.
To request logging the arguments passed to a system service, a process needs SETPRV, CMKRNL, or CMEXEC privilege.
Required Quota
When system service logging is enabled, the log buffers are charged against the process's paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA).
Related Services
$GETJPI
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Access violation.
- SS$_WRONGSTATE
An attempt was made to modify system service logging characteristics of a process when logging is disabled systemwide.
- SS$_NONEXPR
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process identification was specified.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The process does not have the privilege to affect the other process.
- SS$_IVLOGNAM
The process name string has a length of 0 or has more than 15 characters.
$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN
Set Resource Domain — Controls the association between a calling process and resource domains.
Format
SYS$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN
func ,rsdm_id ,domain_number ,[nullarg] ,[access] ,[acmode]C Prototype
int sys$set_resource_domain
(unsigned int func, unsigned int *rsdm_id, unsigned int domain_number,
unsigned int nullarg, unsigned int access, unsigned int acmode);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | function_code |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Function code specifying the action that $SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN is to perform. The
func argument is a longword containing this function code.
See the Function Codes section for a description of $SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN function
codes.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only to join, read only to leave |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Resource domain identification. The rsdm_id argument is the address of
a longword specifying the association of the calling process with the resource
domain.
The RSDM$_JOIN_DOMAIN function returns a resource domain identification. The RSDM$_LEAVE
function requires the rsdm_id argument as input to specify which
resource domain association the process is leaving.
The resource domain identification can be used as input to the $ENQ and $ENQW system services.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Domain number that identifies the resource domain. The domain_number
argument is a longword value containing the resource domain number.
The domain_number argument is required for the RSDM$_JOIN_DOMAIN
function but ignored for the RSDM$_LEAVE function.
| OpenVMS usage: | null_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Placeholder reserved to OpenVMS. You must specify 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Types of access desired when using the lock management services within the resource domain.
The access argument is a longword bit mask specifying the access
types required; these can include read, write, and lock.
|
Symbol |
Access Description |
System Service |
|---|---|---|
|
RSDM$M_READ |
Read lock value blocks |
$DEQ, $ENQ, $ENQW, $GETLKI, $GETLKIW |
|
RSDM$M_WRITE |
Write lock value blocks |
$DEQ, $ENQ, $ENQW, |
|
RSDM$M_LOCK |
Take locks |
$ENQ, $ENQW |
access argument
or if you specify 0, $SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN attempts to access the domain in the following order:Read, write, lock
Read, lock
Write, lock
Lock
The access attempt terminates with the first success.
The access argument defaults to 0. It is ignored for the RSDM$_LEAVE
function.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode requested for the association to the resource domain. The most privileged access mode granted is the access mode of the caller. Locks cannot be taken from access modes less privileged than the access mode of the association.
acmode argument is a longword containing the access mode. The
$PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the access modes.|
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
Privilege Rank |
|---|---|---|
|
PSL$C_KERNEL |
Kernel |
High |
|
PSL$C_EXEC |
Executive |
– |
|
PSL$C_SUPER |
Supervisor |
– |
|
PSL$C_USER |
User |
Low |
The acmode argument is optional for the RSDM$_JOIN_DOMAIN function. If
you do not specify the acmode argument, the access mode is set to
the access mode of the calling process. The acmode argument is
ignored for the RSDM$_LEAVE function.
Function Codes
RSDM$_JOIN_DOMAIN
A process has the option of forming multiple associations with one or more resource domains. Each association can have different access rights to the resource domain, such as to read lock value blocks or to write lock value blocks. This request sets up a new association with a resource domain.
$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN verifies the desired access against the security profile of the resource domain. If the desired access is allowed, a new association to the resource domain is created, and a resource domain identification for the association is returned.
- SS$_NORMAL
- SS$_BADPARAM
- SS$_EXQUOTA
- SS$_INSFMEM
- SS$_NOOBJSRV
- SS$_NOPRIV
RSDM$_LEAVE
This operation requests that a process end an association with a resource domain. A process must leave a resource domain association in the same mode as, or in a more privileged mode than, the mode in which it joined the resource domain.
Before a process can end its association with a resource domain, it must release all locks taken using that association.
- SS$_NORMAL
- SS$_BADPARAM
- SS$_IVMODE
- SS$_RSDM_ACTIVE
- SS$_RSDMNOTFOU
Description
The Set Resource Domain system service enables a process to use the lock management system services $DEQ, $ENQ, $ENQW, $GETLKI, and $GETLKIW.
The lock management services enable processes with the appropriate access rights to take and release locks on resource names and to perform other functions related to lock management. Applications use resource names to represent resources to which they want to synchronize access. A resource domain is a namespace for resource names. A process must join a resource domain to take and release locks and to read and write value blocks associated with resources in that resource domain.
When a process requests to join a resource domain, $SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN performs an access check. After $SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN verifies the desired access to the resource domain, the service creates an association between the resource domain and the calling process. The association is represented by a resource domain identification. A process can request different types of access to the same resource domain; the type of access is a characteristic of the association with the resource domain. Each time a process joins a resource domain, a new association is created. Processes use their resource domain identifications when using $ENQ or $ENQW to request a new lock.
The right to read lock value blocks
The right to write lock value blocks
The right to take and release locks
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN uses system dynamic memory, which uses BYTLM quota, for the creation of the resource domain data structures.
Related Services
$DEQ, $ENQ, $ENQW, $GETLKI, $GETLKIW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_BADPARAM
The
func, thedomain_number, or thersdm_idargument was specified incorrectly.- SS$_EXQUOTA
The caller has insufficient BYTLM quota.
- SS$_INSFMEM
There is insufficient memory to join the resource domain.
- SS$_IVMODE
An attempt was made to leave an association created by a more privileged access mode.
- SS$_NOOBJSRV
The audit server process, which maintains the security profile for resource domains, is not running. The process access rights to the domain cannot be determined, so access is denied.
- SS$_NOPRIV
Access to the resource domain was denied.
- SS$_RSDM_ACTIVE
Unable to leave the resource domain because there are locks still associated with this resource domain.
- SS$_RSDMNOTFOU
The resource domain was not found.
$SET_RETURN_VALUE (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Sets the return value of — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, sets the return values or condition codes in the Mechanism Array, independent of the architecture.
Format
SYS$SET_RETURN_VALUE mechanism_arg, return_type, return_valueC Prototype
int sys$set_return_value
(void *mechanism_arg, unsigned int *return_type, void *return_value);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | mechanism vector address |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The address of the location of the mechanism vector. If the
mechanism_arg argument is 0, the mechanism vector for the
currently active signal is used.
If the address of the return_type argument is 0, the
return_value argument is fetched by value and is treated as
return-type PSIG$K_FR_U32. This combination of arguments can be used to set a condition
code, such as SS$_ACCVIO, as a return value.
| OpenVMS usage: | integer |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The address of the location of a longword that contains one of the function return signature codes.
If the address of the return_type argument is 0, the
return_value argument is fetched by value and is treated as
return-type PSIG$K_FR_U32. This combination of arguments can be used to set a condition
code, such as SS$_ACCVIO, as a return value.
| OpenVMS usage: | buffer |
| type: | scalar |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The address of the location that contains a value of the appropriate type. The referenced value is read as a longword, quadword, or octaword, depending on the return_type.
If the address of the return_type argument is 0, the
return_value argument is fetched by value and is treated as
return-type PSIG$K_FR_U32. This combination of arguments can be used to set a condition
code, such as SS$_ACCVIO, as a return value.
Description
The Set Return Value service allows the caller to specify return values and condition codes in the Mechanism Array, independent of the architecture.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
None
Condition Values Returned
- status
Success or failure. The given return value is placed in the appropriate fields of the specified mechanism vector, according to the return type.
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_NOSIGNAL
No signal is currently active for an exception condition.
$SET_SECURITY
Set Security Characteristics — Modifies the security characteristics of a protected object.
Format
SYS$SET_SECURITY
[clsnam] ,[objnam] ,[objhan] ,[flags] ,[itmlst] ,[contxt] ,[acmode]C Prototype
int sys$set_security
(void *clsnam, void *objnam, unsigned int *objhan, unsigned int flags,
void *itmlst, unsigned int *contxt, unsigned int *acmode);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Name of the object class. The clsnam argument is the address of a
descriptor pointing to a string that contains the name of the object class.
- CAPABILITY
- COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER
- DEVICE
- FILE
- GLXGRP_GLOBAL_SECTION
- GLXSYS_GLOBAL_SECTION
- GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION
- ICC_ASSOCIATION
- LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE
- QUEUE
- RESOURCE_DOMAIN
- SECURITY_CLASS
- SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION
- VOLUME
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor |
Name of the protected object whose associated security profile is going to be retrieved. The
objnam argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a
string containing the name of the protected object.
|
Object Class |
Object Name Format |
|---|---|
|
CAPABILITY |
A character string. Currently, the only capability object is VECTOR. |
|
COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER |
Name of the event flag cluster, as defined in the Associate Common Event Flag Cluster ($ASCEFC) system service. |
|
DEVICE |
Standard device specification, described in the VSI OpenVMS User's Manual. |
|
FILE |
Standard file specification, described in the VSI OpenVMS User's Manual. |
|
GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION |
Section name, as defined in the Create and Map Section ($CRMPSC) system service. |
|
ICC_ASSOCIATION |
ICC security object name node::association_name. The special node name, ICC$::, refers to entries in the clusterwide registry. For registry entries, the Access Access Type does not apply. |
|
LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE |
Table name, as defined in the Create Logical Name Table ($CRELNT) system service. |
|
QUEUE |
Standard queue name, as described in the Send to Job Controller ($SNDJBC) system service. |
|
RESOURCE_DOMAIN |
An identifier or octal string enclosed in brackets. |
|
SECURITY_CLASS |
Any class name shown in the Object Class column of this table, or a class name followed by a period (.) and the template name. Use the DCL command SHOW SECURITY to display possible template names. |
|
SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION |
Section name, as defined in the Create and Map Section ($CRMPSC) system service. |
|
VOLUME |
Volume name or name of the device on which the volume is mounted. |
| OpenVMS usage: | object_handle |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
objhan argument
is an address of a longword containing the object handle. You can use the
objhan argument as an alternative to the
objnam argument; for example, a channel number clearly
specifies the file open on the channel and can serve as an object handle. The following
table shows the format of the object classes.|
Object Class |
Object Handle Format |
|---|---|
|
COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER |
Event flag number |
|
DEVICE |
Channel number |
|
FILE |
Channel number |
|
RESOURCE_DOMAIN |
Resource domain identifier |
|
VOLUME |
Channel number |
| OpenVMS usage: | flags |
| type: | mask_longword |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
flags argument is a longword
bit vector wherein a bit, when set, specifies the corresponding option. The
flags argument requires the contxt
argument. The following table describes each flag.|
Symbolic Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
OSS$M_LOCAL |
Do not update the master profile for the specified object.
This flag allows you to call $SET_SECURITY several times to
modify a local copy of a profile; once the modifications are
satisfactory, you can clear the OSS$M_LOCAL flag, set the
OSS$M_RELCTX flag, and have $SET_SECURITY update the master
profile. The flag applies only to calls made with the
|
|
OSS$M_RELCTX |
Release the context structure at the completion of this request. |
The $OSSDEF macro defines symbolic names for the flag bits. You construct the
flags argument by specifying the symbolic names of each
desired option.
| OpenVMS usage: | item_list_3 |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Item list specifying which information about the process or processes is to be modified. The
itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors,
each of which describes an item of information. The list of item descriptors is
terminated by a longword of 0.
With the item list, the user modifies the protected object's characteristics. The user defines
which security characteristics to modify. If this argument is not present, only the
flags argument is processed. Without the
itmlst argument, you can only manipulate
the security profile locks or release contxt resources.

|
Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Buffer length |
A word containing an integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer from which $SET_SECURITY is to read the information. The length of the buffer needed depends upon the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too small, $SET_SECURITY truncates the data. |
|
Item code |
A word containing a symbolic code specifying the item of information that $SET_SECURITY is to modify. The $OSSDEF macro defines these codes. A description of each item code is given in the Item Codes section. |
|
Buffer address |
A longword containing the address of the buffer from which $SET_SECURITY is to read the information. |
|
Return length address |
Not used. |
| OpenVMS usage: | context |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Value used to maintain protected object processing context when dealing with a single protected object across multiple $GET_SECURITY/$SET_SECURITY calls. Whenever the context value is nonzero, the class name, object name, or object handle arguments are disregarded. An input value of 0 indicates that a new context should be established.
Because an active context block consumes process memory, be sure to release the context block by setting the RELCTX flag when the profile processing is complete. $SET_SECURITY sets the context argument to 0 once the context is released.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Access mode to be used in the object protection check. The
acmode argument is the address of a longword containing the
access mode. The acmode argument defaults to kernel mode;
however, the system compares acmode with the caller's access mode
and uses the least privileged mode. The access modes are defined in the system macro
$PSLDEF library.
VSI recommends that this argument be omitted (passed as zero).
Item Codes
The following table provides a summary of item codes that are valid as an item
descriptor in the itmlst argument. The table lists the
$SET_SECURITY item codes and gives a corresponding description. Complete descriptions of
each item code are provided after the table.
|
Item Code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
OSS$_ACL_ADD_ENTRY |
Adds an access control entry (ACE). |
|
OSS$_ACL_DELETE |
Deletes all unprotected ACEs in an ACL. |
|
OSS$_ACL_DELETE_ALL |
Deletes the ACL, including protected ACEs. |
|
OSS$_ACL_DELETE_ENTRY |
Deletes an ACE. |
|
OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY |
Locates an ACE. |
|
OSS$_ACL_FIND_NEXT |
Positions the next ACE. |
|
OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE |
Locates an ACE of the specified type. |
|
OSS$_ACL_MODIFY_ENTRY |
Replaces an ACE at the current position. |
|
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_BOTTOM |
Sets a marker that points to the end of the ACL. |
|
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_TOP |
Sets a marker that points to the beginning of the ACL. |
|
OSS$_OWNER |
Sets the UIC or general identifier of the object's owner. |
|
OSS$_PROTECTION |
Sets the protection code of the object. |
OSS$_ACL_ADD_ENTRY
When you specify OSS$_ACL_ADD_ENTRY, $SET_SECURITY adds an access control entry (ACE) pointed to by the buffer address so that it is in front of the current ACE in the access control list (ACL). See OSS$_ACL_POSITION for more information on explicit access control list positioning.
OSS$_ACL_DELETE
When you specify OSS$_ACL_DELETE, $SET_SECURITY deletes all unprotected ACEs in an ACL.
OSS$_ACL_DELETE_ALL
When you specify OSS$_ACL_DELETE_ALL, $SET_SECURITY deletes an entire ACL, including protected ACEs.
OSS$_ACL_DELETE_ENTRY
When you specify OSS$_ACL_DELETE_ENTRY, $SET_SECURITY deletes an ACE pointed to by the buffer address or, if the buffer address is specified as 0, the ACE at the current position.
OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY
When you specify OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY, $SET_SECURITY locates an ACE pointed to by the buffer address. OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY sets the position within the ACL for succeeding ACL operations; for example, for a deletion or modification of the ACE. If the buffer address is 0, it returns SS$_ACCVIO.
OSS$_ACL_FIND_NEXT
When you specify OSS$_ACL_FIND_NEXT, $SET_SECURITY advances the current position to the next ACE in the ACL.
OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE
When you specify OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE, $SET_SECURITY returns an ACE of a particular type if there is one in the buffer pointed to by the buffer address. OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE sets the position within the ACL for succeeding ACL operations. If the buffer address is 0, it returns SS$_ACCVIO.
OSS$_ACL_MODIFY_ENTRY
When you specify OSS$_ACL_MODIFY_ENTRY, $SET_SECURITY replaces an ACE at the current position with the ACE pointed to by the buffer address.
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_BOTTOM
When you specify OSS$_ACL_POSITION_BOTTOM, $SET_SECURITY sets the ACL position to point to the bottom of the ACL.
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_TOP
When you specify OSS$_ACL_POSITION_TOP, $SET_SECURITY sets the ACL position to point to the top of the ACL.
OSS$_OWNER
When you specify OSS$_OWNER, $SET_SECURITY sets the owner UIC of the selected object to the value in the buffer. The buffer size must be 4 bytes.
OSS$_PROTECTION
When you specify OSS$_PROTECTION, $SET_SECURITY sets the selected object's protection code to the value in the buffer. The buffer size must be 2 bytes.
Description
The Set Security service modifies the security characteristics of a protected object. Security characteristics include such information as the protection code, the owner, and the access control list (ACL).
The security management services, $SET_SECURITY and $GET_SECURITY, maintain a single master copy of a profile for every protected object in an OpenVMS Cluster system. They also ensure that only one process at a time can modify an object's security profile.
It selects the specified protected object.
It fetches a local copy of the object's security profile, unless the service is operating on an existing context.
It modifies the local profile.
It updates the master copy of the profile if the local flag is clear and there was no error.
It deletes the local copy of the profile and returns if RELCTX is specified or if no context is specified.
Whenever the
contxtargument has a nonzero value, $SET_SECURITY uses the context to select the object and ignores the class name, object name, and object handle.With some types of objects, such as a file or a device, it is possible to select an object on the basis of its
objhanandclsnamvalues.When the
clsnamandobjnamarguments are provided, $SET_SECURITY uses an object's class name and object name to select the object.
The context for a security management operation can be established through either $GET_SECURITY or $SET_SECURITY. Whenever the context is set by one service, the other service can use it provided the necessary locks are being held. A caller to $GET_SECURITY needs to set the write lock flag (OSS$M_WLOCK) to inspect a profile value, maintain the lock on the object's profile, and then modify some value through a call to $SET_SECURITY.
There are many situations in which the contxt argument is essential. By
establishing a context for an ACL operation, for example, a caller can retain an ACL
position across calls to $GET_SECURITY so that a set of ACEs can be read and modified
sequentially. A security context is released by a call to $SET_SECURITY or $GET_SECURITY
that sets the OSS$M_RELCTX flag. Once the context is deleted, the user-supplied context
longword is reset to 0.
Required Access or Privileges
Control access to the object is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully
- SS$_ACCVIO
The parameter cannot be read and the buffer cannot be written.
- SS$_BADPARAM
You specified an invalid object, attribute code, or item size.
- SS$_INSFARG
The
clsnamandobjnamarguments are not specified, theclsnamandobjhanarguments are not specified, or thecontxtargument is not specified.- SS$_INVBUFLEN
The buffer size for one of the item codes was invalid.
- SS$_INVCLSITM
The item code that you specified is not supported for the class.
- SS$_INVFILFOROP
An invalid file name was specified; the file name contained either a node or wildcard specification.
- SS$_MMATORB
The attempted update cannot be performed. The object profile was changed by another process.
- SS$_NOCLASS
The named object class does not exist.
- SS$_OBJLOCKED
The selected object is currently write locked.
$SET_SYSTEM_EVENT (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Set System Event — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, establishes a request for notification when an OpenVMS system event occurs.
Format
SYS$SET_SYSTEM_EVENT event ,astadr ,astprm ,acmode ,flags ,handleC Prototype
int sys$set_system_event
(unsigned int event, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm,
unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, struct _generic_64 * handle);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | event_code |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Event code indicating the type of system event for which an AST is to be delivered. The
event argument is a value indicating which type of event is of
interest.
| Symbolic Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SYSEVT$C_ADD_MEMBER | One or more OpenVMS instances have joined the OpenVMS Galaxy sharing community. |
| SYSEVT$C_DEL_MEMBER | One or more OpenVMS instances have left the OpenVMS Galaxy sharing community. |
| SYSEVT$C_ADD_ACTIVE_CPU | One or more processors have become active within this OpenVMS instance. |
| SYSEVT$C_DEL_ ACTIVE_CPU | One or more processors have become inactive within this OpenVMS instance. |
| SYSEVT$C_ADD_CONFIG_CPU | One or more CPUs have been added to the set of available CPUs for this OpenVMS instance. |
| SYSEVT$C_DEL_CONFIG_CPU | One or more processors have been removed from this OpenVMS instance. |
| SYSEVT$C_TDF_CHANGE | The system's time differential factor has changed. |
| SYSEVT$C_CPU_DEALLOCATE | One or more processors have been deallocated from this OpenVMS instance. |
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit or 64-bit reference |
Notification AST routine to receive control after a change in OpenVMS system configuration occurs.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | quadword |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The quadword AST parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode at which the system event AST is to execute. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
| Symbolic Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PSL$C_KERNEL | Kernel |
| PSL$C_EXEC | Executive |
| PSL$C_SUPER | Supervisor |
| PSL$C_USER | User |
The value of the access mode is maximized with the access mode of the caller.
flags
Defined in SYSEVTDEF.
| SYSEVT$M_REPEAT_NOTIFY | When this flag is set, event notification is repeated. |
| OpenVMS usage: | handle |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read/write |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword for the event handle.
Description
The Set System Event service establishes a request for notification when a system event occurs. It may create a new system event notification object, add an event to a new or existing object, and enable notification on a new or existing object.
If the handle specified is zero, a new system notification
request object is created, and a handle for the new object is returned.
If the event specified is non-zero, that event is added to the
set of events which trigger notification on the notification object.
The service will verify that the input parameters specify a valid request and enable the object for notification. Notification is accomplished by AST delivery. After the AST has been delivered, if the SYSEVT$M_REPEAT_NOTIFY flag is not set, notification must again be enabled on the object before another notification (AST delivery) can occur.
Errors are returned in the following cases:
If quotas are exceeded, an error is returned. It is important to note that this routine returns an error and will not retry an attempt to get quota if quota is exhausted on the first attempt.
See the Condition Values Returned section for types of errors that can be returned.
If the
astadrargument is omitted, and a new notification object is being created, SS$_BADPARAM is returned.If the
eventargument is incorrectly specified, SS$_BADPARAM is returned.If the access mode parameter is more privileged than the mode of the caller, the mode of the caller is used.
If specified, the
handleargument must be writeable from the mode of the caller. SS$_ACCVIO is returned if this is not the case.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
ASTLM
Related Services
$CLEAR_SYSTEM_EVENT
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more arguments.
- SS$_BADPARAM
One of more arguments has an invalid value.
- SS$_EXASTLM
The process exceeded its quota for outstanding ASTs.
- SS$_INSFMEM
The system dynamic memory is insufficient to complete the service.
$SET_UNWIND_TABLE (Integrity servers Only)
Set Unwind Table Routine — Registers or extends unwind table (UT) information.
Format
SYS$SET_UNWIND_TABLE
code_base_va, code_size, ut_base_va, ut_size, gp_value,
unwind_info_base, nameC Prototype
ind SYS$SET_UNWIND_TABLE
(unsigned __int64 code_base_va, unsigned __int64 code_size,
unsigned __int64 ut_base_va,unsigned __int64 ut_size,
unsigned __int64 gp_value, unsigned __int64 unwind_info_base,
void *name);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
With code_size, defines the potential code range.
code_base_va is required for both creation and extension
calls. code_base_va is the process virtual address of the start
of the code region. code_size is the size of the code region in
bytes. An error is returned if this overlaps any existing range.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
With code_base_va, defines the potential code range.
code_base_va is required for both creation and extension
calls. code_base_va is the process virtual address of the start
of the code region. code_size is the size of the code region in
bytes. An error is returned if this overlaps any existing range.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
With ut_size, describes the unwind table (UT).
ut_base_va is the process virtual address of the UT and must
be quadword aligned. ut_size is the size of the UT in bytes and
must be a multiple of the size (24 bytes: 3 quadwords) of an unwind table entry (UTE).
The UTEs must describe nonoverlapping code subregions within the overall code
region.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
With ut_base_va, describes the unwind table (UT).
ut_base_va is the process virtual address of the UT and must
be quadword aligned. ut_size is the size of the UT in bytes and
must be a multiple of the size (24 bytes: 3 quadwords) of an unwind table entry (UTE).
The UTEs must describe nonoverlapping code sub regions within the overall code
region.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Ignored on extension calls, required on create calls. The Global Data Pointer (GP) value for the routines described by these unwind tables.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Ignored on extension calls; required on create calls. The
unwind_info_base plus a particular UTE UIB offset must add up
to the process virtual address of that UIB. Typically for static code (activated images
from disk), this specifies the process virtual base address of the segment containing
the UIBs. However, dynamically generated code, for example, can pass a zero for the
unwind_info_base and have the full process virtual addresses
of the UIBs in their UTEs.
| OpenVMS usage: | pseudo-image-name |
| type: | character-code-text-string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor-fixed-length string descriptor |
Passed by descriptor (ignored on extension calls). May be used for traceback. Need not be unique. Should be less than 255 characters (will be truncated, otherwise).
Description
This interface can be used to register or extend unwind information. It is expected, for example, that applications that dynamically create code will also need to dynamically create unwind tables (UTs) and unwind information blocks (UIBs) for that code. This interface registers such information with the operating system.
The image activator also uses this interface to register unwind information for shareable and main images. Note that the code region, though fully specified in terms of its potential size, need not be full of actual code at its initial registration. The unwind table, however, must describe all the code that could execute within that region and that needs unwind information, at any given time. Note also that the unwind table entries (UTEs) within a registered unwind table must remain sorted (ascending order) at any given time.
To create a new registration, specify a new (not registered) code range. On a creation,
all parameters (except name) must be specified.
To extend an existing registration, specify an existing (registered)
code_base_va. On extension, only the identifying
code_base_va and new UT range need be specified, that is, the
other parameters may be zeros. An extension call can only alter that registration's
ut_base_va and ut_size.
The creator caller's mode defines the mode from which the registration may be extended or removed.
Failure status is returned on creation if the input code range overlaps an already existing range.
Required Access or Privileges
Unwind table information that describes code in process space can be registered from any mode.
Unwind table information that describes code in system space can be registered only from kernel mode or executive mode.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
SYS$CLEAR_UNWIND_TABLE, SYS$GET_UNWIND_ENTRY_INFO. Also see LIB$GET_UIB_INFO in VSI OpenVMS Calling Standard.
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
Routine completed successfully.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Missing or illegal parameter.
- SS$_VA_IN_USE
Overlap detected.
- SS$_ACCVIO
Name descriptor cannot be read.
$SHOW_INTRUSION
Show Intrusion Information — Searches for and returns information about records in the intrusion database matching the caller's specifications.
Format
SYS$SHOW_INTRUSION
user_criteria ,intruder ,intruder_len ,breakin_block ,[flags] ,[context]C Prototype
int sys$show_intrusion
(void *user_criteria, void *intruder, unsigned short int *intruder_len,
void *breakin_block, unsigned int flags, unsigned int *context);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string or item_list_3 |
| type: | character-coded text string or longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed length string descriptor |
If the CIA$M_ITEMLIST flag is FALSE:
The user_criteria argument is the description of intruder or suspect. The
user_criteria argument is the address of a character-string
descriptor pointing to a buffer containing the user criteria to match an intrusion
record's user specification in the intrusion database.
The
user_criteria argument is a character string of between 1 and 1058 bytes containing characters to match the user specification on records in the intrusion database.
A user specification is any combination of the suspect's or intruder's source node name, source user name, source DECnet for OpenVMS address, local failed user name, local terminal, or the string UNKNOWN. The user specification for an intrusion record is based on the input to the $SCAN_INTRUSION service and the settings of the LGI system parameter. For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
Wildcards are allowed for the user_criteria argument. For more
information about using wildcards to scan the intrusion database, see the Description
section.
If the CIA$M_ITEMLIST flag is TRUE:
The user_criteria argument is now the address of an 32-bit item
list. If the item list is used, one item, the CIA$_USER_CRITERIAL item, must be present
in the item list.
user_criteria argument:| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| CIA$_OUTPUT_LIST | Address of an 8192-byte buffer into which the service writes the associated node information for the returned intrusion record. |
| CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST | Address of a list of 8-character null-padded SCS nodenames for which the caller wants to see intrusion information about. |
| CIA$_USER_CRITERIAL | Address of a buffer, 1-1058 bytes long, containing the intruder or suspect. |
If a CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST item is provided, an intrusion record will only be returned if it originated on one of the nodes specified. If a CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST item is not provided, records from all nodes will be candidates for display. Multiple CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST items are permitted in the item list.
If a CIA$_OUTPUT_LIST item is provided, the item is filled with node-count records on return. The returned intrusion record will have a breakin block with a valid attempt-count field. The node-count records will have the name and attempt-count for each node represented.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed length string descriptor |
User specification of the matched intruder or suspect record in the intrusion database. The
intruder argument is the address of a character-string
descriptor pointing to a buffer to receive the user specification of the matched record
in the intrusion database.
The intruder argument is a 1058-byte string that will receive the user
specification of a record in the intrusion database that matches the specifications in
the user_criteria and flags
arguments.
| OpenVMS usage: | string length |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Length of returned string in the intrusion buffer. The intruder_len
argument is the address of a longword to receive the length of the returned intrusion
buffer.
The possible range of the intruder_len argument is 0 to 1058 bytes. If
the longword specified by the argument contains a 0 after the call to the service,
either the service did not find a record that matched the user criteria in the intrusion
database, or there are no more matching items in the intrusion database.
| OpenVMS usage: | record |
| type: | block of 2 longwords (unsigned) and 1 quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Block to receive various information in the intrusion database about a record matching the
user criteria. The breakin_block argument is the address of a
structure with the following format.
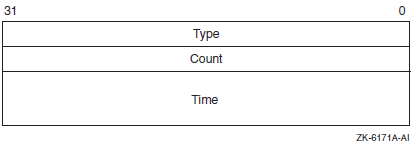
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Type |
Unsigned longword containing two pieces of information: the types of the matched record and the status of the suspect—SUSPECT or INTRUDER. The possible values for the record type are TERM_USER, TERMINAL, USERNAME, and NETWORK. The possible values for the status are SUSPECT or INTRUDER. These constants are defined in $CIADEF in STARLET. The implication is that each type will have two bits set: one bit represents the status, and the other bit represents the record type. |
|
Count |
Unsigned longword containing the number of login failures or break-in attempts made by the specified intruder or suspect. |
|
Time |
Quadword time format indicating the time when the record will expire. |
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Type of records in the intrusion database about which information is to be returned. The
flags argument is a longword bit mask wherein each bit
corresponds to an option.
|
Symbolic Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
CIA$M_ALL |
All records will be shown. If the |
|
CIA$M_INTRUDERS |
Only intruder records matching the criteria specified by the
|
|
CIA$M_ITEMLIST |
If FALSE, the |
|
CIA$M_SUSPECTS |
Only suspect records matching the criteria specified by the
|
Each of these options is mutually exclusive.
| OpenVMS usage: | context |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Context information to keep between related calls to the $SHOW_INTRUSION service. The
context argument is the address of a longword that receives a
context from the service.
The initial value contained in the unsigned longword pointed to by the
context argument must be 0. The contents of the unsigned longword must not be changed after the service has set its value. If the contents of the
context argument are changed between calls to the service, SS$_BADCONTEXT will be returned.
Contexts become invalid after one-half hour of non-use. This means that if you call the
$SHOW_INTRUSION service with a wildcard in the user_criteria
argument and do not call the service to get the next matching record within one-half
hour, the context becomes invalid. If the context has become invalid, you must restart
your search of the intrusion database from the beginning by resetting the context to
0.
Description
The Show Intrusion service returns information about records in the intrusion database that match the criteria you specify.
You can retrieve information about multiple records in the intrusion database by specifying wildcards for the
user_criteria argument. For example, specifying an asterisk
(*) for the
user_criteria argument and CIA$M_ALL_RECORDS for the
flags argument will return information about all records in the database. Specifying TTA4* for the
user_criteria argument and CIA$M_SUSPECTS_ONLY for the
flags argument will return information about all suspects who have had failures on terminal TTA4.
If you specify a wildcard string for the user_criteria argument, you
must also include a context argument. Because the service can
only return information about one intrusion record at a time, you must call the service
repeatedly to retrieve information about more than one record. The service will return
SS$_NOMOREITEMS when information about all of the matching records has been returned. No
intrusion information is returned from the call that returns SS$_NOMOREITEMS.
Required Access or Privileges
SECURITY privilege is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$DELETE_INTRUSION, $SCAN_INTRUSION
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
user_criteriaorcontextargument cannot be read, or theintruder,intruder_len,breakin_block, orcontextargument cannot be written.- SS$_BADBUFLEN
The length of one of the specified arguments is out of range.
- SS$_BADCONTEXT
The
contextargument did not contain a 0 on the first call to the service. Thecontextargument's value changed between consecutive calls to the service.- SS$_BADPARAM
An invalid value was specified in the
flagsargument, or mutually exclusive options were specified in theflagsargument.- SS$_NOMOREITEMS
All items matching the specified criteria have been returned.
- SS$_NOSECURITY
The caller does not have SECURITY privilege.
This service can also return any of the following messages passed from the security server:
- SECSRV$_NOSUCHINTRUDER
No records matching the specified criteria were found in the intrusion database.
- SECSRV$_SERVERNOTACTIVE
The security server is not currently active. Try the request again later.
$SIGNAL_ARRAY_64
Signal Array — Returns the address of a 64-bit signal array. A 32-bit signal array and a mechanism array are passed to a condition handler when it is called. $SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 provides the address of the 64-bit signal array, which might be required for programs that use 64-bit address space. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 mcharg, sigarg_64C Prototype
int sys$signal_array_64
(unsigned __int64 mcharg, unsigned __int64 sigarg_64);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | mechanism array |
| type: | vector quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference, array reference |
The mechanism array. The
mcharg argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of this array, which was passed to the condition handler. $SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 uses this structure to determine the 64-bit signal array address.
| OpenVMS usage: | 64-bit signal array |
| type: | vector quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference, array reference |
The 32- or 64-bit address of the 64-bit signal array is returned in this argument.
Description
$SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 provides the address of the 64-bit version of the signal array for condition handlers that need it. It is normally needed only by applications that use 64-bit address space and want to handle errors involving addresses in that region.
For example, if an access violation occurs on a 64-bit address, the 32-bit signal array passed to the handler will contain only the low 32 bits of the effective address, because each entry is a longword. The 64-bit signal array, which can be obtained using this service, contains quadword entries, so the 64-bit address can be fully expressed.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$PUTMSG, which accepts either a 32-bit or 64-bit signal array as an argument.
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
sigarg_64argument cannot be written.- SS$_BADPARAM
The
mchargargument is not a mechanism array in the expected format.
$SNDERR
Send Message to Error Logger — Writes a user-specified message to the system error log file, preceding it with the date and time.
Format
SYS$SNDERR msgbufC Prototype
int sys$snderr (void *msgbuf);Argument
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Message to be written to the error log file. The msgbuf argument is the
address of a character string descriptor pointing to the message text.
Description
The Send Message to Error Logger service writes a user-specified message to the system error log file, preceding it with the date and time. The $SNDERR service requires system dynamic memory.
Required Access or Privileges
To send a message to the error log file, the calling process must have BUGCHK privilege.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The message buffer or buffer descriptor cannot be read by the caller.
- SS$_INSFMEM
The system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the service.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The process does not have the required BUGCHK privilege.
$SNDJBC
Send to Job Controller — Creates, stops, and manages queues and the batch and print jobs in those queues. The $SNDJBC service completes asynchronously; to synchronize the completion of most operations, use the Send to Job Controller and Wait ($SNDJBCW) service.
Format
SYS$SNDJBC
[efn] ,func [,nullarg] [,itmlst] [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm]C Prototype
int sys$sndjbc
(unsigned int efn, unsigned short int func, unsigned int nullarg,
void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params),
int astprm);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of the event flag to be set when $SNDJBC completes. The efn
argument is a longword containing this number; however, $SNDJBC uses only the low-order
byte.
When you queue the request, $SNDJBC clears the specified event flag (or event flag 0 if
efn was not specified). Then, when the operation completes,
$SNDJBC sets the specified event flag (or event flag 0).
| OpenVMS usage: | function_code |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Function code specifying the function that $SNDJBC is to perform. The
func argument is a word containing this function code. The
$SJCDEF macro defines the names of each function code.
You can specify only one function code in a single call to $SNDJBC. Most function codes
require or allow for additional information to be passed in the call. You pass this
information by using the itmlst argument, which specifies a list
of one or more item descriptors. Each item descriptor in turn specifies an item code,
which modifies, restricts, or otherwise affects the action designated by the function
code.
| OpenVMS usage: | null_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to OpenVMS.
| OpenVMS usage: | item_list_3 |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Item list supplying information to be used in performing the function specified by the
func argument. The itmlst argument is
the address of the item list. The item list consists of one or more item descriptors,
each of which specifies an item code. The item list is terminated by an item code of 0
or by a longword of 0. The following diagram depicts the structure of a single item
descriptor.

|
Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Buffer length |
A word specifying the length of the buffer; the buffer either supplies information to be used by $SNDJBC or receives information from $SNDJBC. The required length of the buffer varies, depending on the item code specified, and is given in the description of each item code. |
|
Item code |
A word containing an item code, which identifies the nature of the information supplied for use by $SNDJBC or received from $SNDJBC. Each item code has a symbolic name. The $SJCDEF macro defines these symbol names. |
|
Buffer address |
A longword containing the address of the buffer that specifies or receives the information. |
|
Return length address |
A longword containing the address of a word to receive the length (in bytes) of information returned by $SNDJBC. If you specify this address as 0, no length is returned. |
SJC$_codeBoolean item code. Boolean item codes specify a true or false value: the form SJC$_code specifies a true value; SJC$_NO_code specifies a false value. The default value for the Boolean item codes is false. For all Boolean item codes, the buffer length, buffer address, and return length fields of the item descriptor must be 0.
Input value item code. Input value item codes specify an input value to be used by $SNDJBC. The buffer length and buffer address fields of the item descriptor must be nonzero; the return length field must be 0. Specific buffer length requirements are given in the description of each item code.
Output value item code. Output value item codes specify a buffer for information returned by $SNDJBC. The buffer length and buffer address fields of the item descriptor must be nonzero; the return length field can be 0 or nonzero. Specific buffer length requirements are given in the description of each item code.
Several item codes specify a queue name, form name, or characteristic name. For these item codes, the buffer must specify a string containing from 1 to 31 characters, exclusive of spaces, tabs, and null characters, which are ignored. Allowable characters in the string are uppercase alphabetic characters, lowercase alphabetic characters (which are converted to uppercase), numeric characters, the dollar sign ($), and the underscore (_).
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
I/O status block into which $SNDJBC writes the completion status after the requested operation
has completed. The iosb argument is the address of the I/O status
block.
At request initiation, $SNDJBC sets the value of the quadword I/O status block to 0. When the requested operation completes, $SNDJBC writes a condition value in the first longword of the I/O status block. It writes the value 0 into the second longword; this longword is unused and reserved for future use.
The condition values returned by $SNDJBC in the I/O status block are usually condition values from the JBC facility. These condition values are defined by the $JBCMSGDEF macro. In some cases, the condition value returned by $SNDJBC can be an error return from a system service or an OpenVMS RMS service that is used in executing the request. For the SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB request, the condition value returned is the completion status of the requested job.
The condition values returned from the JBC facility are listed in the Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block section.
If you are using an event flag to signal the completion of the service, you can test the I/O status block for a condition value to be sure that the event flag was not set by an event other than service completion.
If you are using the $SYNCH service to synchronize completion of the service, the I/O status block is a required argument for $SYNCH.
The condition value returned in R0 and the condition value returned in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of the call to the $SNDJBC service. The condition value returned in R0 gives you information about the success or failure of the service call itself; the condition value returned in the I/O status block gives you information about the success or failure of the service operation. Therefore, to accurately assess the success or failure of the call to $SNDJBC, you must check the condition values returned in both R0 and the I/O status block.
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
AST service routine to be executed when $SNDJBC completes. The astadr
argument is the address of this routine.
If specified, the AST routine executes at the same access mode as the caller of $SNDJBC.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine specified by the
astadr argument. The astprm argument
is this longword parameter.
Function Codes
This section describes the various function codes that are applicable to the $SNDJBC system service.
SJC$_ABORT_JOB
This request aborts the execution of the current job from an output execution queue or the job you specified from a batch queue. By default, the job is deleted. However, for a restartable job, you can requeue it to the same queue or to another queue.
- SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
- SJC$_QUEUE
- SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
|
SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE |
— |
|
SJC$_HOLD |
SJC$_NO_HOLD |
|
SJC$_PRIORITY |
— |
|
SJC$_REQUEUE |
— |
SJC$_ADD_FILE
This request adds a file to the open job owned by the requesting process. You use this operation as part of a sequence of calls to the $SNDJBC service to create a job with one or more files. The first call in the sequence specifies the SJC$_CREATE_JOB operation to create an open job. Each subsequent SJC$_ADD_FILE request associates an additional file with the job. Finally, you make an SJC$_CLOSE_JOB request to complete the batch or print job specification. To create a job that contains only one file, you can make a single call to $SNDJBC that specifies the SJC$_ENTER_FILE function code.
- SJC$_FILE_IDENTIFICATION
- SJC$_FILE_SPECIFICATION
|
SJC$_DELETE_FILE |
SJC$_NO_DELETE_FILE |
|
SJC$_DOUBLE_SPACE |
SJC$_NO_DOUBLE_SPACE |
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST |
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST |
|
SJC$_FILE_COPIES |
— |
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG |
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG |
|
SJC$_FILE_SETUP_MODULES |
SJC$_NO_FILE_SETUP_MODULES |
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER |
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER |
|
SJC$_FIRST_PAGE |
SJC$_NO_FIRST_PAGE |
|
SJC$_LAST_PAGE |
SJC$_NO_LAST_PAGE |
|
SJC$_PAGE_HEADER |
SJC$_NO_PAGE_HEADER |
|
SJC$_PAGINATE |
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE |
|
SJC$_PASSALL |
SJC$_NO_PASSALL |
SJC$_ALTER_JOB
This request alters the parameters of an existing job that is not currently executing.
- SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
|
SJC$_AFTER_TIME |
SJC$_NO_AFTER_TIME |
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME |
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS |
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER |
— |
|
— |
SJC$_NO_CHECKPOINT_DATA |
|
SJC$_CLI |
SJC$_NO_CLI |
|
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT |
SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT |
|
— |
SJC$_NO_DELETE_FILE |
|
SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE |
— |
|
SJC$_DOUBLE_SPACE |
SJC$_NO_DOUBLE_SPACE |
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST |
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST |
|
SJC$_FILE_COPIES |
— |
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG |
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG |
|
SJC$_FILE_SETUP_MODULES |
SJC$_NO_FILE_SETUP_MODULES |
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER |
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER |
|
SJC$_FIRST_PAGE |
SJC$_NO_FIRST_PAGE |
|
SJC$_FORM_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER |
— |
|
SJC$_HOLD |
SJC$_NO_HOLD |
|
SJC$_JOB_COPIES |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_DEFAULT_RETAIN |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_ERROR_RETAIN |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN_TIME |
— |
|
SJC$_LAST_PAGE |
SJC$_NO_LAST_PAGE |
|
SJC$_LOG_DELETE |
SJC$_NO_LOG_DELETE |
|
SJC$_LOG_QUEUE |
— |
|
SJC$_LOG_SPECIFICATION |
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPECIFICATION |
|
SJC$_LOG_SPOOL |
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPOOL |
|
SJC$_LOWERCASE |
SJC$_NO_LOWERCASE |
|
SJC$_NOTE |
SJC$_NO_NOTE |
|
SJC$_NOTIFY |
SJC$_NO_NOTIFY |
|
SJC$_OPERATOR_REQUEST |
SJC$_NO_OPERATOR_REQUEST |
|
SJC$_PAGE_HEADER |
SJC$_NO_PAGE_HEADER |
|
SJC$_PAGINATE |
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE |
|
SJC$_PARAMETER_1 through 8 |
SJC$_NO_PARAMETERS |
|
SJC$_PASSALL |
SJC$_NO_PASSALL |
|
SJC$_PRIORITY |
— |
|
SJC$_QUEUE |
— |
|
SJC$_RAD |
SJC$_NO_RAD |
|
SJC$_RESTART |
SJC$_NO_RESTART |
|
SJC$_WSDEFAULT |
SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT |
|
SJC$_WSEXTENT |
SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT |
|
SJC$_WSQUOTA |
SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA |
If you specify the SJC$_QUEUE item code, the $SNDJBC service verifies that the selected job entry exists on the specified queue before modifying the job.
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
This request alters the parameters of a queue. The execution of current jobs is unaffected.
- SJC$_QUEUE
|
SJC$_BASE_PRIORITY |
— |
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME |
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS |
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER |
— |
|
SJC$_CLOSE_QUEUE |
— |
|
SJC$_CPU_DEFAULT |
SJC$_NO_CPU_DEFAULT |
|
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT |
SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT |
|
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NUMBER |
— |
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST |
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST |
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE |
— |
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG |
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG |
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE |
— |
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER |
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER |
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER |
— |
|
SJC$_GENERIC_SELECTION |
SJC$_NO_GENERIC_SELECTION |
|
SJC$_JOB_BURST |
SJC$_NO_JOB_BURST |
|
SJC$_JOB_FLAG |
SJC$_NO_JOB_FLAG |
|
SJC$_JOB_LIMIT |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_RESET_MODULES |
SJC$_NO_JOB_RESET_MODULES |
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM |
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM |
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM |
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM |
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING |
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING |
|
SJC$_JOB_TRAILER |
SJC$_NO_JOB_TRAILER |
|
SJC$_OPEN_QUEUE |
— |
|
SJC$_OWNER_UIC |
— |
|
SJC$_PAGINATE |
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE |
|
SJC$_PROTECTION |
— |
|
SJC$_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION |
SJC$_NO_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION |
| SJC$_RAD |
SJC$_NO_RAD |
|
SJC$_RECORD_BLOCKING |
SJC$_NO_RECORD_BLOCKING |
|
SJC$_RETAIN_ALL_JOBS |
SJC$_NO_RETAIN_JOBS |
|
SJC$_RETAIN_ERROR_JOBS |
— |
|
SJC$_SWAP |
SJC$_NO_SWAP |
|
SJC$_WSDEFAULT |
SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT |
|
SJC$_WSEXTENT |
SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT |
|
SJC$_WSQUOTA |
SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA |
SJC$_ASSIGN_QUEUE
This request assigns a logical queue to an execution queue. The SJC$_QUEUE item code specifies the logical queue; the SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE item code specifies the execution queue.
- SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE
- SJC$_QUEUE
SJC$_BATCH_CHECKPOINT
This request establishes a checkpoint in a batch job. No operation is performed if the requesting process is not a batch process.
- SJC$_CHECKPOINT_DATA
SJC$_CLOSE_DELETE
This request deletes the open job owned by the requesting process. No item codes are allowed.
SJC$_CLOSE_JOB
This request completes the specification of the open job owned by the requesting process and places the job in the queue specified in the SJC$_CREATE_JOB request that opened the job. If the SJC$_CLOSE_JOB request completes successfully, the job is no longer an open job; it becomes a normal batch or print job.
- SJC$_JOB_STATUS_OUTPUT
SJC$_CREATE_JOB
This request creates an open job for the requesting process. If the process already owns an open job, that job is deleted.
An open job is a batch or print job that has not yet been completely specified. After you make the SJC$_CREATE_JOB request to open the job, you can make subsequent calls to $SNDJBC using the SJC$_ADD_FILE function code to specify the files associated with the job. Finally, you can complete the job specification with an SJC$_CLOSE_JOB request. If the SJC$_CREATE_JOB operation completes successfully, the open job created is given an entry number; the job is not assigned to the queue specified in the SJC$_CREATE_JOB operation until the SJC$_CLOSE_JOB request completes successfully.
- SJC$_QUEUE
|
SJC$_ACCOUNT_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_AFTER_TIME |
SJC$_NO_AFTER_TIME |
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME |
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS |
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER |
— |
|
SJC$_CLI |
SJC$_NO_CLI |
|
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT |
SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT |
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST |
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST |
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE |
— |
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG |
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG |
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE |
— |
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER |
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER |
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE |
— |
|
SJC$_FIRST_PAGE |
SJC$_NO_FIRST_PAGE |
|
SJC$_FORM_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER |
— |
|
SJC$_HOLD |
SJC$_NO_HOLD |
|
SJC$_JOB_COPIES |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_DEFAULT_RETAIN |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_ERROR_RETAIN |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN_TIME |
— |
|
SJC$_LAST_PAGE |
SJC$_NO_LAST_PAGE |
|
SJC$_LOG_DELETE |
SJC$_NO_LOG_DELETE |
|
SJC$_LOG_QUEUE |
— |
|
SJC$_LOG_SPECIFICATION |
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPECIFICATION |
|
SJC$_LOG_SPOOL |
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPOOL |
|
SJC$_LOWERCASE |
SJC$_NO_LOWERCASE |
|
SJC$_NOTE |
SJC$_NO_NOTE |
|
SJC$_NOTIFY |
SJC$_NO_NOTIFY |
|
SJC$_OPERATOR_REQUEST |
SJC$_NO_OPERATOR_REQUEST |
|
SJC$_PARAMETER_1 through 8 |
SJC$_NO_PARAMETERS |
|
SJC$_PRIORITY |
— |
|
SJC$_RAD |
SJC$_NO_RAD |
|
SJC$_RESTART |
SJC$_NO_RESTART |
|
SJC$_UIC |
— |
|
SJC$_USERNAME |
— |
|
SJC$_WSDEFAULT |
SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT |
|
SJC$_WSEXTENT |
SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT |
|
SJC$_WSQUOTA |
SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA |
- SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER_OUTPUT
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
This request creates a queue. If the queue already exists and is not stopped, this request performs no operation. However, if the queue already exists and is stopped, the request alters the parameters of the queue based on the item codes specified in the request; if you specify the SJC$_CREATE_START item code, the request starts the queue.
- SJC$_QUEUE
|
SJC$_AUTOSTART_ON |
— |
|
SJC$_BASE_PRIORITY |
— |
|
SJC$_BATCH |
SJC$_NO_BATCH |
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME |
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS |
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER |
— |
|
SJC$_CLOSE_QUEUE |
— |
|
SJC$_CPU_DEFAULT |
SJC$_NO_CPU_DEFAULT |
|
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT |
SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT |
|
SJC$_CREATE_START |
— |
|
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NUMBER |
— |
|
SJC$_DEVICE_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST |
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST |
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE |
— |
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG |
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG |
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE |
— |
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER |
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER |
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER |
— |
|
SJC$_GENERIC_QUEUE |
SJC$_NO_GENERIC_QUEUE |
|
SJC$_GENERIC_SELECTION |
SJC$_NO_GENERIC_SELECTION |
|
SJC$_GENERIC_TARGET |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_BURST |
SJC$_NO_JOB_BURST |
|
SJC$_JOB_FLAG |
SJC$_NO_JOB_FLAG |
|
SJC$_JOB_LIMIT |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_RESET_MODULES |
SJC$_NO_JOB_RESET_MODULES |
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM |
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM |
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM |
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM |
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING |
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING |
|
SJC$_JOB_TRAILER |
SJC$_NO_JOB_TRAILER |
|
SJC$_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION |
SJC$_NO_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION |
|
SJC$_OPEN_QUEUE |
— |
|
SJC$_OWNER_UIC |
— |
|
SJC$_PAGINATE |
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE |
|
SJC$_PRINTER |
— |
|
SJC$_PROCESSOR |
SJC$_NO_PROCESSOR |
|
SJC$_PROTECTION |
— |
|
SJC$_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION |
SJC$_NO_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION |
|
SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_RAD |
SJC$_NO_RAD |
|
SJC$_RECORD_BLOCKING |
SJC$_NO_RECORD_BLOCKING |
|
SJC$_RETAIN_ALL_JOBS |
SJC$_NO_RETAIN_JOBS |
|
SJC$_RETAIN_ERROR_JOBS |
— |
|
SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_SERVER |
— |
|
SJC$_SWAP |
SJC$_NO_SWAP |
|
SJC$_TERMINAL |
SJC$_NO_TERMINAL |
|
SJC$_WSDEFAULT |
SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT |
|
SJC$_WSEXTENT |
SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT |
|
SJC$_WSQUOTA |
SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA |
SJC$_DEASSIGN_QUEUE
This request deassigns a logical queue from an execution queue.
- SJC$_QUEUE
SJC$_DEFINE_CHARACTERISTIC
This request defines a characteristic name and number and inserts this definition into the queue file. The characteristic name can be up to 31 characters in length. Each characteristic name must have a unique number in the range 0 to 127. If the characteristic name is already defined, the request alters the definition of the characteristic.
A job cannot execute on an execution queue unless the queue possesses all the characteristics possessed by the job; the queue can possess additional characteristics and the job will still execute.
- SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME
- SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER
SJC$_DEFINE_FORM
This request defines a form name and number, as well as other physical attributes of the paper stock used in printers, and inserts this definition into the system job queue file. If the form name is already defined, this request alters the definition of the form.
Forms are used only by output execution queues and print jobs. A print job cannot execute unless the stock name of a form specified for the queue is the same as the stock name specified for the job. The stock name of a form, which you specify by using the SJC$_FORM_STOCK item code, specifies the paper stock used by the printer. Other item codes specify printing parameters for a job such as the margins, length of paper, and so on.
Each form must have a unique number. Numbers can range from 0 to 9999. When a new queue file is created, the system supplies the definition of a form named DEFAULT with number 0 and default characteristics.
- SJC$_FORM_NAME
- SJC$_FORM_NUMBER
|
SJC$_FORM_DESCRIPTION |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_LENGTH |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_BOTTOM |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_LEFT |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_RIGHT |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_TOP |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_SETUP_MODULES |
SJC$_NO_FORM_SETUP_MODULES |
|
SJC$_FORM_SHEET_FEED |
SJC$_NO_FORM_SHEET_FEED |
|
SJC$_FORM_STOCK |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_TRUNCATE |
SJC$_NO_FORM_TRUNCATE |
|
SJC$_FORM_WIDTH |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_WRAP |
SJC$_NO_FORM_WRAP |
|
SJC$_PAGE_SETUP_MODULES |
SJC$_NO_PAGE_SETUP_MODULES |
SJC$_DELETE_CHARACTERISTIC
This request deletes the definition of a characteristic name.
- SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME
SJC$_DELETE_FORM
This request deletes the definition of a form name. There must be no queues or jobs that reference the form.
- SJC$_FORM_NAME
SJC$_DELETE_JOB
This request deletes a job from the system job queue file. If the job is currently executing, it is aborted. If you specify the SJC$_QUEUE item code, the $SNDJBC service verifies that the selected job entry exists on the specified queue before deleting the job.
- SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
- SJC$_QUEUE
If you specify the SJC$_QUEUE item code, the $SNDJBC service verifies that the selected job entry exists on the specified queue before deleting the job.
SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE
This request deletes a queue and all of the jobs in the queue. The queue must be stopped, and there must be no other queues or jobs that reference the queue.
- SJC$_QUEUE
SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE_MANAGER
This request removes all references to the specified queue manager from the shared master file. It also deletes the queue and journal files associated with the queue manager. A queue manager must be stopped to be deleted.
- SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME
SJC$_DISABLE_AUTOSTART
This request disables autostart on a node. By default, SJC$_DISABLE_AUTOSTART affects the requesting node. To disable autostart on a node other than the node from which the $SNDJBC request is sent, use the SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME item code to specify the affected node.
Prevent autostart queues from failing over to the node.
Mark all of that queue manager's autostart queues on the node as “stop pending” in preparation for a planned shutdown, allowing jobs currently executing on the queues to complete.
Force all autostart queues with failover lists to fail over to the next available node in the queue manager's failover list on which autostart is enabled. Each queue fails over when all jobs currently executing on any of that queue manager's queues on the node have completed.
- SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME
- SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME
For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
SJC$_ENABLE_AUTOSTART
This request notifies the appropriate queue manager process that a node has progressed sufficiently in its startup procedure that batch and print jobs should execute. By default, SJC$_ENABLE_AUTOSTART affects the requesting node. To enable autostart on a node other than the node from which the $SNDJBC request is sent, use the SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME item code to specify the affected node. Once autostart is enabled, the queue manager starts all autostart-active queues on the appropriate node.
When a node reboots, autostart is disabled until the SJC$_ENABLE_AUTOSTART request is entered.
- SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME
- SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME
For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
SJC$_ENTER_FILE
This request creates a job containing one file and places the job in the specified queue. To create a job with more than one file, you must make a sequence of calls to the $SNDJBC service using the SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ADD_FILE, and SJC$_CLOSE_JOB function codes.
- SJC$_QUEUE
- SJC$_FILE_IDENTIFICATION
- SJC$_FILE_SPECIFICATION
|
SJC$_ACCOUNT_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_AFTER_TIME |
SJC$_NO_AFTER_TIME |
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME |
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS |
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER |
— |
|
SJC$_CLI |
SJC$_NO_CLI |
|
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT |
SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT |
|
SJC$_DELETE_FILE |
SJC$_NO_DELETE_FILE |
|
SJC$_DOUBLE_SPACE |
SJC$_NO_DOUBLE_SPACE |
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST |
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST |
|
SJC$_FILE_COPIES |
— |
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG |
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG |
|
SJC$_FILE_SETUP_MODULES |
SJC$_NO_FILE_SETUP_MODULES |
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER |
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER |
|
SJC$_FIRST_PAGE |
SJC$_NO_FIRST_PAGE |
|
SJC$_FORM_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER |
— |
|
SJC$_HOLD |
SJC$_NO_HOLD |
|
SJC$_JOB_COPIES |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_DEFAULT_RETAIN |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_ERROR_RETAIN |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN_TIME |
— |
|
SJC$_LAST_PAGE |
SJC$_NO_LAST_PAGE |
|
SJC$_LOG_DELETE |
SJC$_NO_LOG_DELETE |
|
SJC$_LOG_QUEUE |
— |
|
SJC$_LOG_SPECIFICATION |
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPECIFICATION |
|
SJC$_LOG_SPOOL |
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPOOL |
|
SJC$_LOWERCASE |
SJC$_NO_LOWERCASE |
|
SJC$_NOTE |
SJC$_NO_NOTE |
|
SJC$_NOTIFY |
SJC$_NO_NOTIFY |
|
SJC$_OPERATOR_REQUEST |
SJC$_NO_OPERATOR_REQUEST |
|
SJC$_PAGE_HEADER |
SJC$_NO_PAGE_HEADER |
|
SJC$_PAGINATE |
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE |
|
SJC$_PARAMETER_1 through 8 |
SJC$_NO_PARAMETERS |
|
SJC$_PASSALL |
SJC$_NO_PASSALL |
|
SJC$_PRIORITY |
— |
|
SJC$_RAD |
SJC$_NO_RAD |
|
SJC$_RESTART |
SJC$_NO_RESTART |
|
SJC$_UIC |
— |
|
SJC$_USERNAME |
— |
|
SJC$_WSDEFAULT |
SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT |
|
SJC$_WSEXTENT |
SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT |
|
SJC$_WSQUOTA |
SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA |
- SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER_OUTPUT
- SJC$_JOB_STATUS_OUTPUT
SJC$_MERGE_QUEUE
This request requeues all jobs in the queue specified by the item code SJC$_QUEUE to the queue specified by the item code SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE. The execution of current jobs is unaffected.
- SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE
- SJC$_QUEUE
SJC$_PAUSE_QUEUE
This request pauses the execution of current jobs in the specified queue and prevents the starting of jobs in that queue.
- SJC$_QUEUE
SJC$_RESET_QUEUE
This request resets the specified queue by (1) terminating and deleting each executing job that is not restartable, (2) terminating and requeuing each executing job that is restartable, and (3) stopping the queue.
- SJC$_QUEUE
SJC$_START_ACCOUNTING
This request performs two functions. If you specify the SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES item code, the request enables recording of the specified types of accounting records; if you do not specify SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES, the request starts the accounting manager and opens the system accounting file.
- SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES
- SJC$_NEW_VERSION
SJC$_START_QUEUE
This request permits the starting of jobs in the specified queue. If the queue was paused, current jobs are resumed.
- SJC$_QUEUE
|
SJC$_ALIGNMENT_MASK |
— |
|
SJC$_ALIGNMENT_PAGES |
— |
|
SJC$_AUTOSTART_ON |
— |
|
SJC$_BASE_PRIORITY |
— |
|
SJC$_BATCH |
SJC$_NO_BATCH |
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME |
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS |
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER |
— |
|
SJC$_CLOSE_QUEUE |
— |
|
SJC$_CPU_DEFAULT |
SJC$_NO_CPU_DEFAULT |
|
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT |
SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT |
|
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NUMBER |
— |
|
SJC$_DEVICE_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST |
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST |
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE |
— |
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG |
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG |
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE |
— |
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER |
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER |
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER |
— |
|
SJC$_GENERIC_QUEUE |
SJC$_NO_GENERIC_QUEUE |
|
SJC$_GENERIC_SELECTION |
SJC$_NO_GENERIC_SELECTION |
|
SJC$_GENERIC_TARGET |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_BURST |
SJC$_NO_JOB_BURST |
|
SJC$_JOB_FLAG |
SJC$_NO_JOB_FLAG |
|
SJC$_JOB_LIMIT |
— |
|
SJC$_JOB_RESET_MODULES |
SJC$_NO_JOB_RESET_MODULES |
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM |
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM |
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM |
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM |
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING |
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING |
|
SJC$_JOB_TRAILER |
SJC$_NO_JOB_TRAILER |
|
SJC$_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION |
SJC$_NO_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION |
|
SJC$_NEXT_JOB |
— |
|
SJC$_OPEN_QUEUE |
— |
|
SJC$_OWNER_UIC |
— |
|
SJC$_PAGINATE |
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE |
|
SJC$_PROCESSOR |
SJC$_NO_PROCESSOR |
|
SJC$_PROTECTION |
— |
|
SJC$_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION |
SJC$_NO_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION |
|
SJC$_RAD |
SJC$_NO_RAD |
|
SJC$_RECORD_BLOCKING |
SJC$_NO_RECORD_BLOCKING |
|
SJC$_RELATIVE_PAGE |
— |
|
SJC$_RETAIN_ALL_JOBS |
SJC$_NO_RETAIN_JOBS |
|
SJC$_RETAIN_ERROR_JOBS |
— |
|
SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME |
— |
|
SJC$_SEARCH_STRING |
— |
|
SJC$_SWAP |
SJC$_NO_SWAP |
|
SJC$_TERMINAL |
SJC$_NO_TERMINAL |
|
SJC$_TOP_OF_FILE |
— |
|
SJC$_WSDEFAULT |
SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT |
|
SJC$_WSEXTENT |
SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT |
|
SJC$_WSQUOTA |
SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA |
SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER
This request starts the clusterwide queue manager for the batch and print queuing system. It also opens the queue database.
To create a queue database and initially start the queue manager, issue a SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER request with the SJC$_NEW_VERSION item code. See the description of the SJC$_NEW_VERSION item code for more information. Once the queue manager has been started, it will remain running unless it is explicitly stopped with an SJC$_STOP_QUEUE_MANAGER request.
If an SJC$_STOP_QUEUE_MANAGER request has been specified, issue a SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER request to restart the queue manager.
In an OpenVMS Cluster environment, issue an SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER request with the SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES item code to modify the list of preferred nodes on which the queue manager can run. See the description of the SJC_QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES item code for more information.
In a cluster, issue an SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER request to ensure that the queue manager process is executing on the most preferred, available node. If the queue manager is not running on the most preferred, available node, the queue manager will be moved to that node without interruption of service. If you are using the default node list (*), the queue manager will not move. For more information, see the description of the SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES item code.
To create additional queue managers, issue an SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER request with the SJC$_ADD_QUEUE_MANAGER and SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME item codes. Note that the queue manager name must be different from the name of any queue manager currently defined. For more information about creating multiple queue managers, see the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
- SJC$_ADD_QUEUE_MANAGER
- SJC$_NEW_VERSION
- SJC$_QUEUE_DIRECTORY
- SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME
- SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES
SJC$_STOP_ACCOUNTING
This request performs two functions. If you specify the SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES item code, the request disables recording of the specified types of accounting records. If you do not specify SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES, the request stops the accounting manager and closes the system accounting file.
- SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES
SJC$_STOP_ALL_QUEUES_ON_NODE
This request stops all queues on a specific node. By default, all queues on the requesting node are stopped. To stop all queues on a node other than the node from which the $SNDJBC request is sent, use the SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME item code to specify the affected node.
Besides stopping all queues on a specific node, this request aborts each job that is currently executing. Aborted jobs that are restartable are requeued. Queues for which an autostart list has been specified fail over to the first available node in the list for which autostart is enabled.
- SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME
- SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME
SJC$_STOP_QUEUE
This request prevents the starting of jobs in the specified queue. The execution of current jobs is unaffected.
- SJC$_QUEUE
SJC$_STOP_QUEUE_MANAGER
This request shuts down the appropriate queue manager. It disables autostart on all nodes; stops all queues; aborts each job that is currently executing, requeuing those jobs that are restartable; and closes the files of the queue database.
- SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME
SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB
This request waits for the completion of a job, then sets the event flag, executes the
completion AST if you specified astadr, and returns the
completion status of the job to the I/O Status Block, provided you specified the
iosb argument.
- SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
- SJC$_QUEUE
- SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
- SJC$_JOB_NAME
- SJC$_JOB_COMPLETION_STATUS
SJC$_WRITE_ACCOUNTING
This request writes an accounting record.
- SJC$_ACCOUNTING_MESSAGE
Item Codes
SJC$_ACCOUNT_NAME
The SJC$_ACCOUNT_NAME item code is an input value item code. It specifies the account name of the user on behalf of whom the request is made. The buffer must specify a string from 1 to 8 characters. By default, the account name for batch and print jobs is taken from the requesting process.
You need CMKRNL privilege to use this item code.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_ACCOUNTING_MESSAGE
The SJC$_ACCOUNTING_MESSAGE item code is an input value item code. It causes the contents of the buffer to be placed in a “user message” accounting record. The buffer must specify a string from 1 to 255 characters.
(Valid for SJC$_WRITE_ACCOUNTING function code)
SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES
The SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES item code is an input value item code. It enables or disables accounting-record types. When an accounting-record type is enabled, the event designated by that type will be recorded in the accounting record. The buffer must contain a longword bit vector wherein each bit set specifies an accounting-record type. Undefined bits must be 0.
|
Accounting-Record Type |
Corresponding System Event |
|---|---|
|
SJC$V_ACCT_IMAGE |
Image terminations |
|
SJC$V_ACCT_LOGIN_FAILURE |
Login failures |
|
SJC$V_ACCT_MESSAGE |
User messages sent |
|
SJC$V_ACCT_PRINT |
Print job terminations |
|
SJC$V_ACCT_PROCESS |
Process terminations |
|
Accounting-Record Type |
Type of Image or Process |
|---|---|
|
SJC$V_ACCT_BATCH |
Batch process |
|
SJC$V_ACCT_DETACHED |
Detached process |
|
SJC$V_ACCT_INTERACTIVE |
Interactive process |
|
SJC$V_ACCT_NETWORK |
Network process |
|
SJC$V_ACCT_SUBPROCESS |
Subprocess |
(Valid for SJC$_START_ACCOUNTING, SJC$_STOP_ACCOUNTING function codes)
SJC$_ADD_QUEUE_MANAGER
The SJC$_ADD_QUEUE_MANAGER item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a new queue manager process should be defined in the master file. The operating system allows no more than five queue managers in a cluster.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER function code)
- SJC$_AFTER_TIME
- SJC$_NO_AFTER_TIME
The SJC$_AFTER_TIME item code is an input value item code. It specifies that the job can execute only if the system time is greater than or equal to the quadword time value contained in the buffer. The buffer must contain either an absolute time value or a delta time value; $SNDJBC converts delta time values to absolute time values by adding the current system time. The time value specified must be in the future, or it will be set to the current time.
The SJC$_NO_AFTER_TIME item code is a Boolean item code. It cancels the effect of a SJC$_AFTER_TIME item code previously specified for the job; the job can execute immediately. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_ALIGNMENT_MASK
The SJC$_ALIGNMENT_MASK item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues and only when the SJC$_ALIGNMENT_PAGES item code is also specified. The SJC$_ALIGNMENT_MASK item code causes the data printed on form alignment pages to be masked: all alphabetic characters are replaced with the letter X and all numeric characters with the number 9.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE function code)
SJC$_ALIGNMENT_PAGES
The SJC$_ALIGNMENT_PAGES item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that the queue be placed in form-alignment state and that a number of alignment pages be printed. The buffer must contain a longword value in the range 1 to 20; this value specifies how many alignment pages are to be printed.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE function code)
SJC$_AUTOSTART_ON
The SJC$_AUTOSTART_ON item code is an input value item code. For a batch queue, it uses as its value a comma-separated list of the nodes on which the specified queue can be located. Each node name must be followed by a double colon (::).
For an output queue, it uses as its value a comma-separated list of the names of the nodes and devices to which the specified queue's output can be sent. Each node name must be followed by a double colon, and each device name can be followed by the optional colon [:].
By specifying this item code, you designate a queue as an autostart queue. If you specify more than one node name (within an OpenVMS Cluster environment), the queue can automatically fail over if the node on which the queue is running is removed from the cluster.
This item code cannot be used with the SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME and SJC$_DEVICE_NAME item codes.
For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_BASE_PRIORITY
The SJC$_BASE_PRIORITY item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for execution queues. It specifies the base priority of batch processes initiated from a batch execution queue or of a symbiont process connected to an output execution queue. A symbiont process can control several queues; however, the base priority of the symbiont process is established by the first queue to which it is connected. The buffer must contain a longword value in the range 0 to 15; this value specifies the base priority.
By default, the base priority is the value of the SYSGEN parameter DEFPRI.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_BATCH
- SJC$_NO_BATCH
The SJC$_BATCH item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the queue is a batch execution queue or a generic batch queue, and thus can process only batch jobs.
The SJC$_BATCH, SJC$_PRINTER, SJC$_SERVER, and SJC$_TERMINAL item codes are mutually exclusive. If none of these item codes are specified, the default is SJC$_PRINTER.
The SJC$_NO_BATCH item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the queue is not a batch queue but rather an output execution or generic output queue, and thus can process only print jobs. It is the default.
For the SJC$_START_QUEUE function code, SJC$_BATCH and SJC$_NO_BATCH are supported for compatibility with VAX/VMS Version 4.n, but might not be supported in the future.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME
- SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER
- SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS
The SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME and SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER item codes are both input value item codes. Both specify characteristics for jobs or queues, and they can be used interchangeably. The characteristics are user-defined.
The SJC$_DEFINE_CHARACTERISTIC and SJC$_DELETE_CHARACTERISTIC function codes include and delete, respectively, a specified characteristic from the system job queue file. A job cannot execute on an execution queue unless the queue possesses all the characteristics possessed by the job; the queue can possess additional characteristics and the job will still execute.
The SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME and SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER item codes can appear as many times as necessary in a single call to $SNDJBC; the set of characteristics so defined in the call completely replaces the set of characteristics defined by a prior call. The SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS item code cancels all defined characteristics for the job or queue. By default, a queue or job has no defined characteristics.
The string can contain uppercase or lowercase characters (lowercase are converted to uppercase), numeric characters, dollar signs ($), and underscores (_). If the string is a logical name, SYS$SNDJBC translates it iteratively until the equivalence string is found or the number of translations allowed by the system has been performed. The maximum length of the final character string is 31 characters; spaces, tabs, and null characters are ignored.
For SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER, the buffer must contain a longword value in the range 0 to 127. This number identifies a characteristic.
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS is a Boolean item code.
- SJC$_ALTER_JOB
- SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
- SJC$_CREATE_JOB
- SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
- SJC$_DEFINE_CHARACTERISTIC
- SJC$_DELETE_CHARACTERISTIC
- SJC$_ENTER_FILE
- SJC$_START_QUEUE)
- SJC$_ALTER_JOB
- SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
- SJC$_CREATE_JOB
- SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
- SJC$_DEFINE_CHARACTERISTIC
- SJC$_ENTER_FILE
- SJC$_START_QUEUE)
SJC$_CHECKPOINT_DATA
The SJC$_CHECKPOINT_DATA item code is an input value item code. It specifies the value of the DCL symbol BATCH$RESTART for a batch job that is restarted. The buffer must contain a string no longer than 255 characters; this string is the value of the symbol BATCH$RESTART.
(Valid for SJC$_BATCH_CHECKPOINT function code)
SJC$_NO_CHECKPOINT_DATA
The SJC$_NO_CHECKPOINT_DATA item code is a Boolean item code. It cancels a previous specification of the BATCH$RESTART symbol; the SJC$_NO_CHECKPOINT_DATA item code also cancels a checkpoint in a print job so that the entire job is reprinted. By default, the BATCH$RESTART symbol is undefined.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB function code)
- SJC$_CLI
- SJC$_NO_CLI
The SJC$_CLI item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for batch jobs. It specifies that the command language interpreter to be executed is SYS$SYSTEM:name.EXE, where name is a valid OpenVMS RMS file name. The buffer must specify a name string from 1 to 39 characters.
The SJC$_NO_CLI item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the command language interpreter to be executed is the one specified in the user authorization file. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_CLOSE_QUEUE
The SJC$_CLOSE_QUEUE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that jobs cannot be entered in the queue. If the queue is closed, you can specify the SJC$_OPEN_QUEUE item code to permit jobs to be entered in the queue. By default, the queue is open.
Whether a queue is open or closed is independent of any other queue states (such as paused, stalled, stopped).
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_CPU_DEFAULT
- SJC$_NO_CPU_DEFAULT
The SJC$_CPU_DEFAULT item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for batch execution queues. It specifies the default CPU time limit in 10-millisecond units. The buffer contains this longword value. The value 0 specifies unlimited CPU time. You can specify a value that represents up to 497 days of CPU time.
The SJC$_NO_CPU_DEFAULT item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for batch execution queues. It specifies that no default CPU time limit is to apply to the job. It is the default.
|
CPU Time Limit Specified for Job? |
Default CPU Time Limit Specified for Queue? |
Maximum CPU Time Specified for Queue? |
Action Taken |
|---|---|---|---|
|
No |
No |
No |
Use UAF value |
|
Yes |
No |
No |
Use smaller of job's limit and UAF value |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Use smaller of job's limit and UAF value |
|
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Use smaller of job's limit and maximum |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Use smaller of job's limit and maximum |
|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Use smaller of queue's default and maximum |
|
No |
No |
Yes |
Use maximum |
|
No |
Yes |
No |
Use smaller of UAF value and queue's default |
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_CPU_LIMIT
- SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT
The SJC$_CPU_LIMIT item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for batch execution queues and batch jobs. It specifies the maximum CPU time limit for batch jobs in 10-millisecond units. The buffer must contain this longword value. The value 0 specifies unlimited CPU time. You can specify a value that represents up to 497 days of CPU time.
The SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for batch execution queues and batch jobs. It specifies that no maximum CPU time limit is to apply to the job. It is the default.
For information about the action taken when you specify a value for SJC$_CPU_LIMIT, refer to the description of the SJC$_CPU_DEFAULT item code and to Table 12.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_CREATE_START
The SJC$_CREATE_START item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a queue be started after it is created. By default, a queue remains stopped after it is created.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE function code)
- SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NAME
- SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NUMBER
The SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NAME and SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NUMBER item codes are input value item codes. They specify the default form for a specific output queue by name and by number, respectively.
When you specify a default form for an output queue, the queue uses the queue-specific default form, rather than the systemwide default form, to process any job that does not explicitly specify a form.
For SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NAME, the buffer must specify a form name. The string can contain uppercase or lowercase characters (lowercase are converted to uppercase), numeric characters, dollar signs ($), and underscores (_). If the string is a logical name, SYS$SNDJBC translates it iteratively until the equivalence string is found or the number of translations allowed by the system has been performed. The maximum length of the final character string is 31 characters; spaces, tabs, and null characters are ignored.
For SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NUMBER, the buffer must specify a longword value. You should use only one of these item codes to identify a default form for the queue.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_DELETE_FILE
- SJC$_NO_DELETE_FILE
The SJC$_DELETE_FILE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a file should be deleted after the job completes. The file that is deleted is the batch or print file submitted for execution. You cannot specify this item code with the SJC$_ALTER_JOB function code, which alters the parameters for an already existing job; you can make a file deletion request only when a job is first submitted to the queue.
The SJC$_NO_DELETE_FILE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a file should not be deleted after execution of the job. It is the default. You can specify this item code with the SJC$_ALTER_JOB function code; this makes it possible to cancel a file deletion request that was made when the job was first submitted to the queue.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE
The SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE item code is an input value item code. When you specify the SJC$_ASSIGN_QUEUE function code, SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE specifies the name of the execution queue to which the logical queue is assigned. When you specify the SJC$_ABORT_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, or SJC$_MERGE_QUEUE function code, SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE specifies the name of the queue into which jobs are placed. By default, jobs remain in the original queue.
The string can contain uppercase or lowercase characters (lowercase are converted to uppercase), numeric characters, dollar signs ($), and underscores (_). If the string is a logical name, SYS$SNDJBC translates it iteratively until the equivalence string is found or the number of translations allowed by the system has been performed. The maximum length of the final character string is 31 characters; spaces, tabs, and null characters are ignored.
(Valid for SJC$_ABORT_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ASSIGN_QUEUE, and SJC$_MERGE_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_DEVICE_NAME
The SJC$_DEVICE_NAME item code is an input value item code. It specifies the name of the device managed by the output execution queue. The buffer must specify a string from 1 to 255 characters. In an OpenVMS Cluster environment, the SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME item code is used to specify the name of the node on which the device is located.
This item code cannot be used with the SJC$_AUTOSTART_ON item code.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_DOUBLE_SPACE
- SJC$_NO_DOUBLE_SPACE
The SJC$_DOUBLE_SPACE item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that the symbiont should print the file with double spacing.
The SJC$_NO_DOUBLE_SPACE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the symbiont should print the file with single spacing. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
The SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER item code is an input value item code. It specifies the entry number of the job on which to perform the function. The buffer must contain this entry number.
(Valid for SJC$_ABORT_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_DELETE_JOB, SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB function codes)
SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER_OUTPUT
The SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER_OUTPUT item code is an output value item code. The buffer must specify a longword into which $SNDJBC will write the entry number of a created job.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_FILE_BURST
- SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE
- SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST
The SJC$_FILE_BURST item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that burst and flag pages are to be printed preceding a file. If you specify SJC$_FILE_BURST for a job, it specifies the default for all files in the job; if you specify it for an output execution queue, it specifies the default for all jobs executed from that queue.
The SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a burst page is to be printed preceding a file. If you specify SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE for a job, this item code specifies that a burst page is to be printed preceding only the first copy of the first file in the job; if you specify SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE for an output execution queue, the item code specifies this behavior as the default for all jobs executed from that queue.
The SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that no burst page should be printed. It is the default.
- SJC$_ADD_FILE
- SJC$_ALTER_JOB
- SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
- SJC$_CREATE_JOB
- SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
- SJC$_ENTER_FILE
- SJC$_START_QUEUE)
- SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
- SJC$_CREATE_JOB
- SJC_CREATE_QUEUE
- SJC_START_QUEUE)
SJC$_FILE_COPIES
The SJC$_FILE_COPIES item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies the number of times a file is printed. By default, a file is repeated once. The buffer must specify a longword value from 1 to 255; this value is the repeat count.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_FILE_FLAG
- SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE
- SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG
The SJC$_FILE_FLAG item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a flag page is to be printed preceding a file. If you specify SJC$_FILE_FLAG for a job, this item code indicates the default for all files in the job; if you specify it for an output execution queue, SJC$_FILE_FLAG indicates the default for all jobs executed from that queue.
The SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a flag page is to be printed preceding a file. If you specify SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE for a job, this item code specifies that a flag page is to be printed preceding only the first copy of the first file in the job; if you specify SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE for an output execution queue, it indicates this behavior as the default for all jobs executed from that queue.
The SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that no flag page should be printed by default for jobs within the queue.
- SJC$_ADD_FILE
- SJC$_ALTER_JOB
- SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
- SJC$_CREATE_JOB
- SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
- SJC$_ENTER_FILE
- SJC$_START_QUEUE)
- SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
- SJC$_CREATE_JOB
- SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
- SJC$_START_QUEUE)
SJC$_FILE_IDENTIFICATION
The SJC$_FILE_IDENTIFICATION item code is an input value item code. It specifies the file to be processed. The buffer contains a 28-byte value that identifies the file to be processed. This value specifies (in order) the following three file-identification fields in the OpenVMS RMS NAM block: the 16-byte NAM$T_DVI field, the 6-byte NAM$W_FID field, and the 6-byte NAM$W_DID field. These fields occur consecutively in the NAM block.
If you specify SJC$_FILE_IDENTIFICATION, you must omit the SJC$_FILE_SPECIFICATION item code.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_FILE_SETUP_MODULES
- SJC$_NO_FILE_SETUP_MODULES
The SJC$_FILE_SETUP_MODULES item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a list of text modules should be extracted from the device control library and copied to the printer before a file is printed. The buffer must contain a list of text module names, with a comma separating each name.
The SJC$_NO_FILE_SETUP_MODULES item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that no text modules should be copied before printing a file. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_FILE_SPECIFICATION
The SJC$_FILE_SPECIFICATION item code is an input value item code. It identifies the file to be processed. The buffer must contain the file specification of the file to be processed. The $SNDJBC service converts the file specification to the corresponding file identification and proceeds as if the SJC$_FILE_IDENTIFICATION item code had been specified. If you specify SJC$_FILE_SPECIFICATION, you must omit the SJC$_FILE_IDENTIFICATION item code.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_FILE_TRAILER
- SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE
- SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER
The SJC$_FILE_TRAILER item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a trailer page is to be printed following a file. If you specify SJC$_FILE_TRAILER for a job, this item code indicates the default for all files in the job; if you specify it for an output execution queue, SJC$_FILE_TRAILER specifies the default for all jobs executed on that queue.
The SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a trailer page is to be printed following a file. If you specify SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE for a job, this item code indicates that a trailer page is to be printed following only the last copy of the last file in the job; if you specify it for an output execution queue, SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE indicates this behavior as the default for all jobs executed on that queue.
The SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that no trailer page should be printed. It is the default.
- SJC$_ADD_FILE
- SJC$_ALTER_JOB
- SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
- SJC$_CREATE_JOB
- SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
- SJC$_ENTER_FILE
- SJC$_START_QUEUE)
- SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
- SJC$_CREATE_JOB
- SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
- SJC$_START_QUEUE)
- SJC$_FIRST_PAGE
- SJC$_NO_FIRST_PAGE
The SJC$_FIRST_PAGE item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for jobs queued to output execution queues. It specifies the page number at which printing should begin. The buffer must contain a nonzero longword value specifying this page number.
The SJC$_NO_FIRST_PAGE item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for jobs queued to output execution queues. It specifies that printing should begin with the first page. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_FORM_DESCRIPTION
The SJC$_FORM_DESCRIPTION item code is an input value item code. It provides operator-supplied information describing the form. By default, the form name is used. The buffer must specify a string of no more than 255 characters.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_LENGTH
The SJC$_FORM_LENGTH item code is an input value item code. It specifies the physical length of the form in lines. The buffer must contain a nonzero longword integer value. By default, the form length is 66 lines.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_BOTTOM
The SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_BOTTOM item code is an input value item code. It specifies the bottom margin of the form in lines. By default, the bottom margin is 6 lines.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_LEFT
The SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_LEFT item code is an input value item code. It specifies the width of the left margin of the form in characters. By default, the left margin is 0. The buffer must specify a longword value.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_RIGHT
The SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_RIGHT item code is an input value item code. It specifies the width of the right margin of the form in characters. By default, the right margin is 0. The buffer must specify a longword value.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_TOP
The SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_TOP item code is an input value item code. It specifies the top margin of the form in lines. By default, the top margin is 0.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
- SJC$_FORM_NAME
- SJC$_FORM_NUMBER
The SJC$_FORM_NAME and SJC$_FORM_NUMBER item codes are input value item codes. They specify a mounted form for the queue by name and by number, respectively. For SJC$_FORM_NAME, the buffer must specify a form name. For SJC$_FORM_NUMBER, the buffer must specify a longword value. You should use only one of these two item codes to identify a form in queue and job related function codes.
The SJC$_DEFINE_FORM and SJC$_DELETE_FORM function codes include and delete, respectively, a specified form name and number from the system job queue file. The mounted form indicates the stock type of the output queue. A job cannot execute on an output queue unless the stock type of the form specified (by name or number) for the job item code is the same as the stock type of the mounted form specified for the queue. For more information about how the stock type of a form affects job processing, see the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
The string can contain uppercase or lowercase characters (lowercase are converted to uppercase), numeric characters, dollar signs ($), and underscores (_). If the string is a logical name, SYS$SNDJBC translates it iteratively until the equivalence string is found or the number of translations allowed by the system has been performed. The maximum length of the final character string is 31 characters; spaces, tabs, and null characters are ignored.
- SJC$_ALTER_JOB
- SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
- SJC$_CREATE_JOB
- SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
- SJC$_DEFINE_FORM
- SJC$_DELETE_FORM
- SJC$_ENTER_FILE
- SJC$_START_QUEUE)
- SJC$_ALTER_JOB
- SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
- SJC$_CREATE_JOB
- SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
- SJC$_DEFINE_FORM
- SJC$_ENTER_FILE
- SJC$_START_QUEUE)
- SJC$_FORM_SETUP_MODULES
- SJC$_NO_FORM_SETUP_MODULES
The SJC$_FORM_SETUP_MODULES item code is an input value item code. The buffer must specify one or more text module names, with a comma separating each name. This item code specifies that these modules should be extracted from the device control library and copied to the printer before each file that is printed on the form.
The SJC$_NO_FORM_SETUP_MODULES item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that no device control modules should be copied. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
- SJC$_FORM_SHEET_FEED
- SJC$_NO_FORM_SHEET_FEED
The SJC$_FORM_SHEET_FEED item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the symbiont should pause at the end of each physical page so that a new sheet can be inserted.
The SJC$_NO_FORM_SHEET_FEED item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the output symbiont should not pause at the end of every physical page. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_STOCK
The SJC$_FORM_STOCK item code is an input value item code. It specifies a name for the paper stock. The buffer must contain a string of 1 to 31 characters. By default, the name of the paper stock is the form name.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
- SJC$_FORM_TRUNCATE
- SJC$_NO_FORM_TRUNCATE
The SJC$_FORM_TRUNCATE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the symbiont should truncate lines that extend beyond the right margin. Specifying SJC$_FORM_TRUNCATE cancels SJC$_FORM_WRAP. The SJC$_FORM_TRUNCATE item code is the default.
The SJC$_NO_FORM_TRUNCATE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the output symbiont should not truncate lines that extend beyond the right margin.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_WIDTH
The SJC$_FORM_WIDTH item code is an input value item code. It specifies the physical width of the form in characters. The buffer must contain a nonzero longword integer. By default, the form width is 132 characters.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
- SJC$_FORM_WRAP
- SJC$_NO_FORM_WRAP
The SJC$_FORM_WRAP item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the symbiont should wrap lines that extend beyond the right margin. Specifying SJC$_FORM_WRAP cancels SJC$_FORM_TRUNCATE.
The SJC$_NO_FORM_WRAP item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the output symbiont should not wrap lines. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
- SJC$_GENERIC_QUEUE
- SJC$_NO_GENERIC_QUEUE
The SJC$_GENERIC_QUEUE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a queue is a generic queue.
The SJC$_NO_GENERIC_QUEUE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a queue is not a generic queue. It is the default. By default, a queue is an execution queue; see the Description section for a full discussion of the types of queue.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_GENERIC_SELECTION
- SJC$_NO_GENERIC_SELECTION
The SJC$_GENERIC_SELECTION item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that an execution queue can accept jobs from a generic queue. It is the default. It is meaningful only for execution queues.
The SJC$_NO_GENERIC_SELECTION item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that an execution queue cannot accept jobs from a generic queue.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_GENERIC_TARGET
The SJC$_GENERIC_TARGET item code is an input value item code. The buffer must specify a queue name. This queue name identifies an execution queue that can accept jobs from a generic queue. This item code is meaningful only for generic queues.
This item code can appear up to 124 times in a single call to $SNDJBC. The set of queues defined in a single call completely replaces the set defined by a prior call.
The string can contain uppercase or lowercase characters (lowercase are converted to uppercase), numeric characters, dollar signs ($), and underscores (_). If the string is a logical name, SYS$SNDJBC translates it iteratively until the equivalence string is found or the number of translations allowed by the system has been performed. The maximum length of the final character string is 31 characters; spaces, tabs, and null characters are ignored.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_HOLD
- SJC$_NO_HOLD
The SJC$_HOLD item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a job cannot execute and must enter a holding status.
The SJC$_NO_HOLD item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a job can execute immediately when used with the SJC$_ALTER_JOB function code. It makes the following types of job eligible for execution: (1) a job that is holding because it was specified with the SJC$_HOLD item code, (2) a job that was refused by the symbiont, and (3) a job that was retained after execution. It is the default. SJC$_NO_HOLD does not release a job that is specified with the SJC$_AFTER_TIME item code.
(Valid for SJC$_ABORT_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_JOB_BURST
- SJC$_NO_JOB_BURST
The SJC$_JOB_BURST item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that burst and flag pages are to be printed preceding each job. It is meaningful only for output execution queues.
The SJC$_NO_JOB_BURST item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a burst page is not to be printed preceding each job. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_JOB_COMPLETION_STATUS
Output item code. Use this item code to receive the completion status of the job being synchronized. You can omit the IOSB in the $SNDJBC call and receive the completion status in this item's value.
(Valid for the SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB function code)
SJC$_JOB_COPIES
The SJC$_JOB_COPIES item code is an input value item code. It specifies the number of times that the entire print job is to be repeated. The buffer must contain this nonzero longword integer value. By default, the print job is repeated once.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_JOB_DEFAULT_RETAIN
The SJC$_JOB_DEFAULT_RETAIN item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that you want the job to be held in the queue as specified by the queue's retention policy.
For more information about user-specified job retention, see the /RETAIN qualifier for the PRINT or SUBMIT command in the VSI OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_JOB_ERROR_RETAIN
The SJC$_JOB_ERROR_RETAIN item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that you want the job to be retained in the queue if the job completes unsuccessfully. However, the job might be held in the queue even if it completes successfully if the queue is set to retain all jobs because the QUI$V_QUEUE_RETAIN_ALL bit is set in the QUI$_QUEUE_FLAGS item code.
For more information about user-specified job retention, see the /RETAIN qualifier for the PRINT or SUBMIT command in the VSI OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SCJ$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_JOB_FLAG
- SJC$_NO_JOB_FLAG
The SJC$_JOB_FLAG item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a flag page is to be printed preceding each job. It is meaningful only for output execution queues.
The SJC$_NO_JOB_FLAG item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a flag page is not to be printed preceding each job. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_JOB_LIMIT
The SJC$_JOB_LIMIT item code is an input value item code. It specifies the maximum number of jobs that can execute simultaneously on a queue. The buffer must contain a longword value in the range 1 to 65535. It is meaningful only for batch execution queues. By default, the job limit is 1.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_JOB_NAME
The SJC$_JOB_NAME item code is an input value item code. It specifies the name of a job. The buffer must specify a string from 1 to 39 characters.
For function codes SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, and SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_JOB_NAME specifies the identifying name of the job. By default, the name used is the name of the first file in the job.
For function code SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB, SJC$_JOB_NAME specifies the name of the job on which to operate. The job name is implicitly qualified by the user name.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB function codes)
- SJC$_JOB_RESET_MODULES
- SJC$_NO_JOB_RESET_MODULES
The SJC$_JOB_RESET_MODULES item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. The buffer must specify the names of one or more text modules, with a comma separating each name. This item code specifies that these modules are to be extracted from the device control library and copied to the printer before each print job.
The SJC$_NO_JOB_RESET_MODULES item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that no text modules should be copied to the printer. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN
The SJC$_JOB_RETAIN item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that you want the job to be retained in the queue after it has executed, regardless of the job's completion status.
For more information about user-specified job retention, see the /RETAIN qualifier for the PRINT or SUBMIT command in the VSI OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN_TIME
The SJC$_JOB_RETAIN_TIME item code is an input value item code. It specifies a quadword time value representing the length of time you want the job to be retained in the queue.
If a delta time is provided, the delta begins when the job completes. However, depending on the queue's job retention policy, the job might be retained indefinitely.
For more information about user-specified job retention, see the /RETAIN qualifier for the PRINT or SUBMIT command in the VSI OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM
- SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM
The SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a print job can execute only if its total size in blocks is less than or equal to the specified value. The buffer specifies this nonzero longword value.
The SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a print job can execute immediately regardless of its size. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM
- SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM
The SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a print job can execute only if its total size in blocks is greater than or equal to the specified value. The buffer specifies this nonzero longword value.
The SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a print job can execute immediately regardless of its size. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING
- SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING
The SJC$_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that print jobs entered in an output queue should be scheduled according to size, with the smallest job of a given priority processed first. It is the default.
The SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that print jobs of a given priority should not be scheduled according to print size.
Changing the value of this item code for a queue while print jobs are pending on any queue produces unpredictable results.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_JOB_STATUS_OUTPUT
The SJC$_JOB_STATUS_OUTPUT item code is an output value item code. When specified, $SNDJBC returns, as a character string, a textual message describing the status of a submitted job. Because the message can include up to 255 characters, the buffer length field of the item descriptor should specify 255 (bytes).
(Valid for SJC$_CLOSE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_JOB_TRAILER
- SJC$_NO_JOB_TRAILER
The SJC$_JOB_TRAILER item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a trailer page is to be printed following each job.
The SJC$_NO_JOB_TRAILER item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a trailer page is not to be printed following each job. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_LAST_PAGE
- SJC$_NO_LAST_PAGE
The SJC$_LAST_PAGE item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for jobs submitted to output execution queues. It specifies the page number at which printing should end. The buffer specifies this nonzero longword value.
The SJC$_NO_LAST_PAGE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that printing should end after the last page. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION
- SJC$_NO_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION
The SJC$_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that the device control library for the queue is SYS$LIBRARY:name.TLB, where name is a valid RMS file name. The buffer must specify the OpenVMS RMS file name.
The SJC$_NO_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the device control library is SYS$LIBRARY:SYSDEVCTL.TLB. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_LOG_DELETE
- SJC$_NO_LOG_DELETE
The SJC$_LOG_DELETE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the log file produced for a batch job is to be deleted. It is meaningful only for batch jobs. It is the default.
The SJC$_NO_LOG_DELETE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the log file produced for a batch job is not to be deleted.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_LOG_QUEUE
The SJC$_LOG_QUEUE item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for batch jobs. It specifies the queue into which the log file produced for the batch job is entered for printing. The buffer must specify the name of the queue. By default, the log file is entered in queue SYS$PRINT.
The string can contain uppercase or lowercase characters (lowercase are converted to uppercase), numeric characters, dollar signs ($), and underscores (_). If the string is a logical name, SYS$SNDJBC translates it iteratively until the equivalence string is found or the number of translations allowed by the system has been performed. The maximum length of the final character string is 31 characters; spaces, tabs, and null characters are ignored.
If your system uses multiple queue managers to run batch queues on a separate queue manager from output queues, certain checks that would otherwise be performed for the SJC$_LOG_QUEUE item code of the $SNDJBC system service are not performed.
When batch and print queues are managed by the same queue manager, the queue manager checks to ensure that the queue specified with the SJC$_LOG_QUEUE is an output queue and that the user has access to the output queue. These checks are not made if the batch queue specified by the $SNDJBC service and the output queue specified by the SJC$_LOG_QUEUE item code are managed by different queue managers. If you explicitly specify an output queue for the log file when submitting a batch job, be sure the queue you specify with the SJC$_LOG_QUEUE is an output queue and not a batch queue. Also, be sure that you have access to the printer queue.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_LOG_SPECIFICATION
- SJC$_NO_LOG_SPECIFICATION
The SJC$_LOG_SPECIFICATION item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for batch jobs. It specifies the file specification of the log file produced for a batch job. The buffer must contain this OpenVMS RMS file specification. Omitted fields in the file specification are supplied from the default file specification SYS$LOGIN:name.LOG, where name is the job name. By default a log file is produced using this default file specification to generate the log file name.
The SJC$_NO_LOG_SPECIFICATION item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that no log file should be produced for the batch job.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_LOG_SPOOL
- SJC$_NO_LOG_SPOOL
The SJC$_LOG_SPOOL item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the log file produced for a batch job is to be printed. It is meaningful only for batch jobs. It is the default.
The SJC$_NO_LOG_SPOOL item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the log file for a batch job is not to be printed.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_LOWERCASE
- SJC$_NO_LOWERCASE
The SJC$_LOWERCASE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a job can execute only on a device that has the LOWERCASE device-dependent characteristic. It is meaningful only for jobs submitted to output execution queues.
The SJC$_NO_LOWERCASE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a job can execute whether or not the output device has the LOWERCASE device-dependent characteristic. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_NEW_VERSION
The SJC$_NEW_VERSION item code is a Boolean item code.
Caution
If you specify this item code and a queue database already exists, the new master and queue files of the queue database supersede existing version of those files. However, the journal files of the queue database are deleted. Thus, jobs and other information are lost.
When used with the SJC$_START_ACCOUNTING function code, the SJC$_NEW_VERSION item code specifies that a new version of the system accounting file is to be created, whether or not the file already exists.
(Valid for SJC$_START_ACCOUNTING, SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER function codes)
SJC$_NEXT_JOB
The SJC$_NEXT_JOB item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for paused output execution queues. It specifies that the current job should be aborted and that printing should be resumed with the next job.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE function code)
- SJC$_NOTE
- SJC$_NO_NOTE
The SJC$_NOTE item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful for batch and output execution queues. It specifies a string to be printed on the job flag and file flag pages. The buffer must specify this string.
The SJC$_NO_NOTE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that no string is to be printed on the job flag and file flag pages. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_NOTIFY
- SJC$_NO_NOTIFY
The SJC$_NOTIFY item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a message is to be broadcast, at the time of job completion, to each logged-in terminal, of the user who submitted the job.
The SJC$_NO_NOTIFY item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that no message is to be broadcast at the time of job completion. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_NO_RAD (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Boolean input item code. When the SJC$_NO_RAD code is specified in a request, the RAD value for the queue or job is removed.
RAD is supported on AlphaServer GS series systems and starting from OpenVMS Version 8.4, support is extended to NUMA capable Integrity servers.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_START_QUEUE)
SJC$_OPEN_QUEUE
The SJC$_OPEN_QUEUE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that jobs can be entered in the queue. To specify that jobs cannot be entered in the queue, use the SJC$_CLOSE_QUEUE item code. By default, the queue is open.
Whether a queue is open or closed is independent of any other queue states (such as paused, stalled, stopped).
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_OPERATOR_REQUEST
- SJC$_NO_OPERATOR_REQUEST
The SJC$_OPERATOR_REQUEST item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. The buffer must contain a text string. This item code specifies that, when a job begins execution, the execution queue is to be placed in the paused state and the specified text string is to be included in a message to the queue operator requesting service.
The SJC$_NO_OPERATOR_REQUEST item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that no message is to be sent to the queue operator. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_OWNER_UIC
The SJC$_OWNER_UIC item code is an input value item code. It specifies the owner UIC of a queue. The buffer must specify the longword UIC. By default, the owner UIC is [1,4].
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_PAGE_HEADER
- SJC$_NO_PAGE_HEADER
The SJC$_PAGE_HEADER item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a page heading is to be printed on each page of output.
The SJC$_NO_PAGE_HEADER item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that no page heading is to be printed. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_PAGE_SETUP_MODULES
- SJC$_NO_PAGE_SETUP_MODULES
The SJC$_PAGE_SETUP_MODULES item code is an input value item code. The buffer must specify one or more text module names, with a comma separating each name. This item code specifies that these modules are to be extracted from the device control library and copied to the printer before each page is printed.
The SJC$_NO_PAGE_SETUP_MODULES item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that no device control modules are to be copied. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
- SJC$_PAGINATE
- SJC$_NO_PAGINATE
The SJC$_PAGINATE item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues and jobs submitted to output execution queues. It specifies that the symbiont should paginate the output by inserting a form feed whenever output reaches the bottom margin of the form. It is the default.
The SJC$_NO_PAGINATE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the symbiont should not paginate the output.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_PARAMETER_1 through SJC$_PARAMETER_8
- SJC$_NO_PARAMETERS
The SJC$_PARAMETER_1 through SJC$_PARAMETER_8 item codes are input value item codes; the last digit of the item code name is a number from 1 through 8. For each item code specified, the buffer must specify a string of no more than 255 characters. For batch jobs, the string becomes the value of the DCL symbol P1 through P8, respectively, within the outermost command procedure.
For print jobs, the system makes the string available to the symbiont, though the standard OpenVMS print symbiont does not use this information. By default, each of the eight parameters specifies a null string.
For function code SJC$_ALTER_JOB, if any SJC$_PARAMETER item is specified, the value of each unspecified item is the null string.
The SJC$_NO_PARAMETERS item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that none of the SJC$_PARAMETER items are to be passed in the batch or print job. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_PASSALL
- SJC$_NO_PASSALL
The SJC$_PASSALL item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for jobs submitted to output execution queues. It specifies that the symbiont is to print the file in PASSALL mode.
The SJC$_NO_PASSALL item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the symbiont is not to print the file in PASSALL mode. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_PRINTER
The SJC$_PRINTER item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output queues. It specifies that the queue being created is a printer queue. The SJC$_BATCH, SJC$_PRINTER, SJC$_SERVER, and SJC$_TERMINAL item codes are mutually exclusive. If none of these item codes are specified, the default is SJC$_PRINTER.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE function code)
SJC$_PRIORITY
The SJC$_PRIORITY item code is an input value item code. The buffer must specify a longword value in the range 0 through 255. This value specifies the scheduling priority of the job in a queue relative to the scheduling priority of other jobs in the same queue.
By default, the scheduling priority of the job is the value of the SYSGEN parameter DEFQUEPRI.
If you specify a value for SJC$_PRIORITY that is greater than the SYSGEN parameter MAXQUEPRI and you do not have either ALTPRI or OPER privilege, the system uses the greater of the following two values: DEFQUEPRI or MAXQUEPRI. If you have either ALTPRI or OPER privilege, the system uses any value you specify for SJC$_PRIORITY, even if it is included in the range between MAXQUEPRI + 1 and 255.
(Valid for SJC$_ABORT_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_PROCESSOR
- SJC$_NO_PROCESSOR
The SJC$_PROCESSOR item code is an input value item code. The buffer must specify a valid OpenVMS RMS file name.
When specified for an output execution queue, SJC$_PROCESSOR specifies that the symbiont image to be executed is SYS$SYSTEM:name.EXE, where name is the RMS file name contained in the buffer.
When specified for a generic output queue, SJC$_PROCESSOR specifies that the generic queue can place jobs only in server queues that are executing the symbiont image SYS$SYSTEM:name.EXE, where name is the RMS file name contained in the buffer.
The SJC$_NO_PROCESSOR item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the symbiont image to be executed is SYS$SYSTEM:PRTSMB.EXE. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_PROTECTION
The SJC$_PROTECTION item code is an input value item code. It specifies the protection of a queue.
The buffer must specify a longword in the format shown in the following diagram.
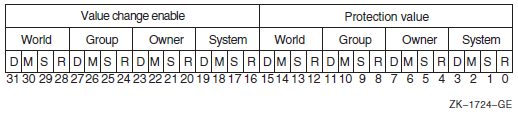
Bits 0 through 15 specify the protection value: the four types of access (read, submit, manage, delete) to be granted to the four categories of user (System, Owner, Group, World). Set bits deny access and clear bits allow access.
Bits 16 through 31 specify the protection enable mask: they identify which part of the protection value (bits 0 through 15) is to be applied to queue protection. If all bits are set in the enable mask, it means that all of the protection values are to be applied. A value other than –1 in the protection enable mask means that only those bits set will affect the corresponding bits in the protection value. When a bit in the protection enable mask is clear, the corresponding bit in the existing queue protection value is unchanged.
By default, the queue protection is (S:M,O:D,G:R,W:S).
Note that on all system types you can assign ACLs to queues using the $SET_SECURITY system service.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_QUEUE
The SJC$_QUEUE item code is an input value item code. It specifies the queue to which the operation is directed. The buffer must specify the name of the queue.
The string can contain uppercase or lowercase characters (lowercase are converted to uppercase), numeric characters, dollar signs ($), and underscores (_). If the string is a logical name, SYS$SNDJBC translates it iteratively until the equivalence string is found or the maximum number of translations allowed by the system has been performed. The maximum length of the final character string is 31 characters; spaces, tabs, and null characters are ignored.
- SJC$_ABORT_JOB
- SJC$_ALTER_JOB
- SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
- SJC$_CREATE_JOB
- SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
- SJC$_DELETE_JOB
- SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE
- SJC$_ENTER_FILE
- SJC$_START_QUEUE
- SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB)
- SJC$_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION
- SJC$_NO_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION
The SJC$_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION item code is an input value item code. It provides operator-supplied information about the queue. The buffer must specify a string of no more than 255 characters.
The SJC$_NO_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that no description is associated with the queue.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_QUEUE_DIRECTORY
The SJC$_QUEUE_DIRECTORY item code is an input value item code. SJC$_QUEUE_DIRECTORY specifies the directory location that contains the system queue and journal files for the queue manager. The queue file has a file type of QMAN$QUEUES and contains queue definitions. The journal file has a file type of .QMAN$JOURNAL and contains job and other information allowing the queue manager to return to its last known state should a system be stopped unexpectedly. These files must reside together in the same directory.
The default location of the queue and journal files is SYS$COMMON:[SYSEXE]. The optional use of SJC$_QUEUE_DIRECTORY is for specifying an alternate location for the queue and journal files. The specification must include at least the device and directory name; wildcard characters are not allowed in the directory specification. The directory specified must be available to all nodes that can run the queue manager. If the directory specification is a concealed logical name, it must be defined identically on all nodes in the cluster.
The location of the queue and journal files is stored in the master file of the queue database. You do not have to respecify the directory location with subsequent use of SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER.
For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER function code)
SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME
The SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME item code is an input value item code. It uniquely identifies the queue manager process that manages some segment of the queues and jobs in the system. If it is not present, a default name of SYS$QUEUE_MANAGER is used.
The maximum length of the final character string is 31 characters. As with queue names, this can be a logical and will be resolved by the system. Once resolved, the name provided will serve as the file name for the queue and journal files, the process name, and the user name for the active process. Only the first 15 and 12 characters of the name are used for the process and user names, respectively.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE_MANAGER, SJC$_DISABLE_AUTOSTART, SJC$_ENABLE_AUTOSTART, SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER, SJC$_STOP_ALL_QUEUES_ON_NODE, SJC$_STOP_QUEUE_MANAGER function codes)
SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES
The SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES item code is an input value item code. In an OpenVMS Cluster, SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES specifies a list of nodes that can run the queue manager. It also gives the explicit order of failover if the node running the queue manager exits the cluster. The specified node list is stored in the queue database.
The default value for the node list is an asterisk (*); it specifies that all nodes in the cluster are eligible to run the queue manager. The asterisk can also be specified as an element of the list. For example, a list can be specified as nodes A, B, C, *. If the node on which the queue manager is running leaves the cluster, the queue manager automatically fails over to any available node in the cluster; that is, if nodes A, B, and C are unavailable, then the queue manager can run on any other node. When establishing the node list, there is no validation of the individual nodes. If, for example, a node name is misspelled, there is no error status returned.
Anytime the SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER function code is used, the job controller checks the queue database to see if the node list is other than the default (*). If the node list is other than the default and the queue manager is running on a node other than the first available node of those specified, then the queue manager process is moved from its current node and restarted on the first available preferred node. When a current call includes the SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES item code, the job controller also updates the node list stored in the database. Despite this transition, queues on the running nodes are not stopped, and all requests to the queuing system complete as expected.
Note that because the specified node list is saved in the database, it is used every time the SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER function code is used, unless the node list has been changed by a more recent call to $SNDJBC with the SJC_$QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES item code.
For more information, see the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER function code)
SJC$_RAD (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Input value item code used to specify a RAD number on which to create a batch process. The item accepts a 32-bit integer value as input. The input is validated to be within the range of 0 to SYI$_RAD_MAX_RADS.
RAD is supported on AlphaServer GS series systems and starting from OpenVMS Version 8.4, support is extended to NUMA capable Integrity servers.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_START_QUEUE)
- SJC$_RECORD_BLOCKING
- SJC$_NO_RECORD_BLOCKING
The SJC$_RECORD_BLOCKING item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that the symbiont can merge the output records it sends to the output device into a single I/O request. For the standard OpenVMS print symbiont, record blocking can have a significant performance advantage over single-record mode. It is the default.
The SJC$_NO_RECORD_BLOCKING item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the symbiont must send each record in a separate I/O request to the output device.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_RELATIVE_PAGE
The SJC$_RELATIVE_PAGE item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. The buffer must specify a signed longword integer. This item code specifies that printing should be resumed after spacing forward (if the buffer value is positive) or backward (if the buffer value is negative) the specified number of pages.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE function code)
SJC$_REQUEUE
The SJC$_REQUEUE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a job is to be requeued. By default, the job is deleted.
(Valid for SJC$_ABORT_JOB function code)
- SJC$_RESTART
- SJC$_NO_RESTART
The SJC$_RESTART item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a job can restart after a system failure or can be requeued during execution. It is the default for print jobs.
The SJC$_NO_RESTART item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a job cannot restart after a system failure or after a requeue operation. It is the default for batch jobs.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_RETAIN_ALL_JOBS
- SJC$_RETAIN_ERROR_JOBS
- SJC$_NO_RETAIN_JOBS
The SJC$_RETAIN_ALL_JOBS item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that jobs are to be retained in the queue with a completion status after they have been executed.
The SJC$_RETAIN_ERROR_JOBS item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that jobs are to be retained only if the job completed unsuccessfully (the job's completion status has the low bit clear).
The SJC$_NO_RETAIN_JOBS item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that jobs are not to be retained in the queue after they have completed. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME
The SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME item code is an input value item code. It specifies the name of the node for which the command is to execute. The buffer must specify a 1- to 6-character string that matches the value of the SYSGEN parameter SCSNODE in effect on the target node.
When used with the function codes of SJC$_STOP_ALL_QUEUES_ON_NODE, SJC$_DISABLE_AUTOSTART, and SJC$_ENABLE_AUTOSTART, this item code requests a function on a node other than the node from which the $SNDJBC request is sent.
SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME is meaningful only for execution queues in a cluster environment. By default, the queue executes on the node from which the queue is first started. For an output execution queue, you use the SJC$_DEVICE_NAME item code to specify the name of the device managed by the queue.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_DISABLE_AUTOSTART, SJC$_ENABLE_AUTOSTART, SJC$_START_QUEUE, SJC$_STOP_ALL_QUEUES_ON_NODE function codes)
SJC$_SEARCH_STRING
The SJC$_SEARCH_STRING item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues. The buffer must specify a string of no more than 63 characters. This item code specifies that printing is to resume at the page containing the first occurrence of the specified string. The search for the string proceeds in the forward direction.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE function code)
SJC$_SERVER
The SJC$_SERVER item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output queues. It specifies that the queue being created is a server queue. The term server indicates that a user-modified or user-written symbiont process is controlling an output execution queue, or a generic queue has server execution queues as its targets.
The SJC$_BATCH, SJC$_PRINTER, SJC$_SERVER, and SJC$_TERMINAL item codes are mutually exclusive. If none of these item codes are specified, the default is SJC$_PRINTER.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE function code)
- SJC$_SWAP
- SJC$_NO_SWAP
The SJC$_SWAP item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for batch execution queues. It specifies that jobs initiated from a queue can be swapped. It is the default.
The SJC$_NO_SWAP item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that jobs in this queue cannot be swapped.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_TERMINAL
- SJC$_NO_TERMINAL
The SJC$_TERMINAL item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output queues. It specifies that the queue being created is a terminal queue.
The SJC$_BATCH, SJC$_PRINTER, SJC$_SERVER, and SJC$_TERMINAL item codes are mutually exclusive. If none of these item codes are specified, the default is SJC$_PRINTER.
The SJC$_NO_TERMINAL item code is a Boolean item code. It designates the queue type as printer rather than terminal. It is the default.
For the SJC$_START_QUEUE function code, SJC$_TERMINAL and SJC$_NO_TERMINAL are supported for compatibility with VAX/VMS Version 4.n, but might not be supported in the future. For SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_NO_TERMINAL is supported for compatibility with VAX/VMS Version 4.n, and might not be supported in the future.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_TOP_OF_FILE
The SJC$_TOP_OF_FILE item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output queues. It specifies that printing is to be resumed at the beginning of the file.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE function code)
SJC$_UIC
The SJC$_UIC item code is an input value item code. This value specifies the 4-byte UIC of the user on behalf of whom the request is made. By default, the UIC is taken from the requesting process.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_USERNAME
The SJC$_USERNAME item code is an input value item code. It specifies the user name of the user on behalf of whom the request is made. The buffer must specify a string from 1 to 12 characters. By default, the user name is taken from the requesting process.
You need CMKRNL privilege to use this item code.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
- SJC$_WSDEFAULT
- SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT
The SJC$_WSDEFAULT item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for batch jobs and execution queues. It specifies pagelets (on Alpha and Integrity server systems), the default working set size for batch jobs or jobs initiated from a batch queue, or the default working set size of a symbiont process connected to an output queue. A symbiont process can control several output queues; however, the default working set size of the symbiont process is established by the first queue to which it is connected. The buffer must contain a longword integer value in the range 1 through 65,535.
The SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the system is to determine the working set default. It is the default.
|
Value Specified for Job? |
Value Specified for Queue? |
Action Taken |
|---|---|---|
|
No |
No |
Use UAF value |
|
No |
Yes |
Use value for queue |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Use lower of the two |
|
Yes |
No |
Compare specified value with UAF value; use lower |
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_WSEXTENT
- SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT
The SJC$_WSEXTENT item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for batch jobs and execution queues. It specifies, pagelets (on Alpha and Integrity server systems), the working set extent for batch jobs or jobs initiated from a batch queue, or the working set extent of a symbiont process connected to an output queue. A symbiont process can control several output queues; however, the working set extent of the symbiont process is established by the first queue to which it is connected. The buffer must contain a longword integer value in the range 1 through 65,535.
The SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the system determine the working set extent. It is the default.
For information about the action taken when you specify a value for SJC$_WSEXTENT for a batch job or batch queue, see the description of the SJC$_WSDEFAULT item code and to 13
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
- SJC$_WSQUOTA
- SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA
The SJC$_WSQUOTA item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful only for batch jobs and execution queues. It specifies, pagelets (on Alpha and Integrity server systems), the working set quota for batch jobs or default WSQUOTA for jobs initiated from a batch queue, or the working set quota of a symbiont process connected to an output queue. A symbiont process can control several output queues; however, the working set quota of the symbiont process is established by the first queue to which it is connected. The buffer must contain a longword integer value in the range 1 through 65,535.
The SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the system is to determine the working set quota. It is the default.
For information about the action taken when you specify a value for SJC$_WSQUOTA for a batch job or batch queue, see the description of the SJC$_WSDEFAULT item code and to 13
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
Description
The Send to Job Controller service creates, stops, and manages queues and the batch and print jobs in those queues. The $SNDJBC and $GETQUI (Get Queue Information) services together provide the user interface to the queue manager and job controller processes. See the description of the $GETQUI service for a discussion of queues and jobs initiated from those queues.
$SNDJBC completes asynchronously; that is, it returns to the caller after queuing the request, without waiting for the operation to complete.
To synchronize the completion of most operations, you use the Send to Job Controller and Wait ($SNDJBCW) service. The $SNDJBCW service is identical to $SNDJBC in every way except that $SNDJBCW returns to the caller after the operation completes.
Types of Queues
The VMS batch and print queuing system supports several types of queues, which aid in the processing of batch and print jobs. The different types of queues can be divided into three major categories according to the way the system processes the jobs assigned to the queue. The three types of queues are execution, generic, and logical. Execution queues schedule jobs for execution; generic and logical queues transfer jobs to execution queues. Within these major classifications, queue type is further defined by the kinds of job the queues can accept for processing. Some types of execution and generic queues accept batch jobs; other types accept print jobs. Logical queues are restricted to print jobs.
- Execution queue. An execution queue schedules jobs for processing. In an OpenVMS Cluster environment, jobs are processed on the node that manages the execution queue. There are two types of execution queues:
Batch execution queue. A batch execution queue can schedule only batch jobs for execution. A batch job executes as a detached process that sequentially runs one or more command procedures; you define the list of command procedures as part of the initial job description. You create a batch execution queue by specifying the SJC$_BATCH item code in the call to the $SNDJBC service.
Output execution queue. An output execution queue schedules print jobs for processing by an independent symbiont process associated with the queue. The job controller sends the symbiont a list of files to process; you define this list of files as part of the initial job description. As the symbiont processes each file, it produces output for the device, such as a printer or terminal, that it controls.
The standard print symbiont image provided by the operating system is designed to print files on hardcopy devices. User-modified or user-written symbionts also can be designed for this or any other file processing activity managed by the batch and print queuing system. The symbiont image that executes jobs from an output queue is specified by the SJC$_PROCESSOR item code. If you omit this item code, the standard print symbiont image, PRTSMB, is associated with the queue.
There are three types of output execution queue:Printer execution queue. This type of queue typically uses the standard print symbiont to direct output to a line printer. You can specify a user-provided symbiont in the SJC$_PROCESSOR item code. You create a printer execution queue by specifying the SJC$_PRINTER item code when you create the output execution queue. A printer execution queue is the default type of output execution queue.
Terminal execution queue. This type of queue typically uses the standard print symbiont to direct output to a terminal printer. You can specify a user-provided symbiont in the SJC$_PROCESSOR item code. You create a terminal execution queue by specifying the SJC$_TERMINAL item code when you create the output execution queue.
Server execution queue. This type of queue uses the user-modified or user-written symbiont you specify in the SJC$_PROCESSOR item code to process the files that belong to jobs in the queue. You create a server execution queue by specifying the SJC$_SERVER item code when you create the output execution queue.
When you create an output execution queue, you can initially mark it as either a printer, terminal, or server execution queue. However, when the queue is started, the symbiont process associated with the queue can change the queue type from the type designated at its creation to a printer, terminal, or server execution queue, as follows:When an output execution queue associated with the standard print symbiont is started, the symbiont determines whether it is controlling a printer or terminal. It communicates this information to the job controller. If necessary, the job controller then changes the type designation of the output execution queue.
When an output execution queue associated with a user-modified or user-written symbiont is started, the symbiont has the option of identifying the queue to the job controller as a server queue. If the user-written or user-modified symbiont does not notify the job controller that it wants to change the queue type designation, the output execution queue retains the queue type designation it received when it was created.
Generic queue. A generic queue holds a job until an appropriate execution queue becomes available to initiate the job; the job controller then requeues the job to the available execution queue. In a cluster environment, a generic queue can direct jobs to execution queues that are located on other nodes in the cluster.
You create a generic queue by specifying the SJC$_GENERIC_QUEUE item code in the call to the $SNDJBC service. You designate each execution queue to which the generic queue can direct jobs by specifying the SJC$_GENERIC_TARGET item code. Because a generic queue can direct jobs to more than one execution queue, you can specify the SJC$_GENERIC_TARGET item code up to 124 times in a single call to $SNDJBC to define a complete set of execution queues for any generic queue. If you do not specify the SJC$_GENERIC_TARGET item code, the generic queue directs jobs to any execution queue that is the same type of queue as the generic queue; that is, a generic batch queue will direct a job to any available batch execution queue, and so on. There is one exception: a generic queue will not direct work to any execution queue that was created in a call to $SNDJBC that specified the SJC$_NO_GENERIC_SELECTION item code.
There are two types of generic queue:Generic batch queue. A generic batch queue can direct jobs only to batch execution queues. You create a generic batch queue by specifying both the SJC$_GENERIC_QUEUE and SJC$_BATCH item codes in the call to the $SNDJBC service.
Generic output queue. A generic output queue can direct jobs to any of the three types of output execution queue: printer, terminal, or server. Creating a generic output queue that directs jobs to any combination of the three types of output execution queue is possible. Typically, however, when you create a generic output queue, you specify a list of type-specific target queues. This way, the generic output queue directs jobs to a single type of output execution queue. Thus, you can control whether the jobs submitted to the generic output execution queue are output on a line printer or a terminal printer or are sent to a server symbiont for processing. You create a generic output queue by specifying the SJC$_GENERIC_QUEUE item code in the call to the $SNDJBC service.
Logical queue. A logical queue performs the same function as a generic output queue, except that a logical queue can direct jobs to only a single printer, terminal, or server execution queue. A logical queue is only an output queue that has been assigned to transfer its jobs to one execution queue.
To change an output queue into a logical queue, you make a call to the $SNDJBC service while the output queue is in a stopped state. The call must specify the SJC$_ASSIGN_QUEUE function code and the SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE item code. You use the SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE item code to specify the execution queue to which the logical queue should direct jobs. When the logical queue is started, it automatically requeues its jobs to the specified execution queue as that execution queue becomes available. You can change a logical queue back to its original output queue definition by specifying the SJC$_DEASSIGN_QUEUE function code in a subsequent call to the $SNDJBC service.
Queue Protection
This section describes UIC-based protection checking that is performed by the $SNDJBC service to control access to queues.
As an alternative to this form of protection checking, you can associate ACLs with queues using the appropriate security services. See the $GET_SECURITY and $SET_SECURITY system services for more information.
When you create a queue, you assign it a UIC by using the SJC$_OWNER_UIC item code. If you do not specify this item code, the queue is given the default UIC [1,4].
You can assign a queue a protection mask by specifying the SJC$_PROTECTION item code. This protection mask specifies read, submit, manage, and delete access for the four categories of user: Owner, Group, World, and System.
In addition, certain queue operations require the caller of $SNDJBC to have certain privileges. The function codes that require privileges are listed in the Privileges and Restrictions section.
When a job is submitted to a queue, it is assigned a UIC that is the same as the UIC of the process submitting the job, unless the SJC$_UIC item code is specified to supply a different UIC.
For each requested operation, the $SNDJBC service checks the UIC and privileges of the requesting process against the UIC of the queue, protection specified for the queue, and the privileges, if any, required for the operation. This checking is performed in a way similar to the way that the file system checks access to a file by comparing the owner UIC and protection of the file with the UIC and privileges of the requester.
Operations that apply to jobs are checked against read and delete protection specified for the queue in which the job is entered and the owner UIC of the job. In general, read access to a job allows you to determine that the job exists; delete access to a job allows you to affect the job.
Operations that apply to queues are checked against the submit and manage protection specified for the queue and the owner UIC of the queue. In general, submit access to a queue allows you to submit jobs to the queue; manage access to a queue allows you to act as an operator for the queue, including the ability to affect jobs in the queue, to affect accounting, and to alter queues. OPER privilege grants manage access to all queues.
Privileges and Restrictions
- SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE_MANAGER
- SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER
- SJC$_STOP_QUEUE_MANAGER
- SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
- SJC$_DEFINE_CHARACTERISTIC
- SJC$_DEFINE_FORM
- SJC$_DELETE_CHARACTERISTIC
- SJC$_DELETE_FORM
- SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE
- SJC$_START_ACCOUNTING
- SJC$_STOP_ACCOUNTING
- SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE
- SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB
- SJC$_ADD_FILE
- SJC$_CLOSE_DELETE
- SJC$_CLOSE_JOB
- SJC$_CREATE_JOB
- SJC$_ENTER_FILE
- SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
- SJC$_ASSIGN_QUEUE
- SJC$_DEASSIGN_QUEUE
- SJC$_DISABLE_AUTOSTART
- SJC$_ENABLE_AUTOSTART
- SJC$_MERGE_QUEUE
- SJC$_PAUSE_QUEUE
- SJC$_RESET_QUEUE
- SJC$_START_QUEUE
- SJC$_STOP_ALL_QUEUES_ON_NODE
- SJC$_STOP_QUEUE
- SJC$_ABORT_JOB
- SJC$_ALTER_JOB
- SJC$_DELETE_JOB
- SJC$_BATCH_CHECKPOINT
- SJC$_WRITE_ACCOUNTING
To specify a scheduling priority (using the SJC$_PRIORITY item code) higher than the value of the system parameter MAXQUEPRI, the caller needs OPER or ALTPRI privilege.
- SJC$_OWNER_UIC
- SJC$_PROTECTION
- SJC$_ACCOUNT_NAME
- SJC$_UIC
- SJC$_USERNAME
Required Quota
To specify the astadr argument, the process must have sufficient ASTLM
quota.
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR, $TRNLNM
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The item list or input buffer cannot be read by the caller; or the return length buffer, output buffer, or status block cannot be written by the caller.
- SS$_BADPARAM
The function code is invalid; the item descriptor contains an invalid buffer length value; a buffer descriptor has an invalid length; or the reserved parameter has a nonzero value.
- SS$_DEVOFFLINE
The job controller process is not running.
- SS$_EXASTLM
You specified the
astadrargument, and the process has exceeded its ASTLM quota.- SS$_ILLEFC
The
efnargument specifies an illegal event flag number.- SS$_INSFMEM
Insufficient space exists for completing the request.
- SS$_IVLOGNAM
Queue form or characteristic name is not a valid logical name.
- SS$_MBFULL
The job controller mailbox is full.
- SS$_MBTOOSML
The mailbox message is too large for the job controller mailbox.
- SS$_SHELVED
The job controller attempted to access a shelved file. The service does not automatically unshelve files.
- SS$_UNASEFC
The
efnargument specifies an unassociated event flag cluster.
Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block
- JBC$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- JBC$_AUTONOTSTART
The queue is autostart active, but not started. You have tried to start an autostart queue when none of its available nodes has autostart enabled.
- JBC$_BUFTOOSMALL
The request could not be completely satisfied due to limited buffer size. The amount of information retrieved in response to the query exceeds the amount of data the queue manager can return in response to a single request.
- JBC$_DELACCESS
The file protection of the specified file, which was entered with the delete option, does not allow delete access to the caller.
- JBC$_DUPCHARNAME
The command specified a duplicate characteristic name. Each characteristic must have a unique name.
- JBC$_DUPCHARNUM
The command specified a duplicate characteristic number. Each characteristic must have a unique number.
- JBC$_DUPFORM
The specified form number is invalid because it is already defined; each form must have a unique form number.
- JBC$_DUPFORMNAME
The command specified a duplicate form name. Each form must have a unique name.
- JBC$_EMPTYJOB
The open job cannot be closed because it contains no files.
- JBC$_EXECUTING
The parameters of the specified job cannot be modified because the job is currently executing.
- JBC$_INCDSTQUE
The type of the specified destination queue is inconsistent with the requested operation.
- JBC$_INCFORMPAR
The specified length, width, and margin parameters are inconsistent; the value of the difference between the top and bottom margin parameters must be less than the form length, and the difference between the left and right margin parameters must be less than the line width.
- JBC$_INCOMPLETE
The requested queue management operation cannot be executed because a previously requested queue management operation has not yet completed.
- JBC$_INCQUETYP
The type of the specified queue is inconsistent with the requested operation.
- JBC$_INTERNALERROR
An internal error caused loss of process status. A system error prevented the queue manager from obtaining the completion status of a process.
- JBC$_INVCHANAM
A specified characteristic name is not syntactically valid.
- JBC$_INVDSTQUE
The destination queue name is not syntactically valid.
- JBC$_INVFORNAM
The form name is not syntactically valid.
- JBC$_INVFUNCOD
The specified function code is invalid.
- JBC$_INVITMCOD
The item list contains an invalid item code.
- JBC$_INVPARLEN
The length of a specified string is outside the valid range for that item code.
- JBC$_INVPARVAL
A parameter value specified for an item code is outside the valid range for that item code.
- JBC$_INVQUENAM
The queue name is not syntactically valid.
- JBC$_ITMREMOVED
The meaningless items were removed from the request. One or more item codes not meaningful to this command were specified. The command is processed and the meaningless items are ignored.
- JBC$_JOBNOTEXEC
The specified job is not executing.
- JBC$_JOBQUEDIS
The request cannot be executed because the system job queue manager has not been started.
- JBC$_JOBQUEENA
The system job queue manager cannot be started because it is already running.
- JBC$_MISREQPAR
An item code that is required for the specified function code has not been specified.
- JBC$_NOAUTOSTART
The node does not have the autostart feature enabled.
- JBC$_NODSTQUE
The specified destination queue does not exist.
- JBC$_NOOPENJOB
The requesting process did not open a job with the SJC$_CREATE_JOB function.
- JBC$_NOPRIV
The queue protection denies access to the queue for the specified operation.
- JBC$_NOQUESPACE
The system job queue file was full and could not be extended.
- JBC$_NORESTART
The specified job cannot be requeued because it was not defined as restartable.
- JBC$_NOSUCHCHAR
The specified characteristic does not exist.
- JBC$_NOSUCHENT
There is no job with the specified entry number.
- JBC$_NOSUCHFORM
The specified form does not exist.
- JBC$_NOSUCHJOB
The specified job does not exist.
- JBC$_NOSUCHMGR
The specified queue manager does not exist.
- JBC$_NOSUCHNODE
The specified node does not exist.
- JBC$_NOSUCHQUE
The specified queue does not exist.
- JBC$_NOTALLREQUE
Not all jobs in the source queue could be requeued to the target queue. Some of the jobs specified were not suitable for execution on the specified target queue.
- JBC$_NOTASSIGN
The specified queue cannot be deassigned because it is not assigned.
- JBC$_NOTMEANINGFUL
The specified item code is no longer meaningful.
- JBC$_NOTSUPPORTED
The specified item code or function code is not supported.
- JBC$_PRIOSMALL
The scheduling priority has a smaller value than requested. A user without ALTPRI or OPER privilege specified a value for a job's priority that exceeded the queue's maximum priority for nonprivileged jobs. The job is entered in the queue, but its scheduling priority is lower than the value requested by the user.
- JBC$_QMANNOTSTARTED
The queue manager could not be started.
- JBC$_QUEDISABLED
The disabled queue cannot be modified, nor can jobs be submitted to it.
- JBC$_QUENOTMOD
The modifications were not made because the queue was not stopped.
- JBC$_QUENOTSTOP
The specified queue cannot be deleted because it is not in a stopped state.
- JBC$_REFERENCED
The specified queue cannot be deleted because of existing references by other queues or jobs.
- JBC$_STARTED
The specified queue cannot be started because it is already running.
- JBC$_STKNOTCHANGE
The stock associated with a form cannot be changed.
- JBC$_TOOMUCHINFO
The size of the data in request exceeds system constraints. The amount of data specified for a record within the queue manager's database is too large.
When you use the SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB function code, the return value is the exit status of the specified job.
When you start a symbiont queue with the SJC$_START_QUEUE function code or the SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE function code with the SJC$_CREATE_START item code, any error encountered by the symbiont process will be returned in the IOSB.
Examples
$ vfyold = f$verify(1) $ create sys$scratch:accounting.c #include <efndef.h> #include <lib$routines.h> #include <sjcdef.h> #include <ssdef.h> #include <starlet.h> #include <stddef.h> #include <stsdef.h> struct ItemList3 { short int ItemLength; short int ItemCode; void *ItemBuffer; void *ItemRetLen; }; #define MAXITMLST 3 main() { int i; struct ItemList3 JbcIL[MAXITMLST]; unsigned short int IOSB[4]; int RetStat, JbcMask, JbcFunc; /* To start accounting: */ JbcFunc = SJC$_START_ACCOUNTING; /* Specify image and interactive */ JbcMask = SJC$M_ACCT_IMAGE | SJC$M_ACCT_INTERACTIVE; i = 0; JbcIL[i].ItemLength = sizeof( JbcMask ); JbcIL[i].ItemCode = SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES; JbcIL[i].ItemBuffer = (void *) &JbcMask; JbcIL[i++].ItemRetLen = NULL; JbcIL[i].ItemLength = 0; JbcIL[i].ItemCode = 0; JbcIL[i].ItemBuffer = NULL; JbcIL[i++].ItemRetLen = NULL; RetStat = sys$sndjbcw(EFN$C_ENF,JbcFunc,0, JbcIL,IOSB,0,0); if (!$VMS_STATUS_SUCCESS( RetStat )) lib$signal( RetStat ); if (!$VMS_STATUS_SUCCESS( IOSB[0] )) lib$signal( IOSB[0] ); return SS$_NORMAL; } $ cc/decc/prefix=all sys$scratch:accounting.c/object=sys$scratch: $ link/executable=sys$scratch:accounting.exe sys$scratch:accounting $ show accounting $ prvold = f$setprv("OPER") $ run sys$scratch:accounting $ show accounting $ priv = f$setprv(prvold) $ vfyold = f$verify(vfyold) $ exit
This C program demonstrates an $SNDJBCW call.
! Declare system service related symbols INTEGER*4 SYS$SNDJBCW, 2 STATUS INCLUDE '($SJCDEF)' ! Define item list structure STRUCTURE /ITMLST/ UNION MAP INTEGER*2 BUFLEN, ITMCOD INTEGER*4 BUFADR, RETADR END MAP MAP INTEGER*4 END_LIST END MAP END UNION END STRUCTURE ! Define I/O status block structure STRUCTURE /IOSBLK/ INTEGER*4 STS, ZEROED END STRUCTURE ! Declare $SNDJBCW item list and I/O status block RECORD /ITMLST/ SUBMIT_LIST(6) RECORD /IOSBLK/ IOSB ! Declare variables used in $SNDJBCW item list CHARACTER*9 QUEUE /'SYS$BATCH'/ CHARACTER*23 FILE_SPECIFICATION /'$DISK1:[COMMON]TEST.COM'/ CHARACTER*12 USERNAME /'PROJ3036 '/ INTEGER*4 ENTRY_NUMBER ! Initialize item list for the enter file operation SUBMIT_LIST(1).BUFLEN = 9 SUBMIT_LIST(1).ITMCOD = SJC$_QUEUE SUBMIT_LIST(1).BUFADR = %LOC(QUEUE) SUBMIT_LIST(1).RETADR = 0 SUBMIT_LIST(2).BUFLEN = 23 SUBMIT_LIST(2).ITMCOD = SJC$_FILE_SPECIFICATION SUBMIT_LIST(2).BUFADR = %LOC(FILE_SPECIFICATION) SUBMIT_LIST(2).RETADR = 0 SUBMIT_LIST(3).BUFLEN = 12 SUBMIT_LIST(3).ITMCOD = SJC$_USERNAME SUBMIT_LIST(3).BUFADR = %LOC(USERNAME) SUBMIT_LIST(3).RETADR = 0 SUBMIT_LIST(4).BUFLEN = 0 SUBMIT_LIST(4).ITMCOD = SJC$_NO_LOG_SPECIFICATION SUBMIT_LIST(4).BUFADR = 0 SUBMIT_LIST(4).RETADR = 0 SUBMIT_LIST(5).BUFLEN = 4 SUBMIT_LIST(5).ITMCOD = SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER_OUTPUT SUBMIT_LIST(5).BUFADR = %LOC(ENTRY_NUMBER) SUBMIT_LIST(5).RETADR = 0 SUBMIT_LIST(6).END_LIST = 0 ! Call $SNDJBCW service to submit the batch job STATUS = SYS$SNDJBCW (, 2 %VAL(SJC$_ENTER_FILE),, 2 SUBMIT_LIST, 2 IOSB,,) IF (STATUS) STATUS = IOSB.STS IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$SIGNAL (%VAL(STATUS)) END
This Fortran program demonstrates the use of the $SNDJBCW service to submit a batch job that is to execute on behalf of another user. No log file is produced for the batch job. This program saves the job's entry number. You need CMKRNL privilege to run this program.
$SNDJBCW
Send to Job Controller and Wait — The Send to Job Controller and Wait and $GETQUI services together provide the user interface to the Job Controller (JBC) facility. The $SNDJBW service allows you to create, stop, and manage queues and the jobs in those queues. Queues can be generic, batch, execution, or output queues. Jobs can be batch or print jobs.
Format
SYS$SNDJBCW
[efn] ,func [,nullarg] [,itmlst] [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm]C Prototype
int sys$sndjbcw
(unsigned int efn, unsigned short int func, unsigned int nullarg,
void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params),
int astprm);Description
The $SNDJBCW service queues a request to the job controller. For most operations, $SNDJBCW completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller after the operation completes. However, if the requested operation is a pause queue, stop queue, or abort job operation, $SNDJBCW returns to the caller after queuing the request. There is no way to synchronize completion of these operations. Also, $SNDJBCW does not wait for a job to complete before it returns to the caller. To synchronize completion of a job, the caller must specify the SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB function code.
The $SNDJBCW service is identical to the Send to Job Controller ($SNDJBC) service except that $SNDJBC completes asynchronously; the $SNDJBC service returns to the caller immediately after queuing the request, without waiting for the operation to complete.
For additional information about $SNDJBCW, refer to the documentation of $SNDJBC.
The $SNDJBC and $SNDJBCW services supersede the Send Message to Symbiont Manager ($SNDSMB) and Send Message to Accounting Manager ($SNDACC) services. You should write new programs using $SNDJBC or $SNDJBCW, instead of $SNDSMB or $SNDACC. You should convert old programs using $SNDSMB or $SNDACC to use $SNDJBC or $SNDJBCW, as convenient.
$SNDOPR
Send Message to Operator — Performs the following functions: 1) Sends a user request to operator terminals 2) Sends a user cancellation request to operator terminals 3) Sends an operator reply to a user terminal 4) Enables an operator terminal 5) Displays the status of an operator terminal 6) Initializes the operator log file
Format
SYS$SNDOPR msgbuf ,[chan]C Prototype
int sys$sndopr (void *msgbuf, unsigned short int chan);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
User buffer specifying the operation to be performed and the information needed to perform
that operation. The msgbuf argument is the address of a character string
descriptor pointing to the buffer.
|
Request Code |
Corresponding Operation |
|---|---|
|
OPC$_RQ_CANCEL |
Sends a user cancellation request to specified operator terminals. You use this
request code to notify one or more operators that a previous request is to be canceled. To
specify OPC$_RQ_CANCEL, you must also specify the |
|
OPC$_RQ_LOGI |
Initializes the operator log file. |
|
OPC$_RQ_REPLY |
Sends an operator reply to a user who has made a request. Operators use this request code to report the status of a user request. The format of the message buffer for this request is the format of the reply found in the user's mailbox after the call to $SNDOPR completes. All functions of $SNDOPR that deliver a reply to a mailbox do so in the format described for this request code. |
|
OPC$_RQ_RQST |
Sends a user request to operator terminals. This request code is used to make an
operator request. If you specify a reply to the request (by using the
|
|
OPC$_RQ_STATUS |
Reports the status of an operator terminal. Operators use this request to display the operator classes for which the specified terminal is enabled and a list of outstanding requests. |
|
OPC$_RQ_TERME |
Enables an operator terminal. You use this request to enable a specified terminal to receive operator messages. |
The following diagrams depict the message buffer for each of these request codes. Each field within a diagram has a symbolic name, which serves to identify the field; in other words, these names specify offsets into the message buffer. The list following each diagram shows each field name and what its contents can or should be. The $OPCDEF macro defines the field names, as well as any other symbolic name that can be specified as the contents of a field.
Message Buffer Format for OPC$_RQ_RQST
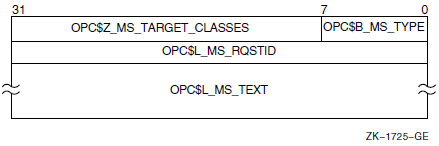
|
OPC$B_MS_TYPE |
This 1-byte field contains the request code OPC$_RQ_RQST. | |
|
OPC$B_MS_TARGET_CLASSES |
This 3-byte field contains a 24-bit bit vector that specifies which operator terminal types are to receive the request. The $OPCDEF macro defines symbolic names for the operator terminal types. You construct the bit vector by specifying the desired symbolic names in a logical OR operation. Following is the symbolic name of each operator terminal type: | |
|
OPC$M_NM_CARDS |
Card device operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_CENTRL |
Central operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_CLUSTER |
OpenVMS Cluster operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_DEVICE |
Device status information | |
|
OPC$M_NM_DISKS |
Disk operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_NTWORK |
Network operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_TAPES |
Tape operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_PRINT |
Printer operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_SECURITY |
Security operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_OPER1 through OPC$M_NM_OPER12 |
System-manager-defined operator functions | |
|
OPC$L_MS_RQSTID |
This longword field contains a user-supplied longword message code. | |
|
OPC$L_MS_TEXT |
This variable-length field contains an ASCII string specifying text to be sent to the specified operator terminals. $SNDOPR uses the buffer size of the device to which the message is being sent. | |
Message Buffer Format for OPC$_RQ_CANCEL

|
OPC$B_MS_TYPE |
This 1-byte field contains the request code OPC$_RQ_CANCEL. | |
|
OPC$B_MS_TARGET_CLASSES |
This 3-byte field contains a 24-bit bit vector that specifies which operator terminal types are to receive the cancellation request. The $OPCDEF macro defines symbolic names for the operator terminal types. You construct the bit vector by specifying the desired symbolic names in a logical OR operation. Following is the symbolic name of each operator terminal type: | |
|
OPC$M_NM_CARDS |
Card device operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_CENTRL |
Central operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_SECURITY |
Security operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_CLUSTER |
OpenVMS Cluster operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_DEVICE |
Device status information | |
|
OPC$M_NM_DISKS |
Disk operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_NTWORK |
Network operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_TAPES |
Tape operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_PRINT |
Printer operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_OPER1 through OPC$M_NM_OPER12 |
System-manager-defined operator functions | |
|
OPC$L_MS_RQSTID |
This longword field contains a user-supplied longword message code. | |
Message Buffer Format for OPC$_RQ_REPLY
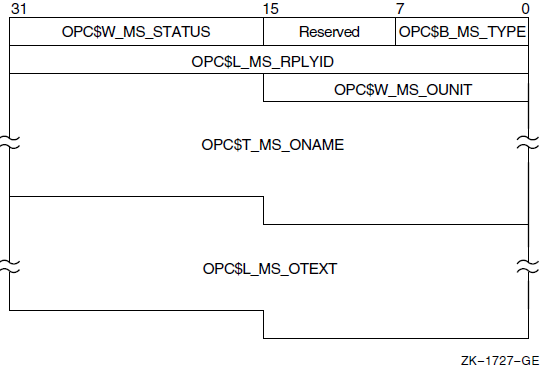
OPC$B_MS_TYPE | This 1-byte field contains the request code OPC$_RQ_REPLY. |
Reserved | This 1-byte field is reserved for future use. |
OPC$W_MS_STATUS | This 2-byte field contains the low-order word of the longword condition value that $SNDOPR returns in the mailbox specified by the
|
OPC$L_MS_RPLYID | This 4-byte field contains a user-supplied message code. |
OPC$W_MS_OUNIT | This 2-byte field contains the unit number of the terminal to which the operator reply is to be sent. To obtain the unit number of the terminal, you can call $GETDVI, specifying the DVI$_FULLDEVNAM item code. The information returned will consist of the node name and device name as a padded string. Because the unit number is found on the tail end of the string, you must parse the string. One way to do this is, starting from the tail end, to search for the first alphabetic character; the digits to the right of this alphabetic character constitute the unit number. After extracting the unit number, count the remaining characters in the string. Then, construct a counted ASCII string and use this for the following field, OPC$T_MS_ONAME. |
OPC$T_MS_ONAME | This variable-length field contains a counted ASCII string specifying the device name of the terminal that is to receive the operator reply. The maximum total length of the string is 14 bytes. See the preceding field description (OPC$W_MS_OUNIT) to learn how to obtain the device name. |
OPC$L_MS_OTEXT | This variable-length field contains an ASCII string specifying operator-written text to be sent to the user terminal. The length of the string must be in the range 0 to 255 bytes. This field is optional. |
Message Buffer Format for OPC$_RQ_TERME
|
OPC$B_MS_TYPE |
This 1-byte field contains the request code OPC$_RQ_TERME. | |
|
OPC$B_MS_ENAB_TERMINALS |
This 3-byte field contains a user-supplied value. The value 0 indicates that the specified terminal is to be disabled for the specified operator classes. Any nonzero value indicates that the specified terminal is to be enabled for the specified operator classes. | |
|
OPC$B_MS_MASK |
This 4-byte field contains a 4-byte bit vector that specifies which operator terminal types are to be enabled or disabled for the specified terminal. The $OPCDEF macro defines symbolic names for the operator terminal types. You construct the bit vector by specifying the desired symbolic names in a logical OR operation. Following is the symbolic name of each operator terminal type: | |
|
OPC$M_NM_CARDS |
Card device operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_CENTRL |
Central operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_SECURITY |
Security operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_CLUSTER |
OpenVMS Cluster operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_DEVICE |
Device status information | |
|
OPC$M_NM_DISKS |
Disk operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_NTWORK |
Network operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_TAPES |
Tape operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_PRINT |
Printer operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_OPER1 through OPC$M_NM_OPER12 |
System-manager-defined operator functions | |
|
OPC$W_MS_OUNIT |
This 2-byte field contains the unit number of the operator terminal to be enabled or disabled for the specified operator terminal types. To obtain the unit number of the terminal, you can call $GETDVI, specifying the DVI$_FULLDEVNAM item code. The information returned will consist of the node name and device name as a padded string. Because the unit number is found on the tail end of the string, you must parse the string. One way to do this is, starting from the tail end, to search for the first alphabetic character; the digits to the right of this alphabetic character constitute the unit number. After extracting the unit number, count the remaining characters in the string. Then, construct a counted ASCII string and use this for the following field, OPC$T_MS_ONAME. | |
|
OPC$T_MS_ONAME |
This variable-length field contains a counted ASCII string specifying the device name of the operator terminal to be enabled or disabled for the specified operator terminal types. The maximum total length of the string is 16 bytes. See the preceding field description (OPC$W_MS_OUNIT) to learn how to obtain the device name. | |
Message Buffer Format for OPC$_RQ_STATUS
OPC$B_MS_TYPE | This 1-byte field contains the request code OPC$_RQ_STATUS. |
Reserved | This 3-byte field is reserved for future use. |
Reserved | This 4-byte field is reserved for future use. |
OPC$W_MS_OUNIT | This 2-byte field contains the unit number of the operator terminal whose status is to be requested. To obtain the unit number of the terminal, you can call $GETDVI, specifying the DVI$_FULLDEVNAM item code. The information returned will consist of the node name and device name as a padded string. Because the unit number is found on the tail end of the string, you must parse the string. One way to do this is, starting from the tail end, to search for the first alphabetic character; the digits to the right of this alphabetic character constitute the unit number. After extracting the unit number, count the remaining characters in the string. Then, construct a counted ASCII string and use this for the following field, OPC$T_MS_ONAME. |
OPC$T_MS_ONAME | This variable-length field contains a counted ASCII string specifying the device name of the operator terminal whose status is requested. The maximum total length of the string is 14 bytes. See the preceding field description (OPC$W_MS_OUNIT) to learn how to obtain the device name. |
Message Buffer Format for OPC$_RQ_LOGI
|
OPC$B_MS_TYPE |
This 1-byte field contains the request code OPC$_RQ_LOGI. | |
|
OPC$B_MS_TARGET_CLASSES |
This 3-byte field contains a 24-bit bit vector that CLASSES specifies which operator terminal types are to receive the cancellation request. The $OPCDEF macro defines symbolic names for the operator terminal types. You construct the bit vector by specifying the desired symbolic names in a logical OR operation. Following is the symbolic name of each operator terminal type: | |
|
OPC$M_NM_CARDS |
Card device operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_CENTRL |
Central operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_SECURITY |
Security operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_CLUSTER |
OpenVMS Cluster operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_DEVICE |
Device status information | |
|
OPC$M_NM_DISKS |
Disk operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_NTWORK |
Network operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_TAPES |
Tape operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_PRINT |
Printer operator | |
|
OPC$M_NM_OPER1 through OPC$M_NM_OPER12 |
System-manager-defined operator functions | |
|
OPC$L_MS_RQSTID |
This longword field contains a user-supplied value. The value 0 specifies that the current operator log file is to be closed and a new log file opened with all classes enabled (OPC$B_MS_TARGET is ignored). The value 1 specifies that the current operator log file is to be closed but no new log file is to be opened. The value 2 specifies that the classes in OPC$B_MS_TARGET are added to the current operator log file classes. A log file is opened if necessary. The value 3 specifies that the operator classes in OPCB_MS_TARGET are to be removed from the operator log file classes. If all classes are removed, the log file is closed. | |
|
OPC$W_MS_OUNIT |
This 2-byte field contains the unit number of the operator terminal that is making the
initialization request. To obtain the unit number of the terminal, you can call $GETDVI,
specifying the
DVI$_FULLDEVNAM After extracting the unit number, count the remaining characters in the string. Then, construct a counted ASCII string and use this for the following field, OPC$T_MS_ONAME. | |
|
OPC$T_MS_ONAME |
This variable-length field contains a counted ASCII string specifying the device name of the operator terminal that is making the initialization request. The maximum total length of the string is 14 bytes. See the preceding field description (OPC$W_MS_OUNIT) to learn how to obtain the device name. | |
| OpenVMS usage: | channel |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Channel assigned to the mailbox to which the reply is to be sent. The
chan argument is a longword value containing the number of the channel.
If you do not specify chan or specify it as the value 0 (the default), no
reply is sent.
If a reply from the operator is desired, you must specify the chan
argument.
Description
Sends a user request to operator terminals
Sends a user cancellation request to operator terminals
Sends an operator reply to a user terminal
Enables an operator terminal
Displays the status of an operator terminal
Initializes the operator log file
This system service requires system dynamic memory; it cannot be called from kernel mode.
Construct the message buffer and place its final length in the first word of the buffer descriptor.
Call the $SNDOPR service.
Check the condition value returned in R0 to make sure the request was successfully made.
Issue a read request to the mailbox specified, if any.
When the read operation completes, check the 2-byte condition value in the OPC$W_MS_STATUS field to make sure that the operation was performed successfully.
%%%%%%%%%%% OPCOM dd-mmm-yyyy hh:mm:ss.cc message specific information
%%%%%%%%%%% OPCOM 30-DEC-2001 13:44:40.37
Operator _NODE$LTA5: has been enabled, username HOEBLE%%%%%%%%%%% OPCOM 30-DEC-2001 12:11:10.48
Operator status for operator _NODE$OPA0:
CENTRAL, PRINTER, TAPES, DISKS, DEVICES, CARDS, CLUSTER, SECURITY,
OPER1, OPER2, OPER3, OPER4, OPER5, OPER6, OPER7, OPER8, OPER9,
OPER10, OPER11, OPER12%%%%%%%%%%% OPCOM 30-DEC-2001 12:57:32.25
Request 1285, from user ROSS on NODE_NAME
Please mount device _NODE$DMA0:Required Access or Privileges
Enabling a terminal as an operator's terminal
Replying to or canceling a user's request
Initializing the operator communication log file
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The message buffer or buffer descriptor cannot be read by the caller.
- SS$_BADPARAM
The specified message has a length of 0 or has more than 986 bytes.
- SS$_DEVNOTMBX
The channel specified is not assigned to a mailbox.
- SS$_INSFMEM
The service was called from kernel mode or the system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the service.
- SS$_IVCHAN
You specified an invalid channel number. An invalid channel number is one that is 0 or a number larger than the number of channels available.
- SS$_MBFULL
The mailbox used to support communication is full. Retry at a later time.
- OPC$_NOPERATOR
The service completed successfully; the Operator Communications Manager (OPCOM) is not running and the message will not be sent. Note that OPC$_NOPERATOR is a success status and must be tested for explicitly.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The process does not have the privilege to reply to or cancel a user's request; the process does not have read/write access to the specified mailbox; or the channel was assigned from a more privileged access mode.
Condition Values Returned in the Mailbox
- OPC$_BLANKTAPE
The service completed successfully; the operator responded with the DCL command REPLY/BLANK_TAPE=n.
- OPC$_INITAPE
The service completed successfully; the operator responded with the DCL command REPLY/INITIALIZE_TAPE=n.
- OPC$_NOPERATOR
The service completed successfully; no operator terminal was enabled to receive the message.
- OPC$_RQSTCMPLTE
The service completed successfully; the operator completed the request.
- OPC$_RQSTPEND
The service completed successfully; the operator will perform the request when possible.
- OPC$_RQSTABORT
The operator could not satisfy the request.
- OPC$_RQSTCAN
The caller canceled the request.
Examples
#include <descrip.h> /* VMS string descriptors */ #include <lib$routines.h> /* VMS LIB$ routine prototypes */ #include <opcdef.h> /* $SNDOPR request structures and definitions */ #include <ssdef.h> /* VMS SS$_x status values */ #include <stsdef.h> /* $VMS_STATUS_SUCCESS */ #include <starlet.h> /* VMS system service prototypes */ #include <stddef.h> /* Define offsetof */ #include <stdlib.h> /* malloc, free, et. al. */ #include <string.h> /* string functions, memcpy, et. al. */ main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int status; /* Status of system calls */ short length = 0; /* Length of message text */ union /* Target OPC$_ classes bitmask */ { int longword_value; /* Longword, for use with OPC$M_ values */ char byte_value[3]; /* By byte, to load opc$z_ms_target_classes */ } target_classes; struct _opcdef *sndopr_rqst; /* Pointer to $SNDOPR message buffer */ /* * Descriptors for input message text string, $SNDOPR message buffer, and prompt. */ struct dsc$descriptor input_desc = { 0, DSC$K_DTYPE_T, DSC$K_CLASS_S, 0 }; struct dsc$descriptor req_desc = { 0, DSC$K_DTYPE_T, DSC$K_CLASS_S, 0 }; $DESCRIPTOR(prompt_desc, "Request> "); /* * Check for too many arguments on command line */ if (argc > 2) return SS$_OVRMAXARG; /* * If provided on the command line, use that as the message string. */ if (argc > 1) { length = strlen(argv[1]); input_desc.dsc$a_pointer = argv[1]; } /* * If no message text so far, prompt the user for the message text. * Use a dynamic string descriptor to contain the supplied text. */ while (length == 0) { input_desc.dsc$b_class = DSC$K_CLASS_D; status = lib$get_input(&input_desc, &prompt_desc, &length); if ( !$VMS_STATUS_SUCCESS(status) ) return status; }; /* * Allocate a $SNDOPR message structure with enough room for the * message text and the fixed header for a OPC$_RQ_RQST message. */ sndopr_rqst = malloc( length + offsetof(struct _opcdef,opc$l_ms_text) ); if (sndopr_rqst == 0) return SS$_INSFMEM; /* * Fill in the $SNDOPR message structure, including the text. */ sndopr_rqst->opc$b_ms_type = OPC$_RQ_RQST; sndopr_rqst->opc$l_ms_rqstid = 0; target_classes.longword_value = OPC$M_NM_CENTRL; sndopr_rqst->opc$z_ms_target_classes[0] = target_classes.byte_value[0]; sndopr_rqst->opc$z_ms_target_classes[1] = target_classes.byte_value[1]; sndopr_rqst->opc$z_ms_target_classes[2] = target_classes.byte_value[2]; memcpy(&sndopr_rqst->opc$l_ms_text, input_desc.dsc$a_pointer, length); /* * Set up the descriptor for the $SNDOPR message structure and call * the $SNDOPR service. */ req_desc.dsc$w_length = length + offsetof(struct _opcdef,opc$l_ms_text); req_desc.dsc$a_pointer = (char *) sndopr_rqst; status = sys$sndopr(&req_desc, 0); /* * Clean up time. Free the $sndopr request block. If we got a dynamic * string for the input message text, free that too. */ free( sndopr_rqst); if ( input_desc.dsc$b_class == DSC$K_CLASS_D ) lib$sfree1_dd( (unsigned __int64 *) &input_desc ); return status; }
This example allows you to build an operator request and send the request to the operator.
IMPLICIT NONE ! Symbol definitions INCLUDE '($DVIDEF)' INCLUDE '($OPCDEF)' ! Structures for SNDOPR STRUCTURE /MESSAGE/ UNION MAP BYTE TYPE, 2 ENABLE(3) INTEGER*4 MASK INTEGER*2 OUNIT CHARACTER*14 ONAME END MAP MAP CHARACTER*24 STRING END MAP END UNION END STRUCTURE RECORD /MESSAGE/ MSGBUF ! Length of MSGBUF.ONAME INTEGER*4 ONAME_LEN ! Status and routines INTEGER*4 STATUS, 2 LIB$GETDVI, 2 SYS$SNDOPR ! Type MSGBUF.TYPE = OPC$_RQ_TERME ! Enable MSGBUF.ENABLE(1) = 1 ! Operator type MSGBUF.MASK = OPC$M_NM_OPER1 ! Terminal unit number STATUS = LIB$GETDVI (DVI$_UNIT, 2 , 2 'SYS$OUTPUT', 2 MSGBUF.OUNIT,,) IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$SIGNAL (%VAL(STATUS)) ! Terminal name STATUS = LIB$GETDVI (DVI$_FULLDEVNAM, 2 , 2 'SYS$OUTPUT',, 2 MSGBUF.ONAME, 2 ONAME_LEN) IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$SIGNAL (%VAL(STATUS)) ! Remove unit number from ONAME and set up counted string ONAME_LEN = ONAME_LEN - 3 MSGBUF.ONAME(2:ONAME_LEN+1) = MSGBUF.ONAME(1:ONAME_LEN) MSGBUF.ONAME(1:1) = CHAR(ONAME_LEN) ! Call $SNDOPR STATUS = SYS$SNDOPR (MSGBUF.STRING,) IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$SIGNAL(%VAL(STATUS)) ENDThis VSI Fortran for OpenVMS program enables the current terminal to receive OPER1 operator messages.
$SPACE
Skip Tape File — The Space service lets you space (skip) a tape file forward or backward a specified number of blocks. For additional information about this service, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Start Alignment Fault Reporting — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, initializes user image alignment fault reporting.
Format
SYS$START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
report_method ,report_buffer ,buffer_lengthC Prototype
int sys$start_align_fault_report
(int report_method, void *report_buffer, int buffer_length);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_signed |
| type: | longword (signed) |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by value |
report_method argument.|
Value |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
AFR$C_BUFFERED |
Alignment fault PCs and fault addresses are saved in a user-supplied buffer. |
|
AFR$C_EXCEPTION |
Alignment faults are elevated to user mode exceptions. |
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The 32-bit address of the buffer into which to write the fault data. The
report_buffer argument is needed only if the value of the
report_method argument is AFR$C_BUFFERED.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | longword (signed) |
| access: | read |
| mechanism: | by value |
Length of the buffer specified in the report_buffer argument. The
buffer must have a minimum size of AFR$K_USER_LENGTH + 32. However, a larger buffer
allows for more information to be collected.
Description
The Start Alignment Fault Reporting service initializes user image alignment fault reporting.
The $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service allows the user to gather alignment fault data for one image. Reporting is enabled for the life of the image. When the image terminates, the alignment fault reporting is disabled.
User alignment fault data can be written to a buffer or broadcast as an informational exception message.
If the AFR$C_BUFFERED value is given in the
report_method buffer, alignment fault PCs and fault addresses are saved in a user-supplied buffer.
The following diagram illustrates the format in which user alignment fault data is stored in the buffer.
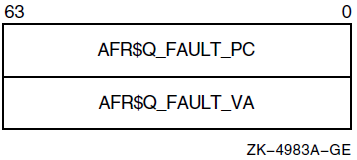
If the AFR$C_EXCEPTION value is given in the report_method argument,
alignment faults are elevated to user mode exceptions. These exceptions can be trapped
in a handler. Otherwise, an informational exception message might be broadcast and the
program continues to execute.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT, $STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The buffer specified in the
report_bufferargument is not accessible.- SS$_AFR_ENABLED
The service has already been called for this image.
- SS$_ARG_GTR_32_BITS
The report buffer's virtual address lies in 64-bit virtual address space.
- SS$_ALIGN
The buffer specified in the
report_bufferargument is not quadword aligned.- SS$_BADPARAM
The buffer size is smaller than that defined by the AFR$K_USER_LENGTH + 32 symbol.
Example
#include <afrdef> #include <stdio> #include <ssdef> #define USER_BUFFER_ITEMS 10 #define GET_BUFFER_SIZE USER_BUFFER_ITEMS*AFR$K_USER_LENGTH #define SAVE_BUFFER_SIZE 128+64 #define fault_pc afr$l_fault_pc_l #define fault_va afr$l_fault_va_l static int usr_buff_len; static char *usr_buff; static int rep_method; void cause_af() { int addr; int *ptr; int arr[2]; addr = (int) &arr[0]; ptr = (int *) ++addr; *ptr = 1; /* cause alignment fault */ } main() { int i; char get_buffer[GET_BUFFER_SIZE]; struct afrdef *data_item; int offset; int status; int return_size; rep_method = AFR$C_BUFFERED; usr_buff_len = SAVE_BUFFER_SIZE; usr_buff = (char *)malloc (usr_buff_len); if(( status = sys$start_align_fault_report(rep_method, usr_buff, usr_buff_len)) != SS$_NORMAL) return(status); for (i=0;i<USER_BUFFER_ITEMS;i++) cause_af(); while (((status = sys$get_align_fault_data (get_buffer, GET_BUFFER_SIZE, &return_size)) > 0) && (return_size > 0)) { /* got some data, print it */ offset = 0; while (offset < return_size) { data_item = (struct afrdef *)(&get_buffer[offset]); printf ("Alignment fault at PC = %8.8X, VA = %8.8X\n", data_item->fault_pc, data_item->fault_va); offset += AFR$K_USER_LENGTH; } } return (status); }
This example shows how to use the $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service to initialize user image alignment fault reporting on Alpha and Integrity server systems.
$START_BRANCH
Start Branch — Adds a new branch to a transaction.
Format
SYS$START_BRANCH
[efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,tid ,tm_name
,bid [,[timout], [acmode], [tx_class]]C Prototype
int sys$start_branch
(unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int tid [4],
void *tm_name, unsigned int bid [4],...);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
flags argument
is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to an option flag. The $DDTMDEF macro
defines symbolic names for these option flags, described in Table 14.
All undefined bits must be 0. If this argument is omitted, no flags are used.| Flag Name | Description |
|---|---|
| DDTM$M_BRANCH_UNSYNCHED | Specifies that the new branch is unsynchronized. If this flag is clear, the new branch is synchronized. |
| DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT | Set this flag if you do not want the transaction to be the default transaction of the calling process. If this flag is clear, the transaction becomes the default transaction of the calling process. An error is returned if this flag is clear and the calling process has an current default transaction. |
| DDTM$M_SYNC | Specifies successful synchronous completion by returning SS$_SYNCH. When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the AST routine is not called, the event flag is not set, and the I/O status block is not filled in. |
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned section.

| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure entry mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The AST routine executed when the service completes, if SS$_NORMAL is returned in R0.
The astadr argument is the address of the entry mask of this
routine. The routine is executed in the same access mode as that of the caller of the
$START_BRANCH service.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The AST parameter passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | trans_id |
| type: | octaword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The identifier (TID) of the transaction to which the new branch will be added.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
The name of the node on which the call was made to $ADD_BRANCH that authorized the new branch to be added to the transaction. Note that this cannot be a cluster alias.
To ensure smooth operation in a mixed-network environment, refer to the chapter entitled Managing DECdtm Services in the VSI OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, for information on defining node names.
| OpenVMS usage: | branch_id |
| type: | octaword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The identifier (BID) of the new branch that is to be added to the transaction.
An BID value of zero is invalid.
| OpenVMS usage: | date_time |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Reserved to OpenVMS.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The access mode of the new branch in this process. This is the least privileged mode that a caller must be in to remove this branch from the transaction by calling $END_BRANCH. Note that it can be removed from the transaction by calling $ABORT_TRANS from any access mode.
This argument only influences the access mode of the first branch in this process. Subsequent branches have the same access mode as the first. The access mode of the new branch is the least privileged of:
The access mode of the caller.
The access mode specified by the
acmodeargument.
Note that if a branch already exists in this process, then neither the access mode of
the caller nor the access mode specified by the acmode argument
may be less privileged than that branch.
The default value of this argument is the access mode of the caller.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
A string that specifies the transaction class for the transaction on the local node if the transaction does not already have a transaction class on the local node. This string is passed in the event reports delivered to Resource Manager identifiers (RMIs) and Resource Manager (RM) participants on the local node.
This argument is ignored if the transaction already has a transaction class on the local node.
This string must be no longer than 31 characters.
Description
The $START_BRANCH system service:
Adds a new branch running in the calling process to the specified transaction.
Adds the local DECdtm transaction manager to the specified transaction if the local DECdtm transaction manager is not already a participant in that transaction.
Sets the default transaction of the calling process to the new transaction, if the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag is clear and the process does not have a default transaction.
Delivers a transaction started event to each RMI in the calling process that meets both of the following conditions:
Requested Transaction Started events for the corresponding transaction type (default or non-default)
Has an access mode that is the same as or more privileged than that specified in this call to $START_BRANCH.
The new branch should have been previously authorized. Authorization is provided either by a matching call to $JOIN_RM with the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag set or by a matching call to $ADD_BRANCH. Two calls, one to $ADD_BRANCH and one to $START_BRANCH or one to $JOIN_RM and one to $START_BRANCH, are said to be matching when the following conditions are true:
The same TID values are passed to both calls.
The BID returned by the call to $ADD_BRANCH or $JOIN_RM is the same as that passed to the call to $START_BRANCH.
The call to $START_BRANCH is made on the node identified by the
tm_nameargument passed to the call to $ADD_BRANCH or on the node on which the call to $JOIN_RM was made.The call to $ADD_BRANCH or $JOIN_RM is made on the node identified by the
tm_nameargument passed to the call to $START_BRANCH.
$START_BRANCH does not check that there has been a matching call to $ADD_BRANCH or
$JOIN_RM unless the tm_name argument passed to $START_BRANCH
specifies the local node.
Note
The atomicity of the transaction is not guaranteed if there is a call to $START_BRANCH that does not have a matching call to $ADD_BRANCH or $JOIN_RM.
Preconditions for the successful completion of $START_BRANCH are:
The local node must have a DECdtm transaction log.
The TP_SERVER process must be running on the local node.
There must not have been a successful call to $START_BRANCH on the local node that passed the specified BID.
If the
tm_nameargument specifies the local node, there must have been a matching call to $ADD_BRANCH or $JOIN_RM on the local node.If the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag is clear, the calling process must not have an unended default transaction.
If this process already contains a branch of this transaction, then the access mode of the caller must be the same as or more privileged than the access mode of that branch.
$START_BRANCH may fail because:
Preconditions were not met.
An abort event occurred for the transaction.
A call to $END_TRANS to end the transaction is in progress and it is too late to add a new branch to the transaction.
The DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear and a call to $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS by the calling process is in progress.
When $START_BRANCH completes successfully:
A new branch running in the calling process has been added to the transaction.
All Transaction Started events reported to RMIs in the calling process have been acknowledged.
If the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear, the transaction is the default transaction of the calling process.
A branch may:
Invoke resource manager operations, explicitly passing the TID.
Invoke resource manager operations without specifying the TID, if the transaction is the default transaction of the calling process, and the resource manager supports default transactions.
Call $ADD_BRANCH to authorize another branch to be added to the transaction.
(The way to invoke a resource manager operation is defined by the interfaces provided by the resource manager; see the resource manager documentation.)
A synchronized branch is removed from the transaction by calling $END_BRANCH, specifying the appropriate BID and TID. An unsynchronized branch is removed from the transaction by DECdtm during commit or abort processing.
The branch is also removed from the transaction (and the transaction aborted):
On termination of the current image or process.
On successful completion of a call to $ABORT_TRANS in the calling process that passes the appropriate TID and BID.
There is also a wait form of the service, $START_BRANCHW.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quotas
BYTLM, ASTLM
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW, $CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW, $END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW, $GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCHW, $START_TRANS, $START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
If returned in R0, the request was successfully queued. If returned in the I/O status block, the service completed successfully.
- SS$_SYNCH
The service completed successfully and synchronously (returned only if the DDTM$M_SYNC flag is set).
- SS$_ACCVIO
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
- SS$_ALRCURTID
- Either:
An attempt was made to make the transaction specified by the
tidargument the default transaction (the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear) when the calling process had an unended default transaction.The DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear and a call to $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS by the calling process was in progress.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Either the options flags were invalid or the
tidargument was omitted but thebidargument was not zero.- SS$_BRANCHSTARTED
There has already been a call to $START_BRANCH on the local node specifying that TID and BID (returned only if the node specified by the
tm_nameargument was the local node).- SS$_CONNECFAIL
The node specified by the
tm_nameargument was not the local node, and there was no communications link between the DECdtm transaction managers on the local node and the specified node.- SS$_EXASTLM
The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
The job buffered I/O byte limit quota (BYTLM) was exceeded.
- SS$_ILLEFC
The event flag number was invalid.
- SS$_INSFARGS
A required argument was missing.
- SS$_INSFMEM
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
- SS$_INVBUFLEN
The string passed in the
tx_classargument was longer than 31 characters, or the string passed in thetm_nameargument was longer than 256 characters.- SS$_NOLOG
The local node did not have a transaction log.
- SS$_NOSUCHBID
- Either:
The specified BID was not returned by any call to $ADD_BRANCH or $JOIN_RM on the local node (returned only if the node specified by the
tm_nameargument was the local node).An BID of zero was supplied.
- SS$_NOSUCHTID
The local node did not have any branches in the specified transaction (returned only if the node specified by the
tm_nameargument was the local node).- SS$_TPDISABLED
The TP_SERVER process was not running on the local node.
- SS$_WRONGSTATE
- The transaction was in the wrong state for the attempted operation because either:
An abort event has occurred for the transaction.
A call to $END_TRANS to end the transaction is in progress and it is now too late to add a new branch to the transaction.
$START_BRANCHW
Start Branch and Wait — Adds a new branch to a transaction. $START_BRANCHW always waits for the request to complete before returning to the caller. Other than this, it is identical to $START_BRANCH.
Format
SYS$START_BRANCHW
[efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,tid ,tm_name
,bid [,[timout] ,[acmode], [tx_class]]C Prototype
int sys$start_branchw
(unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int tid [4],
void *tm_name, unsigned int bid [4],...);$START_TRANS
Start Transaction — Starts a new transaction.
Format
SYS$START_TRANS
[efn] ,[flags] ,iosb [,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[tid] ,[timout] ,[acmode]
,[tx_class]]C Prototype
int sys$start_trans
(unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb *iosb,...);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is set.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Flags specifying options for the service. The flags argument is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to an option flag. The $DDTMDEF macro defines symbolic names for these option flags, which are described in the following table:
|
Flag |
Description |
|---|---|
|
DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT |
Set this flag if you do not want the new transaction to be the default transaction of the calling process. An error is returned if this flag is set and the
If this flag is clear, the new transaction becomes the default transaction of the calling process. An error is returned if this flag is clear and the calling process already has a default transaction. |
|
DDTM$M_SYNC |
Set this flag to specify that successful synchronous completion is to be indicated by returning SS$_SYNCH. When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the AST routine is not called, the event flag is not set, and the I/O status block is not filled in. |
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned section.
The following diagram shows the structure of the I/O status block.
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure entry mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
AST routine that is executed when the service completes if SS$_NORMAL is returned in R0. The
astadr argument is the address of this routine. This routine
is executed in the same access mode of the caller of the $START_TRANS service.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
AST parameter that is passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | trans_id |
| type: | octaword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Address of an octaword in which the service returns the identifier (TID) of the new transaction.
No other call to $START_TRANS on any node ever returns the same TID value.
The default value of this argument is zero. An error is returned if the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag is set and this argument is either omitted or zero.
| OpenVMS usage: | date_time |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Timeout for the new transaction. This is the time at which the DECdtm transaction manager is to abort the transaction if the transaction has not already committed.
A positive time value specifies an absolute time. The absolute value of a negative time specifies an offset (delta time) from the current time.
The transaction is aborted at the next timer interval if you specify either a zero time value or any time in the past. If this argument is omitted, the new transaction has no timeout.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
An access mode of the new branch of the new transaction.
An access mode is maintained for each transaction per process. All branches in a transaction in a process have the same access mode. Subsequent operations do not alter it. The access mode of a branch is the least privileged mode in which a successful call to $END_TRANS may be made.
Note that the transaction may be aborted by a call to $ABORT_TRANS from any access mode.
The access mode of the branch is the least privileged of the following:
The access mode of the caller
The access mode specified by the
acmodeargument
If the acmode argument is omitted, the access mode of the new
branch is the same as that of the caller.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor – fixed-length string descriptor |
A string that specifies the transaction class for the new transaction on the local node. This string is passed in the event reports delivered to RMIs and RM participants on the local node.
This string must be no longer than 31 characters. If this argument is omitted or the string is of length zero, the new transaction has no transaction class on the local node. In this case, the class of the transaction on the local node can be specified by a subsequent call to $START_BRANCH on that node.
Description
The $START_TRANS system service starts a new transaction whose commit or abort processing is to be coordinated by the local DECdtm transaction manager. The service:
Adds a branch running in the calling process to the new transaction. The identifier (BID) of the new branch is 0.
Sets the default transaction of the calling process to the new transaction, if the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag is clear and the process does not have a default transaction.
Delivers an event of type Transaction Started to each RMI in the calling process that requested Transaction Started events and has an access mode that is the same as or more privileged than that specified in this call to $START_TRANS. See the description of the acmode argument.
The event delivered to all such RMIs is either a default transaction-started event or a nondefault transaction-started event, depending on whether the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag is clear or not.
Preconditions for the successful completion of $START_TRANS are:
The local node must have a DECdtm transaction log.
The TP_SERVER process must be running on the local node.
If the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag is clear, the calling process must not have an unended default transaction.
$START_TRANS may fail for various reasons including:
Preconditions were not met.
The DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear and a call to $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS by the calling process is in progress.
When $START_TRANS completes successfully:
A new transaction has started, with a unique identifier.
The transaction has a single branch, with a BID of 0.
All Transaction Started events reported to RMIs in the calling process have been acknowledged.
If the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear, the transaction is the default transaction of the calling process.
A branch may:
Invoke resource manager operations, explicitly passing the TID.
Invoke resource manager operations without specifying the TID, if the transaction is the default transaction of the calling process, and the resource manager supports default transactions.
Call $ADD_BRANCH to authorize another branch to be added to the transaction.
(The way to invoke a resource manager operation is defined by the interfaces provided by the resource manager. For additional information, see the resource manager documentation.)
DECdtm cannot commit the transaction until the process calls $END_TRANS.
The transaction is aborted:
On termination of the current image or process.
On successful completion of a call to $ABORT_TRANS in the calling process, specifying a BID of 0.
There is also a wait form of the service, $START_TRANSW.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quotas
ASTLM, BYTLM
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW, $CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW, $END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW, $GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW, $START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
If returned in R0, the request was successfully queued. If returned in the I/O status block, the service completed successfully.
- SS$_SYNCH
The service completed successfully and synchronously (returned only if the DDTM$M_SYNC flag is set).
- SS$_ACCVIO
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
- SS$_ALCURTID
- Either:
An attempt was made to start a default transaction (the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear) when the calling process had an unended default transaction.
The DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear and a call to $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS by the calling process was in progress.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Either the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was set and the
tidargument was omitted, or the options flags were invalid.- SS$_CURTIDCHANGE
The DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear and a call to change the default transaction of the calling process was in progress.
- SS$_EXASTLM
The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
The job buffered I/O byte limit quota (BYTLM) was exceeded.
- SS$_ILLEFC
The event flag number was invalid.
- SS$_INSFARGS
A required argument was missing.
- SS$_INSFMEM
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
- SS$_INVBUFLEN
The string passed to the
tx_classargument was longer than 31 characters.- SS$_NOLOG
The local node did not have a transaction log.
- SS$_TPDISABLED
The TP_SERVER process was not running on the local node.
$START_TRANSW
Start Transaction and Wait — Starts a new transaction. $START_TRANSW always waits for the request to complete before returning to the caller. Other than this, it is identical to $START_TRANS.
Format
SYS$START_TRANSW
[efn] ,[flags] ,iosb [,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[tid] ,[timout] ,[acmode]]C Prototype
int sys$start_transw
(unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb *iosb,...);$STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Stop Alignment Fault Reporting — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, disables user image alignment fault reporting.
Format
SYS$STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORTC Prototype
int sys$stop_align_fault_report (void);Arguments
None
Description
The Stop Alignment Fault Reporting service disables user image alignment fault reporting.
The service returns SS$_AFR_NOT_ENABLED if user image alignment fault reporting is not enabled. Otherwise, it returns success.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT, $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_AFR_NOT_ENABLED
The $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service has not been called.
$STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Stop System Alignment Fault Reporting — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, disables systemwide alignment fault reporting.
Format
SYS$STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORTC Prototype
int sys$stop_sys_align_fault_report (void);Arguments
None
Description
The Stop System Alignment Fault Reporting service disables systemwide alignment fault reporting.
The service returns SS$_AFR_NOT_ENABLED if systemwide alignment fault reporting is not enabled. Otherwise, it returns success.
Required Access or Privileges
CMKRNL privilege is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT, $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The caller lacks sufficient privilege.
- SS$_AFR_NOT_ENABLED
The $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service has not been called.
$SUBSYSTEM
Subsystem — Saves or restores the process image rights for the current protected subsystem.
Format
SYS$SUBSYSTEM enbflgC Prototype
int sys$subsystem (unsigned int enbflg);Argument
| OpenVMS usage: | boolean |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Value specifying whether the protected subsystem identifiers are to be saved or restored. If
the enbflg argument is set to 0, the active subsystem is saved.
If it is set to 1, the subsystem is restored.
Description
A protected subsystem image is a main image that has in its access control list a special type of ACE that names a set of identifiers and their attributes. Whenever the operating system activates a main image that has protected subsystem identifiers associated with it, these identifiers are automatically granted to the process for the duration of the image.
In essence, a protected subsystem provides the same behavior as if the image had been installed with the identifiers. Subsystem identifiers are sometimes referred to as image rights, in contrast to process rights and system rights.
The Subsystem service provides an easy way for a protected subsystem image to dynamically save and restore its subsystem identifiers. A protected subsystem might choose to turn off its subsystem identifiers at certain times to temporarily revoke the user's access to the objects comprising the protected subsystem. For example, DCL uses the $SUBSYSTEM service to temporarily remove any image identifiers from the process during Ctrl/Y interrupt processing.
The image rights are saved in the process control region and automatically deleted on image rundown ($RMSRUNDWN).
For more information about protected subsystems, see the VSI OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
None
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully; protected subsystem had no identifiers associated with it.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully; protected subsystem had identifiers associated with it.
$SUSPND
Suspend Process — Allows a process to suspend itself or another process.
Format
SYS$SUSPND [pidadr] ,[prcnam] ,[flags]C Prototype
int sys$suspnd (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, unsigned int flags);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Process identification (PID) of the process to be suspended. The pidadr
argument is the address of the longword PID. The pidadr argument
can refer to a process running on the local node or a process running on another node in
the OpenVMS Cluster system.
You must specify the pidadr argument to suspend a process whose UIC
group number is different from that of the calling process.
| OpenVMS usage: | process_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the process to be suspended. The prcnam argument is the address
of a character string descriptor pointing to the process name. A process running on the
local node can be identified with a 1- to 15-character string. To identify a process on
a particular node on a cluster, specify the full process name, which includes the node
name as well as the process name. The full process name can contain up to 23
characters.
A process name is implicitly qualified by its UIC group number. Because of this, you can use
the prcnam argument only to suspend processes in the same UIC
group as the calling process.
To suspend processes in other groups, you must specify the pidadr
argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Longword of bit flags specifying options for the suspend operation. Currently, only bit 0 is
used for the flags argument. When bit 0 is set, the process is
suspended at kernel mode and ASTs are not deliverable to the process.
To request a kernel mode suspend, the caller must be in either kernel mode or executive mode. The default (bit 0 is clear) is to suspend the process at supervisor mode, where executive or kernel mode ASTs can be delivered to the process. If executive or kernel mode ASTs have been delivered to a process suspended at supervisor mode, that process will return to its suspended state after the AST routine executes.
Description
The Suspend Process service allows a process to suspend itself or another process.
A suspended process can receive executive or kernel mode ASTs, unless it is suspended at
kernel mode. If a process is suspended at kernel mode, the process cannot receive any
ASTs or otherwise be executed until another process resumes or deletes it. If you
specify neither the pidadr nor the prcnam
argument, the caller process is suspended.
If the longword value at address pidadr is 0, the PID of the target
process is returned.
The $SUSPND service requires system dynamic memory.
The $SUSPND service completes successfully if the target process is already suspended.
Unless it has pages locked in the balance set, a suspended process can be removed from the balance set to allow other processes to execute.
Note that a kernel mode suspend request can override a supervisor mode suspend state, but a supervisor suspend request cannot override a kernel mode suspend state.
The Resume Process ($RESUME) service allows a suspended process to continue. If one or more resume requests are issued for a process that is not suspended, a subsequent suspend request completes immediately; that is, the process is not suspended. No count is maintained of outstanding resume requests.
Note
When the $SUSPND service is called and the target process is on a different cluster node than that of the process calling the $SUSPND service, the kernel mode suspend flag (bit 0) is ignored. As a result, any suspend is treated as a supervisor-mode suspend.
Required Access or Privileges
GROUP privilege to suspend another process in the same group, unless the process to be suspended has the same UIC as the calling process
WORLD privilege to suspend any other process in the system
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER, $PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $WAKE
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The process name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the caller, or the process identification cannot be written by the caller.
- SS$_INCOMPAT
The remote node is running an incompatible version of the operating system.
- SS$_INSFMEM
The system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the service.
- SS$_IVLOGNAM
The specified process name has a length of 0 or has more than 15 characters.
- SS$_NONEXPR
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process identification was specified.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The target process was not created by the caller and the calling process does not have GROUP or WORLD privilege, or flag bit 0 was set from outer mode.
- SS$_NOSUCHNODE
The process name refers to a node that is not currently recognized as part of the OpenVMS Cluster system.
- SS$_NOSUSPEND
The process was previously marked as not suspendable by the PCB$V_NOSUSPEND flag.
- SS$_REMRSRC
The remote node has insufficient resources to respond to the request. (Bring this error to the attention of your system manager.)
- SS$_UNREACHABLE
The remote node is a member of the cluster but is not accepting requests. (This is normal for a brief period early in the system boot process.)
- SS$_WAIT_CALLERS_MODE
Bit 1 was used in the
flagsargument.
$SYNCH
Synchronize — Checks the completion status of a system service that completes asynchronously. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$SYNCH [efn] ,[iosb]C Prototype
int sys$synch (unsigned int efn, struct _iosb *iosb);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of the event flag specified in the call to the system service whose completion status is to be checked by $SYNCH. The
efn argument is a longword containing this number; however, $SYNCH uses only the low-order byte.
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
I/O status block specified in the call to the system service whose completion status is to be
checked by $SYNCH. The iosb argument is the address of this
quadword I/O status block.
Description
The Synchronize service checks the completion status of a system service that completes
asynchronously. The service whose completion status is to be checked must have been
called with the efn and iosb arguments
specified, because the $SYNCH service uses the event flag and I/O status block of the
service to be checked.
When called, $SYNCH waits (by calling $WAITFR) for the event flag to be set.
When the event flag is set, $SYNCH checks to see whether the I/O status block is nonzero. If it is nonzero, then the asynchronous service has completed, and $SYNCH returns to the caller.
If the I/O status block is the value 0, then the asynchronous service has not yet completed and the event flag was set by the completion of an event not associated with the completion of $GETJPI. In this case, $SYNCH clears the event flag (by calling $CLREF) and waits again (by calling $WAITFR) for the event flag to be set, repeating this cycle until the I/O status block is nonzero.
The $SYNCH service always sets the specified event flag when it returns to the caller. This ensures that different program segments can use the same event flag without conflicting. For example, assume that calls to $GETJPI and $GETSYI both specify the same event flag and that $SYNCH is called to check for the completion of $GETJPI. If $GETSYI sets the event flag, $SYNCH clears the flag and waits for $GETJPI to set it. When $GETJPI sets the flag, $SYNCH returns to the caller and sets the event flag. In this way, the flag set by $GETSYI is not lost, and another call to $SYNCH will show the completion of $GETSYI.
The $SYNCH service is useful when a program calls an asynchronous service but must perform some other work before testing for the completion of the asynchronous service. In this case, the program should call $SYNCH at that point when it must know that the service has completed and when it is willing to wait for the service to actually complete.
When a program calls an asynchronous service (for example, $QIO) and actually waits in line (by calling $WAITFR) for its completion without performing any other work, you could improve that program by calling the synchronous form of that service (for example, $QIOW). The synchronous services such as $QIOW execute code that checks for the true completion status in the same way that $SYNCH does.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully. The asynchronous service has completed, and the I/O status block contains the condition value describing the completion status of the asynchronous service.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The I/O status block cannot be read by the caller.
- SS$_ILLEFC
An illegal event flag was specified.
- SS$_UNASEFC
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified event flag.
$TIMCON
Time Converter — Converts 128-bit Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) format to 64-bit system format or 64-bit system format to 128-bit UTC format based on the value of the convert flag. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$TIMCON [smnadr] ,[utcadr] ,cvtflgC Prototype
int sys$timcon
(struct _generic_64 *smnadr, unsigned int *utcadr [4],
unsigned long int cvtflg);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | date_time |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read/write |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The 64-bit system format value that $TIMCON will use in the conversion. The
smnadr argument will be read from or written to based on the value of the
cvtflg argument. The
smnadr is required when converting UTC time to 64-bit system format.
| OpenVMS usage: | coordinated universal time |
| type: | utc_date_time |
| access: | read/write |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
UTC time value that $TIMCON will use in the conversion. The utcadr
argument will be read from or written to based on the value of the
cvtflg argument. The utcadr argument
is required when converting 64-bit system format to UTC time.
| OpenVMS usage: | conversion flag |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
A longword indicating the direction of the conversion. If the cvtflg
value is 0, UTC time is converted to 64-bit system value. If the
cvtflg value is 1, 64-bit system format is converted to UTC
time.
Description
The Time Converter service converts 64-bit system format time to UTC format, and vice versa.
When converting a 64-bit system format time to 128-bit UTC format time, the time zone of the local system is used.
When converting a 128-bit UTC format time to a 64-bit system time, the time zone differential factor encoded in the 128-bit buffer is used.
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_INVTIME
The input time cannot be converted because its value is out of the legal range or is a delta time, or the UTC is of an illegal format.
$TRANS_EVENT
Transaction Event — Forces a transaction state change for a transaction in which there is at least one RM participant that has set the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag.
Format
SYS$TRANS_EVENT
[efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,tid ,rm_id ,tx_eventC Prototype
int sys$trans_event
(unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params),int astprm, unsigned int tid [4],
unsigned int rm_id, unsigned int tx_event);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Reserved to OpenVMS. This argument must be zero.
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned section.
The outcome of the state change is indicated by the contents of the I/O status block.
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure entry mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The AST routine that is executed when the service completes, if SS$_NORMAL is
returned in R0. The astadr argument is the address of the entry
mask of this routine. The routine is executed in the same access mode as that of the
caller of the $TRANS_EVENT service.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The AST parameter passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | trans_id |
| type: | octaword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The identifier (TID) of transaction to which the state change is to be applied.
| OpenVMS usage: | identifier |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The identifier of the Resource Manager identifier (RMI) with which the coordinating Resource Manager (RM) participant is associated.
| OpenVMS usage: | identifier |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The operation to be performed on the transaction. The permitted values and the possible successful outcomes are listed in Table 15.
Description
The $TRANS_EVENT system service is used by coordinating RM participants to change the state of transactions.
Preconditions for the successful completion of $TRANS_EVENT include:
The caller must have the SYSPRV privilege or be in either executive or kernel mode.
The RM participant must have set the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag on the call to $JOIN_RM. Coordinating resource managers cannot join the transaction by calling $ACK_EVENT.
The access mode of the caller must be the same as or more privileged than that of the transaction within the process.
| Operation | Completion Semantics |
| DDTM$K_TX_PREPARE |
A vote has been received from each RM participant and synchronized branch. The status code returned is the combination of the individual votes. The possible values are:
|
| DDTM$K_TX_COMMIT | The only status code returned on successful completion is SS$_FORGET. Sufficient information has been hardened by the DECdtm transaction manager to commit the transaction. |
| DDTM$K_TX_ABORT | The only status code returned on successful completion is SS$_FORGET. Abort processing has been initiated. |
Required Privileges
SYSPRV is required unless the caller is in executive or kernel mode.
Required Quotas
None
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW, $CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW, $END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW, $GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW, $START_TRANS, $START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The request was successfully queued. This value is only returned in R0.
- SS$_ACCVIO
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
- SS$_BADPARAM
Invalid value for
tx_eventparameter.- SS$_EXASTLM
The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded.
- SS$_FORGET
- No further $TRANS_EVENT calls are required for this transaction.
If
tx_event= DDTM$K_TX_ABORT, then abort processing has been initiated.If
tx_event= DDTM$K_TX_COMMIT, then sufficient information has been hardened to commit the transaction.If
tx_event= DDTM$K_TX_PREPARE, then one of the following has occurred:All participants voted read-only.
The
tidwas not known.The
rm_idwas not known.
- SS$_ILLEFC
The event flag number was invalid.
- SS$_INSFARGS
A required argument was missing.
- SS$_INSFMEM
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
- SS$_NOLOG
The local node did not have a transaction log.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The specified
rm_idwas not a coordinator of the specified transaction.- SS$_NOSYSPRV
The caller is in user or supervisor mode but did not have SYSPRV set.
- SS$_PREPARED
All participants are ready to commit the transaction. A further operation (commit or abort) is necessary to complete the transaction.
- SS$_TPDISABLED
The TP_SERVER process was not running on the local node.
- SS$_VETO
The
tx_eventparameter contains the value DDTM$K_TX_PREPARE, and DECdtm or a participant was not in a position to accept an order to commit. One reason why the transaction must abort is supplied in the abort reason code field of the IOSB. No further call to $TRANS_EVENT is needed for a transaction when this condition code is returned.- SS$_WRONGACMODE
The access mode of the caller was less privileged than that of a branch of the transaction in this process.
- SS$_WRONGSTATE
- The transaction was in the wrong state for the attempted operation:
Commit operation when transaction is not prepared.
Any operation while another call is in progress.
$TRANS_EVENTW
Transaction Event and Wait — Forces a transaction state change for a transaction in which there is at least one RM participant that has specified the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag. $TRANS_EVENTW always waits for the request to complete before returning to the caller. Other than this, it is identical to $TRANS_EVENT.
Format
SYS$TRANS_EVENTW
[efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm],tid ,rm_id ,tx_eventC Prototype
int sys$trans_eventw
(unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, )$TRNLNM
Translate Logical Name — Returns information about a logical name. On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$TRNLNM [attr] ,tabnam ,lognam ,[acmode] ,[itmlst]C Prototype
int sys$trnlnm
(unsigned int *attr, void *tabnam, void *lognam,
unsigned char *acmode, void *itmlst);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Attributes controlling the search for the logical name. The attr argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of a longword bit mask specifying these attributes.
Each bit in the longword corresponds to an attribute and has a symbolic name. The $LNMDEF macro defines these symbolic names. To specify an attribute, use its symbolic name or set its corresponding bit. All undefined bits in the longword have the value 0.
|
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
LNM$M_CASE_BLIND |
If set, $TRNLNM does not distinguish between uppercase and lowercase letters in the logical name to be translated. |
|
LNM$M_INTERLOCKED |
If set, $TRNLNM does not translate the current logical name until any clusterwide logical name modifications in progress are completed. This attribute is not set by default. If your application requires translation using the most recent definition of a clusterwide logical name, use this attribute to ensure that the translation is stalled until all pending modifications have been made. |
| OpenVMS usage: | logical_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Name of the logical name table or the name of a searchlist logical name that
translates the name of one or more tables in which to search for the specified logical
name. The tabnam argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha
and Integrity server systems) of a descriptor pointing to this name. This argument is
required.
The name must be entered in uppercase letters. (This requirement differs from the
$CRELNT system service, which automatically changes tabnam to
uppercase.)
If the table name is not the name of a logical name table, it is assumed to be a logical name and is translated iteratively until either the name of a logical name table is found or the number of translations allowed by the system have been performed. If the table name translates to a list of logical name tables, the tables are searched in the specified order.
| OpenVMS usage: | logical_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Logical name about which information is to be returned. The
lognam argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and
Integrity server systems) of a descriptor pointing to the logical name string. This
argument is required.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | byte (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Access mode to be used in the translation. The acmode argument
is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of a byte
specifying the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines symbolic names for the four access
modes.
When you specify the acmode argument, $TRNLNM ignores all names
(both logical names and table names) at access modes less privileged than the specified
access mode. The specified access mode is not checked against that of the caller.
If you do not specify acmode, $TRNLNM performs the translation
without regard to access mode; however, the translation process proceeds from the
outermost to the innermost access modes. Thus, if two logical names with the same name
but at different access modes exist in the same table, $TRNLNM translates the name with
the outermost access mode.
| OpenVMS usage: | 32-bit item_list_3 or 64-bit item_list_64b |
| type: | longword (unsigned) for 32-bit; quadword (unsigned) for 64-bit |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
tem list describing the information that $TRNLNM is to return. The
itmlst argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and
Integrity server systems) of a list of item descriptors, each of which specifies or
controls an item of information to be returned. An item list in 32-bit format is
terminated by a longword of 0; an item list in 64-bit format is terminated by a quadword
of 0. All items in an item list must be of the same format—either 32-bit or
64-bit.
The following diagram depicts the 32-bit format of a single item descriptor:

|
Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Buffer length |
A word specifying the number of bytes in the buffer pointed to by the buffer address field. |
|
Item code |
A word containing a symbolic code describing the nature of the information currently in the buffer, to be returned in the buffer, or to be returned by the buffer pointed to by the buffer address field. |
|
Buffer address |
A longword containing the 32-bit address of the buffer that specifies or receives the information. |
|
Return length address |
A longword containing the 32-bit address of a word specifying the actual length (in bytes) of the information returned by $TRNLNM in the buffer pointed to by the buffer address field. |
The following diagram depicts the 64-bit format of a single item descriptor:
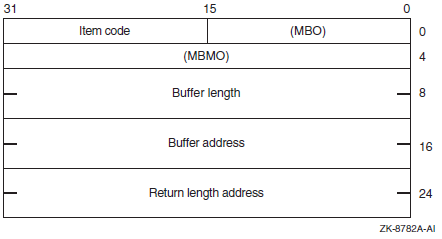
|
Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
MBO |
The field must contain a 1. The MBO and MBMO fields are used to distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries. |
|
Item code |
A word containing a symbolic code describing the nature of the information currently in the buffer, to be returned in the buffer, or to be returned by the buffer pointed to by the buffer address field. |
|
MBMO |
The field must contain a –1. The MBMO and MBO fields are used to distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries. |
|
Buffer address |
A quadword containing the 64-bit address of the buffer that specifies or receives the information. |
|
Return length address |
A quadword containing the 64-bit address of a word specifying the actual length (in bytes) of the information returned by $TRNLNM in the buffer pointed to by the buffer address field. |
Item Codes
LNM$_ACMODE
Returns the access mode that was associated with the logical name at the time of its creation. The buffer address field in the item descriptor is the address of a byte in which $TRNLNM writes the access mode.
LNM$_ATTRIBUTES
Returns the attributes of the logical name and the equivalence name associated with the current LNM$_INDEX value.
The buffer address field of the item descriptor points to a longword bit mask wherein each bit corresponds to an attribute. The $TRNLNM service sets the corresponding bit for each attribute possessed by either the logical name or the equivalence name.
|
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
LNM$M_CONCEALED |
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the equivalence name at the current index value for the logical name is a concealed logical name, as interpreted by OpenVMS RMS. |
|
LNM$M_CONFINE |
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the logical name is not copied from a process to any of its spawned subprocesses. The DCL command SPAWN creates subprocesses. |
|
LNM$M_CRELOG |
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the logical name was created using the $CRELOG system service. |
|
LNM$M_EXISTS |
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, an equivalence name with the specified index does exist. |
|
LNM$M_NO_ALIAS |
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the name of the logical name cannot be given to another logical name defined in the same table at an outer access mode. |
|
LNM$M_TABLE |
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the logical name is the name of a logical name table. |
|
LNM$M_CLUSTERWIDE |
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the logical name is in a clusterwide table. |
|
LNM$M_TERMINAL |
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the equivalence name for the logical name cannot be subjected to further (recursive) logical name translation. |
LNM$_CHAIN
Processes another item list immediately following the current item list. The LNM$_CHAIN item code must be the last one in the current item list. The buffer address field of the item descriptor points to the next item list.
You can chain together 32-bit and 64-bit item lists.
LNM$_INDEX
Searches for an equivalence name that has the specified index value. The buffer address field of the item descriptor points to a longword containing a user-specified integer in the range 0 to 127.
If you do not specify this item code, the implied value of LNM$_INDEX is 0 and $TRNLNM returns information about the equivalence name at index 0.
Because a logical name can have more than one equivalence name and each equivalence name is identified by an index value, you should specify the LNM$_INDEX item code first in the item list, before specifying LNM$_STRING, LNM$_LENGTH, or LNM$_ATTRIBUTES. These item codes return information about the equivalence name identified by the current index value, LNM$_INDEX.
LNM$_LENGTH
Returns the length of the equivalence name string corresponding to the current LNM$_INDEX value. The buffer address field in the item descriptor is the address of the longword in which $TRNLNM writes this length.
If an equivalence name does not exist at the current LNM$_INDEX value, $TRNLNM returns the value 0 to the longword pointed to by the return length field of the item descriptor.
LNM$_MAX_INDEX
Each equivalence name for the logical name has an index associated with it. When you specify LNM$_MAX_INDEX, $TRNLNM returns a value equal to the largest equivalence name index. The buffer address field in the item descriptor is the address of a longword in which $TRNLNM writes this value. If the logical name exists but has no equivalence name (and, therefore, no index value), $TRNLNM returns a value of –1.
LNM$_STRING
Returns the equivalence name string corresponding to the current LNM$_INDEX value. The buffer address field of the item descriptor points to a buffer containing this string. The return length address field of the item descriptor contains an address of a word that contains the length of this string in bytes. The maximum length of the equivalence name string is 255 characters.
If an equivalence name does not exist at the current LNM$_INDEX value, $TRNLNM returns the value 0 in the return length address field of the item descriptor.
LNM$_TABLE
Returns the name of the table containing the logical name being translated. The buffer address field of the item descriptor points to the buffer in which $TRNLNM returns this name. The return length address field of the item descriptor specifies the address of a word in which $TRNLNM writes the size of the table name. The maximum length of the table name is 31 characters.
Description
The Translate Logical Name service returns information about a logical name. You need read access to a shareable logical name table to translate a logical name located in that shareable logical name table.
For conventions regarding logical names for process-permanent files, see the chapter "Logical Name Services" in the VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Required Access or Privileges
Read access is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRELNM, $CRELNT, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELLNM, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET, $MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC, $UPDSECW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully. An equivalence name for the logical name has been found.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The service cannot access the location or locations specified by one or more arguments.
- SS$_BADPARAM
One or more arguments have an invalid value, or a logical name table name or logical name was not specified. Or, an item list containing both 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries was found.
- SS$_BUFFEROVF
The service completed successfully. The buffer length field in an item descriptor specified an insufficient value, so the buffer was not large enough to hold the requested data.
- SS$_IVLOGNAM
The
tabnamargument orlognamargument specifies a string whose length is not in the required range of 1 through 255 characters.- SS$_IVLOGTAB
The
tabnamargument does not specify a logical name table.- SS$_NOLOGNAM
The logical name was not found in the specified logical name table or tables.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The caller lacks the necessary privilege to access the specified name.
- SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
Logical name translation of the table name exceeded the allowable depth (10 translations).
$TRUNCATE
Shortens Sequential File — The Truncate service shortens a sequential file. For additional information about this service, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$TSTCLUEVT
Test Cluster Event — Simulates the occurrence of a cluster configuration event to test the functionality of the notification AST.
Format
SYS$TSTCLUEVT [handle] ,[acmode] ,[event]C Prototype
int sys$tstcluevt
(unsigned int *handle, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int event);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | identifier |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Identification of the asynchronous system trap (AST) to be tested. The
handle argument uniquely identifies the request and is
returned when the $SETCLUEVT service is called.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode for which a configuration event AST is to be triggered. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access mode.
|
Symbol |
Access Mode |
|---|---|
|
PSL$C_KERNEL |
Kernel |
|
PSL$C_EXEC |
Executive |
|
PSL$C_SUPER |
Supervisor |
|
PSL$C_USER |
User |
| OpenVMS usage: | event_code |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Event code indicating the type of configuration for which an AST is to be triggered.
|
Symbolic Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
CLUEVT$C_ADD |
One or more OpenVMS nodes have been added to the OpenVMS Cluster system. |
|
CLUEVT$C_REMOVE |
One or more OpenVMS nodes have been removed from the OpenVMS Cluster system. |
Description
The Test Cluster Event service simulates the occurrence of a cluster configuration event to test the functionality of the notification ASTs. The service allows an application to test itself and must be issued from within the same process as the application being tested. $TSTCLUEVT does not affect other processes in the cluster.
The service will allow one specific AST to be fired via the
handle argument, or all ASTs for a specific configuration event via the
event argument. Specifying both the
event and the
handle arguments will return an error.
If the
handle argument is specified, the value of the
acmode argument must not be greater than the access mode of the caller and must match the mode specified when the $SETCLUEVT service was called.
If the
event argument is specified, those ASTs that match the value specified in the
acmode argument, or that match the caller's mode, will be triggered.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CLRCLUEVT, $SETCLUEVT
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_BADPARAM
There is an unsatisfactory combination of event and handle parameters, or the event was specified incorrectly.
- SS$_NOSUCHOBJ
No request was found that matches the description supplied.
$ULKPAG
Unlock Pages from Memory — Unlocks pages that were previously locked in memory by the Lock Pages in Memory ($LCKPAG) service. Locked pages are automatically unlocked and deleted at image exit.
Format
SYS$ULKPAG inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode]C Prototype
int sys$ulkpag
(struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr, unsigned int acmode);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the pages to be unlocked. The
inadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array
containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses. Only the
virtual page number portion of each virtual address is used; the low-order
byte-within-page bits are ignored. If the starting and ending virtual addresses are the
same, a single page is unlocked.
If more than one page is being unlocked and you need to determine specifically which pages had been previously unlocked, you should unlock the pages one at a time, that is, one page per call to $ULKPAG. The condition value returned by $ULKPAG indicates whether the page was previously unlocked.
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference—array reference or descriptor |
Starting and ending process virtual addresses of the pages actually unlocked by $ULKPAG. The
retadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array
containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses.
If an error occurs while multiple pages are being unlocked, retadr
specifies those pages that were successfully unlocked before the error occurred. If no
pages were successfully unlocked, both longwords in the retadr
array contain the value –1.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode on behalf of which the request is being made. The acmode
argument is a longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines the symbols
for the four access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. To unlock any specified page, the resultant access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the access mode of the owner of that page.
Description
The Unlock Pages from Memory service unlocks pages that were previously locked in memory by the Lock Pages in Memory ($LCKPAG) service. Locked pages are automatically unlocked and deleted at image exit.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, if you are attempting to unlock executable code, you should issue multiple $ULKPAG calls: one to unlock the code pages and others to unlock the linkage section references to these pages.
Required Access or Privileges
To call the $ULKPAG service, a process must have PSWAPM privilege.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
For more information, see the chapter on memory management in the VSI OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages was previously unlocked.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were previously locked.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The input array cannot be read by the caller; the output array cannot be written by the caller; or a page in the specified range is inaccessible or does not exist.
$ULKPAG_64 (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Unlock Pages from Memory — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, unlocks pages that were previously locked in memory by the Lock Pages in Memory ($LCKPAG_64) service. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ULKPAG_64
start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,return_va_64 ,return_length_64C Prototype
int sys$ulkpag_64
(void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode,
void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address of the pages to be unlocked. The specified virtual address will be rounded down to a CPU-specific page boundary.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Length of the virtual address space to be unlocked. The specified length will be rounded up to a CPU-specific page boundary so that it includes all CPU-specific pages in the requested range.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode on behalf of which the request is being made. The acmode
argument is a longword containing the access mode.
|
Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
PSL$C_KERNEL |
Kernel |
|
1 |
PSL$C_EXEC |
Executive |
|
2 |
PSL$C_SUPER |
Supervisor |
|
3 |
PSL$C_USER |
User |
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. To unlock any specified page, the resultant access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the access mode of the owner of that page.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the unlocked virtual address range. The
return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of
a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns the virtual address.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the virtual address range unlocked. The return_length_64
argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which
the service returns the length of the virtual address range in bytes.
Description
The Unlock Pages from Memory service unlocks pages that were previously locked in memory by the Lock Pages in Memory ($LCKPAG_64) service.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments.
SS$_ACCVIO
return_va_64 argument will contain the value -1, and a value
cannot be returned in the memory location pointed to by the
return_length_64 argument. Required Privileges
To call the $ULKPAG_64 service, a process must have PSWAPM privilege.
Required Quota
None.
Related Services
$LCKPAG_64, $ULKPAG
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages was previously unlocked.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were previously locked in the working set.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
return_va_64orreturn_length_64argument cannot be written by the caller, or an attempt was made to unlock pages by a caller whose access mode is less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages.
$ULWSET
Unlock Pages from Working Set — Unlocks pages that were previously locked in the working set by the Lock Pages in Working Set ($LKWSET) service.
Format
SYS$ULWSET inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode]C Prototype
int sys$ulwset
(struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr, unsigned int acmode);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference—array reference or descriptor |
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the pages to be unlocked. The
inadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array
containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses.
Only the virtual page number portion of each virtual address is used; the low-order byte-within-page bits are ignored. If the starting and ending virtual address are the same, a single page is unlocked.
If more than one page is being unlocked and you need to determine specifically which pages had been previously unlocked, you should unlock the pages one at a time, that is, one page per call to $ULWSET. The condition value returned by $ULWSET indicates whether the page was previously unlocked.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, if the first address in the 2-longword array is within an image mapped to your process, the entire image specified by the address is unlocked from the working set.
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference—array reference or descriptor |
Starting and ending process virtual addresses of the pages that were actually unlocked by
$CRMPSC. The retadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array
containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses.
If an error occurs while multiple pages are being unlocked, retadr
specifies those pages that were successfully unlocked before the error occurred. If no
pages were successfully unlocked, both longwords in the retadr
array contain the value –1.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, if the inadr argument
specifies an address within an image mapped to your process,
retadr specifies only one range of pages unlocked from the
working set. Many ranges of pages might be unlocked.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode on behalf of which the request is being made. The acmode
argument is a longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines the symbols
for the four access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. To unlock any specified page, the resultant access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the access mode of the owner of that page.
Description
The Unlock Pages from Working Set service unlocks pages that were previously locked in the working set by the Lock Pages in Working Set ($LKWSET) service. Unlocked pages become candidates for replacement within the working set of the process.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, if the first address specified to SYS$ULWSET is within an image mapped to your process, a success status indicates that the entire image containing the specified address is either unlocked from the working set, or the count of times the image has been locked in the working set has been decremented. This behavior helps to ensure that privileged processes entering kernel mode and raising IPL higher than IPL 2 do not access an invalid page and cause a PGFIPLHI bugcheck. The system keeps a count of the number of times each image within your process has been locked in the working set. This count is maintained so that calls to SYS$ULWSET unlock the image only when it has been called the same number of times as SYS$LKWSET.
The LIBRTL routines LIB$LOCK_IMAGE and LIB$UNLOCK_IMAGE are preferable to SYS$LKWSET and SYS$ULWSET for locking and unlocking code and related data in the working set. For more information about locking images in the working set, see the LIBRTL manual and the description of LIB$LOCK_IMAGE and LIB$UNLOCK_IMAGE.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET, $MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $UPDSEC, $UPDSECW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages was previously unlocked.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were previously locked in the working set.
If the image has been locked in the working set, the count of times the image has been locked in the working set has been decremented. Only when the count is zero is the image unlocked from the working set.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
inadrargument cannot be read by the caller; theretadrargument cannot be written by the caller; or a page in the specified range is inaccessible or does not exist.- SS$_NOPRIV
A page in the specified range is in the system address space.
$ULWSET_64 (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Unlock Pages from Working Set — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, unlocks a virtual address range that was previously locked in the working set by the Lock Pages in Working Set ($LKWSET_64) service. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ULWSET_64
start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,return_va_64 ,return_length_64C Prototype
int sys$ulwset_64
(void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode,
void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address of the pages to be unlocked from the working set. The specified virtual address will be rounded down to a CPU-specific page boundary.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Length of the virtual address space to be unlocked from the working set. The specified length will be rounded up to a CPU-specific page boundary so that it includes all CPU-specific pages in the requested range.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode on behalf of which the request is being made. The acmode
argument is a longword containing the access mode.
|
Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
PSL$C_KERNEL |
Kernel |
|
1 |
PSL$C_EXEC |
Executive |
|
2 |
PSL$C_SUPER |
Supervisor |
|
3 |
PSL$C_USER |
User |
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. To unlock any specified page, the resultant access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the access mode of the owner of that page.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the unlocked virtual address range. The
return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of
a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns the virtual address.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the virtual address range unlocked. The return_length_64
argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which
the service returns the length of the virtual address range in bytes.
Description
The Unlock Pages from Working Set service unlocks pages that were previously locked in the working set by the Lock Pages in Working Set ($LKWSET_64) service. Unlocked pages become candidates for replacement within the working set of the process.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned address and returned
length indicate the pages that were successfully unlocked before the error occurred. If
no pages were unlocked, the return_va_64 argument will contain
the value -1, and a value cannot be returned in the memory location
pointed to by the return_length_64 argument.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, if the first address specified to SYS$ULWSET_64 is within an image mapped to your process, a success status indicates that the entire image containing the specified address is either unlocked from the working set, or the count of times the image has been locked in the working set has been decremented. This behavior helps to ensure that privileged processes entering kernel mode and raising IPL higher than IPL 2 do not access an invalid page and cause a PGFIPLHI bugcheck. The system keeps a count of the number of times each image within your process has been locked in the working set. This count is maintained so that calls to SYS$ULWSET_64 unlock the image only when it has been called the same number of times as SYS$LKWSET_64.
The LIBRTL routines LIB$LOCK_IMAGE and LIB$UNLOCK_IMAGE are preferable to SYS$LKWSET_64 and SYS$ULWSET_64 for locking and unlocking code and related data in the working set. For more information about locking images in the working set, see the LIBRTL manual and the description of LIB$LOCK_IMAGE and LIB$UNLOCK_IMAGE.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$LKWSET_64, $PURGE_WS, $ULWSET
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_WASCLR
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages was previously unlocked.
- SS$_WASSET
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were previously locked in the working set.
If the image had been locked in the working set, the count of times the image has been locked in the working set has been decremented. Only when the count is zero is the image unlocked from the working set.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
return_va_64orreturn_length_64argument cannot be written by the caller, or an attempt was made to unlock pages by a caller whose access mode is less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages.- SS$_PAGNOTINREG
A page in the specified range is not within process private address space.
$UNWIND
Unwind Call Stack — Unwinds the procedure call stack.
Format
SYS$UNWIND [depadr] ,[newpc]C Prototype
int sys$unwind (unsigned int *depadr, void *newpc);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Depth to which the procedure call stack is to be unwound. The depadr
argument is the address of a longword value. The value 0 specifies the call frame of the
procedure that was executing when the condition occurred (that is, no call frames are
unwound); the value 1 specifies the caller of that frame; the value 2 specifies the
caller of the caller of that frame, and so on.
If depadr specifies the value 0, no unwind occurs and $UNWIND returns a
successful condition value in R0.
If you do not specify depadr (or with some languages you specify an
address of 0), $UNWIND unwinds the stack to the call frame of the procedure that called
the procedure that established the condition handler that is calling the $UNWIND
service. This is the default and the normal method of unwinding the procedure call
stack.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
New value for the program counter (PC); this value replaces the current value of the PC in the
call frame of the procedure that receives control when the unwinding operation is
complete. The newpc argument is a longword value containing the
address at which execution is to resume.
Execution resumes at this address when the unwinding operation is complete.
If you do not specify newpc, execution resumes at the location
specified by the PC in the call frame of the procedure that receives control when the
unwinding operation is complete.
Description
The Unwind Call Stack service unwinds the procedure call stack; that is, it removes a specified number of call frames from the stack. Optionally, it can return control to a new program counter (PC) unwinding the stack. The $UNWIND service is intended to be called from within a condition-handling routine.
The actual unwind is not performed immediately. Rather, the return addresses in the call stack are modified so that, when the condition handler returns, the unwind procedure is called from each frame being unwound.
During the actual unwinding of the call stack, $UNWIND examines each frame in the call stack to see if a condition handler has been declared. If a handler has been declared, $UNWIND calls the handler with the condition value SS$_UNWIND (indicating that the call stack is being unwound) in the condition name argument of the signal array. When you call a condition handler with this condition value, that handler can perform any procedure-specific cleanup operations that might be required. After the condition handler returns, the call frame is removed from the stack.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$DCLCMH, $SETEXV
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The call stack is not accessible to the caller. This condition is detected when the call stack is scanned to modify the return address.
- SS$_INSFRAME
There are insufficient call frames to unwind to the specified depth.
- SS$_NOSIGNAL
No signal is currently active for an exception condition.
- SS$_UNWINDING
An unwind operation is already in progress.
- SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA or other condition values that can be returned by SS$EXPREG_64 (Integrity servers only)
The process exceeded its paging file quota while allocating memory to perform the unwind operation. As a result, no unwind is performed. The condition handler return proceeds as though $UNWIND was not called.
$UPDSEC
Update Section File on Disk — Writes all modified pages in an active private or global section back into the section file on disk. One or more I/O requests are queued, based on the number of pages that have been modified.
Format
SYS$UPDSEC
inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode] ,[updflg] ,[efn] ,[iosb] ,[astadr] ,[astprm]C Prototype
int sys$updsec
(struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr, unsigned int acmode,
char updflg, unsigned int efn, struct _iosb *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference—array reference or descriptor |
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the pages that are to be written to the section file
if they have been modified. The inadr argument is the address of
a 2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual
addresses. Addresses are adjusted up or down to CPU-specific pages.
Only the virtual page number portion of each virtual address is used; the low-order byte-within-page bits are ignored.
$UPDSEC scans pages starting at the address contained in the first longword specified by
inadr and ending at the address contained in the second longword. Within this range, $UPDSEC locates read/write pages that have been modified and writes them (contiguously, if possible) to the section file on disk. Unmodified pages are also written to disk if they share the same cluster with modified pages.
If the starting and ending virtual addresses are the same, a single page is written to the section file if the page has been modified.
The address specified by the second longword might be smaller than the address specified by the first longword.
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference—array reference or descriptor |
Addresses of the first and last pages that were actually queued for writing, in the first $QIO
request, back to the section file on disk. The retadr argument is
the address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the addresses of the first and
last pages. Addresses always are adjusted up or down to fall on CPU-specific
boundaries.
If $UPDSEC returns an error condition value in R0, each longword specified by
retadr contains the value –1. In this case, an event
flag is not set, no asynchronous system trap (AST) is delivered, and the I/O status block
is not written to.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode on behalf of which the service is performed. The acmode
argument is a longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines the symbols
for the four access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. A page cannot be written to disk unless the access mode used by $UPDSEC is equal to or more privileged than the access mode of the owner of the page to be written.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Update specifier for read/write global sections. The updflg
argument is a longword value. The value 0 (the default) specifies that all read/write
pages in the global section are to be written to the section file on disk, whether or
not they have been modified. The value 1 specifies that the caller is the only or the
last process having the global section mapped for write access and that only modified
pages should be written to the section file on disk.
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Event flag to be set when the section file on disk is actually updated. The
efn argument is a longword specifying the number of the event
flag; however, $UPDSEC uses only the low-order byte.
If you do not specify efn, event flag 0 is used.
When you invoke $UPDSEC, the specified event flag or event flag 0 is cleared; when the update operation is complete, the event flag is set.
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
I/O status block to receive the final completion status of the updating operation. The
iosb argument is the address of the quadword I/O status
block.
The first word contains the condition value returned by $QIO, indicating the final completion status.
The first bit in the second word is set only if an error occurred during the I/O operation and the error was a hardware write error. The remaining bits of the second word are zeros.
The second longword contains the virtual address of the first page that was not written.
If you are using an event flag to signal the completion of the service, you can test the I/O status block for a condition value to be sure that the event flag was not set by an event other than service completion.
If you are using $SYNCH to synchronize completion of the service, the I/O status block is a required argument for $SYNCH.
The condition value returned in R0 and the condition value returned in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of the call to $UPDSEC. The condition value returned in R0 gives you information about the success or failure of the service call itself; the condition value returned in the I/O status block gives you information about the success or failure of the service operation. Therefore, to accurately assess the success or failure of the call to $UPDSEC, you must check the condition values returned in both R0 and the I/O status block.
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference—procedure reference or descriptor |
AST routine to be executed when the section file has been updated. The
astadr argument is the address of this routine.
If you specify astadr, the AST routine executes at the access mode from
which the section file update was requested.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST routine. The astprm
argument is this longword parameter.
Description
The Update Section File on Disk service writes all modified pages in an active private or global section back into the section file on disk. One or more I/O requests are queued, based on the number of pages that have been modified.
Proper use of this service requires the caller to synchronize completion of the update request. You do this by first checking the condition value returned in R0 by $UPDSEC. If SS$_NOTMODIFIED is returned, the caller can continue. If SS$_NORMAL is returned, the caller should wait for the I/O to complete and then check the first word of the I/O status block for the final completion status. You can use the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service to determine whether the I/O operation has actually completed.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
$UPDSEC uses the calling process's direct I/O limit (DIRIO) quota in queuing the I/O request and uses the calling process's AST limit (ASTLM) quota if the
astadr argument is specified.
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET, $MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSECW
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully. One or more I/O requests were queued.
- SS$_NOTMODIFIED
The service completed successfully. No pages in the input address range were section pages that had been modified. No I/O requests were queued.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The input address array cannot be read by the caller, or the output address array cannot be written by the caller.
- SS$_EXQUOTA
The process has exceeded its AST limit quota.
- SS$_ILLEFC
You specified an illegal event flag number.
- SS$_IVSECFLG
You specified an invalid flag.
- SS$_NOPRIV
A page in the specified range is in the system address space.
- SS$_PAGOWNVIO
A page in the specified range is owned by an access mode more privileged than the access mode of the caller.
- SS$_UNASCEFC
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified event flag.
$UPDSECW
Update Section File on Disk and Wait — Writes all modified pages in an active private or global section back into the section file on disk. One or more I/O requests are queued, based on the number of pages that have been modified. The $UPDSECW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller after writing all updated pages. For asynchronous completion, use the Update Section File on Disk ($UPDSEC) service; $UPDSEC returns to the caller after queuing the update request, without waiting for the pages to be updated. In all other respects, $UPDSECW is identical to $UPDSEC. For all other information about the $UPDSECW service, refer to the description of $UPDSEC. For additional information about system service completion, refer to the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
Format
SYS$UPDSECW
inadr [,retadr] [,acmode] [,updflg] [,efn] [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm]C Prototype
int sys$updsecw
(struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr, unsigned int acmode,
char updflg, unsigned int efn, struct _iosb *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);$UPDSEC_64 (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Update Global Section File on Disk — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, writes all pages (or only those pages modified by the current process) in an active private or global disk file section back into the section file on disk. One or more I/O requests are queued to perform the write operation. The $UPDSEC_64 service completes asynchronously. For synchronous completion, use the Update Global Section File on Disk and Wait ($UPDSEC_64W) service. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$UPDSEC_64
start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,updflg ,efn ,iosa_64 ,return_va_64
,return_length_64 [,astadr_64 [,astprm_64]]C Prototype
int sys$updsec_64
(void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode,
unsigned int updflg, unsigned int efn, struct _iosa *iosa_64,
void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64,...);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address of the pages to be written to the section file. The specified virtual address is rounded down to a CPU-specific page boundary.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Length of the virtual address range to be written to the section file. The length specified is rounded up to a CPU-specific page boundary so that it includes all CPU-specific pages in the requested range.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Access mode on behalf of which the service is performed. The acmode
argument is a longword containing the access mode.
|
Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
PSL$C_KERNEL |
Kernel |
|
1 |
PSL$C_EXEC |
Executive |
|
2 |
PSL$C_SUPER |
Supervisor |
|
3 |
PSL$C_USER |
User |
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. A page cannot be written to disk unless the access mode used by $UPDSEC_64 is equal to or more privileged than the access mode of the owner of the page to be written.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The update specifier for read/write global sections. The updflg
argument is a longword value. The value 0 (the default) specifies that all read/write
pages in the global section are to be written to the section file on disk, whether or
not they have been modified. The value UPDFLG$M_WRT_MODIFIED specifies that the caller
is the only process actually writing the global section and that only those pages that
were actually modified by the caller are to be written to the section file on
disk.
Definitions for this flag can be found in the file SECDEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB for C and in $SECDEF in STARLET.MLB for macro.
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read_only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The event flag to be set when the section file on disk is actually updated. The
efn argument is a longword specifying the number of the event
flag; however, this service only uses the low-order byte. If you do not specify the
efn, event flag 0 is used.
When you invoke $UPDSEC_64, the specified event flag or event flag 0 is cleared. When the update operation is complete, the event flag is set.
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_area |
| type: | IOSA structure |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The I/O status area to receive the final completion status of the updating operation. The
iosa_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of the
I/O status area. The I/O status area structure is 32 bytes in length. The I/O status
area structure definition can be found in $IOSADEF in STARLET.MLB for macro and in the
file IOSADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB for C.
isoa$l_status (offset 0)
The first word contains the condition value return by SYS$QIO, indicating the final completion status.
The first bit in the second word is set only if an error occurred during the I/O operation and the error was a hardware write error. The remaining bits of the second word are zeros.
iosa$l_resd (offset 4)
This field is reserved for future OpenVMS use. The value in this field is unpredictable.
iosa$q_count_q (offset 8)
This field is reserved for future OpenVMS use. The value in this field is unpredictable.
iosa$ph_upsec_nowrt_va (offset 16)
This field contains the virtual address of the first byte in the first disk block that was not written. In the case of an I/O error, this virtual address indicates the disk block for which the error occurred.
iosa$q_resq (offset 24)
This field is reserved for future OpenVMS use. The value in this field is unpredictable.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The process virtual address of the first page that was actually queued for writing (in the
first I/O request) back to the section file on the disk. The
return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of
a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns the virtual address.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the first I/O request to write modified pages back to the section file on disk.
The return_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns the length of the
virtual address range, in bytes, written by the first I/O request.
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The asynchronous system trap (AST) routine to be executed when the section file has been
updated. The astadr_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of
this routine. If you specify the astadr_64 argument, the AST
routine executes at the access mode from which the section file update was requested.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | quadword |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The AST parameter to be passed to the AST routine. The astprm_64
argument is a quadword argument that is passed to the AST routine.
Description
The Update Global Section File on Disk service writes all pages in an active
private or global section back into the section file on disk. If the
updflg argument indicates that only modified pages are to be
written back to the disk file, only those global pages modified by the current process
are queued to be written back into the section file on disk.
Proper use of this service requires the caller to synchronize completion of the update request. To do this, first check the condition value returned. If SS$_NOTMODIFIED is returned, the caller can continue. If SS$_NORMAL is returned, the caller should wait for the I/O to complete and then check the I/O status for final completion status.
If any error is returned by this service, a value cannot be
returned in the memory locations pointed to by the iosb_64,
return_va_64, and return_length_64
arguments.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
$UPDSEC_64 uses the calling process' direct I/O limit (DIRIO) quota in queuing the I/O request
and uses the calling process' AST limit (ASTLM) quota if the
astadr_64 argument is specified.
Related Services
$CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_FILE_64, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64, $MGBLSC_64, $UPDSEC
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully. One or more I/O requests were queued.
- SS$_NOTMODIFIED
The service completed successfully. No pages in the input address range were section pages that had been modified. No I/O requests were queued.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
return_va_64,return_length_64, oriosb_64argument cannot be written by the caller.- SS$_EXASTLM
The process has exceeded its AST limit quota.
- SS$_EXBYTLM
The process has exceeded the byte count quota.
- SS$_ILLEFC
An illegal event flag number was specified.
- SS$_PAGNOTINREG
A page in the specified range is not within the process private address space.
- SS$_PAGOWNVIO
A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more privileged access mode.
- SS$_UNASCEFC
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified event flag.
$UPDSEC_64W (Alpha and Integrity servers)
Update Global Section File on Disk and Wait — On Alpha and Integrity server systems, writes all modified pages in an active private or global disk file section back into the section file on disk. Zero or more I/O requests are queued, based on the number of pages that have been modified. The $UPDSEC_64W service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller after writing all updated pages. In all other respects, $UPDSEC_64W is identical to $UPDSEC_64. For additional information about the $UPDSEC_64W service, see the description of $UPDSEC_64 in this manual. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$UPDSEC_64W
start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,updflg ,efn ,iosa_64 ,return_va_64
,return_length_64 [,astadr_64 [,astprm_64]]C Prototype
int sys$updsec_64w
(void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode,
unsigned int updflg, unsigned int efn, struct _iosa *iosa_64,
void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64,...);$VERIFY_PROXY
Verify a Proxy — Verifies that a proxy exists and returns a valid local user for the caller to use to create a local login.
Format
SYS$VERIFY_PROXY
rem_node ,rem_user ,[proposed_user] ,local_user ,local_user_length
,[flags]C Prototype
int sys$verify_proxy
(void *rem_node, void *rem_user, void *proposed_user, void *local_user,
unsigned short int *local_user_len, unsigned int flags);
Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Remote node name of the proxy to be verified. The rem_node argument is
the address of a character-string descriptor pointing to the remote node name string.
A remote node name consists of 1 to 1024 characters. No specific characters, format, or case are required for a remote node name string. All node names are converted to their DECnet for OpenVMS full name unless the PRX$M_BYPASS_EXPAND flag is set with the
flags argument.
Wildcards are not recognized. If you specify a wildcard character in the
rem_node argument, it is ignored and assumed to be part of the requested
node name.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Remote user name of the proxy to be verified. The rem_user argument is
the address of a character-string descriptor pointing to the user name string.
A remote user name consists of 1 to 32 alphanumeric characters, including dollar signs ($), underscores (_), and brackets ([ ]). Any lowercase characters specified are automatically converted to uppercase.
The
rem_user argument can be specified in user identification code (UIC) format
([
group,
member]). Brackets are allowed only if the remote user name string specifies a UIC. Group and member are character-string representations of octal numbers with no leading zeros.
Wildcards are not allowed for the remote user specification. If wildcard characters are
present in the string specified by the rem_user argument, the service
returns SS$_BADPARAM.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Local user the caller suggests be used for the proxy login. The
proposed_user argument is the address of a character-string descriptor
pointing to the proposed local user name.
The proposed local user consists of 1 to 32 alphanumeric characters, including dollar signs ($) and underscores (_). Any lowercase characters specified are automatically converted to uppercase.
See the Description section for information about the interaction of this argument with the
return value of the local_user argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor–fixed-length string descriptor |
Local user the caller must use for a proxy login. The local_user
argument is the address of a 32-byte character-string descriptor pointer to receive the local
user name the caller must use for a proxy login for the proxy with the remote node name specified
by the rem_node argument and the remote user name specified by the
rem_user argument.
A local user name is a 32-character blank padded string of alphanumeric characters, including dollar signs ($) and underscores (_).
| OpenVMS usage: | output length |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Length of the returned local user name in the local_user argument. The
local_user_length argument is the address of an unsigned word to receive
the length, in bytes, of the character string returned in the local_user
argument.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Functional specification for the service and type of user the
local_user argument represents. The flags argument
is a longword bit mask wherein each bit corresponds to an option.
|
Symbolic Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
PRX$M_BYPASS_EXPAND |
The service should not convert the node name specified in the
|
Description
The Verify Proxy service verifies the existence of a proxy in the proxy database and returns the local user name the caller must use for any proxy logins.
The following description shows how the service determines which local user name the caller must use for proxy logins.
rem_node and rem_user arguments, respectively, are
searched in the following order if the remote user name is not a UIC:rem_node::rem_user
*::rem_user
rem_node::*
*::*
rem_node and rem_user arguments, respectively, are
searched for in the following order if the remote user name is a UIC:rem_node::rem_user
*::rem_user
rem_node::[group,*]
rem_node::[*,member]
rem_node::[*,*]
*::*
|
Remote User |
Proposed User |
Proxy Default User |
Proxy Local User Names |
Returned Local User Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
rem_user |
null |
null |
n/a |
error |
|
rem_user |
null |
default user |
n/a |
default user |
|
rem_user |
null |
* |
n/a |
rem_user |
|
rem_user |
prop_user |
default user |
n/a |
prop_user |
|
rem_user |
prop_user |
default user |
prop_user |
prop_user |
|
rem_user |
prop_user |
default user |
local user |
error |
|
rem_user |
prop_user |
default user |
* |
rem_user if it equals prop_user |
|
rem_user |
prop_user |
* |
local user |
rem_user if it equals prop_user |
Required Access or Privileges
You must have SYSPRV privilege.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_PROXY, $DELETE_PROXY, $DISPLAY_PROXY
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The
rem_node,rem_user, orproposed_userargument cannot be read by the service; or thelocal_userorlocal_user_lengthargument cannot be written by the service.- SS$_BADBUFLEN
The length of the
rem_node,rem_user,proposed_user, orlocal_userargument was out of range.- SS$_BADPARAM
The
rem_userorproposed_userargument contains an invalid user name.- SS$_NOREADALL
The caller does not have access to the proxy database.
This service can also return any of the following messages passed from the security server, or any OpenVMS RMS error message encountered during operations on the proxy database:
- SECSRV$_BADLOCALUSERLEN
The local user name length is out of range.
- SECSRV$_BADNODENAMELEN
The node name length is out of range.
- SECSRV$_BADREMUSERLEN
The remote user name length is out of range.
- SECSRV$_NOSUCHPROXY
The proxy specified by the
rem_nodeandrem_userarguments does not exist in the proxy database.- SECSRV$_NOSUCHUSER
No valid user was found for the requested proxy.
- SECSRV$_PROXYNOTACTIVE
Proxy processing is currently stopped. Try the request again later.
- SECSRV$_SERVERNOTACTIVE
The security server is not currently active. Try the request again later.
$WAIT
Suspends Image Execution — The Wait service suspends image execution until an asynchronous record service completes. Upon completion of the service, RMS returns control to your program at the point following the Wait service call. For additional information about this service, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$WAITFR
Wait for Single Event Flag — Tests a specific event flag and returns immediately if the flag is set. Otherwise, the process is placed in a wait state until the event flag is set.
Format
SYS$WAITFR efnC Prototype
int sys$waitfr (unsigned int efn);Argument
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of the event flag for which to wait. The efn argument is a
longword containing this number; however, $WAITFR uses only the low-order byte.
Description
The Wait for Single Event Flag service tests a specific event flag and returns immediately if the flag is set. Otherwise, the process is placed in a wait state until the event flag is set. The wait state caused by this service can be interrupted by an asynchronous system trap (AST) if (1) the access mode at which the AST executes is equal to or more privileged than the access mode from which the $WAITFR service was issued and (2) the process is enabled for ASTs at that access mode.
When a wait state is interrupted by an AST and after the AST service routine completes execution, the operating system repeats the $WAITFR request on behalf of the process. At this point, if the event flag has been set, the process resumes execution.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ASCEFC, $CLREF, $DACEFC, $DLCEFC, $READEF, $SETEF, $WFLAND, $WFLOR
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ILLEFC
You specified an illegal event flag number.
- SS$_UNASEFC
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified event flag.
$WAKE
Wake Process from Hibernation — Activates a process that has placed itself in a state of hibernation with the Hibernate ($HIBER) service. This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$WAKE [pidadr] ,[prcnam]C Prototype
int sys$wake (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | modify |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Process identification (PID) of the process to be activated. The
pidadr argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a longword
that contains the PID. The pidadr argument can refer to a process
running on the local node or a process running on another node in the cluster.
| OpenVMS usage: | process_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor – fixed-length string descriptor |
Process name of the process to be activated. The prcnam
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a 32- or 64-bit character string descriptor
pointing to the process name. A process running on the local node can be identified with
a 1 to 15 character string.
To identify a process on a particular node in a cluster, specify the full process name, which includes the node name as well as the process name. The full process name can contain up to 23 characters.
The process name is implicitly qualified by the UIC group number of the calling
process. For this reason, you can use the prcnam argument only if
the process to be activated is in the same UIC group as the calling process. To activate
a process in another UIC group, you must specify the pidadr
argument.
Description
The Wake Process from Hibernation service activates a process that has placed itself
in a state of hibernation with the Hibernate ($HIBER) service. If you specify neither
the pidadr nor the prcnam argument, the
wake request is issued for the calling process.
If the longword at address pidadr is the value 0, the PID of
the target process is returned.
If one or more wake requests are issued for a process not currently hibernating, a subsequent hibernate request completes immediately; that is, the process does not hibernate. No count of outstanding wakeup requests is maintained.
You can also activate a hibernating process with the Schedule Wakeup ($SCHDWK) service.
Required Access or Privileges
GROUP privilege to wake another process in the same group, unless the process has the same UIC as the calling process
WORLD privilege to wake any other process in the system
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER, $PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ACCVIO
The process name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the caller, or the process identification cannot be written by the caller.
- SS$_INCOMPAT
The remote node is running an incompatible version of the operating system.
- SS$_IVLOGNAM
The specified process name string has a length of 0 or has more than 15 characters.
- SS$_NONEXPR
The specified process does not exist, or you specified an invalid process identification.
- SS$_NOPRIV
The process does not have the privilege to wake the specified process.
- SS$_NOSUCHNODE
The process name refers to a node that is not currently recognized as part of the VSMcluster system.
- SS$_NOSUCHTHREAD
The specified kernel thread does not exist.
- SS$_REMRSRC
The remote node has insufficient resources to respond to the request. (Bring this error to the attention of your system manager.)
- SS$_UNREACHABLE
The remote node is a member of the cluster but is not accepting requests. (This is normal for a brief period early in the system boot process.)
$WFLAND
Wait for Logical AND of Event Flags — Allows a process to specify a set of event flags for which it wants to wait.
Format
SYS$WFLAND efn ,maskC Prototype
int sys$wfland (unsigned int efn, unsigned int mask);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of any event flag within the event flag cluster to be used. The
efn argument is a longword containing this number; however,
$WFLAND uses only the low-order byte. Specifying the number of an event flag within the
cluster serves to identify the event flag cluster.
There are two local event flag clusters: cluster 0 and cluster 1. Cluster 0 contains event flag numbers 0 to 31, and cluster 1 contains event flag numbers 32 to 63.
There are two common event flag clusters: cluster 2 and cluster 3. Cluster 2 contains event flag numbers 64 to 95, and cluster 3 contains event flag numbers 96 to 127.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Event flags for which the process is to wait. The mask argument is a
longword bit vector wherein a bit, when set, selects the corresponding event flag for
which to wait.
Description
The Wait for Logical AND of Event Flags service allows a process to specify a set of event flags for which it wants to wait. The process is put in a wait state until all specified event flags are set, at which time $WFLAND returns to the caller and execution resumes.
The wait state caused by this service can be interrupted by an asynchronous system trap (AST) if (1) the access mode at which the AST executes is equal to or more privileged than the access mode from which the $WAITFR service was issued and (2) the process is enabled for ASTs at that access mode.
When a wait state is interrupted by an AST and after the AST service routine completes execution, the operating system repeats the $WFLAND request on behalf of the process. At this point, if all the specified event flags have been set, the process resumes execution.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ASCEFC, $CLREF, $DACEFC, $DLCEFC, $READEF, $SETEF, $WAITFR, $WFLOR
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ILLEFC
You specified an illegal event flag number.
- SS$_UNASEFC
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified event flag.
$WFLOR
Wait for Logical OR of Event Flags — Allows a process to specify a set of event flags for which it wants to wait.
Format
SYS$WFLOR efn ,maskC Prototype
int sys$wflor (unsigned int efn, unsigned int mask);Arguments
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Number of any event flag within the event flag cluster to be used. The
efn argument is a longword containing this number; however,
$WFLOR uses only the low-order byte. Specifying the number of an event flag within the
cluster serves to identify the event flag cluster.
There are two local event flag clusters: cluster 0 and cluster 1. Cluster 0 contains event flag numbers 0 to 31, and cluster 1 contains event flag numbers 32 to 63.
There are two common event flag clusters: cluster 2 and cluster 3. Cluster 2 contains event flag numbers 64 to 95, and cluster 3 contains event flag numbers 96 to 127.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Event flags for which the process is to wait. The mask argument is a
longword bit vector wherein a bit, when set, selects the corresponding event flag for
which to wait.
Description
The Wait for Logical OR of Event Flags service allows a process to specify a set of event flags for which it wants to wait. The process is put in a wait state until any one of the specified event flags is set, at which time $WFLOR returns to the caller and execution resumes.
The wait state caused by this service can be interrupted by an asynchronous system trap (AST) if (1) the access mode at which the AST executes is equal to or more privileged than the access mode from which the $WFLOR service was issued and (2) the process is enabled for ASTs at that access mode.
When a wait state is interrupted by an AST and after the AST service routine completes execution, the operating system repeats the $WFLOR request on behalf of the process. At this point, if any of the specified event flags has been set, the process resumes execution.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ASCEFC, $CLREF, $DACEFC, $DLCEFC, $READEF, $SETEF, $WAITFR, $WFLAND
Condition Values Returned
- SS$_NORMAL
The service completed successfully.
- SS$_ILLEFC
You specified an illegal event flag number.
- SS$_UNASEFC
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified event flag.
$WRITE
Transfers Bytes to File — The Write service transfers a user-specified number of bytes (beginning on a block boundary) to an RMS file of any file organization. For additional information about this service, see the VSI OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
Appendix A. Obsolete Services
| Obsolete Service | Current Service |
|---|---|
|
$BRDCST |
$BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW |
|
$CHANGE_ACL |
$GET_SECURITY, $SET_SECURITY |
|
$CNTREG |
$DELTVA |
|
$CRELOG |
$CRELNM |
|
$DELLOG |
$DELLNM |
|
$GETCHN |
$GETDVI, $GETDVIW |
|
$GETDEV |
$GETDVI, $GETDVIW |
|
$INPUT |
$QIO, $QIOW |
|
$OUTPUT |
$QIO, $QIOW |
|
$SETSFM |
This service is still supported but its use is discouraged. |
|
$SETSSF |
This service is still supported but its use is discouraged. |
|
$SNDACC |
$SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW |
|
$SNDSMB |
$SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW |
|
$TRNLOG |
$TRNLNM |
The value of this symbol might be changed in future releases if an additional algorithm is introduced.
Use descriptions are: Query, Modify, and Find.
Use descriptions are: Query, Modify, and Find.
Use descriptions are: Query, Modify, and Find.
Use descriptions are: Query, Modify, and Find.
Use descriptions are: Query, Modify, and Find.
Use descriptions are: Query, Modify, and Find.
Also, physical memory or system page table entries under rare circumstances.